CSD 115 Exam #1
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Communication
Common system of symbols, signs, or behavior.
What info is exchanged in communication?
Thoughts, ideas, feelings, and emotions
How is comm. info exchanged?
say, sign, text, gestures, body language, facial expressions
The Communication Process
Formulating
Transmitting
Receiving
Comprehending
SLPs
trained to identify, diagnose, treat, and help prevent communicative and swallowing disorders
Audiologists
nonmedical treatment of hearing, balance, and other ear problems
Neurology
Nervous system and nerves
CNS
Brain and Spinal Cord
PNS
Cranial nerves
Spinal Nerves
Autonomic Nervous system (Sympathetic and Parasympathetic system)
What protects CNS?
Bone:
Skull and Spinal Column
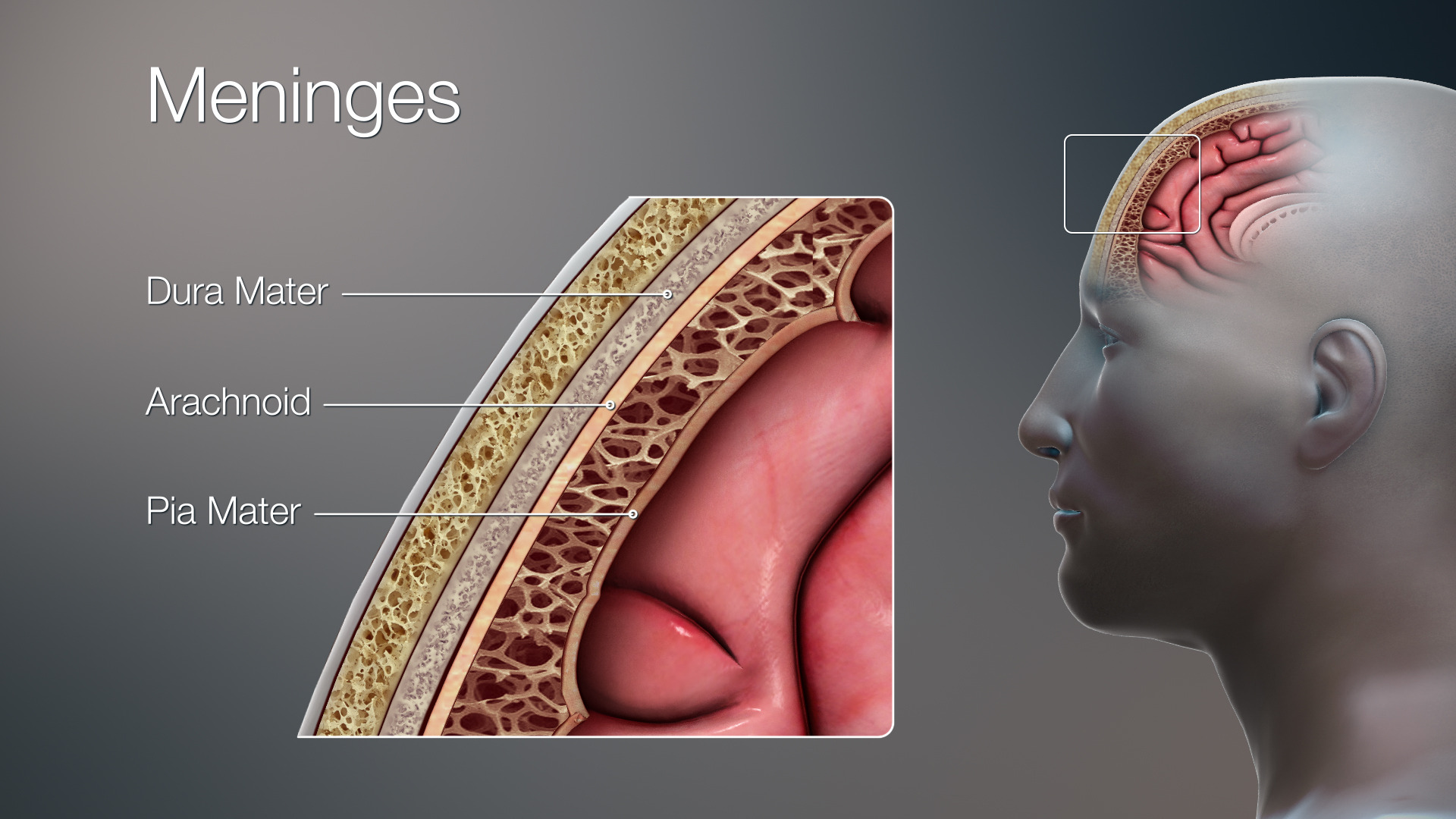
Meninges (for brain AND spinal cord:
Dura mater
Arachnoid mater
Pia mater
Brain includes…
cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem
Cerebrum
L and R hemis (Corpus Callosum connects them- allows them to communicate)
Each hemi has four lobes (F, P, T, O)
Gyri, Sulci, Fissures
Left Hemisphere?
SPEECH AND COMM
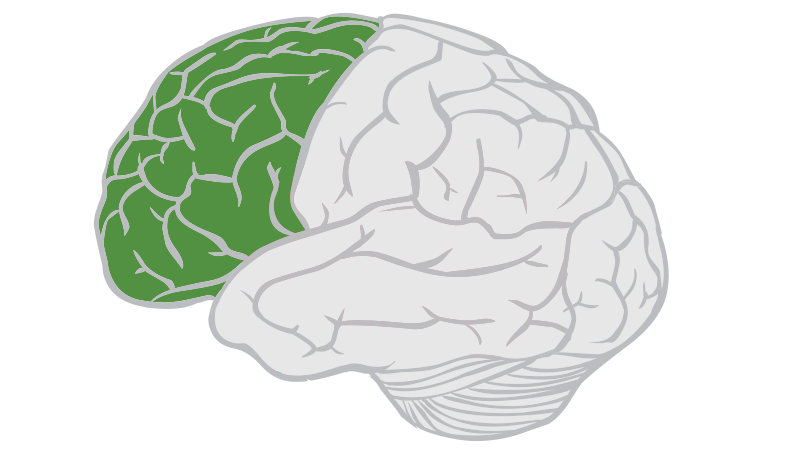
Primary Motor cortex: voluntary m. movement
Premotor cortex: planning/coordinating mvmt
Prefrontal cortex
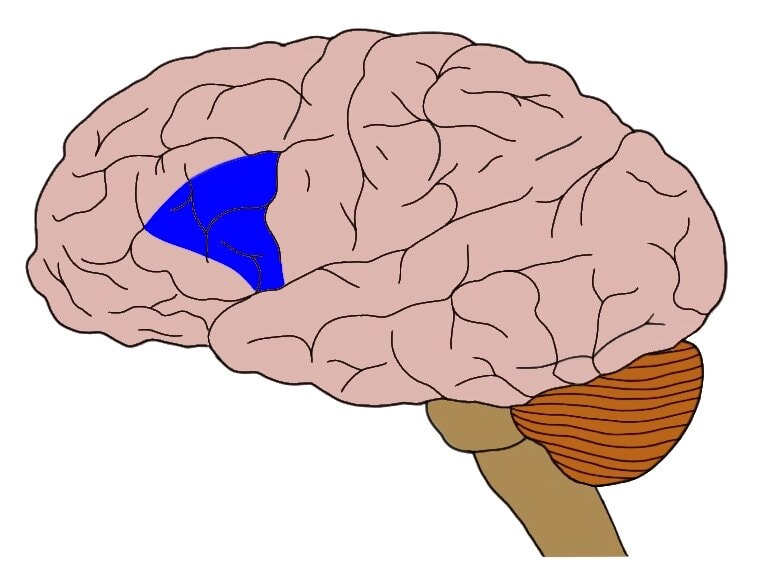
BROCA’s AREA- m. control center for speech!
What’s difference between Broca’s and Wernicke’s?
Broca’s in Frontal Lobe, plans speech motor control
Wernicke’s in Temporal, comprehends lang.
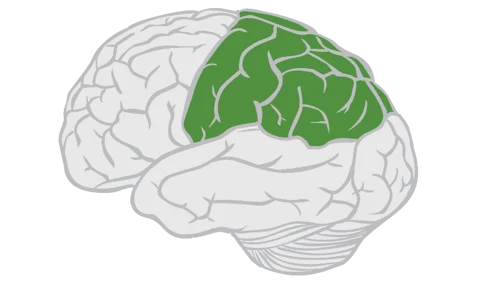
Broca’s
Primary Motor Cortex
F. Voluntary M. Mvmt
Premotor
F. Plans/coordinates movement
Prefrontal Cortex
F. Exectutive Functions, behavior, personality
Primary Sensory cortex: RECEIVES
Sensory Association Area: interprets
Sensory specific to pain, touch and temp.
Processing/analyzing somatic sensations
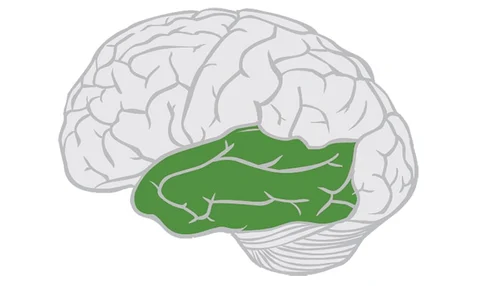
Primary auditory area
Process sound
Comprehend Lang. (WERNICKE’s)
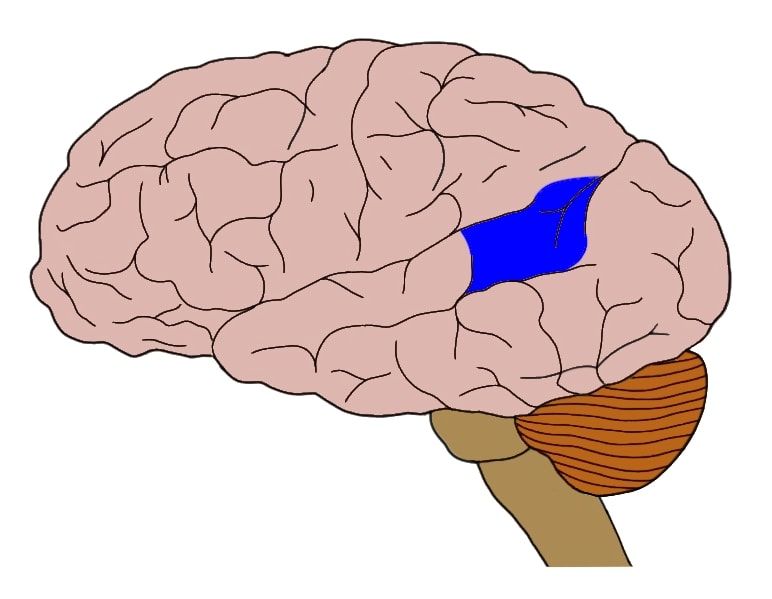
Wernicke’s
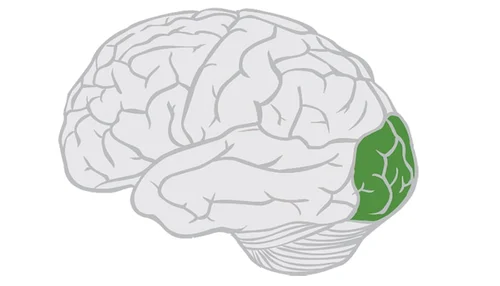
Primary Visual Area
Not involved in Speech and Lang
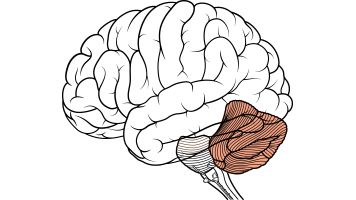
Bellow and to back of cerebrum
Motor coordination, balance, and movement
Abnormalities here could be related to autism/stuttering
Brain Stem
Heart rate, breathing, pupils
PATHWAY for motor and sensory nerves carrying information to and from brain
Pathways CROSS OVER in brainstem!
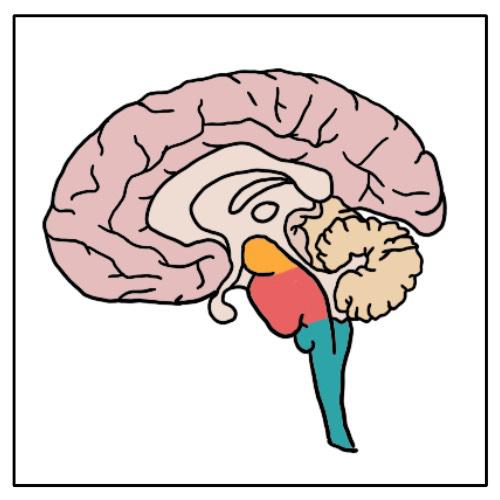
Top to bottom
Midbrain
Pons
Medulla
Spinal Cord
Extension of brain stem
Pathways for neural information
Protected by meninges and spinal column
PNS
12 pairs of cranial nerves
31 pairs of spinal nerves
Autonomic Nervous system
Cranial nerves
12 pairs
enter and exit in brainstem
Transmit motor singnals for mvmt of eyes, mouth, lips, tongue, and layrnx
Sensory info: pain, touch, temp
Also carry “special” sensory info: smell, vision, hearing, and taste to brain
Spinal Nerves
31 pairs
Enter and exit at various points along spinal cord
Carry MOTOR and SENSORY info for rest of body
Autonomic Nervous System
Executive Control of Speech and Hearing Steps
1.) Linguistic message created in multiple supporting areas in LEFT hemi
2.) Message carried to Broca’s, where MOTOR PLAN is created to move articulatory ms.
3.) Signals sent to MOTOR CORTEX, then carried to Ms
4.) Signals travel through CEREBELLUM to check/modify for coordination
5.) Them to CRANIAL NERVES for distribution to ms
6.) SPEECH HAPPENS
What are the 4 systems for speech production?
1.) Breathe
2.) Vibration (make sound)
3.) Articulate
4.) Direct air flow (resonate)
Respiratory system
Primary function: breathe
Speech function: source/energy for speech
Where is respiratory system?
In thorax (chest cavity)
Protective System?
Spinal column (back)
Ribs (sides)
sternum (front)
main structures:
Diaphragm
Lungs
Trachea
The lungs are attached to…
diaphragm and ribs
Trachea
2 bronchi, then bronchioles, then alveoli
Lungs
Spongy and elastic
Covered by moist plural sac
pluarl sac binds to rib cage + diaphragm
Diaphragm
Dome/parachute shaped, umbrella like muscle
Boye’s Law
Energy=pressure X volume
Energy in the thorax is…
CONSTANT
Pressure and Volume are…
INVERSELY related
Inhale
Diaphragm flattens and moves DOWN, contracts, stretches lungs down, making them bigger.
Pressure DECREASES
Exhalation
Everything contracts
Diaphragm moves UP
Quiet Breathing
“Breathing for life”
17-19 breaths per minute in adults
Tidal volume
system is ALL OPEN (no constriction)
uses 10-15% of vital capacity
Equal-time: inhalation and exhalation
Tidal Volume
amount of air that enters then exits the lungs during quiet breathing
IRV
Take a deeper breath in
ERV
push more air out
Vital Capacity
IRV + TV + ERV
The amount of air the lungs can hold following max inhalation and max exhalation
Reserve Volume
There’s always some air in our lungs
To produce voice and sound….
RESTRICTED AIR FLOW at VFs and in oral cavity
Speech breathing
usses 25-40% of vital capacity based on loudness level
Quick inhalation- 10% followed by long exhalation (90%)
Laryngeal System- Valve
When open: VFs open
When closed: VFs closed
Speech function:
open=voiceles
closed=vibration=VOICED
Thyroid Cartilage
Largest, Adam’s Apple
Cricoid Cartilage
Under thyroid
Arytenoid
in back
VFs are atatched to arytenoid cartilages
Abductor
Open
Adductor
Closing
VFs
Paired
Attached anteriorly to thyroid
Attached posteriorly to arytenoid cartilages
When open: glottis
Phonemes
Smallest unit of sound distinct from other sounds in word (have to count them on the test) :)
All vowels are…
voiced
What type of babbling is bababa?
Reduplicated
Manana is…
variegated babbling
what describes meaningless combos…
jargon