Paper 2
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
What are Vector and Scalar quantities?
Vector - A quantity with a magnitude and a direction - Force, Velocity, Displacement, Acceleration, Moment, etc
Scalar - A quantity with a magnitude and no direction - Speed, Distance, Mass, Temperature, Time
What are Contact and Non-Contact Forces?
Contact Force - When two objects have to be touching for a force to act - Friction, Air Resistance, Normal Contact Force, etc
Non-Contact Force - If the objects do not need to be touching - Magnetic, Electrostatic, Gravitational, etc
What is the formula for weight?
Weight (N) = Mass (Kg) x Gravitational Field Strength (N/Kg)
What is the formula for Work Done?
Work Done (J) = Force (N) x Distance (S)
What is the formula for Force?
Force (N) = Spring Constant (N/m) x Extension (m)
Describe a practical to investigate the link between Force and Extension?
Setup a apparatus using a stand, clamp and a spring
Measure the natural length of the spring with a ruler and record the length in metres
Then add a 100g mass and measure the new length of the spring
Repeat until you have all your desired results
Then take away the natural length from each result to find the extension
Repeat it all if you want repeat reading for greater accuracy and less anomalies
What is a moment and the equation?
A moment is the turning effect of a force.
Moment (Nm) = Force (N) x Distance (m)
If the total anticlockwise moment is equal to the total clockwise moment about a pivot, then the object is balanced.
The greater the distance from a pivot means less force needs to be put in. This is good for things like levers.
What is a Fluid?
A substance that can flow because their particles are able to move around (Liquids and Gases). This results in pressure from collisions.
What is the formula for Pressure?
Pressure at Surface: Pressure (Pa) = Force (N) x Area (m²)
Pressure in liquids: Pressure (Pa) = Depth (m) x Gravitational Field Strength (N/Kg) x Density (Kg/m³)
What is Upthrust?
The resultant force equal to the weight of fluid that is displaced. This is due to pressure exerted in all directions underwater, and pressure being greater at the bottom from the greater depth.
An object can float if the upthrust is equal to the weight
What are these typical speeds?
Walking - 1.5 m/s
Running - 3 m/s
Cycling - 6 m/s
Car - 25 m/s
Train - 30 m/s
Plane - 250 m/s
What are the two equations for Acceleration?
Acceleration (m/s²) = Change in Velocity (m/s) / Time (s)
V² - U² = 2as
What is Terminal Velocity?
The maximum velocity a falling object can reach without any added driving forces. It’s the velocity at which the resistive forces acting on the object match the force due to gravity.
What is Newton’s First Law?
If the resultant force on a stationary object is zero, the object will remain stationary. If the resultant force on a moving object is zero, it will keep the same velocity. (Inertia)
What is Newton’s Second Law?
The larger the resultant force acting on an object, the more the object accelerates.
Force (N) = Acceleration (m/s²) x Mass (Kg)
What is Newton’s Third Law?
When two objects interact, the forces they exert are equal and opposite.
Describe a practical to investigate how Mass and Force affect Acceleration (Newton’s Second Law)?
Setup a apparatus with a trolley, card with a gap in the middle, light gate, pulley and mass
Measure the length of the gap in the card with a ruler
Connect the trolley to the mass over the pulley
Mark a starting line for your trolley
Add a 100g mass, hold the trolley so the string is not loose and release
Record the acceleration from the data logger
Repeat with more masses
Take repeat readings for more accuracy and to eliminate anomalies
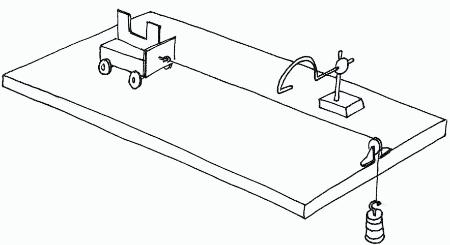
What is the formula for Stopping Distance?
Stopping Distance = Thinking Distance + Braking Distance
What is the formula for Momentum?
Momentum (Kg m/s) = Mass (Kg) x Velocity (m/s)
Momentum is conserved throughout in a closed system
What is another formula for Force?
Force (N) = Chang in Momentum (Kg m/s) / Change in Time (s)
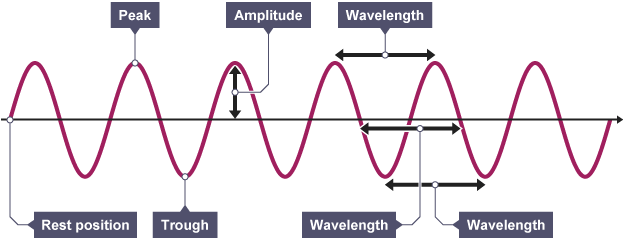
Describe a diagram of a wave
See Image:
What is the formula for Frequency?
F = 1/T
F - Frequency (Hz)
T - Time (s)
Describe a Transverse Wave?
In transverse waves, the oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer.
Examples:
Electromagnetic Waves
Ripples in water
Describe a Longitudinal Wave?
In Longitudinal Waves, the oscillations are parallel to the direction of energy transfer.
Examples:
Sound Waves
Ultrasound
Shock Waves
What is the formula for Wave Speed?
V = F * λ
V = Wave Speed (m/s)
F = Frequency (Hz)
λ = Wavelength (m)
Describe the Ripple Tank Experiment?
Using a signal generator attached to the dipper of a ripple tank you can create water waves at a set frequency.
Use a lamp to see wave crests on a screen below the tank.
The distance between each shadow line is equal to one wavelength.
Measure the distance between shadow lines that are 10 wavelengths apart, then divide this distance by 10 to find the average wavelength.
Use V = F * λ to find the speed of the waves.
What is the rule of Reflected Waves?
Angle of Incidence = Angle of Reflection
What are the two types of reflection?
Specular Reflection - This happens when a wave is reflected in a single direction by a smooth surface.
Diffuse Reflection - This happens when a wave is reflected by a rough surface and the reflected rays are scattered in lots of different direction.
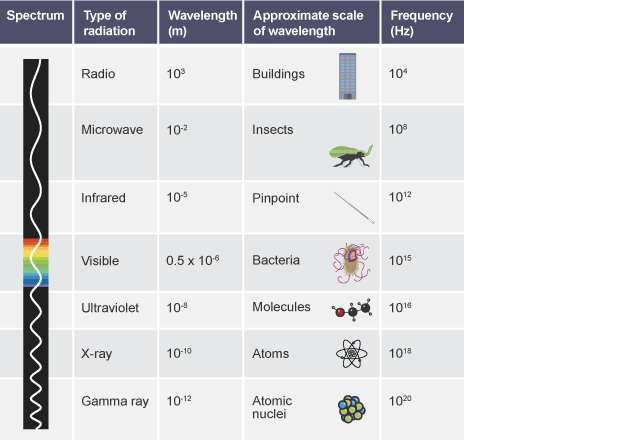
Describe the Electromagnetic Spectrum?
See Image:
Describe the Investigating Light experiment?
Shine a light with a ray box at a transparent material block.
Trace the incident ray and mark the ray on the other side of the block.
Join up the incident ray with the refracted ray.
Draw the normal at the point where the light ray entered the block.
Measure the angle between the incident and the normal, and the angle between the refracted ray and the normal.
Describe Radio Waves?
Radio Waves are EM radiation with wavelengths longer than about 10cm. They work with a receiver and a transmitter which emit radio waves which transfer energy.
Long-Wave Radio (1-10 Km Wavelength)(Across the Earth) can travel very long distances as they bend around the curved surfaces.
Short- Wave Radio (10-100m Wavelength) can also be received at long distances as they reflect off the ionosphere.
TV and FM Radio have very short wavelengths and must be in direct sight of the transmitter.
Describe Microwaves?
Communication to and from satellites uses microwaves. They are good as they pass easily through the Earth’s water atmosphere.
They are used in Microwave Ovens as the microwaves are absorbed by water molecules in food. They then transfer energy to the food causing it to heat up.
Describe Infrared Radiation?
It is given out by hot objects. Infrared Cameras can be used to detect infrared radiation and monitor temperature. Absorbing IR Radiation causes objects to get hotter.
Describe the use of Fibre Optic Cables?
They are thin glass or plastic fibres that can carry data over very long distances as pulses of visible light. They work because of reflection as they are bounced back and forth.
Describe Ultraviolet Radiation?
Fluorescence is a property of certain chemicals, where ultra-violet radiation radiation is absorbed and then visible light is emitted. It is also emitted by the sun and can be used for a suntan.
Describe X-Rays and Gamma Rays uses in medicine?
X-rays pas easily through flesh but not bone so is used for images. Gamma Rays can be used for Radiotherapy.
Describe the dangers of Electromagnetic Waves?
Low frequency waves don’t transfer much energy so mostly pass through soft tissue. (Radio Waves)
High frequency waves transfer lots of energy so cause lots of damage. (UV, X, Gamma)
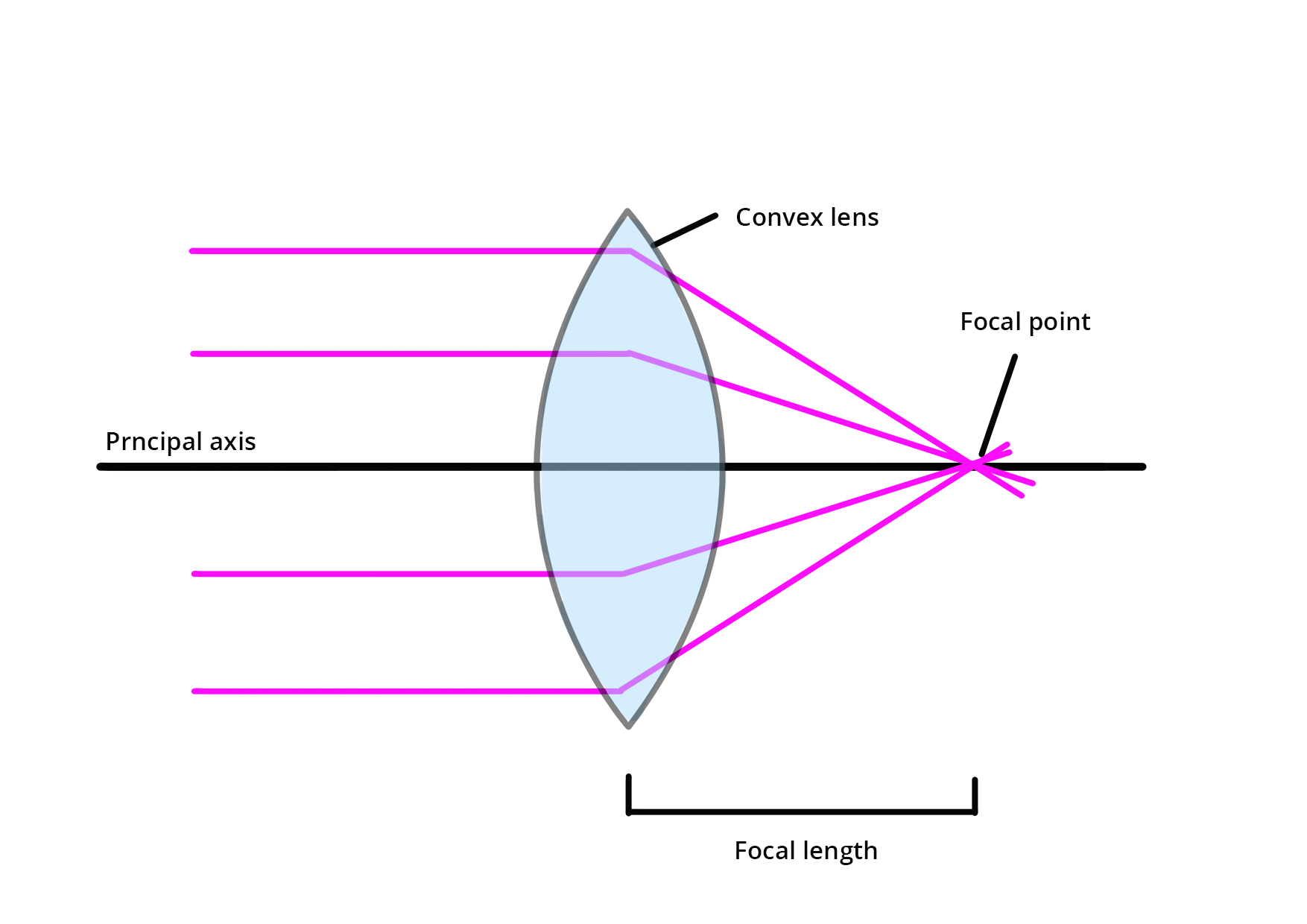
Describe Convex Lens?
A convex lens bulges outwards. It causes rays of light parallel to the axis to be brought together at the principal focus.
The principal focus of a convex lens is where rays hitting the lens parallel to the axis all meet.
The three rules for refraction:
An incident ray parallel to the axis refracts through the lens and passes through the principal focus on the other side.
An incident ray passing through the principal focus refracts through the lens and travels parallel to the axis
An incident ray passing through the centre of the lens carries on in the same direction.
Describe Concave Lens?
A concave lens caves inwards. It causes parallel rays of light to spread out.
The principal focus of a convex lens is the point where rays hitting the lens parallel to the axis appear to all come from.
The three rules for refraction:
An incident ray parallel to the axis refracts through the lens and travels with the principal focus
An incident ray passing through the lens towards principal focus refracts through the lens and travels parallel to the axis
An incident ray passing through the centre of the lens carries on in the same direction.
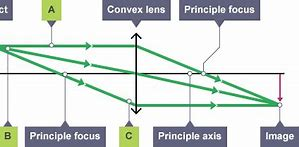
How do you draw a Ray Diagram with a Convex Lens?
Draw a ray from the top of the object to the lens, parallel to the axis (Incident Ray)
Draw another ray from the object through the lens
Draw a ray from the incident ray and through the principle focus on the other side (Refracted Ray)
Mark where the lines meet, which is the top of the image
Connect the image to the axis
If the object is after the focal point, the image will be beyond the focus and inverted onto the other side of the lens
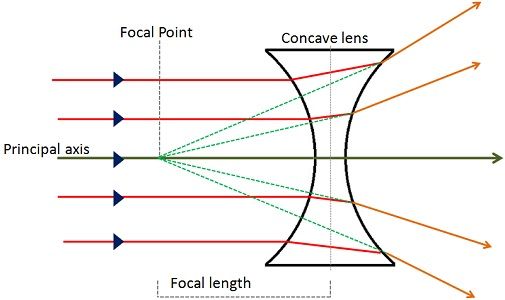
How do you draw a Ray Diagram with a Concave Lens?
Draw a ray from the top of the object parallel to the axis (Incident Ray)
Draw another ray directed towards the principal focus on the same side of the lens
Draw a ray from the top of the object through the center of the lens, which will continue straight
Extend the refracted rays backward to find where they appear to originate, marking the position of the top of the image
Connect the image to the axis
These are always Virtual Images
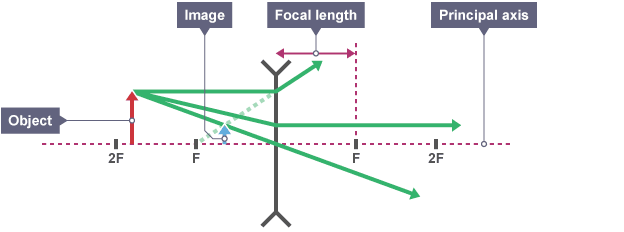
How is an image described?
Upright or Inverted (Which direction the Image is facing)
Magnified or Diminished (How big the image is compared to the object)
Real or Virtual (If the image is on the opposite (Real) or same (Virtual) side of the Object)
What is the formula for magnification?
Magnification = Image Height/Object Height
How do Objects appear the colour they are?
Objects appear the color they are by absorbing certain wavelengths of light and reflecting others. The colour seen is the result of the wavelengths reflected to the observer's eyes.
For example, an apple appears red because it absorbs all wavelengths of light except for those corresponding to red, which are reflected.
White objects reflect all wavelengths of visible light equally.
Black objects absorb all wavelengths of visible light equally.
How can a Leslie Cube be used to investigate Infrared Radiation?
A Leslie Cube can be used to investigate infrared radiation by measuring the temperature differences of its four sides, which are painted different colors. This demonstrates how different colours absorb and emit infrared radiation at varying rates.
What is Black Body Radiation?
A Black Body is an object that absorbs all electromagnetic radiation that hits it. No radiation is reflected or transmitted. They are the perfect emitters and absorbers of radiation.
How does Radiation affect the Earth’s Temperature?
Radiation affects the Earth's temperature by transferring energy from the sun to the planet and through the greenhouse effect, where certain gases trap heat in the atmosphere. This process regulates the climate and maintains temperatures suitable for life.
What are Sound Waves and how are they created?
Sound waves are longitudinal waves that are created by the vibration of objects, which causes fluctuations in air pressure. These pressure variations travel through a medium, such as air or water, and can be detected as sound.
They can be reflected, refracted, or absorbed depending on their interaction with different surfaces.
What is Ultrasound?
Ultrasound is a type of sound wave with frequencies higher than 20000 Hz, the audible range of human hearing. It is used in medical imaging, echo sounding in boats and various industrial applications.
What are P-waves and S-waves?
P-waves (primary waves) are compressional seismic waves that move through solids and liquids. They are Longitudinal and faster
S-waves (secondary waves) are shear waves that can only travel through solids. They are Transverse and slower
They are both generated during an earthquake and are used to study the Earth's internal structure.
P-waves can travel through the Earth’s core and S-waves cannot.
Describe a magnet?
A magnet is an object that produces a magnetic field, attracting magnetic materials such as iron, nickel, and cobalt.
Magnets have two poles, north and south, where the magnetic force is strongest. If two poles of a magnet are put near each other they will exert a force on eachother.
How can you create a Magnetic Field Diagram?
Place a magnet in the centre of a piece of paper
Draw 8 dots around the north pole of the magnet
Place a compass on your first point
Place a dot at the end of the compass where the arrow is pointing
Repeat this for the next few points until your line reaches the other pole
Connect the points together
Repeat the whole process for the next 7 points around the pole
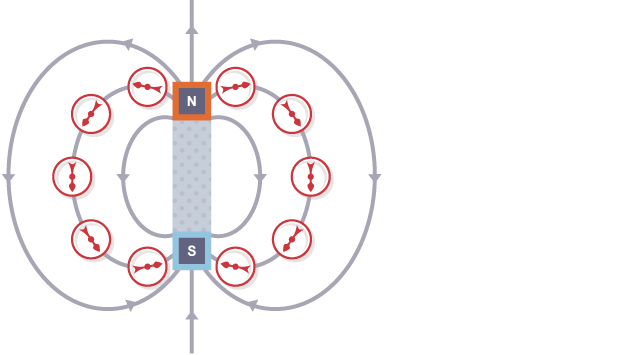
What are the two types of magnets?
Permanent Magnets - They produce their own magnetic field
Induced Magnets - They become magnetized in the presence of an external magnetic field and lose their magnetism when removed from the field
How does a wire create a magnetic field?
When an electric current flows through a wire, it generates a magnetic field around it. This field forms concentric circles around the wire, with the strength of the field depending on the current's intensity.
The direction of the magnetic field can be determined using the right-hand rule.
The right-hand rule states that if you point your thumb in the direction of the current, the curled fingers show the direction of the magnetic field.
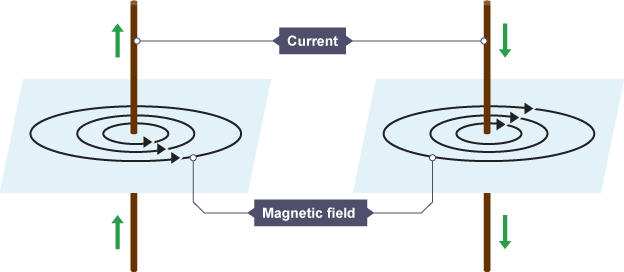
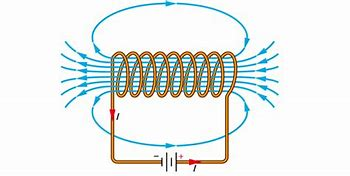
What is a Solenoid?
A solenoid is a coil of wire that generates a magnetic field when an electric current is passed through it. This magnetic field is similar to that of a bar magnet and can be controlled by varying the current.
Inside the solenoid, the strength is very high as there are lots of field line pointing in the same direction due to the coils.
You can increase the field strength with an iron core, creating an electromagnet.
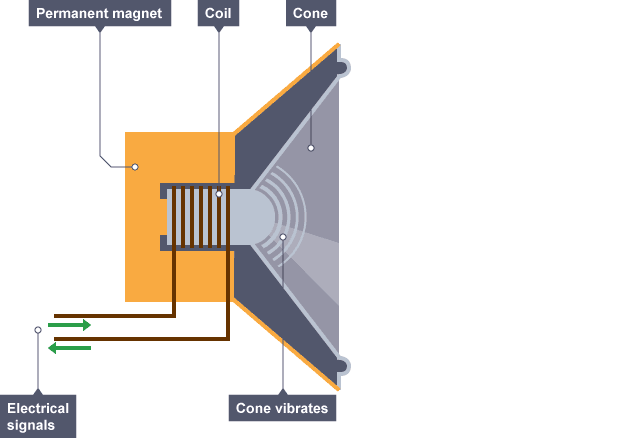
What can Electromagnets be used for?
Electromagnets can be used in various applications such as electric motors, generators, magnetic locks and loudspeakers.
What is the Motor effect?
When a current-carrying wire in a magnetic field experiences a force that causes it to move.
What is the formula for Force?
Force (N) = Magnetic Field Strength (T) × Current (A) × Length (m)
F=BIL
What is Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule?
A rule used to determine the direction of force experienced by a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field.
The thumb represents the direction of the motion, the index finger represents magnetic field direction, and the middle finger represents current direction.
How do Loudspeakers work?
An alternating current is sent through a coil of wire creating a electromagnetic field
The field interacts with the permanent magnet, generating a force that pushes the cone outwards
When the current reverses, the force acts in the opposite direction
This causes the cone to vibrate and produce sound waves
By controlling the frequency of the ac you can alter the sound wave produced
What is the Generator Effect?
The induction of a potential difference in a wire which is moving relative to a magnetic field, or experiencing a change in magnetic field.
This effect occurs when a magnet is moved near a coil of wire or when the coil is moved within a magnetic field, resulting in the generation of electrical energy.
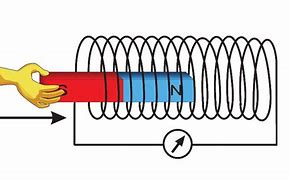
Why does the induced current oppose the change made?
The direction of induced current will be such that it opposes the change in magnetic flux that produced it. This is a consequence of the conservation of energy.
What are Alternators?
A device which generates an ac supply using the generator effect.
As the coil spins, a current is induced in the coil. This current changes direction every half turn.
Ac generators have slip rings and brushes so the contacts don’t swap every half turn.
This produces an alternating potential difference.
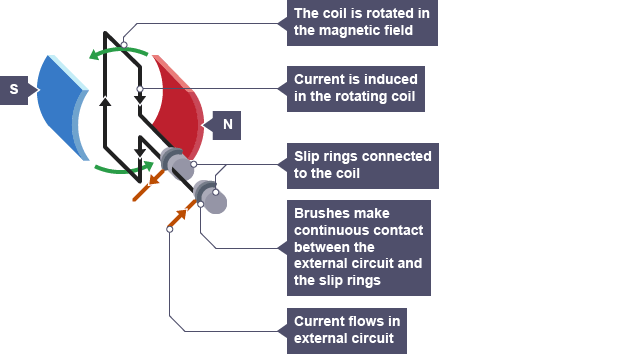
What are Dynamos?
A device which generates a dc supply using the generator effect.
They work in the same way as alternators except they have a split ring commutator instead of slip rings.
This swaps the connection every half turn to keep the current flowing in the same direction.
How do Microphones work?
Sound waves enter a flexible diaphragm that is attached to a coil of wire wrapped around a magnet
This causes the coil of wire to move in the magnetic field creating a current
The movement of the coil depends on the sound wave's pressure variations, converting sound into an electrical signal
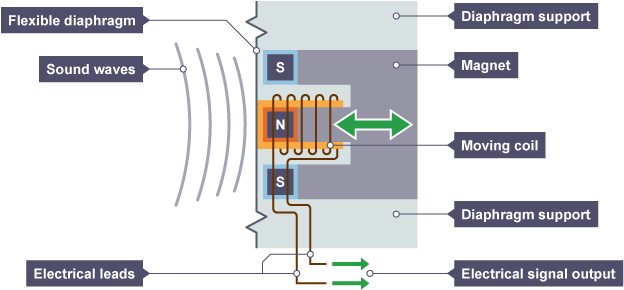
What do Transformers do?
They change the size of the potential difference of an alternating current.
Transformers consist of two coils of wire, known as the primary and secondary coils, which are wound around a core.
When an alternating current passes through the primary coil, the iron core magnetises and demagnetises quickly. This changing magnetic field induces an alternating pd in the secondary coil.
If the second coil is part of a complete circuit, this causes a current to be induced.
The ration between the primary and secondary pds is the same as the number of coils.

What is the Transformer Equation
Input PD / Output PD = Primary coils / Secondary coils
What is the Life Cycle of Stars?
Nebula - Stars initially form from a cloud of dust and gas.
Protostar - Gravity pulls the dust and gas together to form a protostar.
Temperature rises as the star gets denser causing more particles to collide, eventually leading to nuclear fusion of hydrogen nuclei creating helium nuclei.
This releases lots of energy keeping the core hot, creating a star.
Main Sequence Star - The star enters a long stable period where outward pressure caused by the fusion that tries to expand the star balances gravity pulling it together. It usually lasts several billion years (The Sun is in this stage).
Red Giant - Once hydrogen in the core is depleted, the star swells into a Red Giant/Super Red Giant. It becomes red due to the surface cooling. Fusion of helium occurs and heavier elements are created in the core.
White Dwarf/Black Dwarf - After the red giant phase, the outer layers are shed as it becomes unstable, and the remaining core becomes a white dwarf, which will eventually cool and fade into a black dwarf
Red super giants start to glow brightly again as they undergo more fusion and expand and contract multiple times, forming elements as heavy as iron in nuclear reactions.
Supernova - Eventually it explodes, forming elements heavier then iron and ejecting them into the universe to form new planets and stars.
Neutron Star/Black Hole - The exploding supernova throws the outer lauers of dust and gas into space, leaving a very dense core called a neutron star. If it big enough it will become a black hole.
What is a Black Hole?
A super dense point in space that not even light can escape from
What orbits our Solar System?
Planets - Large objects in which their gravity is strong enough to have pulled in any nearby objects apart from natural satellites
Dwarf planets - Planet-like objects that orbit stars but don’t meet the requirements to be a planet
Moons - Objects that orbit planets and are natural
Artificial Satellites - Objects that humans have built that orbit in space
How does something orbit?
If an object is travelling in a circle it is constantly changing direction, which means it is constantly accelerating. This means it is constantly changing velocity.
For an object to accelerate, there must be a force acting on it. This force is directed towards the centre of the circle
This force would cause the object to just fall towards whatever it was orbiting, but as the object is already moving, It just causes it to change direction.
The object keeps accelerating towards what it is orbiting but the instantaneous velocity keeps it travelling in a circle.
This force is Gravity.
How does speed change with orbit?
The closer you get to a star/planet, the stronger the gravitational force is.
The stronger the force, the faster the orbiting object needs to travel to remain in orbit.
For an object in a stable orbit, if the speed of the object changes, the size of its orbit must do so too. Faster moving objects will move in a stable orbit with a smaller radius than slower moving ones.
What is Red-shift?
The shift in observed wavelength of light from a source moving away from a stationary observer. The wavelength is shifted towards the red end of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Why does the Universe seem to be Expanding?
The Universe appears to be expanding due to the observation of red-shift in distant galaxies, indicating that they are moving away from us. This phenomenon suggests that space itself is stretching, causing galaxies to recede from one another.
What is the Big Bang Theory?
Initially, all the matter in the universe occupied a singular point which was very dense and so very hot. It then exploded, causing the expansion of the universe and the formation of matter as it cooled.
What is Dark Matter and Dark Energy?
Dark Matter refers to the unseen mass that does not emit light or energy, making it undetectable by current instruments
Dark Energy is the mysterious force driving the accelerated expansion of the universe.