Politics
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Politics
associated with decisions in groups, making decisions in groups, managing power relations allocating resources esp. within a state or a organized community
Decisions = impact
involves processes and activities
influences choices
factors that leads to political views
Demographics
Psychological
Social
Economic
Political
Demographic
Age
Gender
Education
Race and Ethnicity
Socio Economic
Place or residence
Psychological
Personality traits
Belief/Values
Cognitive Biases
Emotional Responses
Social
Family
peers
Social group and identity
Socialization
Movement and Activism
Economic
condition
policies
stocks (inflation)
Political
events
Institution
Election
Media
Policies
Polis
greek for city
Types of Government
legislative
Excutive
Judicial
Legislative
gumagawa ng batas/makes laws
Judicial
Implements the law
Excecutive
taga approve ng batas (15 days before approval)
Governance
the ways, the impact
uses clear framework and efficent communication to make decisions
Government
body/Group of people that leads a state
has authourity to create for the community
Political Science
systematic study of the state and the government
Political Ideology
belief on how society should be governed
“Blueprint” for organizing power, shaping policy and defining justice
Logos
Greek for Idea, form or Pattern
Functions of Political Ideology
Analysis of Status Quo (What works and what doesn’t work) and find alternatives to perscribe a preferred or desired social order
specifies means (or ways) to achieve the desired social order
Liberalism
Individual freedom and equality & Protection of Rights however it is under the law of the country
most influential
Consists of:
Individual Rights
Consent of the Governed
Equality before the law
Rule of Law
Democracy
Effects of Liberalism
Cons
Going against the law
Going against belief
Injustice
division or Inequality
Pros
Freedom (with limitation)
Equality (Ex. are Human rights)
Limited Government = Individual freedom
Conservatism
Resistence to change
tied to the past
has an impact on cultural values, economic systems and cultural values
Consists of:
Tradition
Limited Government intervetion in economic and social matters
Individual Freedom
National Identity by perserving heritage
Pros and Cons of Conservatism
Pros
Stability and Identity Order
Perserve Culture
Promotes Law and Discipline
Cons
Slow Innovation
Inequality
Limit Adaptability and Freedom
Anarchism
No Authourity, law or Rule with cooperation
rejection of Authourity
Individual Freedom
Voluntary Association
Utopian Idea
Pros and Cons of Anarchism
Pros
Bayanihan
lessens Corruption
Lessens Discrimination
Group Decsions
A voice for everyone
Cons
too much Freedom
unorganized spaces
No rules
vulnerable to attacks
crime rates increases
Socialism
laborers are the backbones
Equality vs Equity
where the people collectively own or control the means of production
Communism
common
classless, stateless. social society
total control
no private property
can only be achieved through a revolution
Ex. USSR - a socialist that aims for communism
Fascism
oppresion of oposition
extreme nationalism
authouritarian
militarian
Pros and Cons of Fascism
Pros
Nationalism
Preservation og Culture and Trasdition
Law and Order
Strong Leadership
Cons
Pro-violent
Racism and Xenophobia
Autocracy
Suppression of Freedom
Full government control
censorship of media
Feminism
equality, social justice, empowermetn and challenges patriarchy
Internationality
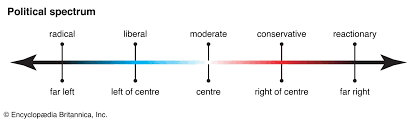
Political Spectrum