ARP & ICMP (week 4-ish)
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
when you want to communicate on a network, the information that is sent between nodes is encapsulated in ___
an ethernet frame
ethernet frames need the ___ of the nodes involved in the conversation in order to send the frame to the correct recipients
MAC addresses
how does a node learn the MAC address of a destination?
ARP! (use Address Resolution Protocol)
(hey everybody: i’m looking for the MAC that goes with this IP)
Address Resolution
the process of mapping ___ to ___
only addresses ___ are resolved
___ addresses are never resolved
protocol addresses (IP); hardware addresses (MAC)
on the same network as the host
remote
RFC 826 An Ethernet Address Resolution Protocol -- or -- Converting Network Protocol Addresses to 48.bit Ethernet Address for Transmission on Ethernet Hardware
The purpose of this RFC is ___
to present a method for Converting Protocol Addresses (e.g., IP addresses to Local Network Addresses (e.g., Ethernet addresses)
Address Resolution w/ Message Exchange
___ approach
Host sends out a ___ and receives back a ___
Adds ___ but no ___
distributed
message with the request; reply
net traffic; management
Address Resolution w/ Message Exchange
Message exchange is used on ___ with ___ addressing
ARP is part of the ___ suite - standard
two type messages defined: ___
LANs; static
TCP/IP
request & reply
ARP message format
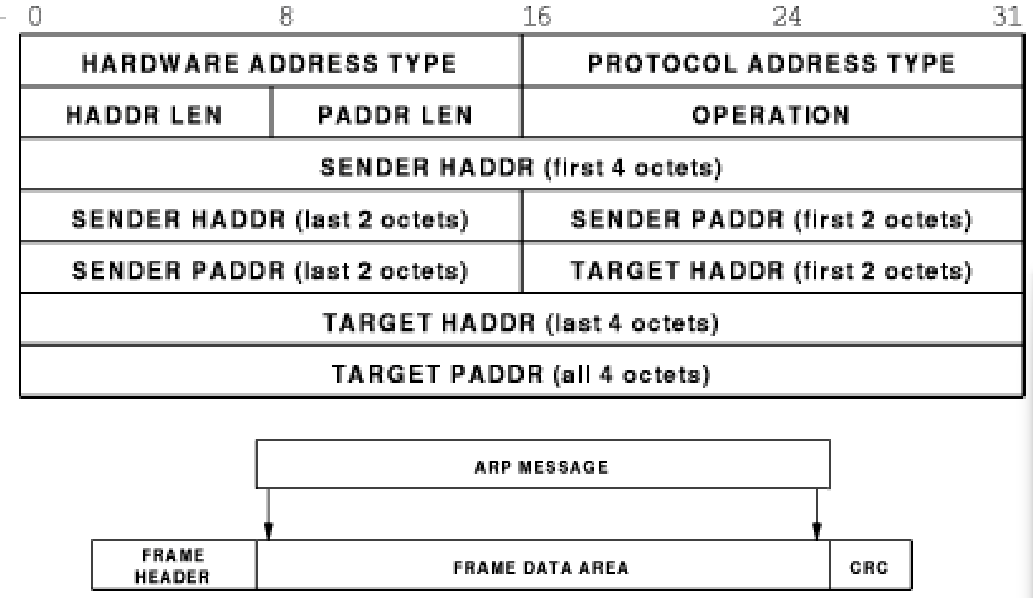
example of ARP packet exchange resulting from a PING

what kinds of traffic result in ARP messages being generated?
all kinds! not just PING/ICMP!
ARP table
what is stored in an ARP table?
who has an ARP table?
what happens to old entries?
what types of entries can be added?
the results from an ARP exchange are stored in the requestors ARP table
all IP based hosts have an ARP table
a timer (~2 min for Windows) will age out the entries
dynamic (resulting from ARP exchange?) and static (added manually?)
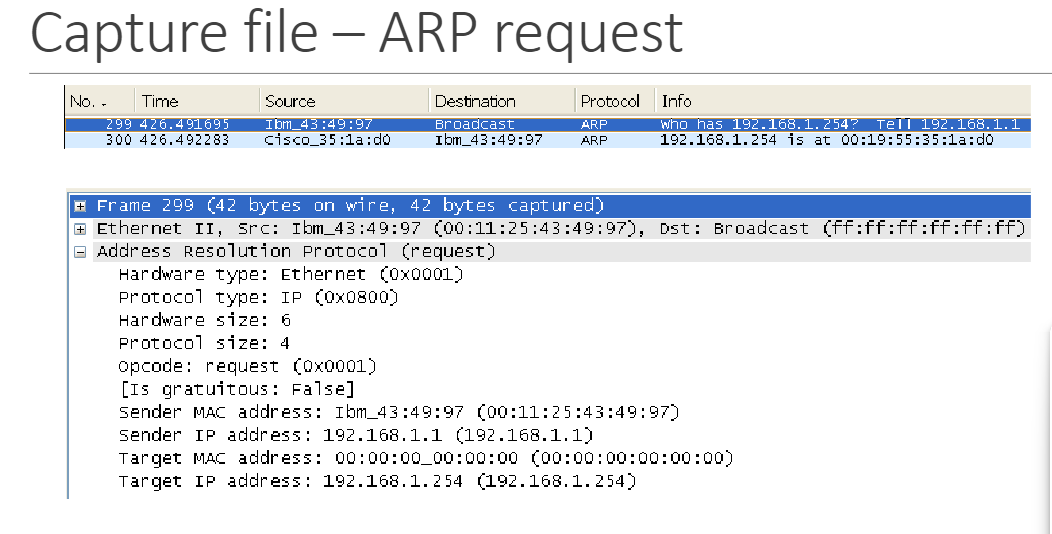
capture file - ARP request
note the 0s in the target MAC address (we don’t know it)
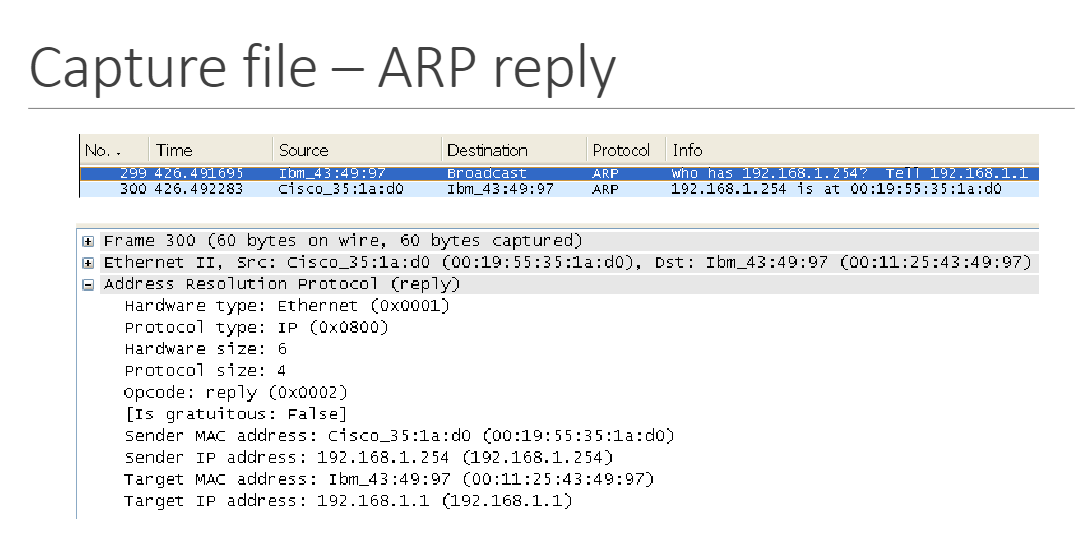
capture file - ARP reply
ARP messages have no ___
IP header
“Effect on filters”
gratuitous ARP
basically asking if anyone else is using the IP address you’re trying to use as your own

reverse ARP
a method for workstations to dynamically find their protocol address (e.g. their Internet Address) when they only know their hardware address (e.g. their attached physical network address
(i guess through BOOTP?)
proxy ARP
technique involving the use of the Ethernet Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) by subnet gateways to permit hosts on the connected subnets to communicate without being aware of the existence of subnets
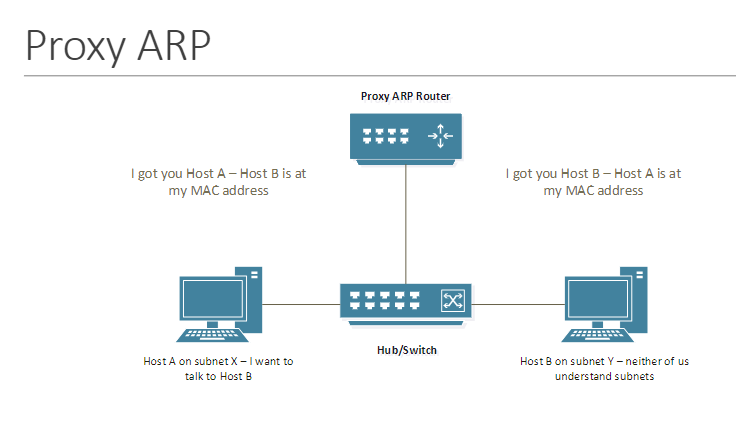
many events (related to routing and workstations, reachability, settings, different points of view, etc.), most based on the IP fields, will trigger ___ messages
ICMP
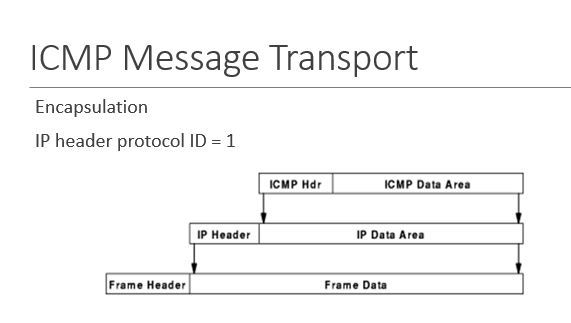
ICMP is encapsulated in ___
IP (no layer 4 protocol)
when the IP header protocol ID = ___, it’s encapsulating an ICMP message
standard ICMP header
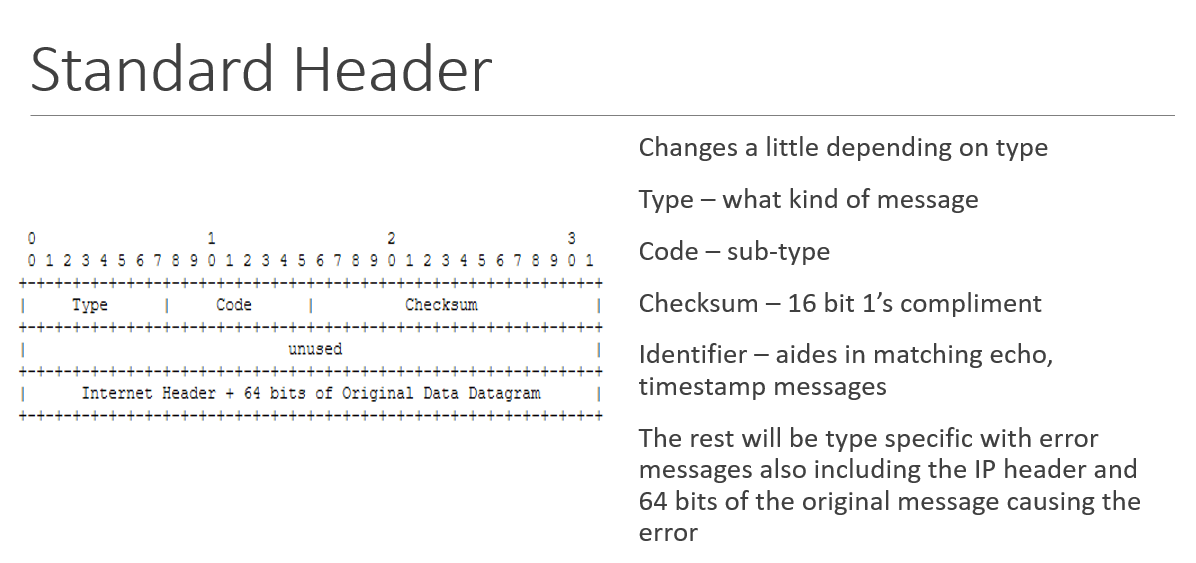
ICMP error message types
3 - Destination Unreachable
4 – Source Quench
5 – Redirect
11 – Time exceeded
12 – Parameter problem
ICMP information message types
0 – Echo Reply
8 – Echo request
13 – Timestamp message
14 – Timestamp reply message
15 – Information (network) Request
16 – Information Reply
ICMP echo request/replies provide proof of ___ and are generated using the ___ program
life; ping
capture file - ICMP echo request
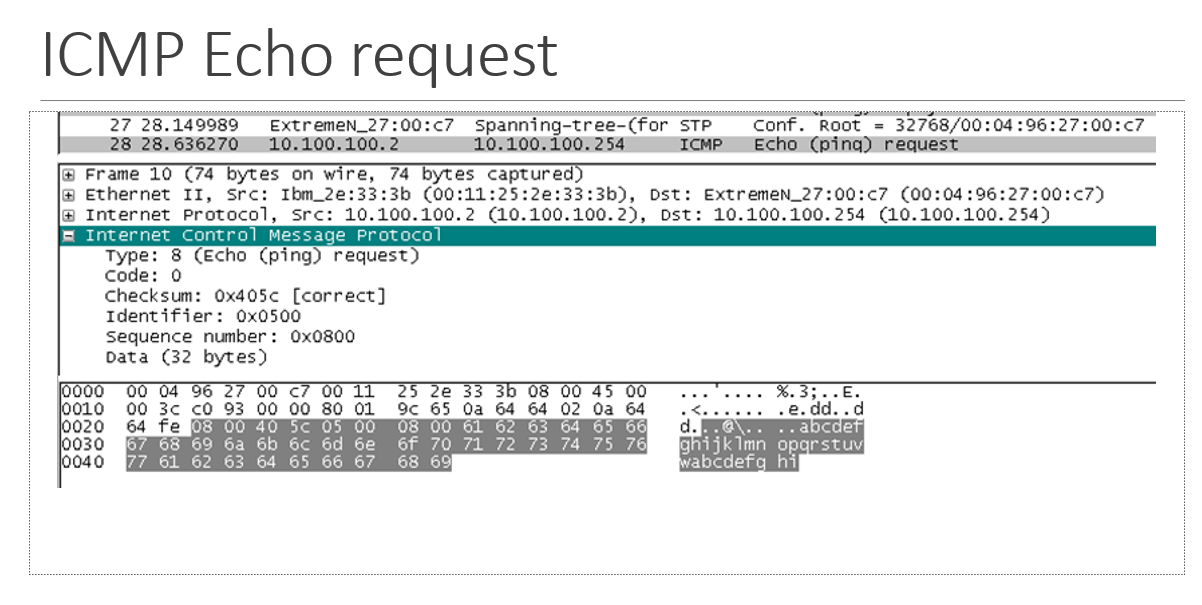
when a host has a datagram for another network, it sends the datagram ___
to the router (default gateway)
when is an ICMP redirect message sent?
a router which has received a message for forwarding determines that another router should be used
sends a redirect message (type 5)
it also forwards the datagram, but hopefully only once
what are the requirements for an ICMP redirect message?
no source routing information
new forwarding router must be on the same network as the sender
old router must have to send the packet out the same interface that it came in
result of an ICMP redirect
original datagram is encapsulated and the new info is included; results in a host routing table update
capture file - ICMP redirect
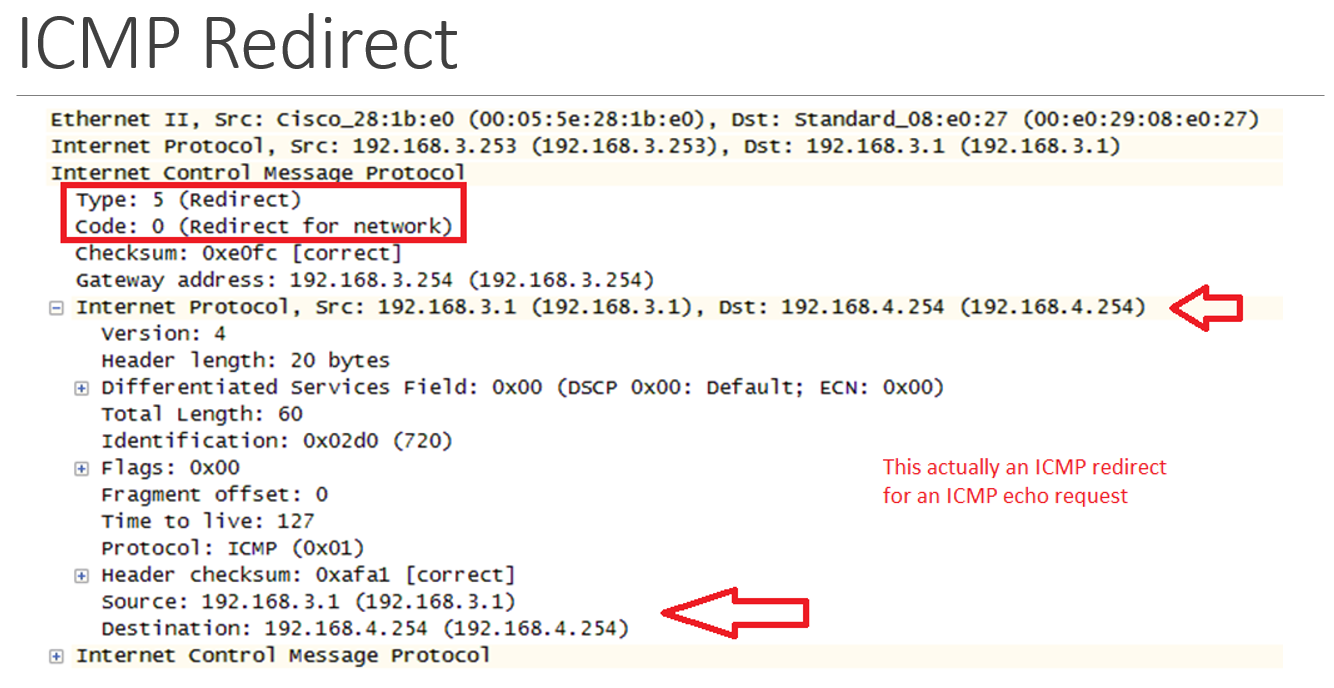
why must routing loops be allowed
distributed nature of network design, redundancy
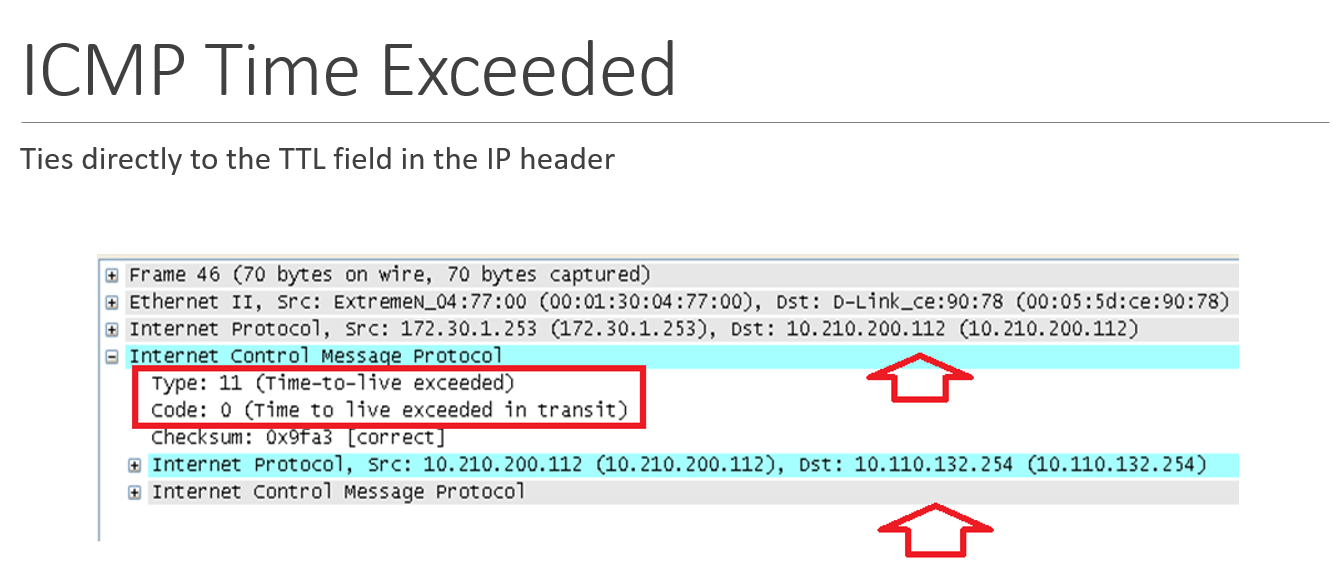
ICMP time exceeded
these messages keep a packet from wandering in a routing loop forever
each datagram include a TTL (time-to-live) field (varying in length)
the TTL value is decremented by each router through which the datagram passes
once it reaches 0, a Time to live Exceeded (type 11) ICMP message, including the original message info, is sent to the sender
capture file - ICMP Time Exceeded
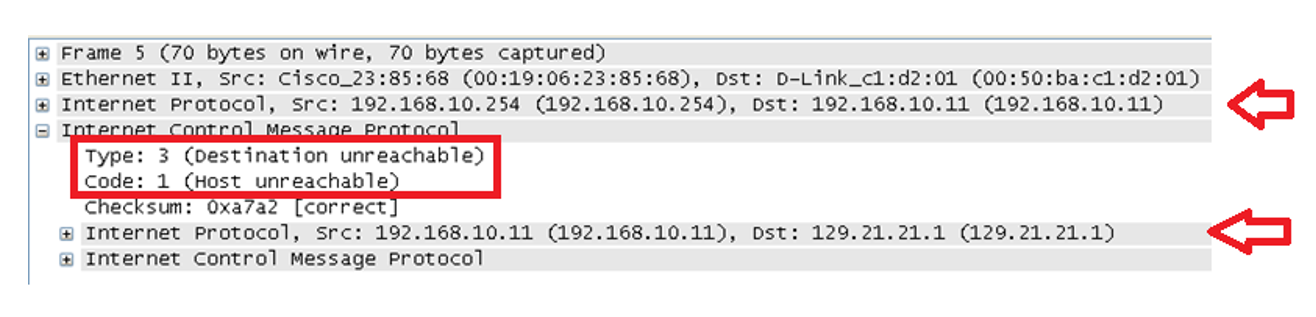
ICMP destination unreachable
type 3
sent when a router determines that a datagram cannot be delivered ( destination IP address doesn’t exist, machine is down, router is offline, entire network is disconnected, router doesn’t know)
the different reasons for being “unreachable” are handled with the code field
this type is also used when a firewall filters a packet
IP header and 64 bits of original packet info is included
ICMP destination unreachable codes
0 = net unreachable
1 = host unreachable
2 = protocol unreachable
3 = port unreachable
4 = fragmentation needed and DF set
5 = source route failed
Note: There are other codes
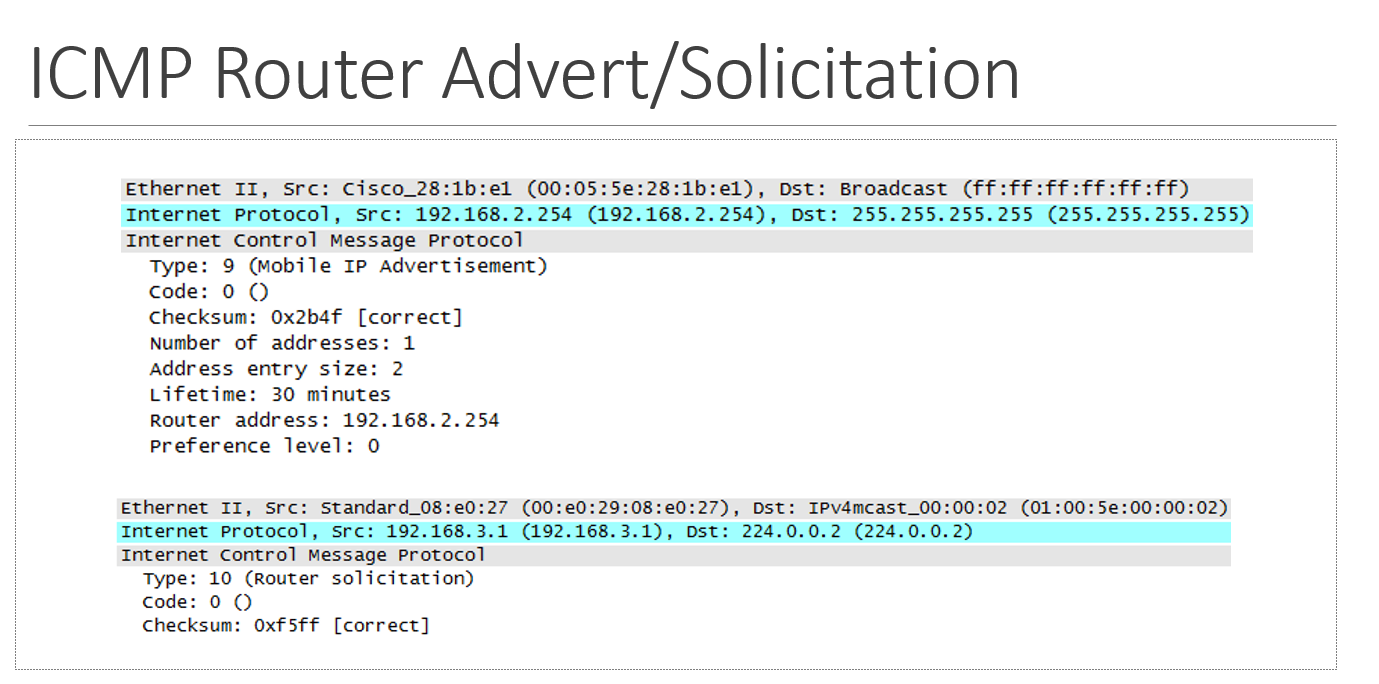
we no longer use router advertisements (ICMP type 9) or solicitations since we have ___
DHCP
(but in a MobileIP environment, we may have to)
(IPv6 uses these messages (ICMP router discovery messages) in the neighbor discovery process)
capture file - ICMP router advert/solicitation
MTU
maximum transmission unit; a measurement representing the largest data packet that a network-connected device will accept
Don’t Fragment (DF) bit (IP header)
can be set by host to disallow fragmentation of the IP packet
Path MTU Discovery

ICMP address mask request/reply
types 17 and 18
request for correct subnet mask for this network
responded to by router
today this is also handled by the DHCP server
ICMP domain name message
lets you learn the fully qualified domain name associated with an IP address
deprecated
ICMP source quench
when a router runs out of buffer space
discards packets
sends a source quench ICMP packet to source of each packet discarded
when a host receives a source quench packet, it reduces the rate at which it sends packets to the router
deprecated
ICMP messages alternate host address (6), information request/reply (15/16), mask request/reply (17/18), and traceroute (30) (among others) are ___.
deprecated
ICMPv6 vs ICMPv4
operates in similar fashion to ICMPv4
both have error and info messages
but there are several new messages types
and ICMPv6 can take a very active role in IPv6 topology resolution
Neighbor discovery
Several message types: […]
Router advertisement
Router solicitation
Neighbor advertisement
Neighbor solicitation
Redirect
There are others …
(this is from the ICMP slides)
IPv6 has no ___ messages so no ___
broadcast; ARP
(uses Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP))
when node A sends ARP request, a connected switch will ___
add A to its source address table
ICMP is part of IP protocol stack (so no ___ numbers)
port
? = most common ICMP errors
Destination Unreachable, Redirect, and Time exceeded
How many addresses are defined in ARP?
2
Is an ARP message routable?
No, the messages do not contain an IP header.
Describe the Ethernet addressing used in the standard ARP request. Are the source and destination addresses unicast, broadcast, or multicast?
The ARP request uses a unicast address for the source and a broadcast address for the destination.
Describe the Ethernet addressing used in the standard ARP reply. Are the source and destination addresses unicast, broadcast, or multicast?
The ARP reply uses a unicast address for the source and a unicast address for the destination.
Is ARP a secure protocol?
No. False ARP messages can be created to fool ARP tables. Hosts then make in correct forwarding decisions. ARP transmissions are also sent in the clear.
Linux vs Windows pings
64 bytes in size; sends continuous pings by default
32 bytes in size; sends only 4 pings by default