Cell Membrane & Extracellular Matrix
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 14
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Fluid Mosaic Model
the plasma membrane is composed of lipids, proteins, and carbs
Cholesterol
a temperature mediator; prevents too much fluidity or solidification of the phospholipid bilayer
What moves laterally and what drifts within the phospholipid bilayer?
Lipid molecules move laterally and proteins drift across the phospholipid bilyaer.
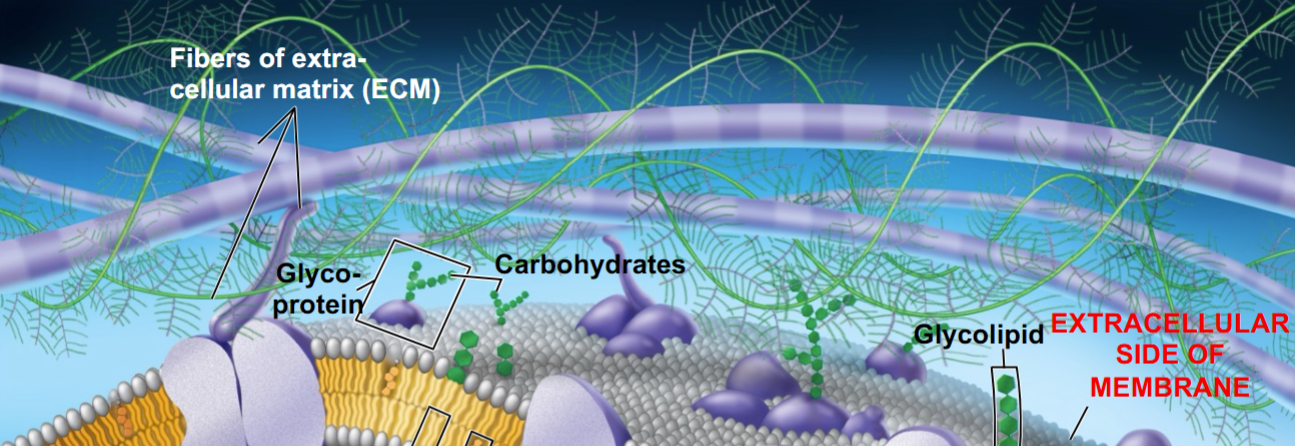
Glycoproteins & Glycolipids
carbs added to proteins and lipids; faces the extracellular (outer) surfaces
acts as an “ID tag” for cell recognition
Integral (Transmembrane) Proteins
spans the entire bilayer; amphipathic (fluid movement) with the hydrophobic tails
Peripheral Proteins
loosely bound to the inner or outersurface
What are the 6 major functions of membrane proteins?
Transport across the membrane
Catalyzes reactions (enzymatic)
Relays external signals
Recognizes neighboring cells
Forms junctions between cells (adhesion)
Attaches the cytoskeleton to the ECM
How do saturated vs unsaturated fatty acids affect membrane fluidity?
Saturated fatty acids decreases fluidity.
Unsaturated fatty acids increase fluidity.
Passive Transport
no-energy movement along a concentration gradient
Active Transport
ATP moves substances against the concentration gradient
Aquaporins
channel proteins that allow rapid water passages across membranes
Plasmodesmata
(in plants) opening in the cell walls so small molecules/ions can pass through
Tight Junctions
(in animals) seals neighboring cells, preventing leakage
Gap Junctions
(in animals) opening in the cell walls so small molecules/ions can pass through
Desmosomes
(in animals) anchors cells together by connecting their intermediate filaments
Extracellular Matrix (ECM) (structure)
*ONLY IN ANIMALS*
composed of collagen fibers in a web of proteoglycan complexes
Extracellular Matrix (ECM) (function)
support
adhesion
communication
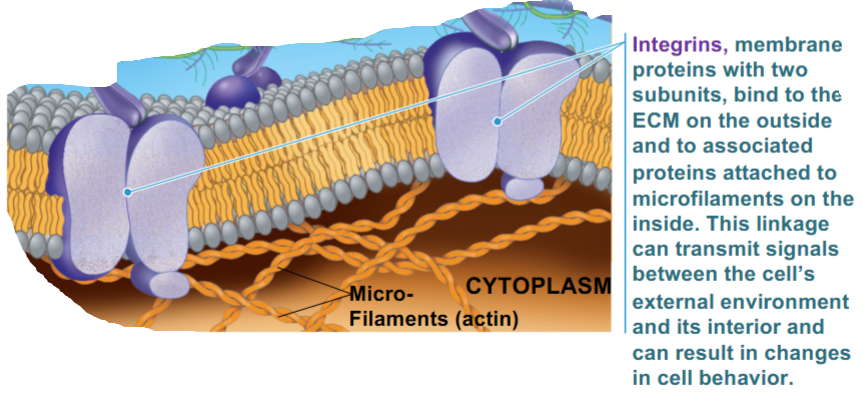
Integrins
cell surface’s receptor proteins
anchors the cytoskeleton (microfilaments) to the ECM
transmits signals
influences gene expression and movement
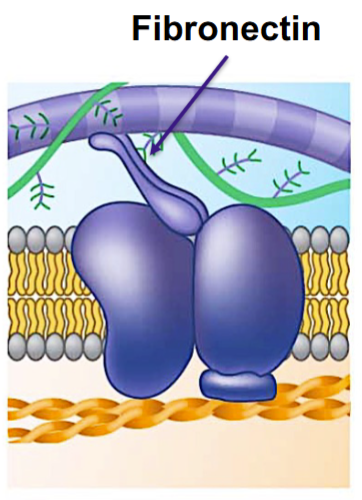
Fibronectin
connects the ECM to integrins