first part
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Explain the History of Ultrasound (sunod-sunod dapat)
19th century → WW2 → Sonar → Damage to marine life →
EUREKA → TISSUE HEATING
Ultrasound most effectively heats _____ with a _____ such as _____, _____, _____, and _____
deep tissue; high collagen
content; tendons; ligaments; joint capsules; fascia
Ultrasound has both _____ and _____ effects
thermal; non-thermal
Soundwaves that transmit energy by alternately ____
and _____ material
compressing; rarefying
Ultrasound has a frequency greater than _____
20,000 cycles/second (Hz)
Frequency of Therapeutic Ultrasound
•_____ to _____ to maximized energy absorption at a
depth of _____
0.7 to 3.3 MHz; 2 to 5 cm
What are the physical effects of ultrasound? (include the bpts)
Thermal
increase in tissue temperature
Non-thermal
Acoustic streaming
Microstreaming
Cavitation
Ultrasound Sound Wave can be described by:
• Intensity (w/cm2)
• Frequency (MHz)
• Duty cycle (%)
• Effective radiating area (ERA)
• Beam Nonuniformity Ratio (BNR)
unit of measurent of Intensity
(w/cm2)
unit of measurent of frequency
(MHz)
unit of measurent of duty cycle
(%)
The decrease in US intensity as it travels through tissue
Attenuation
Attenuation
The _____ in US intensity as it travels through tissue
decrease
Attenuation
The decrease in US _____ as it travels through tissue
intensity
Attenuation is _____ and _____ specific
tissue; frequency
As it enters the body, US is attenuated by:
Absorption
Reflection
Refraction
50% of attenuation; 50% of sound is
absorbed by tissues
Absorption:
no absorption, bounce back
• Reflection –
not absorbed by target tissue; bounces to
other areas
• Refraction –
Attenuation, dB/cm of blood
0.12
Attenuation, dB/cm of fat
0.61
Attenuation, dB/cm of nerve
0.88
Attenuation, dB/cm of muscle
1.2
Attenuation, dB/cm of blood vessel
1.7
Attenuation, dB/cm of skin
2.7
Attenuation, dB/cm of tendon
4.9
Attenuation, dB/cm of cartilage
5.0
Attenuation, dB/cm of bone
13.9
TRUE OR FALSE: When US is used in bones, it is more on for fracture healing
TRUE
When US is used in bones, it is more on for _____
fracture healing
The proportion of the total treatment time during which
ultrasound is being delivered
The duty percentage or the ratio of the on time to the total
cycle time
Duty Cycle
The proportion of the total treatment time during which
ultrasound is being delivered
Duty Cycle
The duty percentage or the ratio of the on time to the total
cycle time
Duty Cycle
TRUE OR FALSE: Higher duty cycle = more heat
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE Higher duty cycle = less heat
FALSE; more heat*
• High Frequency AC (alternating current) – crystal of transducer
head is made of material with piezoelectric properties
• Crystal expansion – compression of material in front
• Crystal contraction – rarefies material in front
• Alternating compression – rarefaction à US wave
Generation of Ultrasound
crystal of transducer head is made of material with piezoelectric properties
• High Frequency AC (alternating current) –
crystal of transducer head is made of material with _____
piezoelectric properties
compression of material in front
• Crystal expansion –
• Crystal expansion –
compression of material in front
rarefies material in front
• Crystal contraction –
• Crystal contraction –
rarefies material in front
US wave is generated from?
• Alternating compression – rarefaction →
• The ratio of the highest intensity in the field to the spatial
average intensity
• Heat/hotness of US
• 5:1; 6:1; 2:1
Beam Nonuniformity Ratio (BNR)
• The ratio of the highest intensity in the field to the spatial
average intensity
Beam Nonuniformity Ratio (BNR)
• Heat/hotness of US
Beam Nonuniformity Ratio (BNR)
• 5:1; 6:1; 2:1
Beam Nonuniformity Ratio (BNR)
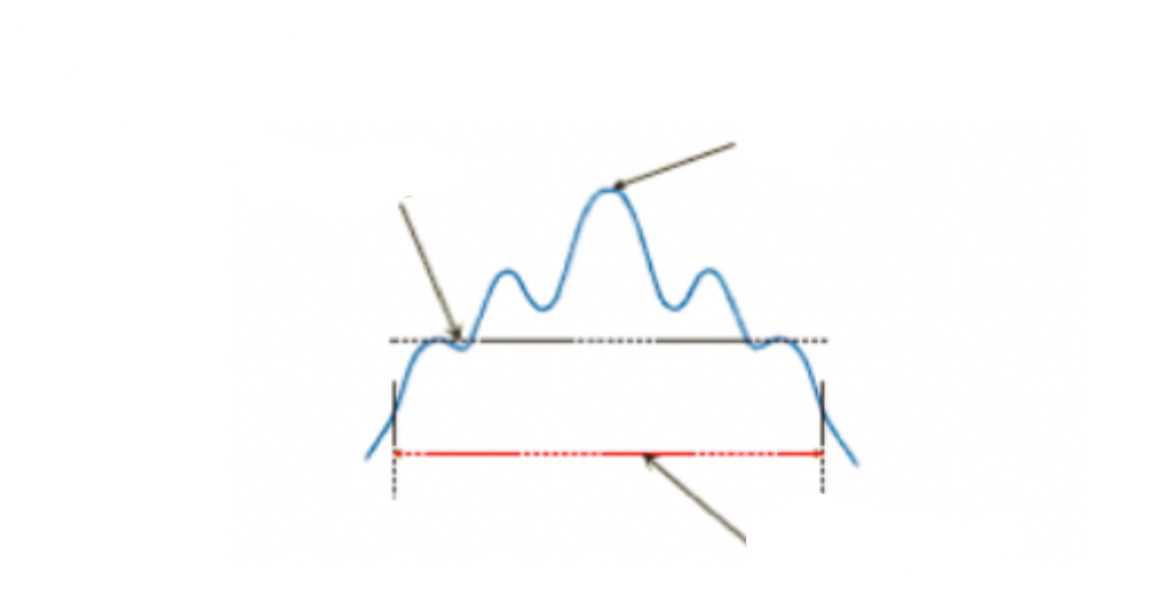
Label
Average
Peak
E.R.A diameter
These/this have/has high water content
Blood
Fat
Nerve
These/this are/is neutral
muscle
These/this have/has high collagen content
Blood vessel
Skin
Tendon
Cartilage
Bone
What is the %/cm of Blood
3
What is the %/cm of Fat
13
What is the %/cm of Nerve
0
What is the %/cm of Muscle
24
What is the %/cm of Blood vessel
32
What is the %/cm of Skin
39
What is the %/cm of Tendon
59
What is the %/cm of Cartilage
68
What is the %/cm of Bone
96