Monetary Policy
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Monetary Policy
Monetary policy is carried out by the central bank and involves the control of money supply and interest rates to influence aggregate demand and fulfil macroeconomic objectives.
Central bank
The monetary authority responsible for an economy’s monetary policy and financial system regulation.
Interest rates
The cost of borrowing and reward for saving of money, expressed as a percentage.
Money supply
The amount of money circulating in the economy, which includes notes and coins, loans, credits and deposits.
Demand-side policy
Government policy that aims to influence the level of AD of the economy.
Goals of monetary policy (4)
Low and stable rate of inflation → Promote a stable economic environment for a long-term growth
Low unemployment
Reduce business cycle fluctuations
Balance of payments or External balance
Inflation target
An inflation target is the practice of using monetary policy to achieve a predetermined level of inflation. The increased transparency of the central bank creates a stable economic environment
Why does a real GDP increase influence unemployment (3)
Increase in Real GDP means higher demand for goods and services → increased demand so companies need to produce more → hire more workers → reduced unemployment
Increased GDP means economic growth → encourages business expansion as more profits due to more demand → need to hire more workers to expand → reduced unemployment
Increase GDP → more tax revenue as increase in income due to increase in GDP → more government projects → need to hire more people → reduced unemployment
How does monetary policy reduce unemployment with diagram
The government reduced the interest rate → it becomes easier to borrow money → people have more money with them → AD shifts to the right → Real GDP increases → encourages investment → more people employed unemployment decreases
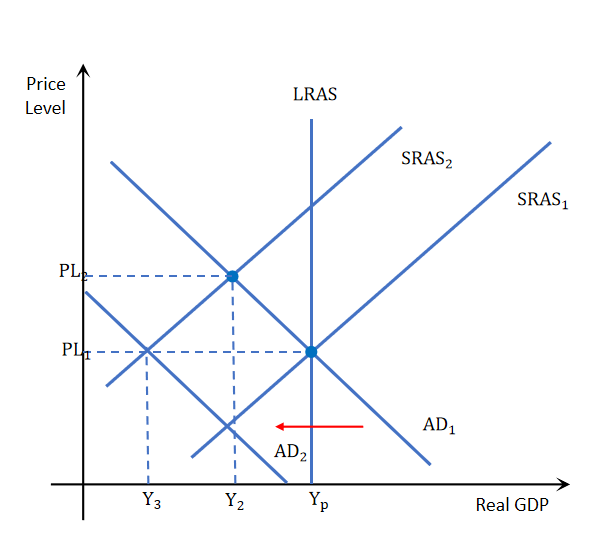
How does monetary policy reduce business cycle fluctuations
When the economy is in a downturn monetary policy can be used to increase aggregate demand by simply reducing the interest rate and vice versa
How does monetary policy affect BOP or External balance
If the interest rates are lowered → currency less attractive to foreigners → exchange rate decreases people arent demanding INR → Export prices then reduce → demand for exports increase → export revenue > import expenditure → inflationary pressure as more money flows in
Vice versa
Credit creation
Credit creation is the process by which banks create money by providing loans using saving deposits.
How do banks profit from loans (no MRR)
Saver deposits 100$ → Bank loans out that 100$ → asks the borrower to pay 105$ back to 5% interest → and the saver asks the bank for 1% interest so 101$ → the extra 4$ is the banks profit and the cycle continues
Concept of MRR with relation to Money supply
Saver deposits 100$ → bank needs to keep a percent of it for themselves called the Minimum requires reserve ration (10%) → loans out 90$ → borrower spends 90$ → the company the earnt 90$ gives it to the central bank as depositor → bank keep 10% → gives 81$ to the next borrower and the cycle continues
Money multiplier
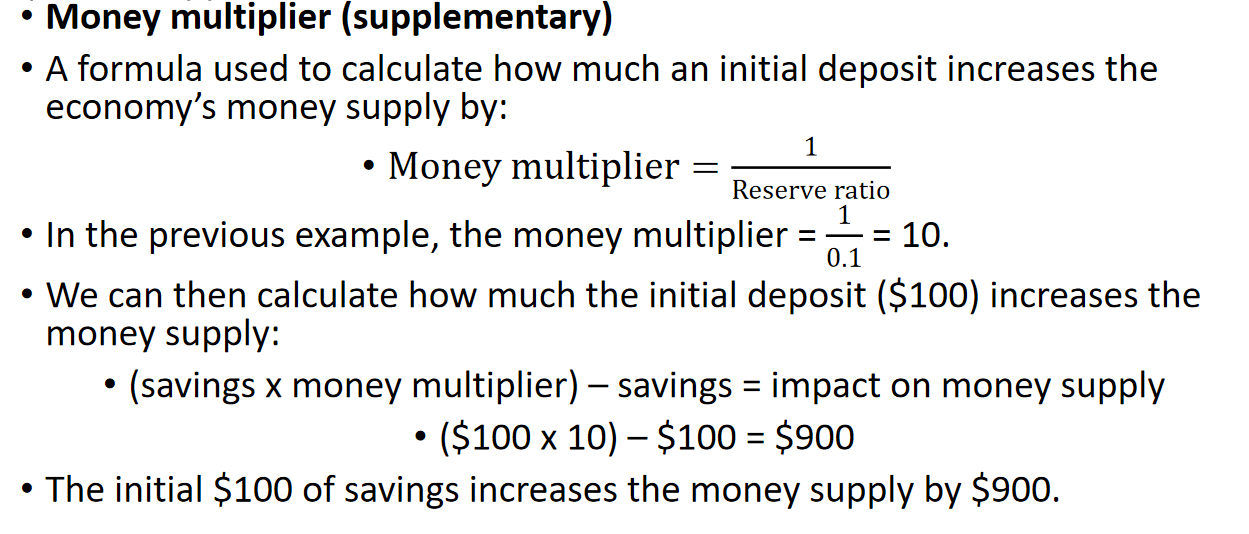
Why does MRR exist
to ensure that banks have money on hand to prevent them from running out of cash in the event of panicked depositors wanting to make mass withdrawals
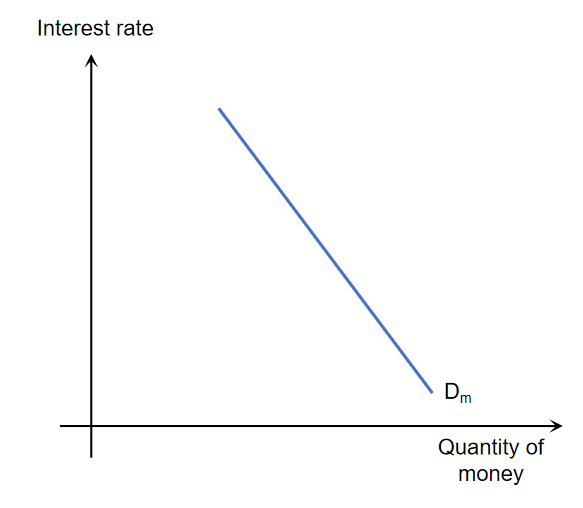
Demand for money
The demand for money (Dm) refers to the willingness and ability of borrowers to obtain loans.
it shows the inverse relationship between interest rates and the quantity of money/loans demanded.
Supply of money
supply of money (Sm) refers to the amount of money circulating in the economy at any time.
supply of money is fixed by the central bank and is not dependent on interest rates and so a vertical line
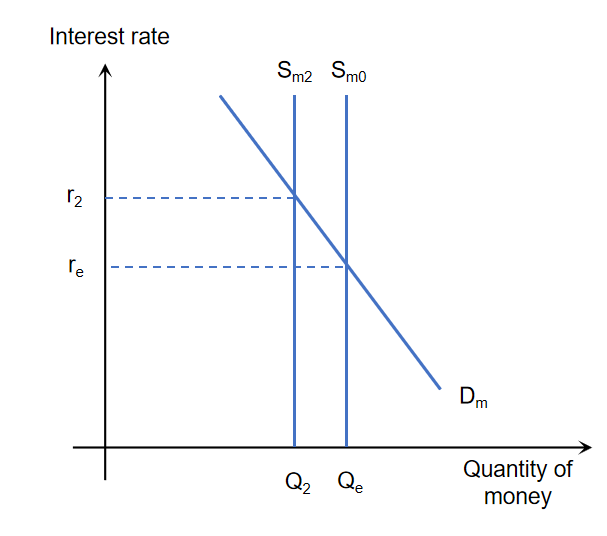
Demand and Supply of money diagram and Interest rates effect
IR increase → cost of borrowing higher → less money in circulation → supply of money shifts left
IR decrease → cost of borrowing lower → more money in circulation → supply of money shifts right
Factors when setting interest rates (5)
Exchange rate
property prices → can affect confidence in economy
rate of growth and nominal wages → higher wage rate implied higher prices → possible inflation
state of economy
business confidence levels
Tools of Monetary Policy
Open market operations
Minimum reserve requirements
Changes in the central bank minimum lending rate
Quantitative easing (QE).
Interest rates
Open market operations
Open market operations refers to the buying and selling of government bonds by a central bank to control money supply and interest rates.
Open market operation Contractionary and Expansionary
Expansionary : Government buys the bonds from commercial banks → commercial banks get money government gets bonds back → if commercial banks have money they can lend more → money supply increases → AD increases as people spend more
Contractionary : Government sells bonds to commercial banks → commercial banks have less money with them instead have bonds → money supply decreases as they cant lend more → AD decreases as people have less to spend
MRR
required percentage of deposits that commercial banks keep in their vaults.
MRR Contractionary and Expansionary
Expansionary : Decrease the MRR → banks keep less money with them → more money in circulation → money supply increases → AD increases as more money to spend
Contractionary : Increase the MRR → banks must keep more money with them → less money in circulation → money supply decreases → AD decreases as less money to spend
Minimum lending rate
The minimum lending rate is the interest rate charged by the central bank on loans to commercial banks.
Minimum lending rate Contractionary and Expansionary
Expansionary : decrease the minimum lending rate → easier to get more money → money supply increases → AD increases cause people can spend more
Contractionary : increase the minimum lending rate → more incentive to save → money supply decreases → AD decrease cause people spend less
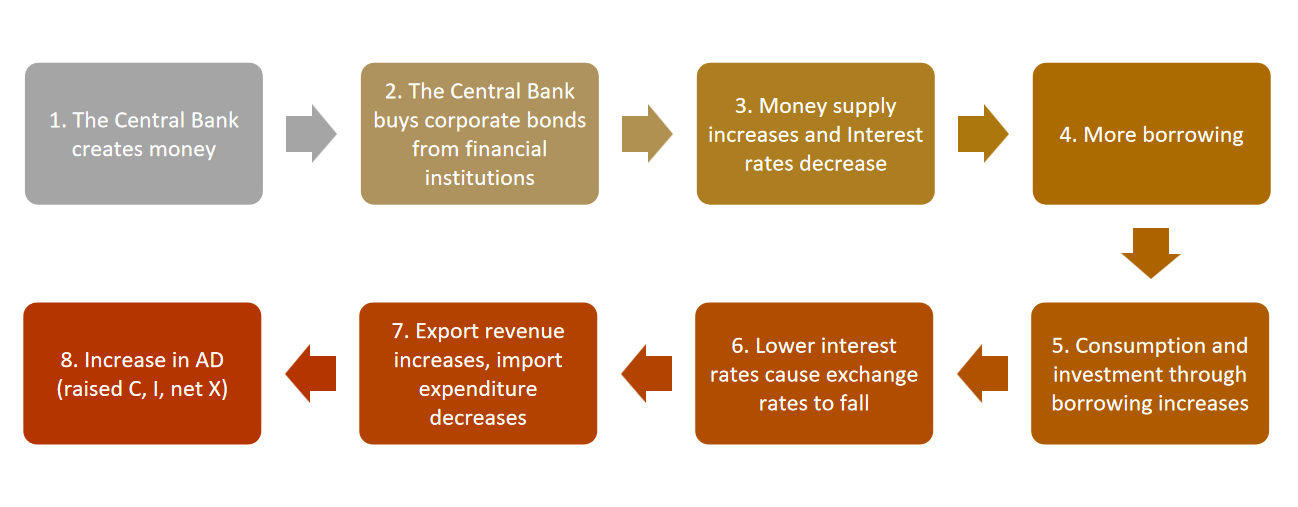
Quantative easing
Quantitative easing is a tool of monetary policy in which the central bank injects money directly into the economy through purchasing corporate bonds.
Bonds
Bonds are a type of debt.
How does Quantive easing affect economy
Note there is no contractionary version of this
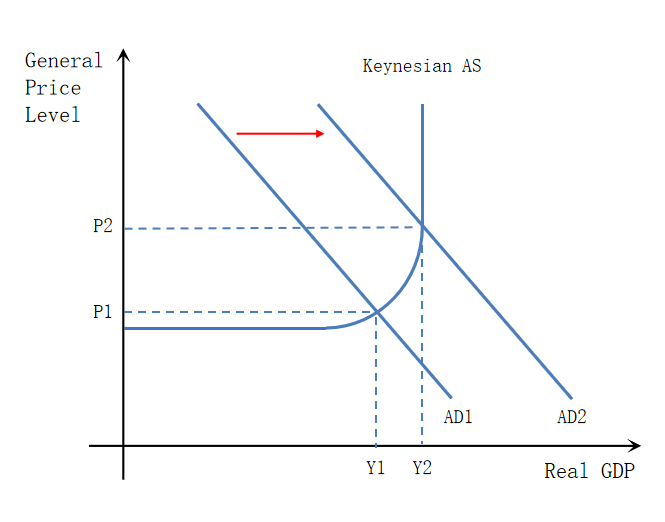
Expansionary monetary policy
Expansionary monetary policy aims to increase the level of aggregate demand by increasing money supply and reducing interest rates.
Increase money supply & reduce interest rates → Increases C & I → Increases AD
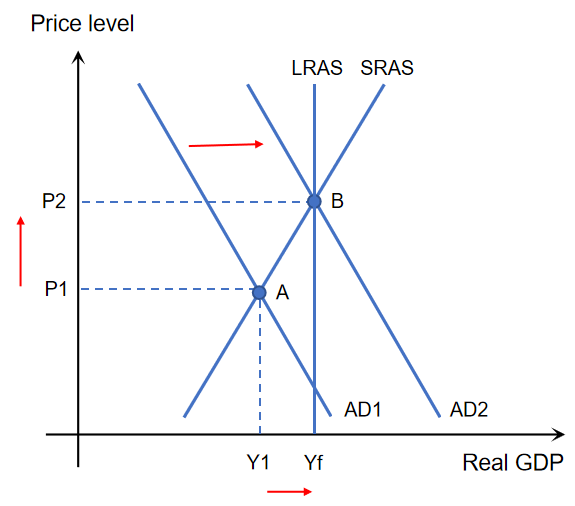
Expansionary Policy using diagram
Expansionary monetary policy → C & I increase → AD curve shifts right → Real GDP increases closing deflationary gap → Price level increases → causes inflationary pressure → Unemployment reduces
When is expansionary policy (2)
When inflation is below the target rate.
When the economy is suffering from a recessionary gap where unemployment is high and economic growth is low or negative.
Contractionary monetary policy
Contractionary monetary policy aims to decrease the level of aggregate demand by decreasing money supply and increasing interest rates.
Decrease money supply & increase interest rate → decrease C & I → Decrease AD
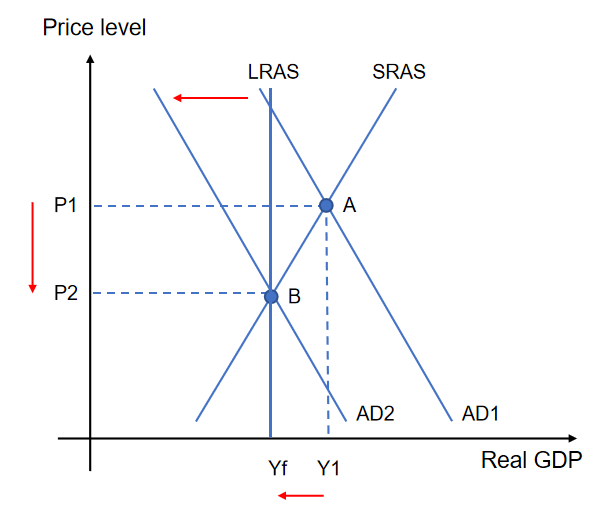
Contractionary Policy using diagram
Contractionary monetary policy → C & I decrease→ AD curve shifts left→ Real GDP decrease closing inflationary gap → Price level decreases → causes deflationary pressure → Unemployment increases
Constraints of monetary policy (2)
Limited scope of reducing interest rates, when close to zero as Low consumer and business confidence → times of recessions, consumers may be unwilling to purchase goods and services. Firms may not borrow money to invest even though interest rates are low.
Trade-offs with other macroeconomic aims like inflation
Pros of monetary policy
Short time lag → Can be implemented quickly
Incremental → can be adjusted incrementally
Flexible → central bank independent of politics so flexible
Easily reversible
Tradeoff with other macroeconomic aims when dealing with cost push inflation
Cost push inflation is caused when there is decrease in SRAS which causes price levels to be high
When dealing with this ideally you should use supply side policies in order to increase SRAS while maintaining low price level
But if we use Monetary policy we can use contractionary policy and decrease the aggregate demand this will cause inflation to decrease but will also cause real GDP to decrease and with it unemployment to increase