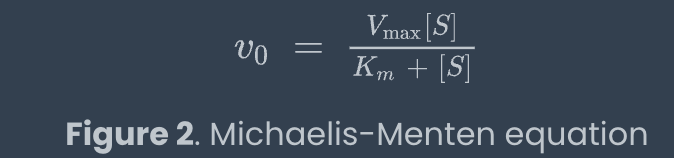Bio 1AL- lab 4 (enzymes, seawater platin & vibrio colony streak)
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Calculate the initial velocity of β-galactosidase enzyme activity at different concentrations of the substrate, ONPG, and in the presence of an inhibitor
formula = [cell reference] /0.0023 × 0.0015
initial rxn velocity is steepest initial slope of ONP curve produced over time
Create Michaelis-Menten and Lineweaver-Burk graphs to communicate the quantitative relationships between ONPG substrate concentration and β-gal activity
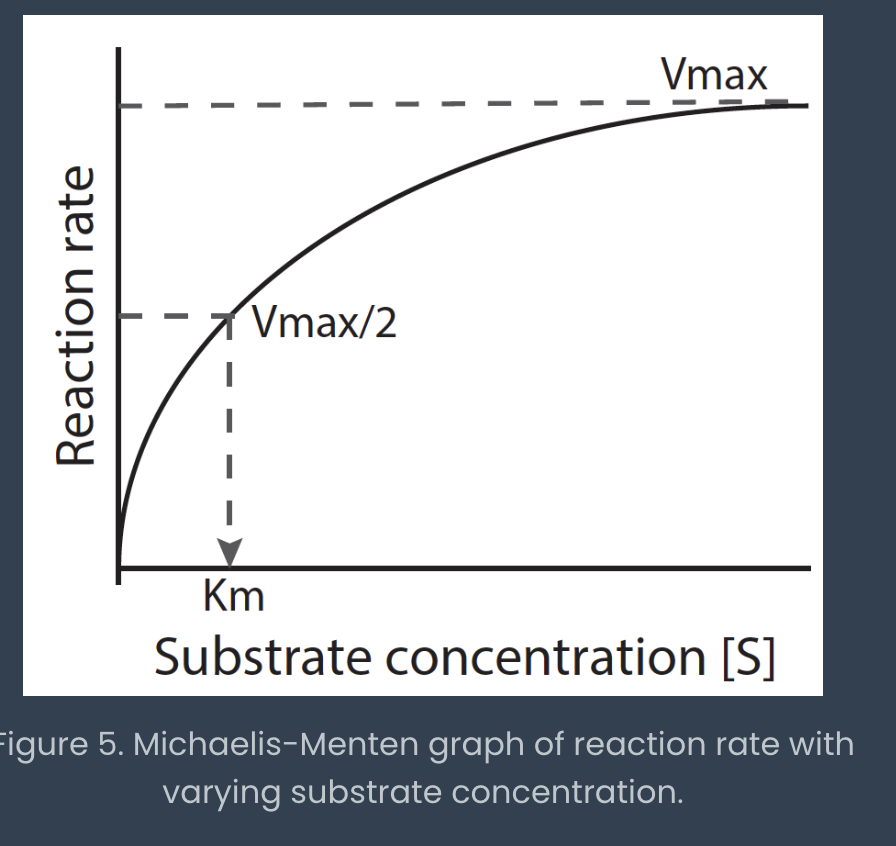
michaelis-menton graph and how to find Km/Vmax
reaction rate as a function of substrate concentration (velocity)
Vmax is where it levels out
Km is the x value (substrate concentration) corresponding to ½ Vmax
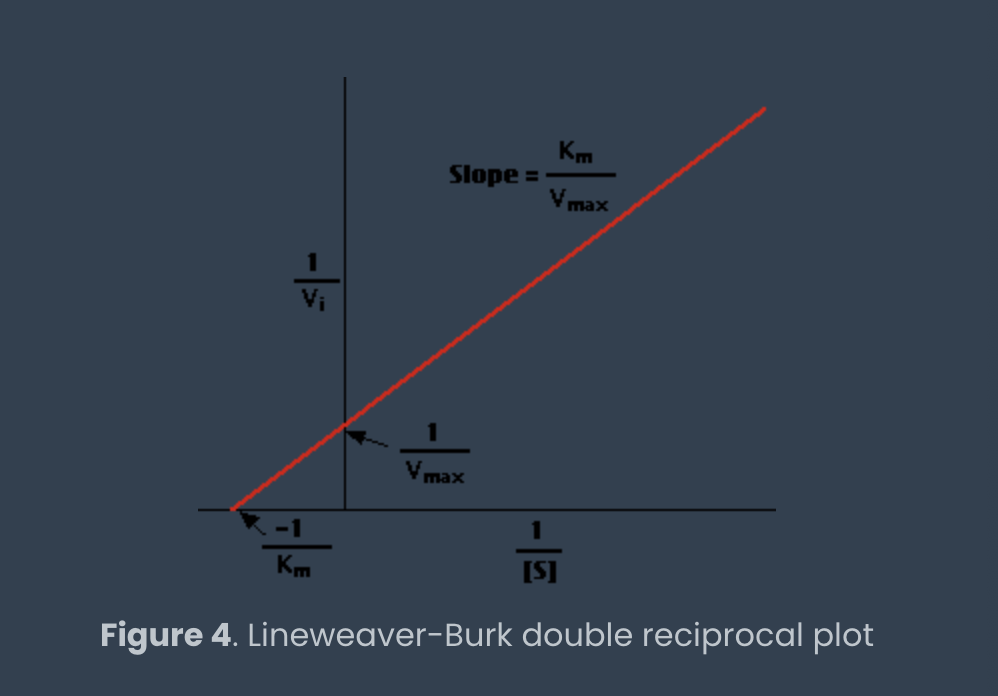
lineweaver-burk graph and how to determine Km/Vmax
Vmax is reciprocal of y-intercept
Km is reciprocal of negative X intercept
competitive, noncompetitive, or mixed inhibitor
competitive- prevent binding of substrate by binding in the substrate parking spot
Km INCREASED, Vmax stays same
noncompetitive- binds reversibly, randomly, and independently of substrate at different sites
Km unaffected, Vmax LOWERS
allosteric inhibitor (mixed)-
Km INCREASES and Vmax LOWERS
β-galactosidase
enzyme whose substrate is lactose
hydrollyzes lactoseinto glucose and galactose
must be kept on ice or will be denatured
energy of activation Ea
initial input of energy for an enzyme to convert a substrate
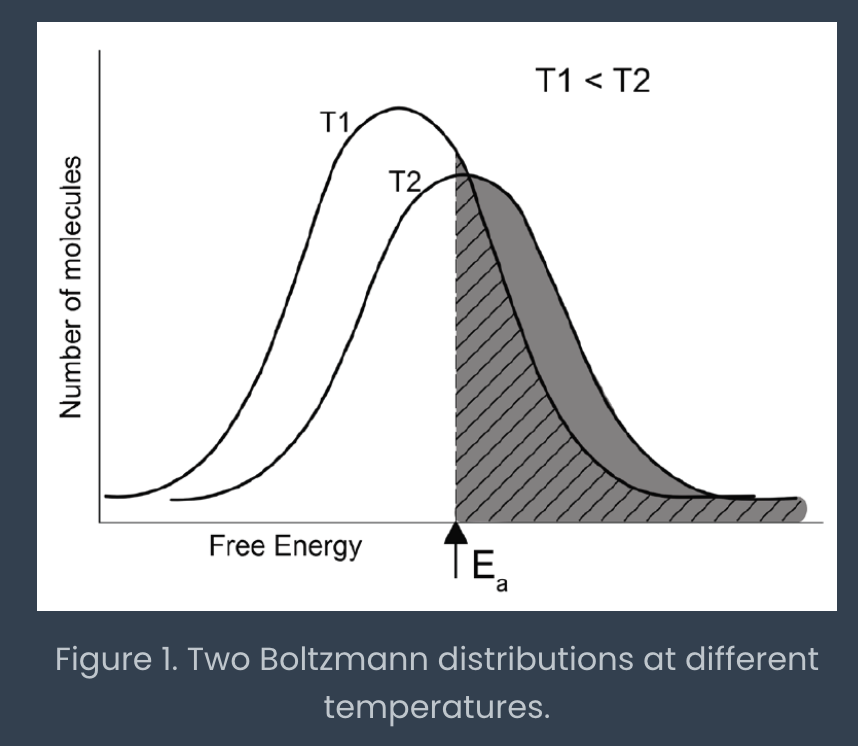
boltzmann distribution
energy distribution of product molecules
can shift temperature to increase number of molecules with sufficient energy
can also lower activation energy by using an enzyme
TCEP
buffer to maintain enzyme conformation
in enzyme solution
reducing agent to maintain enzyme activity
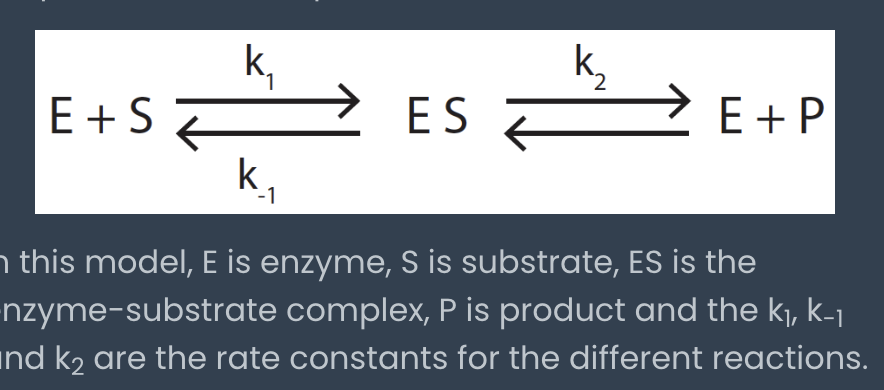
Michaelis constant Km
rate at which the ES complex dissociates to form either E+S or E+P
Km = (k-1 + k2) / k1
low Km = HIGH enzyme substrate affinity
high Km = LOW enzyme substrate affinity
IPTG
small molecule which affects B-gal activity
competitive inhibitor
michaelis menton equation
as substrate concentration increases, the rxn rate approaches Vmax at infinite substrate concentration