Chemistry Exam 2
5.0(3)Studied by 43 people
Card Sorting
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:54 PM on 3/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
1
New cards
At time = 0, the concentration of the reactants is _____
\
\
the highest it will be during the reaction.
2
New cards
In the reaction A → B, the rate of reaction triples when the concentration of \[A\] is tripled.
a)What is the correct value of m in rate = k\[A\]m ?
\
b) What is the value of m if the rate is unchanged when \[A\] is tripled?
a)What is the correct value of m in rate = k\[A\]m ?
\
b) What is the value of m if the rate is unchanged when \[A\] is tripled?
a) 1
b)0
b)0
3
New cards
Consider the reaction A + B → C. If this reaction has the rate law *rate = k*\[A\]\[B\], what are the units of *k*?
M^-1 x S^-1
4
New cards
A certain reaction is second order in E and first order in F, what will happen to the rate of double the concentration of E while keeping the concentration of F the same
The rate will quadruple
5
New cards
For a certain reaction with reactants P and Q, doubling \[Q\] has no effect and doubling \[P\] causes the initial reaction rate to double. What are the reaction orders of P and Q?
first order in P and zero order in Q
6
New cards
For a reaction with reactants A and B, doubling \[B\] while keeping \[A\] constant caused the initial rate of the reaction to increase by a factor of 2.6. Describe the order of the reaction in B?
The reaction order is between 1 and 2
7
New cards
Why does the rate of the reaction slow down with time?
The reaction rate depends upon the concentrations of the reactants. As the reaction progresses, the reactants are converted into products and their concentrations decrease
8
New cards
Consider the reaction A → B.
What is the rate law for a first-order reaction, A → B?
What is the rate law for a first-order reaction, A → B?
Rate = k\[A\]
9
New cards
Consider the reaction A → B.
What is the integrated rate law for this reaction?
\
What is the integrated rate law for this reaction?
\
ln\[A\] = -kt + ln\[A\]0
10
New cards
What is the rate law for a zero-order reaction?
Rate=k
11
New cards
For a certain reaction with reactants P and Q, doubling \[P\] has no effect and doubling \[Q\] causes the initial reaction rate to increase by a factor of four. What are the reaction orders of P and Q?
zero order in P and second order in Q
12
New cards
The Arrhenius equation is shown below. Determine what happens to the rate of the reaction (*k*) as various parameters are changed.
k=Ae^(-Ea/RT)
1. Temperature increases
2. *Ea* decreases
3. *A* increases
k=Ae^(-Ea/RT)
1. Temperature increases
2. *Ea* decreases
3. *A* increases
1. k increases
2. k increases
3. k increases
13
New cards
For which of these rate laws does the overall order = 2?
rate=k\[A\]
rate=k\[A\]\[B\]\[C\]
rate=k\[A\]\[B\]
rate=k\[A\]^2
rate=k\[A\]^2\[B\]
rate=k\[A\]
rate=k\[A\]\[B\]\[C\]
rate=k\[A\]\[B\]
rate=k\[A\]^2
rate=k\[A\]^2\[B\]
rate=k\[A\]\[B\]
14
New cards
Which of the following is true about activation energies?
* Exothermic reactions have negative activation energies
* Fast reactions have large rate constants and large activation energies
* Endothermic reactions always have large activation energies
* The forward reaction sometimes has a lower activation energy than the reverse reaction
* Exothermic reactions have negative activation energies
* Fast reactions have large rate constants and large activation energies
* Endothermic reactions always have large activation energies
* The forward reaction sometimes has a lower activation energy than the reverse reaction
The forward reaction sometimes has a lower activation energy than the reverse reaction
15
New cards
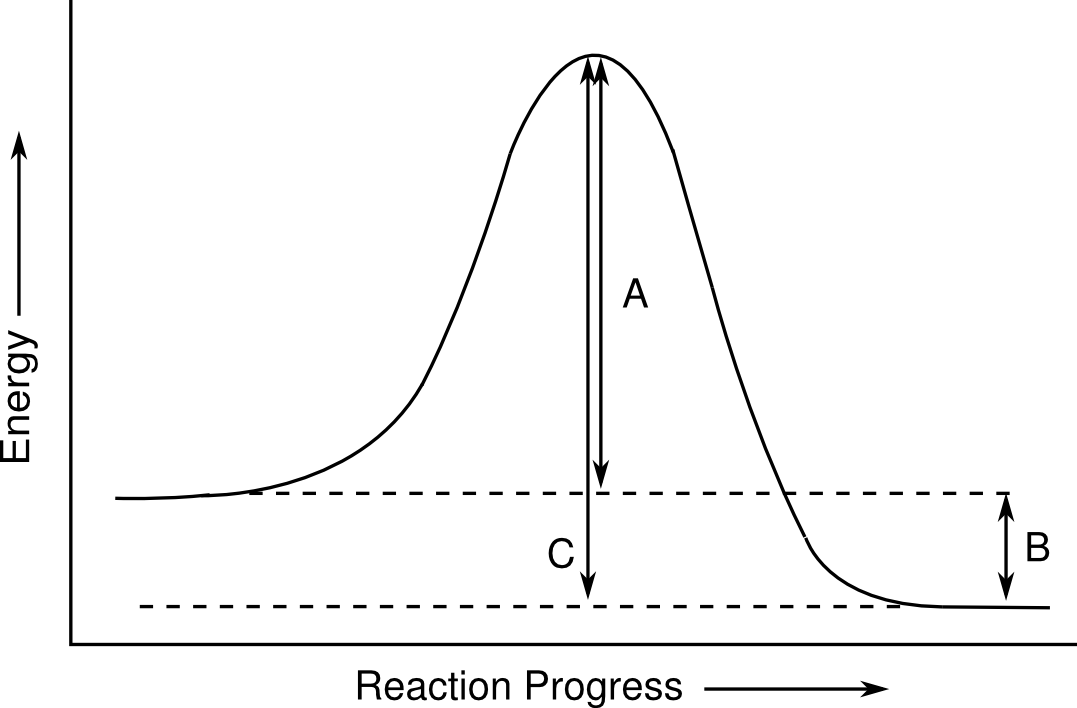
1. Which of the energies marked in the diagram represents the activation energy?
2. Which of the following is true about the reaction represented by the diagram above?
* The reverse reaction is slower than the forward reaction
* The rate of the reaction is the same forward and reverse directions
* The forward reaction is slower than the reverse reaction
* It is not possible to tell from the figure which way the reaction will be faster
1. A
2. The reverse reaction is slower than the forward reaction
16
New cards
What does the Arrhenius equation predict?
As the temperature increases, the rate constant increases
17
New cards
For the following elementary reactions, give the molecularity and the rate law.
1. CH3NC(g) → CH3CN(g)
2. O3(g) +NO(g) → O2(g) + NO2(g)
3. O3(g) → O2(g) + O(g)
4. O3(g) + O(g) → 2O2(g)
1. CH3NC(g) → CH3CN(g)
2. O3(g) +NO(g) → O2(g) + NO2(g)
3. O3(g) → O2(g) + O(g)
4. O3(g) + O(g) → 2O2(g)
1. unimolecular
Rate = k\[CH3NC\]
2. bimolecular
Rate = k\[O3\]\[NO\]
3. unimolecular
Rate = k\[O3\]
4. bimolecular
Rate = k\[O3\]\[O\]
18
New cards
1. Write the overall reaction that consists of the following elementary steps.
\
N2O5(g) → NO3(g) + NO2(g)
NO3(g) → NO2(g) + O(g)
2O(g) → O2(g)
N2O5 + O → 2NO2 + O2
19
New cards
Describe how a catalyst speeds up the rate of a reaction.
A catalyst creates another pathway for the reaction to follow that has a lower activation energy than the uncatalyzed reaction. A lower activation energy results in more molecules having enough energy to react, which increases the rate of the reaction.
20
New cards
Indicate whether each example is a homogenous or a heterogeneous catalyst.
1. 2CO(g) + O2(g) → 2CO2(g) in a catalytic converter
2. NO2 catalyzes the breakdown of O3 in the upper atmosphere.
3. ammonia is synthesized from N2 and H2 using iron.
4. an acid (water) is used to catalyze the hydrolysis of an ester
CH3CO2CH3(aq) + H2O(ℓ) ⇌ CH3CO2H(aq) + CH3OH(aq)
1. 2CO(g) + O2(g) → 2CO2(g) in a catalytic converter
2. NO2 catalyzes the breakdown of O3 in the upper atmosphere.
3. ammonia is synthesized from N2 and H2 using iron.
4. an acid (water) is used to catalyze the hydrolysis of an ester
CH3CO2CH3(aq) + H2O(ℓ) ⇌ CH3CO2H(aq) + CH3OH(aq)
1. heterogeneous catalysts
2. homogeneous catalyst
3. heterogeneous catalysts
4. homogeneous catalyst
21
New cards
1. What is the rate law for the following elementary step?
2 N O 2 → N O 3 ( g ) + N O ( g )
2. What is the molecularity of the reaction above?
1. Rate= k\[NO2\]^2
2. Bimolecular
22
New cards
In order to be considered consistent with a given reaction, a proposed mechanism must ______.
1. have elementary reactions that sum to the overall balanced equation for the reaction
2. have as many steps as there are reactants
3. have a bimolecular reaction as the rate limiting step
4. predict the experimental rate law
5. have at least one unimolecular step
1. have elementary reactions that sum to the overall balanced equation for the reaction
2. have as many steps as there are reactants
3. have a bimolecular reaction as the rate limiting step
4. predict the experimental rate law
5. have at least one unimolecular step
1 and 4
23
New cards
A proposed mechanism for the reaction between nitrogen dioxide and fluorine is as follows:
1. NO 2 ( g ) + F 2 ( g ) → N O 2 F ( g ) + F ( g )
2. F( g ) + N O 2 ( g ) → N O 2 F ( g )
The rate law was experimentally determined to be k\[NO2\]\[F2\]
\-What is/are the rate determining step(s)?
1. NO 2 ( g ) + F 2 ( g ) → N O 2 F ( g ) + F ( g )
2. F( g ) + N O 2 ( g ) → N O 2 F ( g )
The rate law was experimentally determined to be k\[NO2\]\[F2\]
\-What is/are the rate determining step(s)?
Reaction 1
24
New cards
Describe a catalyst.
A catalyst speeds up a reaction without being consumed by providing a low energy pathway for the reaction
25
New cards
A heterogeneous catalyst ______.
exists in a different phase than the reactants
26
New cards
Which of the following would be a valid rate law given the following two-step mechanism?
Step 1 A+ 2 B → C (fast)
Step 2 C + 2 D → 2 E (slow)
Step 1 A+ 2 B → C (fast)
Step 2 C + 2 D → 2 E (slow)
Rate= k\[C\]\[D\]^3
27
New cards
Describe the idea of a dynamic equilibrium.
At equilibrium, reactants are being continuously converted to products and products are continuously being converted to reactants
28
New cards
The following reaction is at equilibrium in a flask.
2O3(g) ⇌ 3O2(g)
1. Which way does the equilibrium shift (to the left or to the right) if more O2 is added to the flask?
2. Which way does the equilibrium shift if more O3 is added to the flask?
3. If the volume of the flask is reduced, which way does the equilibrium shift?
2O3(g) ⇌ 3O2(g)
1. Which way does the equilibrium shift (to the left or to the right) if more O2 is added to the flask?
2. Which way does the equilibrium shift if more O3 is added to the flask?
3. If the volume of the flask is reduced, which way does the equilibrium shift?
1\.To the left
2\.To the right
3\.To the left
\
2\.To the right
3\.To the left
\
29
New cards
Consider the Haber-Bosch reaction:
N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3
∆Hrxn = -92.1 kJ/mol
Which of the following conditions will increase the production of ammonia?
\-Increase the pressure
-Decrease the pressure
\-Increase the temperature
\-Decrease the temperature
N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3
∆Hrxn = -92.1 kJ/mol
Which of the following conditions will increase the production of ammonia?
\-Increase the pressure
-Decrease the pressure
\-Increase the temperature
\-Decrease the temperature
Increase the pressure and Decrease the temperature
30
New cards
Consider the Haber-Bosch reaction:
N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3
∆Hrxn = -92.1 kJ/mol
When the Haber-Bosch process is used to produce ammonia it is run at 300 – 550oC and 150 – 260 atm. Does the use of high temperature surprise you given your answer to the previous question? Why are high temperatures used for this reaction? (Hint: it has nothing to do with the equilibrium)
N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3
∆Hrxn = -92.1 kJ/mol
When the Haber-Bosch process is used to produce ammonia it is run at 300 – 550oC and 150 – 260 atm. Does the use of high temperature surprise you given your answer to the previous question? Why are high temperatures used for this reaction? (Hint: it has nothing to do with the equilibrium)
The high temperatures increase the rate or the reaction would be too slow. The high pressures shift the equilibrium to the right (toward products). The combination of high pressure and high temperature makes the reaction practical for the production of ammonia.
31
New cards
Consider the reaction below and answer the following questions.
2H2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2H2O ∆Hrxn = -283 kJ/mol \n
1. Which way does the equilibrium shift if you increase the temperature?
2. The reaction is contained in a closed flask. Which way does the equilibrium change if the volume is decreased?
3. Which way does the equilibrium shift if the pressure is increased by the addition of argon?
4. In both questions #2 and #3 the pressure increases. What is the difference between the two situations?
2H2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2H2O ∆Hrxn = -283 kJ/mol \n
1. Which way does the equilibrium shift if you increase the temperature?
2. The reaction is contained in a closed flask. Which way does the equilibrium change if the volume is decreased?
3. Which way does the equilibrium shift if the pressure is increased by the addition of argon?
4. In both questions #2 and #3 the pressure increases. What is the difference between the two situations?
1. To the left
2. To the right
3. No shift
4. In #2, decreasing the volume results in an increase in the partial pressures of all the gasses so the equilibrium is affected. In #3, the partial pressures of the reactants and products do not change so the equilibrium doesn't change.
\
32
New cards
Consider the following reaction below:
CO(g) + H2O(g) ⇌ CO2(g) + H2(g) ∆Hrxn = +2220 kJ
Which of the following conditions will increase the production of CO2? Explain…
\
\-Increase the pressure
\-Decrease the pressure
\-Increase the temperature
\-Decrease the temperature
CO(g) + H2O(g) ⇌ CO2(g) + H2(g) ∆Hrxn = +2220 kJ
Which of the following conditions will increase the production of CO2? Explain…
\
\-Increase the pressure
\-Decrease the pressure
\-Increase the temperature
\-Decrease the temperature
Increase the temperature
\-Changing the pressure won't work because there are the same number of molecules in the products and reactants. The reaction is endothermic so increasing the temperature will shift the reaction to the right.
\-Changing the pressure won't work because there are the same number of molecules in the products and reactants. The reaction is endothermic so increasing the temperature will shift the reaction to the right.
33
New cards
For which of the following reactions is Kp = Kc?
\
2N H 3 ( g ) + 2 O 2 ( g ) ⇌ N 2 O ( g ) + 3 H 2 O ( g )
\
C a C O 3 ( s ) ⇌ C a O ( s ) + C O 2 ( g)
\
2N 2 H 4 ( ℓ ) + 2 N O 2 ( g ) ⇌ 3 N 2 ( g ) + 4 H 2 O ( ℓ )
\
4H C l ( a q ) + M n O 2 ( s ) ⇌ M n C l 2 ( a q ) + 2 H 2 O ( ℓ ) + C l 2 ( g )
\
2N H 3 ( g ) + 2 O 2 ( g ) ⇌ N 2 O ( g ) + 3 H 2 O ( g )
\
C a C O 3 ( s ) ⇌ C a O ( s ) + C O 2 ( g)
\
2N 2 H 4 ( ℓ ) + 2 N O 2 ( g ) ⇌ 3 N 2 ( g ) + 4 H 2 O ( ℓ )
\
4H C l ( a q ) + M n O 2 ( s ) ⇌ M n C l 2 ( a q ) + 2 H 2 O ( ℓ ) + C l 2 ( g )
2N H 3 ( g ) + 2 O 2 ( g ) ⇌ N 2 O ( g ) + 3 H 2 O ( g )
\
\
34
New cards
For the following reaction, what is the expression for Q in terms of the partial pressures of the gases?
N2 ( g ) + O 2 ( g ) ⇌ 2 N O ( g )
N2 ( g ) + O 2 ( g ) ⇌ 2 N O ( g )
Q= (P^2No) / (PN2)(PO2)
35
New cards
For the reaction below
Q= 2.61x10^-3 and Kc= 7.81x10^-4
Choose the answer that best describes this situation.
A→B
Q= 2.61x10^-3 and Kc= 7.81x10^-4
Choose the answer that best describes this situation.
A→B
Q>Kc so the reaction will proceed from products to reactants
36
New cards
PC l 3 ( g ) + C l 2 ( g ) ⇌ P C l 5 ( g )
1. Which direction does the reaction shift if you increase the partial pressure of the Cl2(g)?
2. Which direction does the reaction shift if you increase the temperature?
3. Which direction does the reaction shift if you increase the pressure by adding helium to the flask?
1. Which direction does the reaction shift if you increase the partial pressure of the Cl2(g)?
2. Which direction does the reaction shift if you increase the temperature?
3. Which direction does the reaction shift if you increase the pressure by adding helium to the flask?
1. Towards the products
2. Towards the reaction
3. No shift