MRAD 4218 Module 1-2 Pathology Radiographic Appearances
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
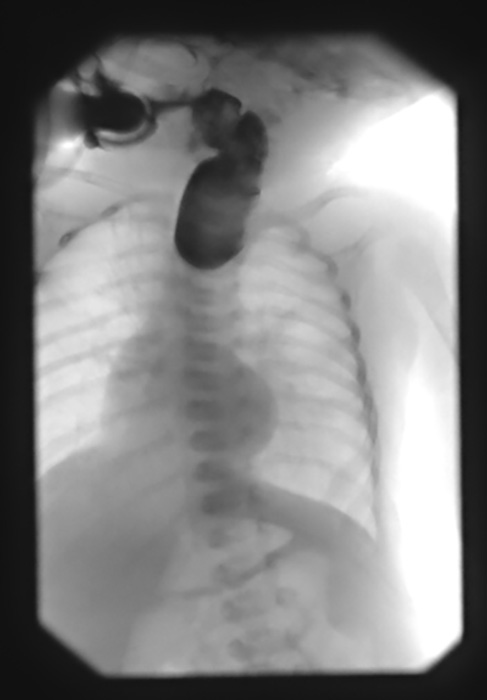
Esophageal Atresia w/ TEF
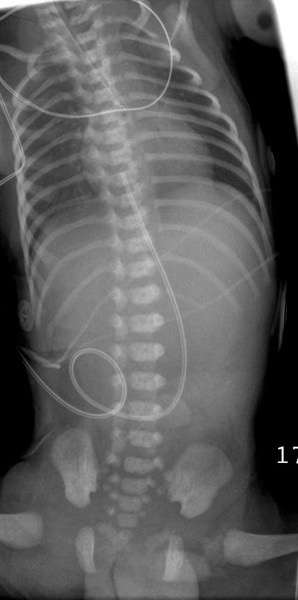
Esophageal Atresia w/ TEF
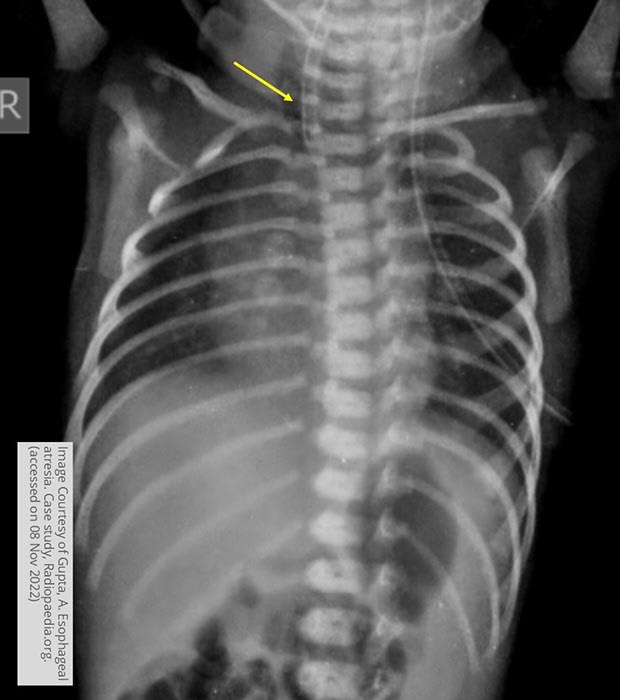
Esophageal Atresia w/ TEF
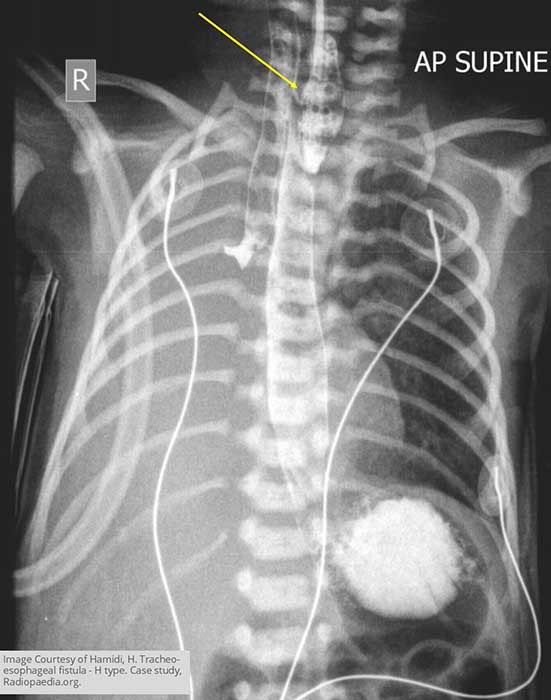
Esophageal Atresia w/ TEF
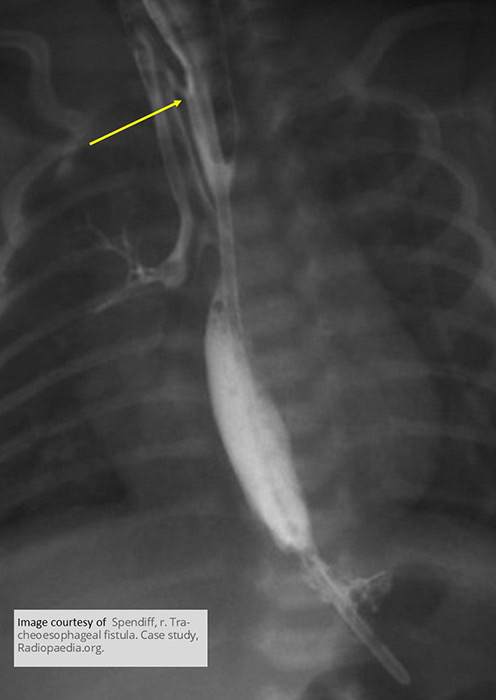
Esophageal Atresia w/ TEF
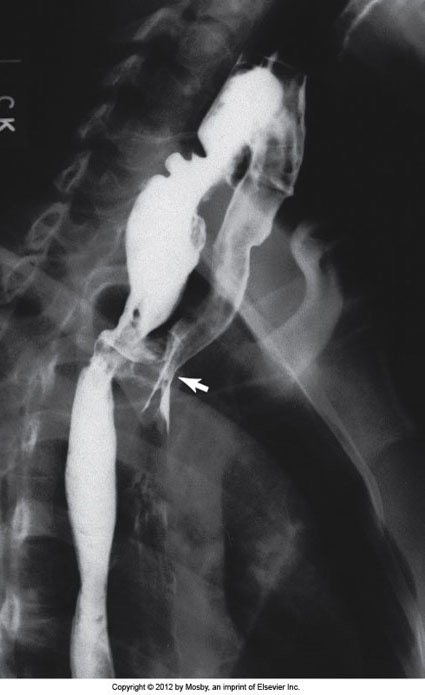
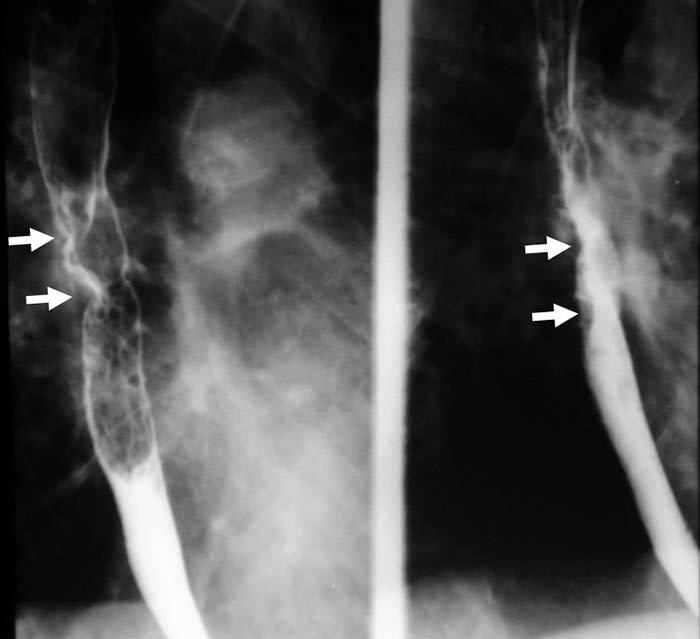
Acquired Tracheosophageal Fistula
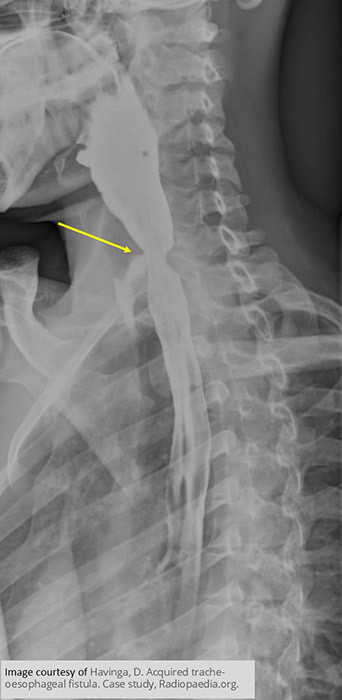
Acquired Tracheosophageal Fistula
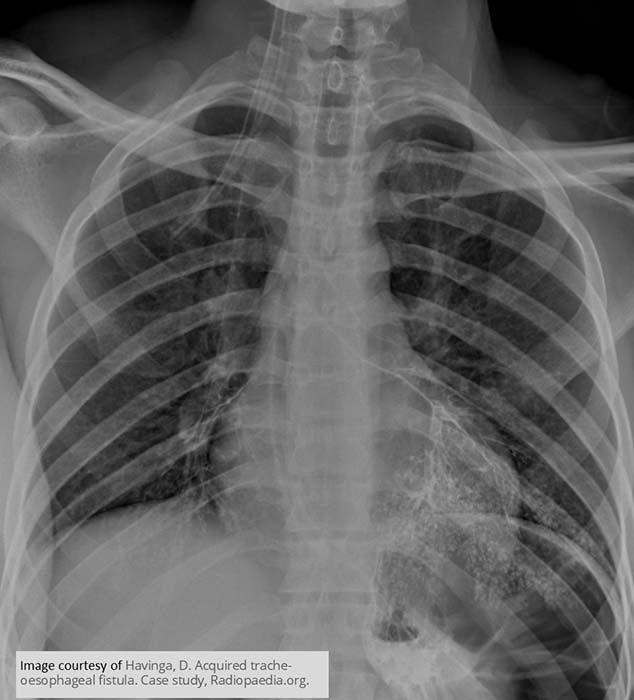
Acquired Tracheosophageal Fistula
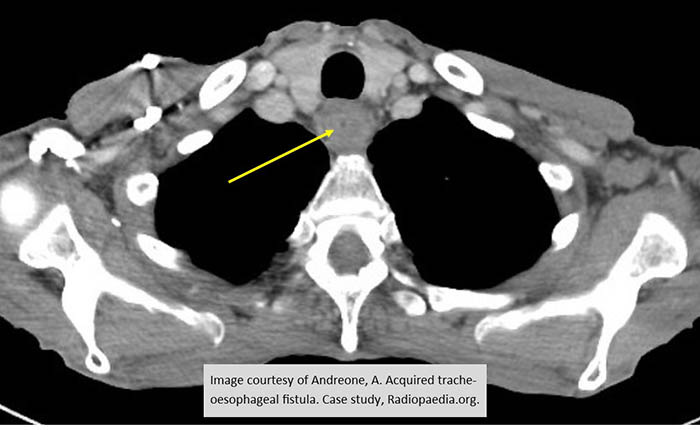
Acquired Tracheosophageal Fistula
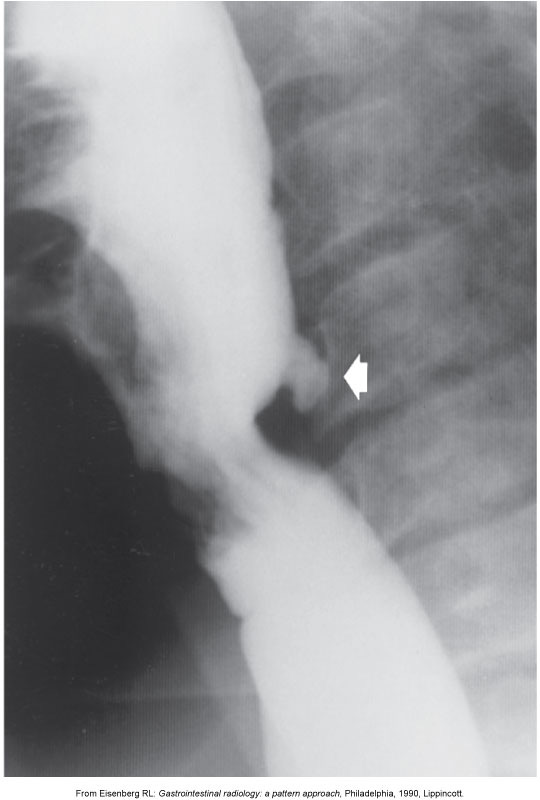
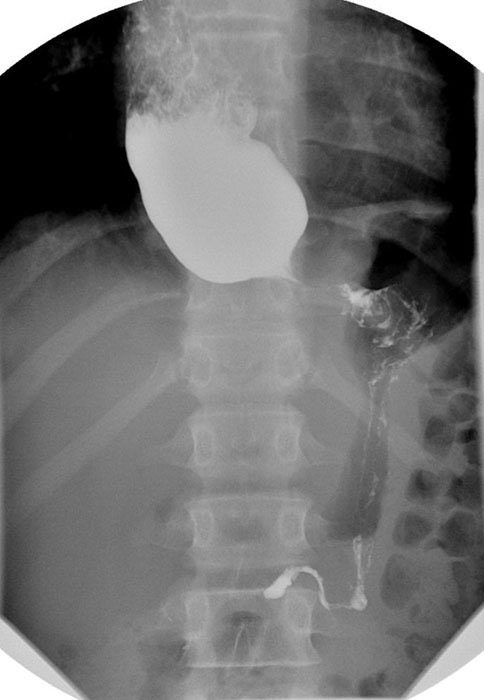
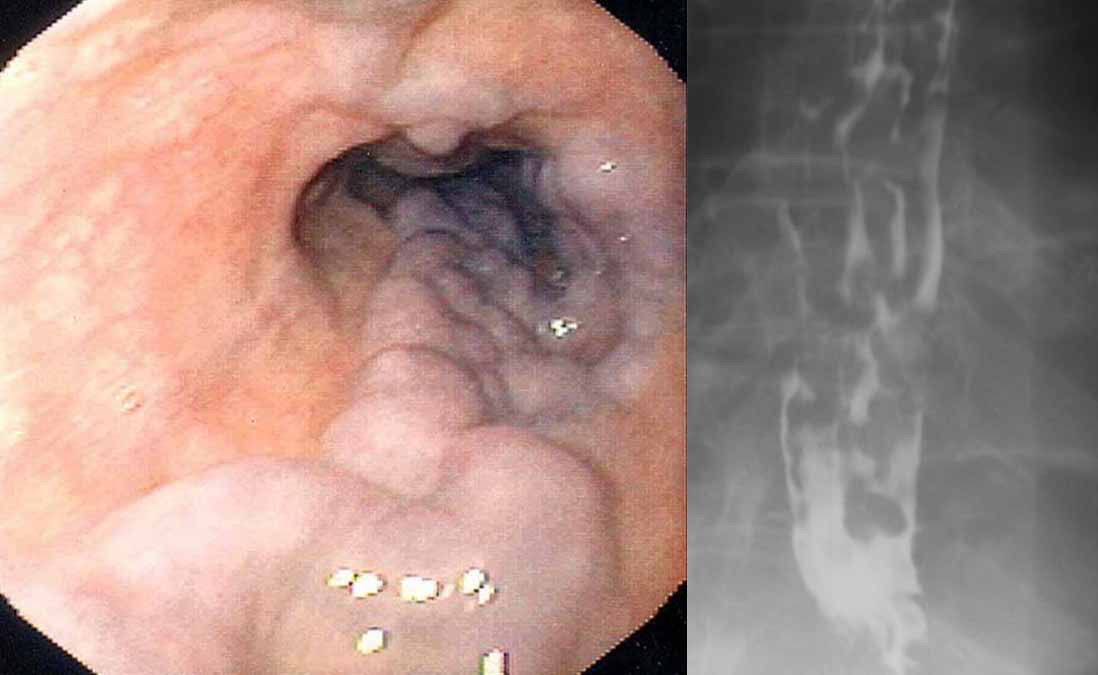
Zenker’s Diverticulum
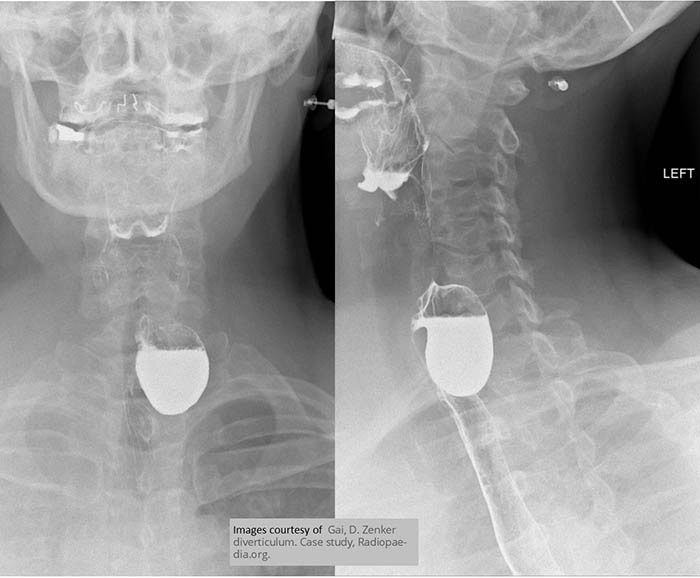
Zenker’s Diverticulum
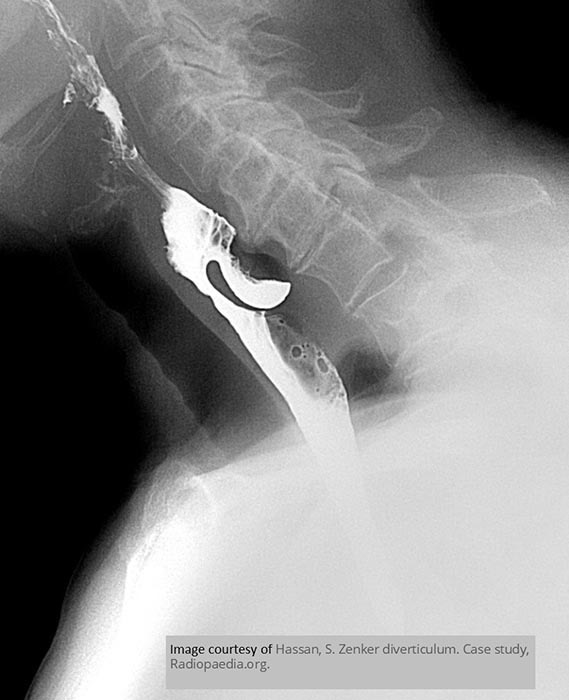
Zenker’s Diverticulum
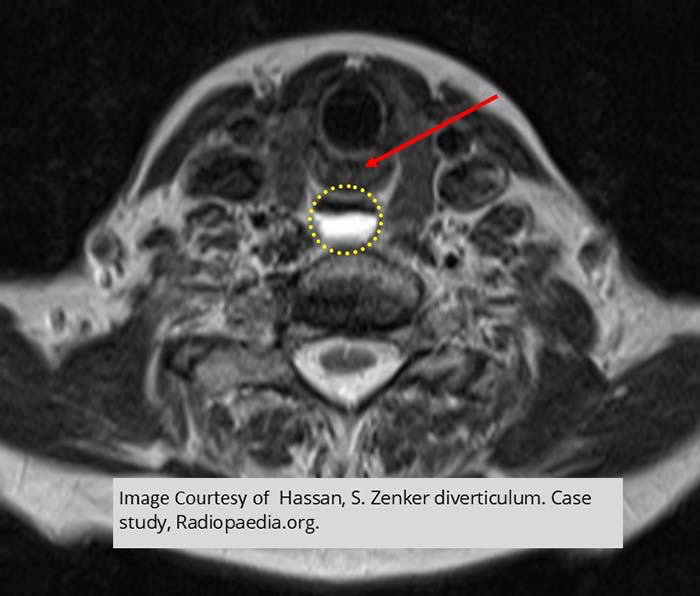
Zenker’s Diverticulum
Esophageal Achalasia
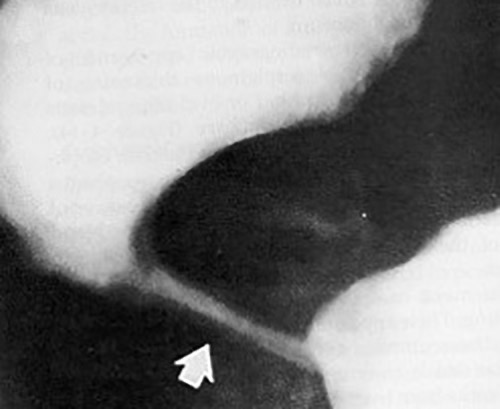
Esophageal Achalasia
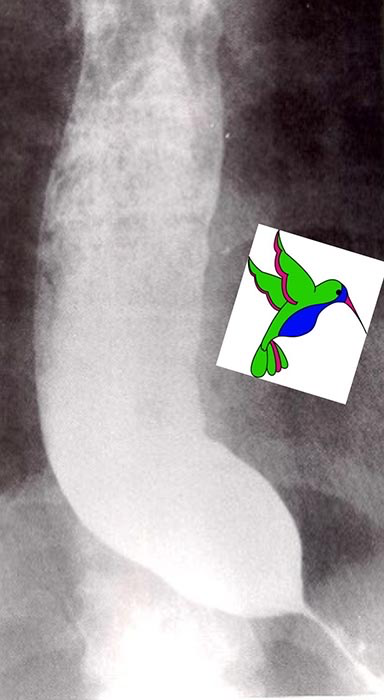
Esophageal Achalasia
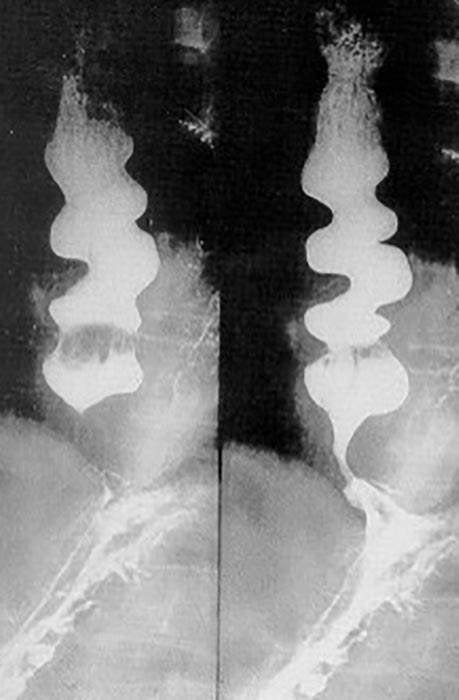
Esophageal Achalasia
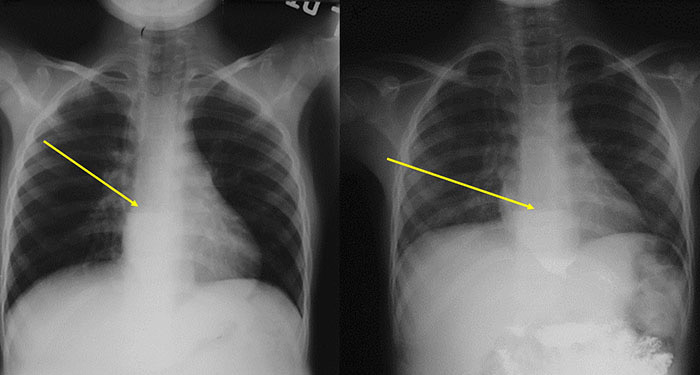
Esophageal Achalasia
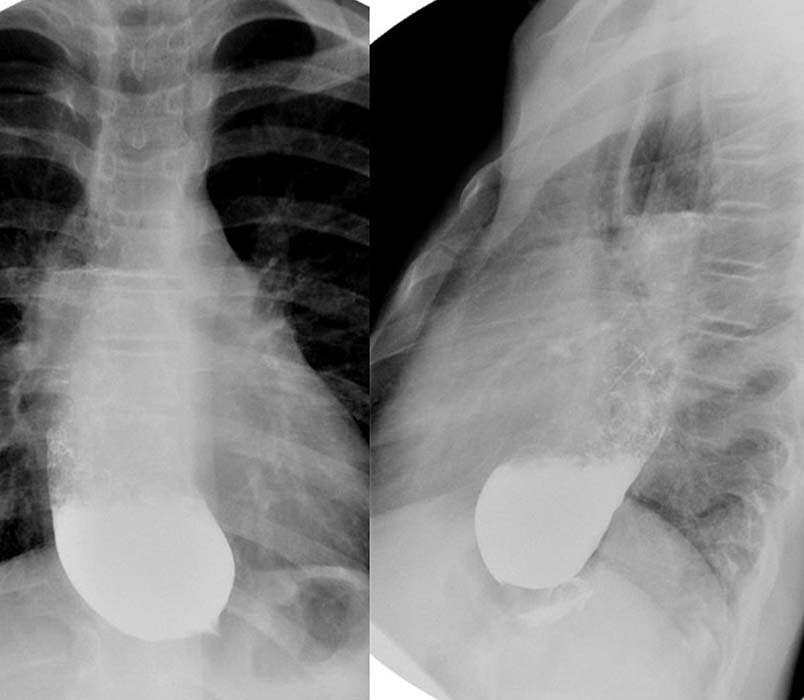
Esophageal Achalasia
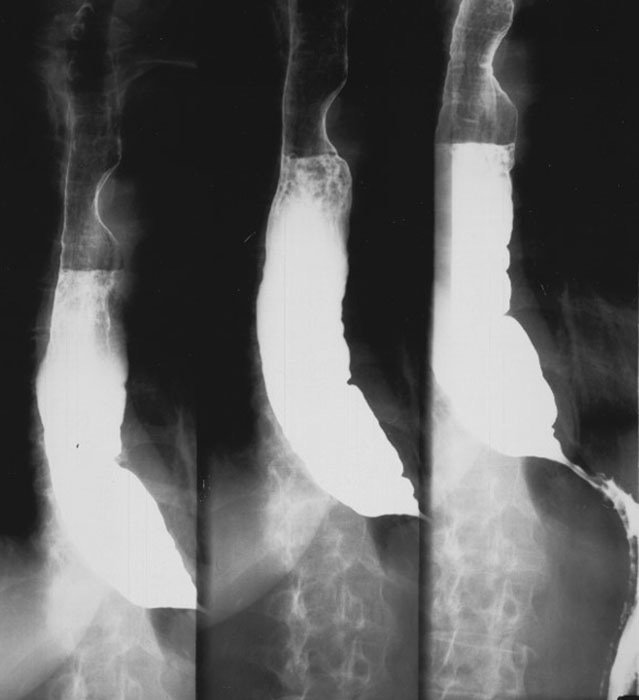
Esophageal Achalasia
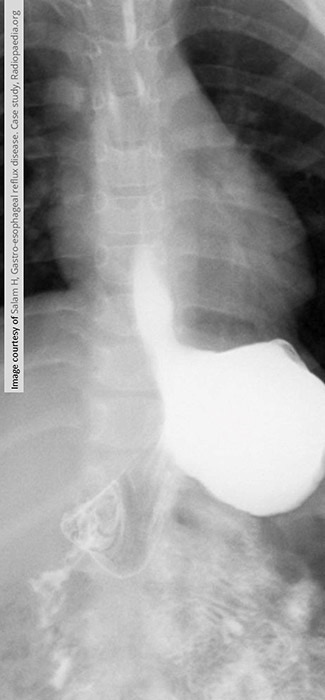
GERD
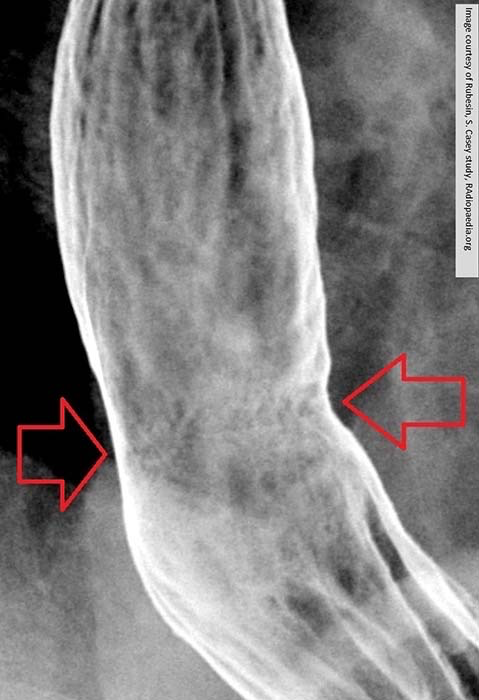
GERD - Barrett’s Esophagus
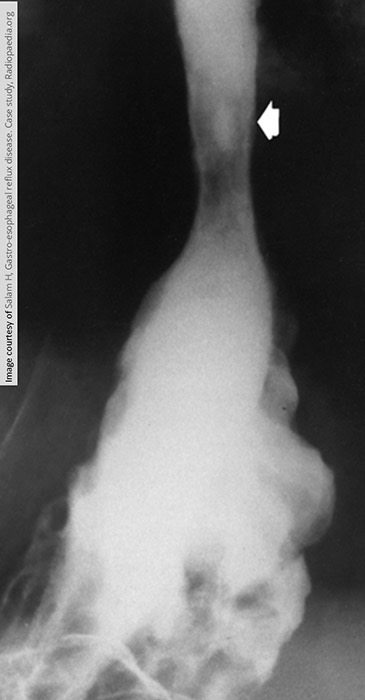
GERD: Progression of GERD
Erosion of the tissue and ulcerations may occur

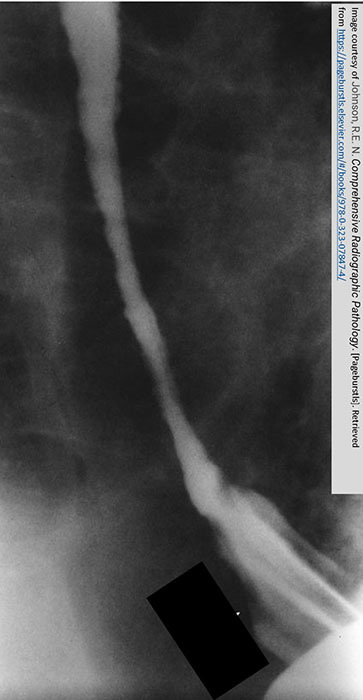
GERD: Advanced GERD
Narrowing of the lower esophagus
Erosion evident by the hazy and serrated appearance of the esophageal borders

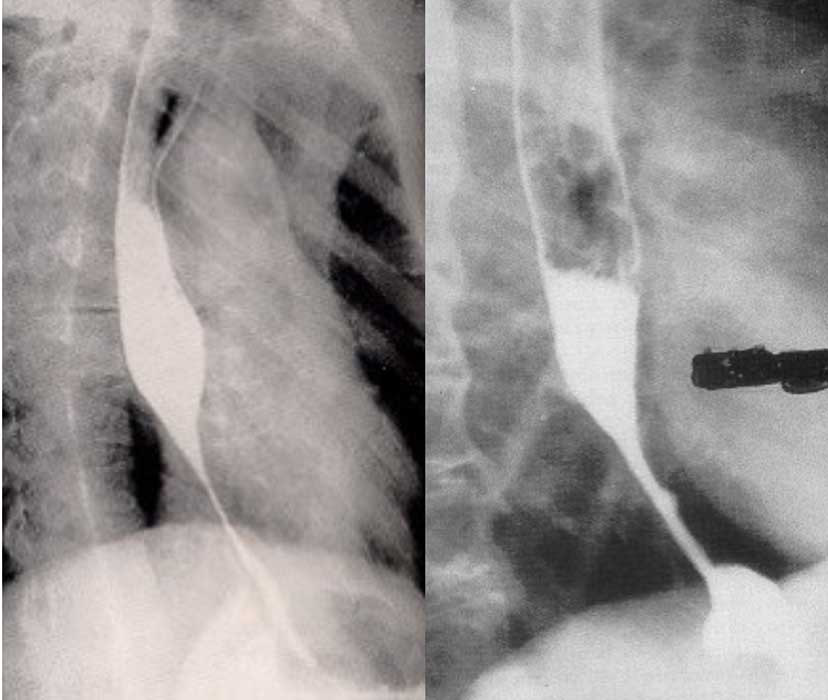
GERD: Advanced GERD
Narrowed, eroded mucosa
Narrowing comes from the inflammation at this stage

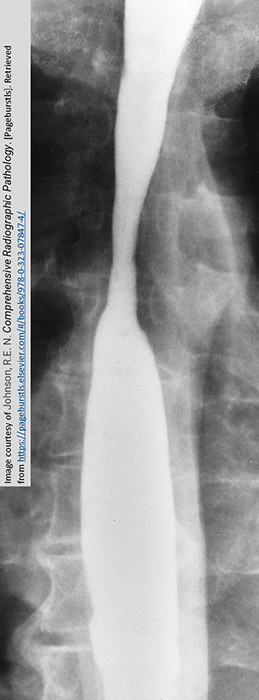
GERD: Area affected demonstrates a smooth tapered appearance
Barrett's esophagus will further alter the tissue to take on a "stomach like" appearance

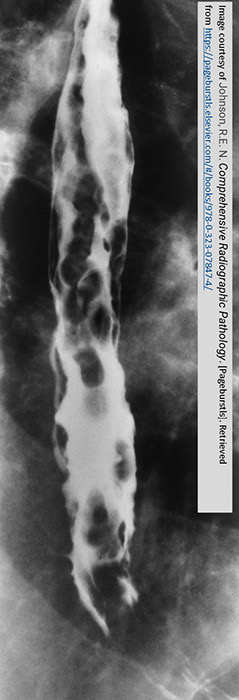
Esophageal Varices: Rosary Beads
Round and oval fillings defects
Caused by the varices pressing on the outer esophagus

Esophageal Varices
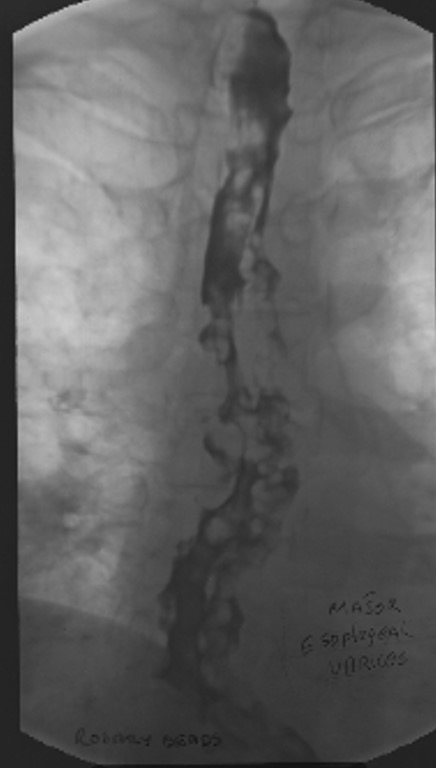
Esophageal Varices: Rosary Beads
Round and oval fillings defects
Caused by the varices pressing on the outer esophagus

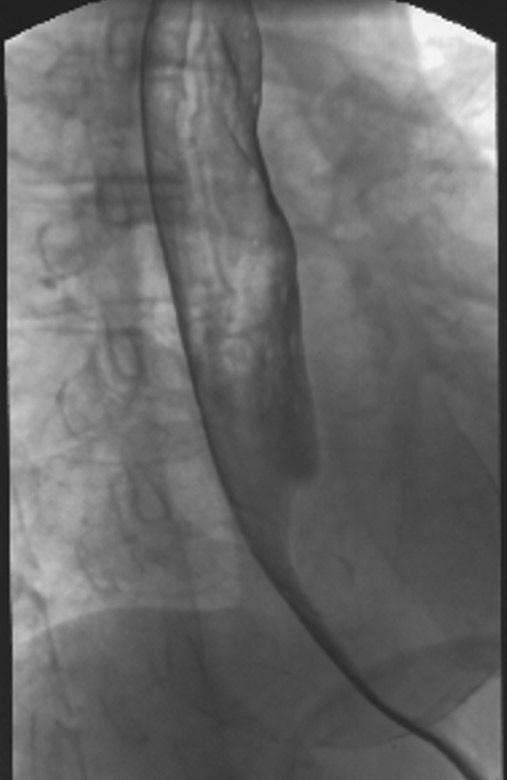
Esophageal Varices: Worm Tracings
Long wavy impressions
Made by the varices pressing on the outer esophagus

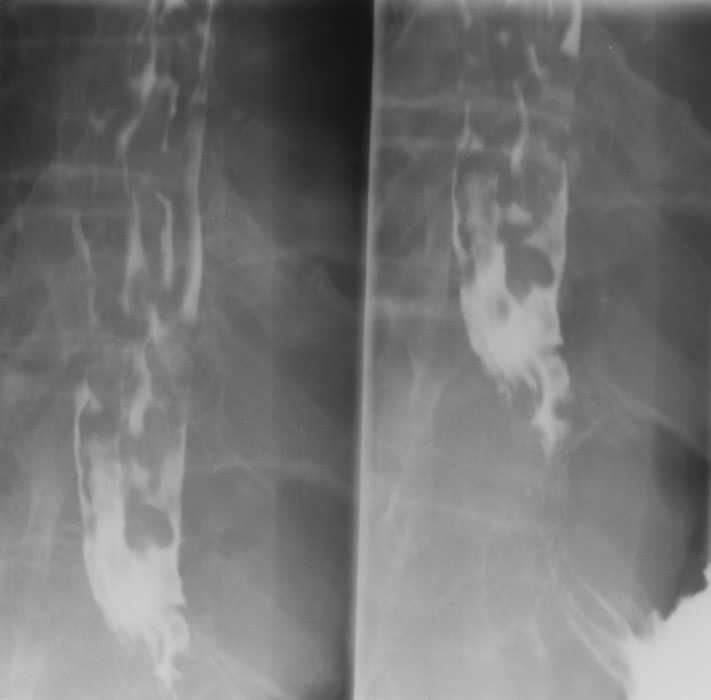
Esophageal Varices: Worm Tracings
Long wavy impressions
Made by the varices pressing on the outer esophagus

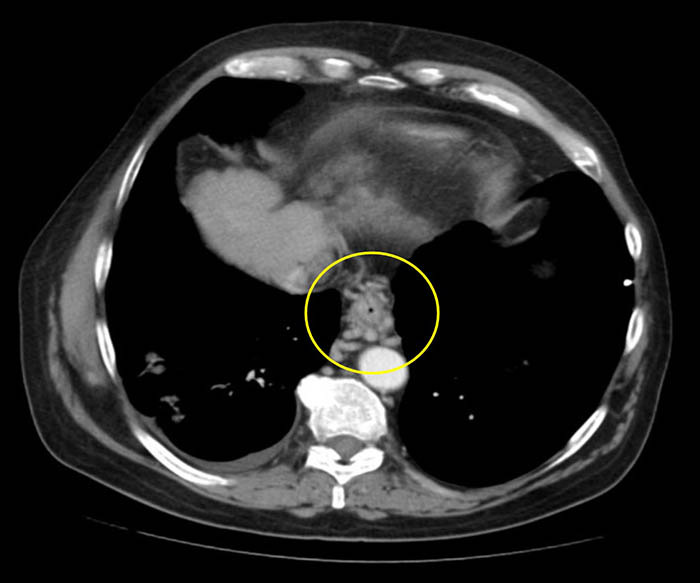
Esophageal Varices: CT Varices
Varices surrounding the esophagus as indicated by the circle
Gastric collateral veins dilation

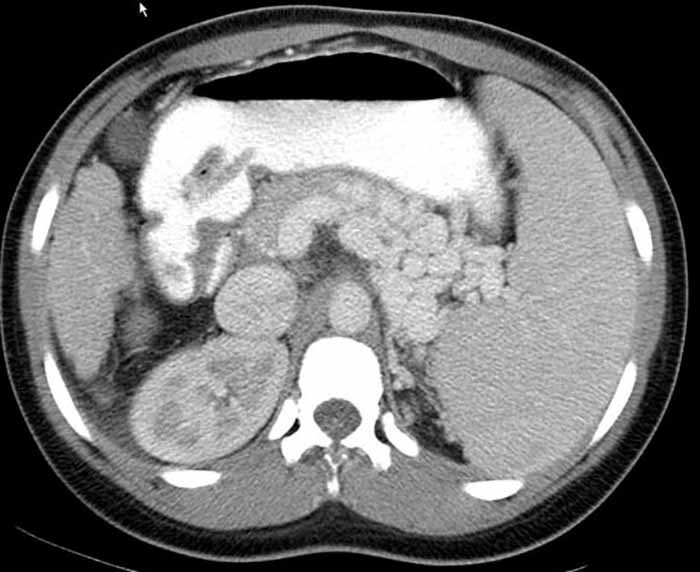
Esophageal Varices: CT Varices
Varices surrounding the esophagus as indicated by the circle
Gastric collateral veins dilation

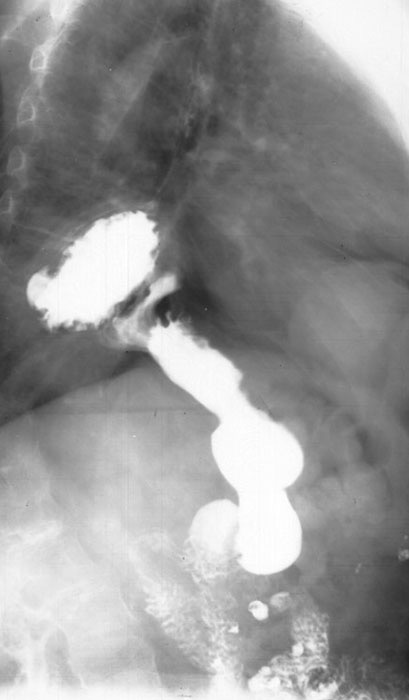
Hiatus Hernia: Roughened contours represent the stomach

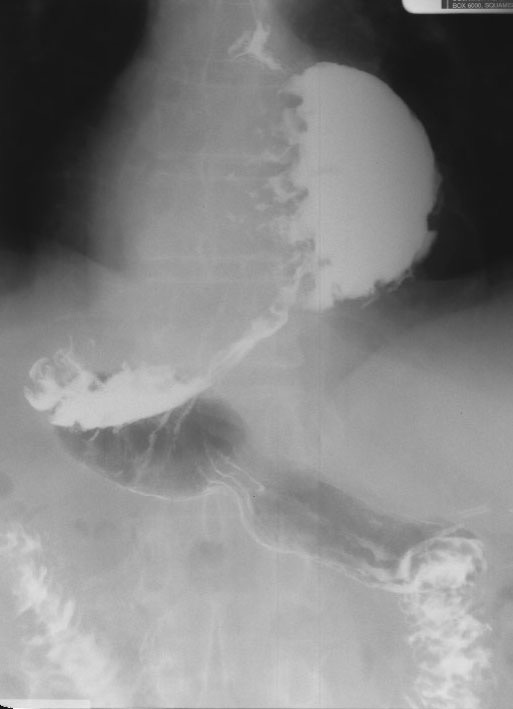
Hiatus Hernia: Rugal folds seen above the diaphragm

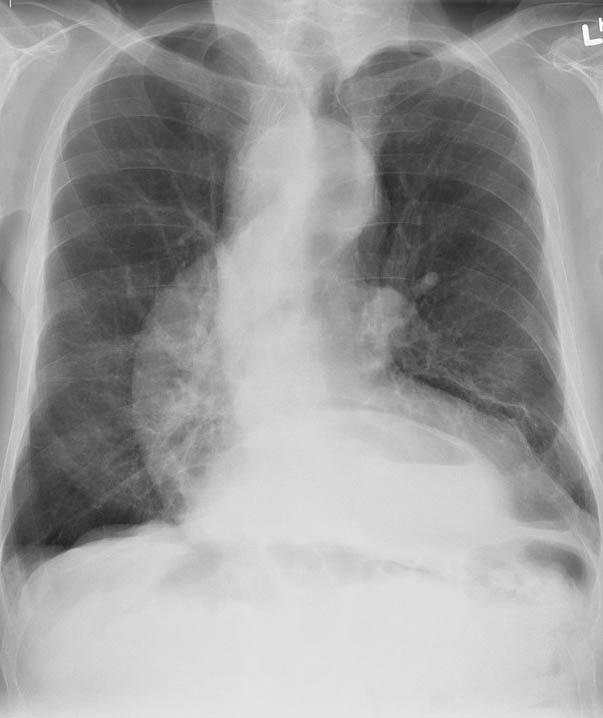
Hiatus Hernia: Mass w/ an air-fluid level in the mediastinum

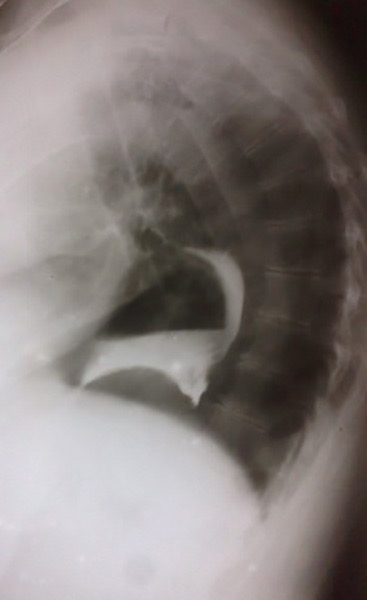
Hiatus Hernia:Majority of the stomach is in the thoracic cavity = diaphragmatic hiatus hernia

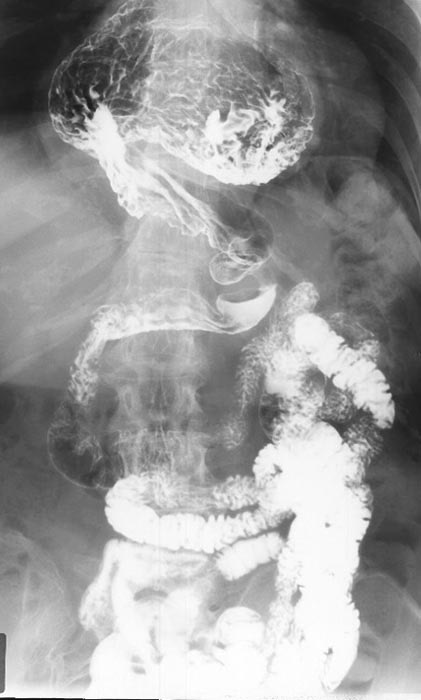
Hiatus Hernia: Diaphragmatic hiatus hernia

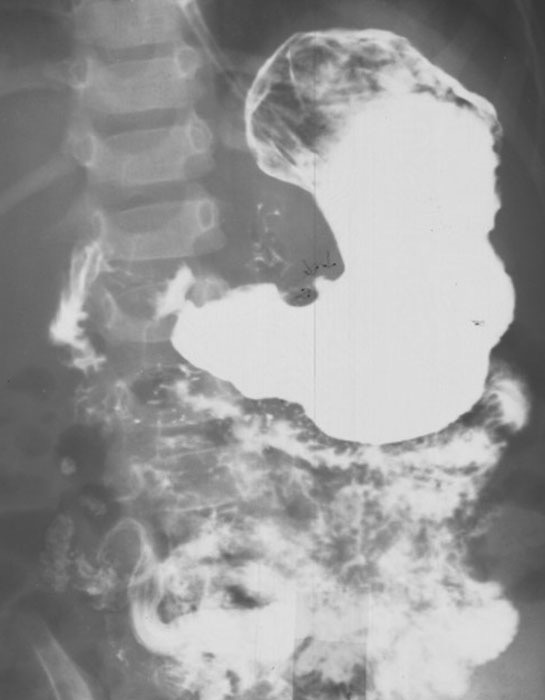
Ulcers
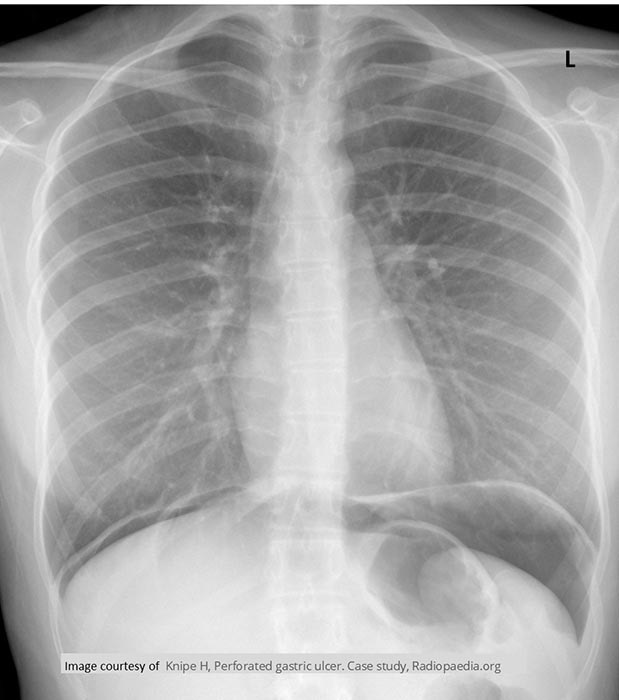
Ulcer - Pneumoperitoneum
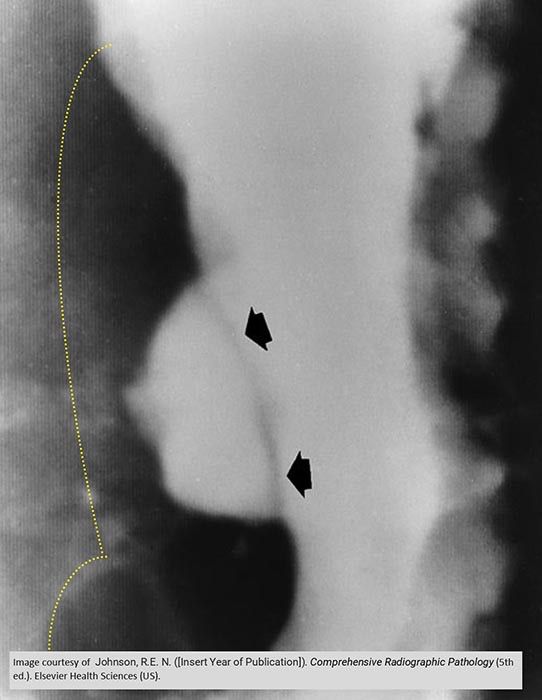
Ulcer
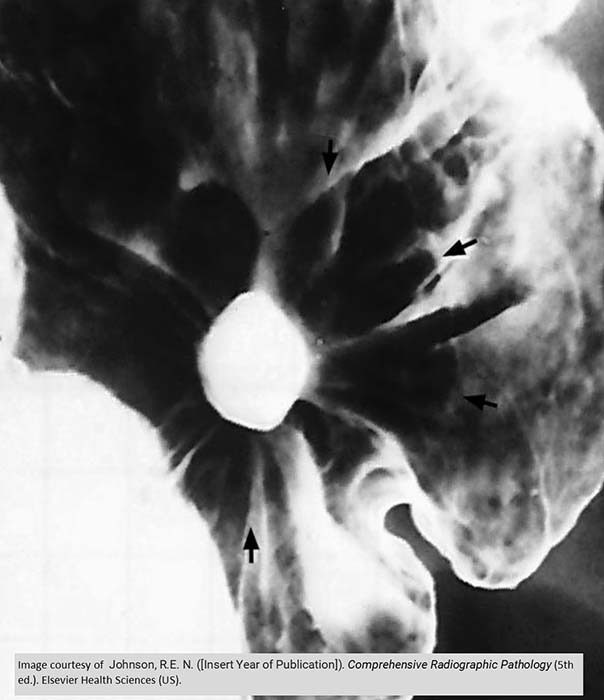
Gastric Ulcer
Gastric folds radiate out from the ulcer
Due to inflammation, there is very little barium coating the tissue surrounding the ulcer

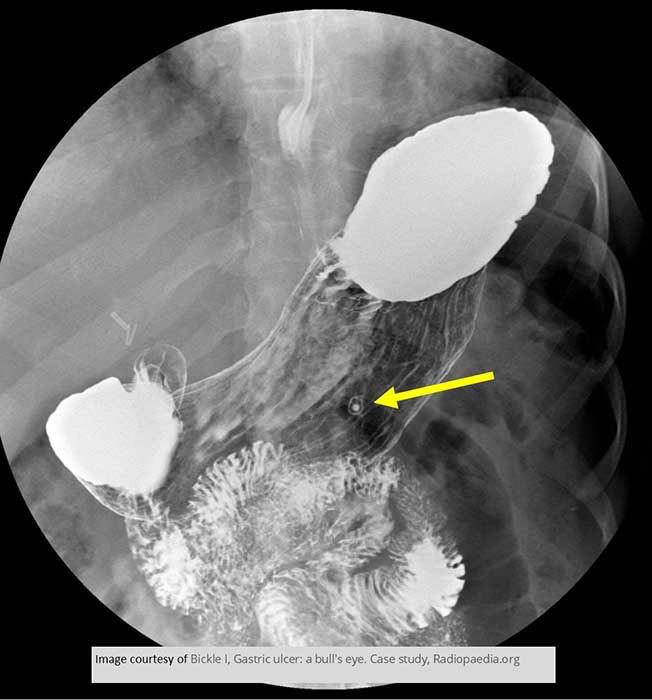
Gastric ulcer on the lesser curvature of the stomach

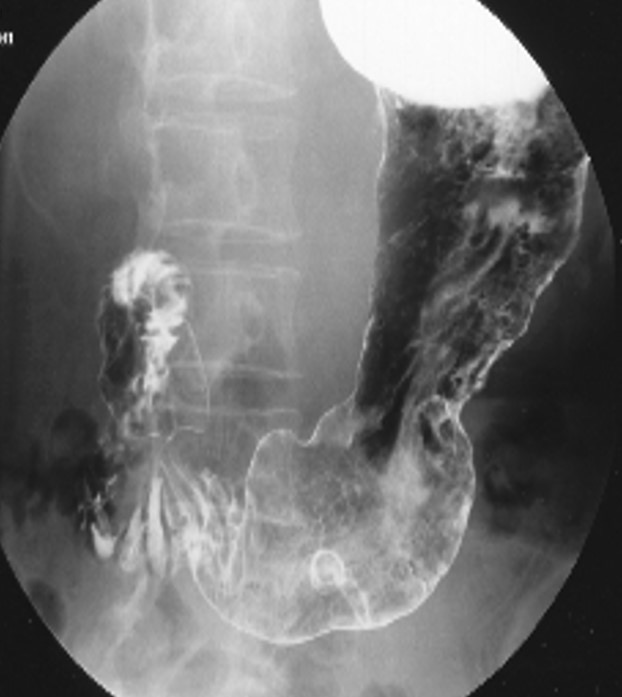
Duodena Ulcer
Location in the pylorus
PT had an ulcer in the past, higher up
Healing sometimes causes scarring and rigidity of the stomach at the site
No longer expands properly

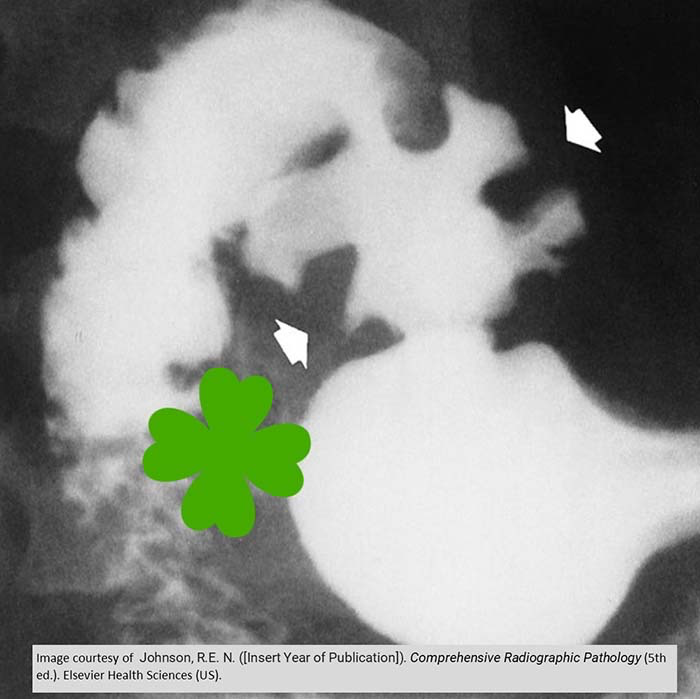
"Clover Leaf" deformity
Caused by fibrosis and scarring from a chronic duodenal ulcer
Deformity lasts even after healing

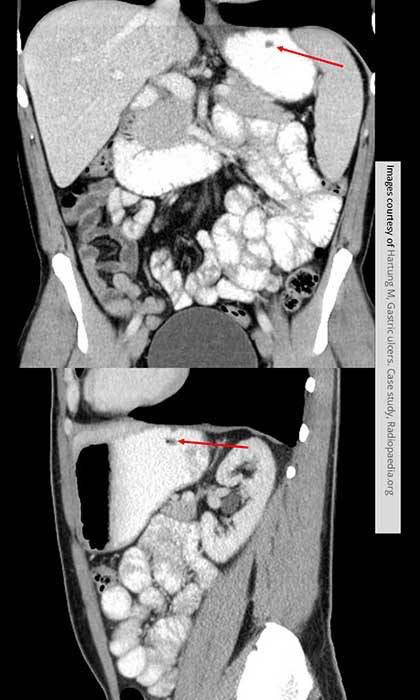
Gastric Ulcer
In the fundus

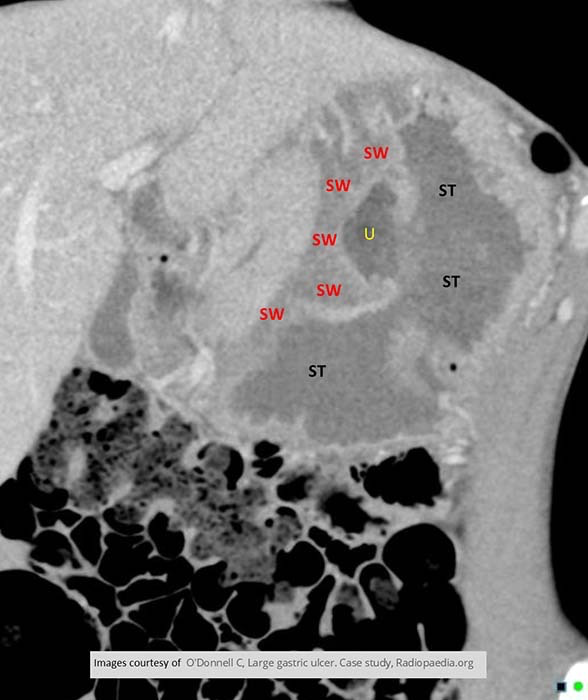
Gastric Ulcer
Surrounding swelling associated with it (SW)
ST is the inner lumen of the stomach

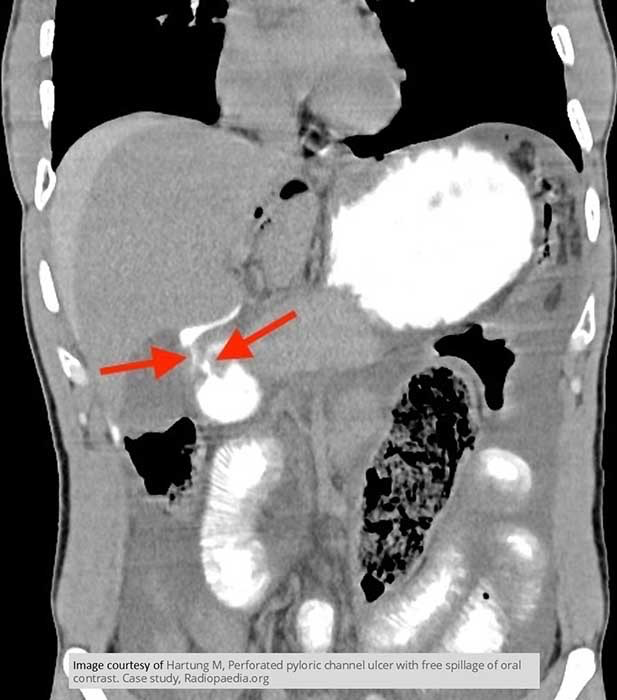
Duodenal perforation
Contrast leaking out

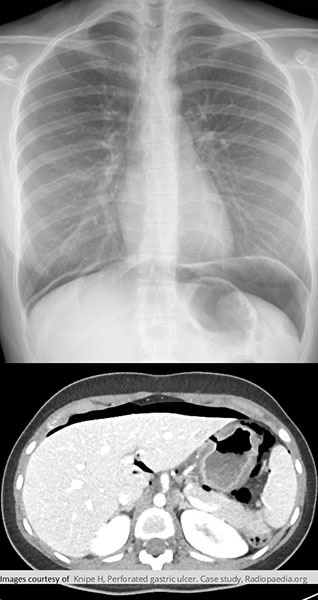
Perforation of Gastric Ulcer
Massive amount of free air anterior to the liver

CXR demonstrating the free air

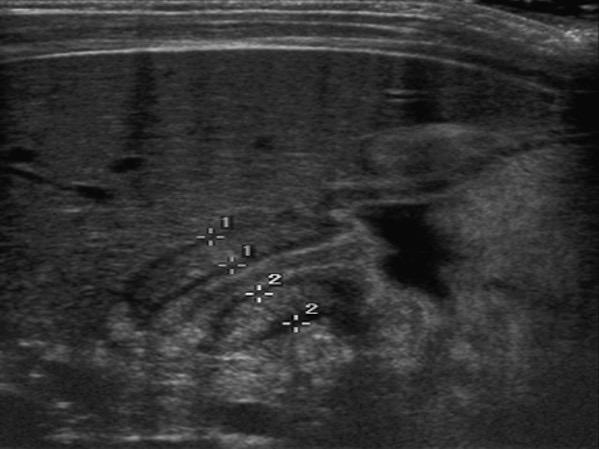
Plyoric Stenosis: U/S
Showing narrowing of the pyloric canal

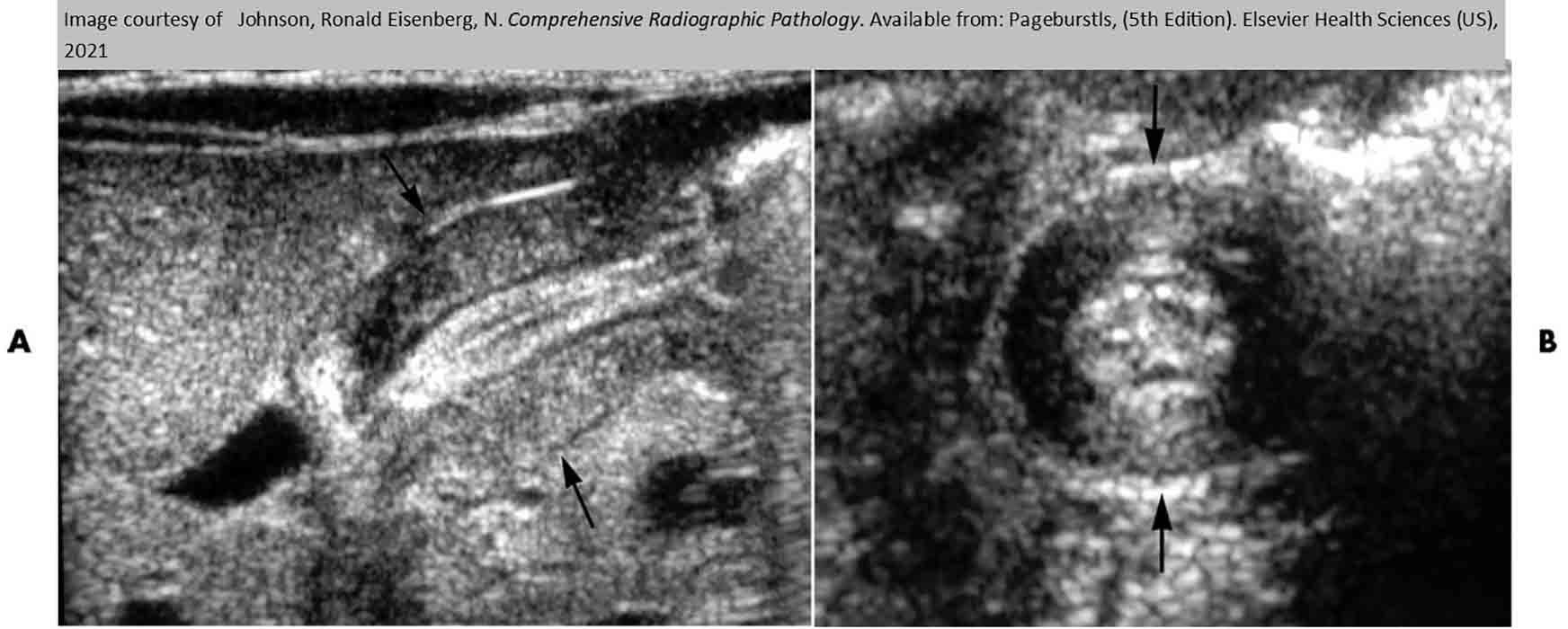
Plyoric Stenosis: U/S
Showing thickness of the gastric antral muscle in longitudinal (A) and transverse (B) plane

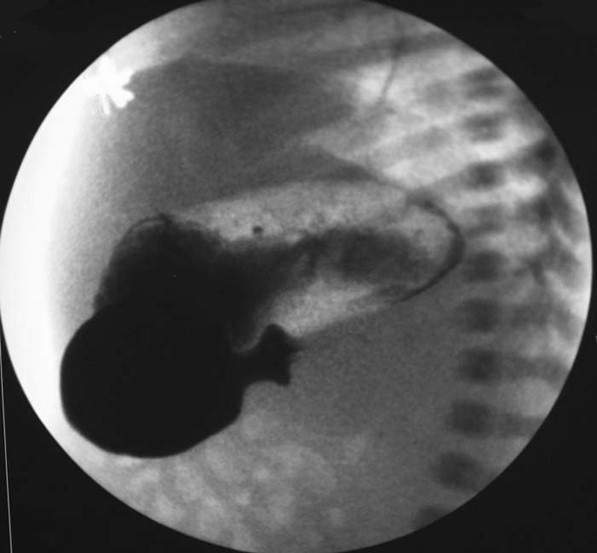
Plyoric Stenosis: Fluoroscopy
Showing a complete blockage

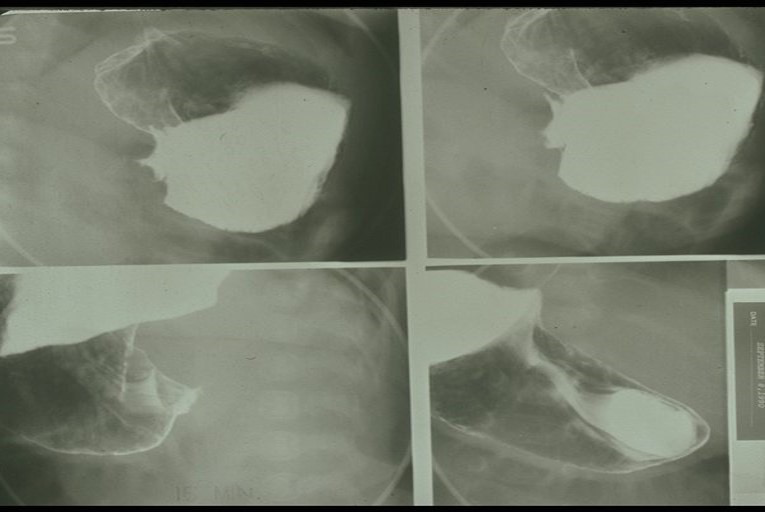
Plyoric Stenosis: Fluoroscopy
Showing a complete blockage
Impression of antrum into the stomach on the top two images

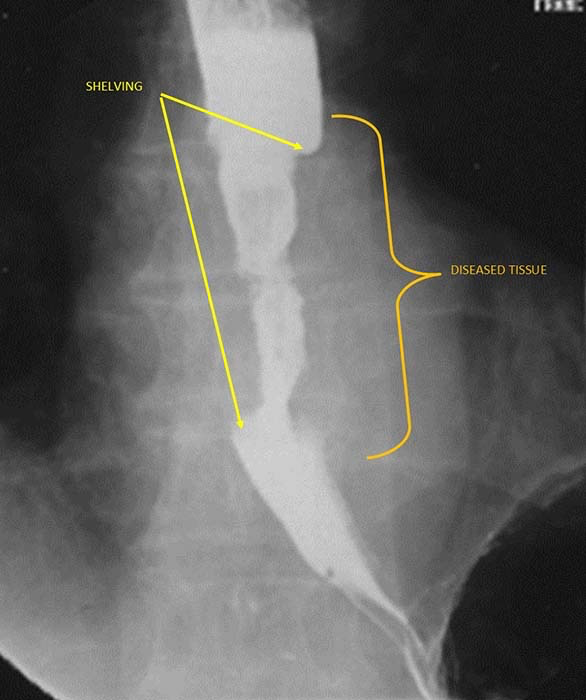
Esophageal Carcinoma: Infiltrative
Esophageal Carcinoma: Infiltrative
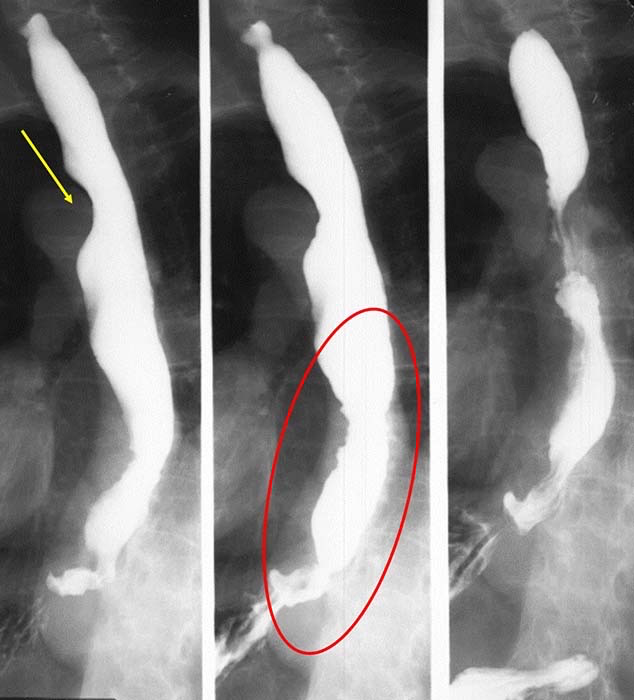
Esophageal Carcinoma: Proliferating
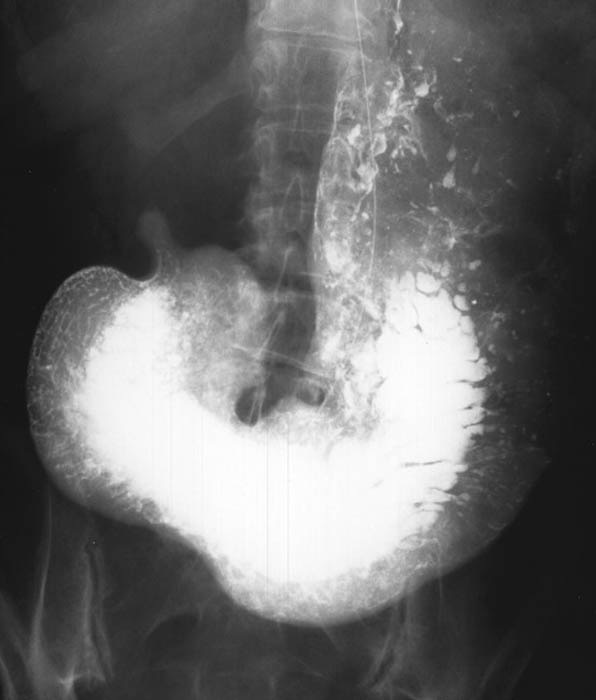
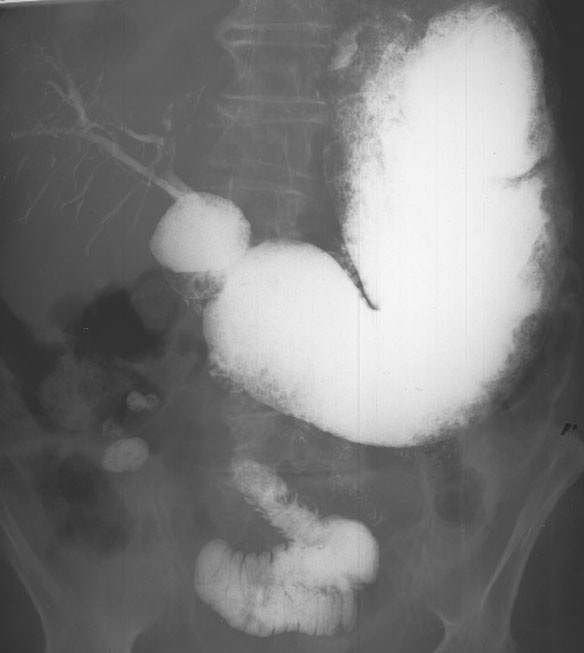
Gastric Carcinoma: Infiltrative Total involvement of the stomach
Lack of any rugae

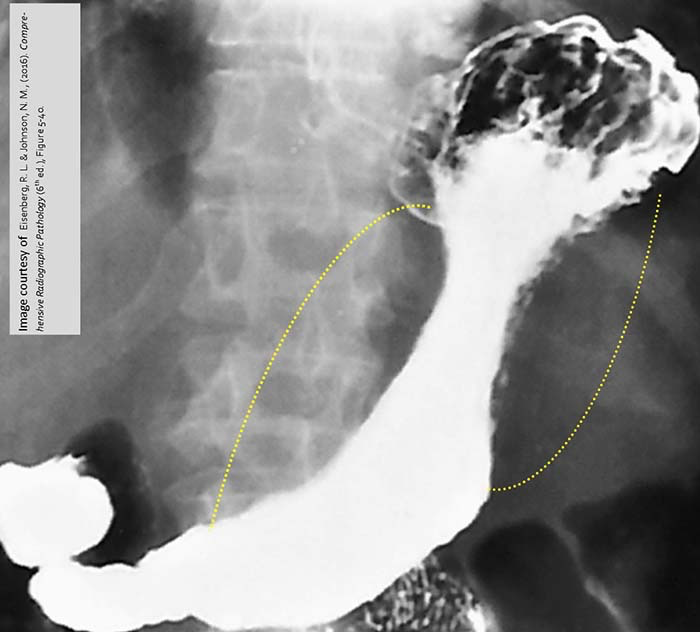
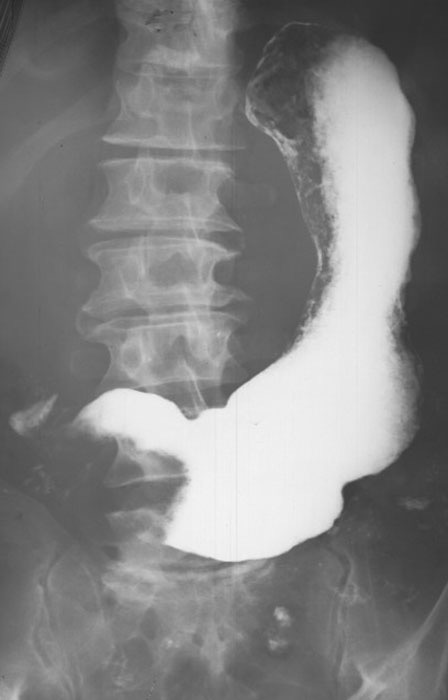
Gastric Carcinoma: Infiltrative Elongation of the stomach (rigid stomach)
Yellow dotted lines = areas of the diseased tissues

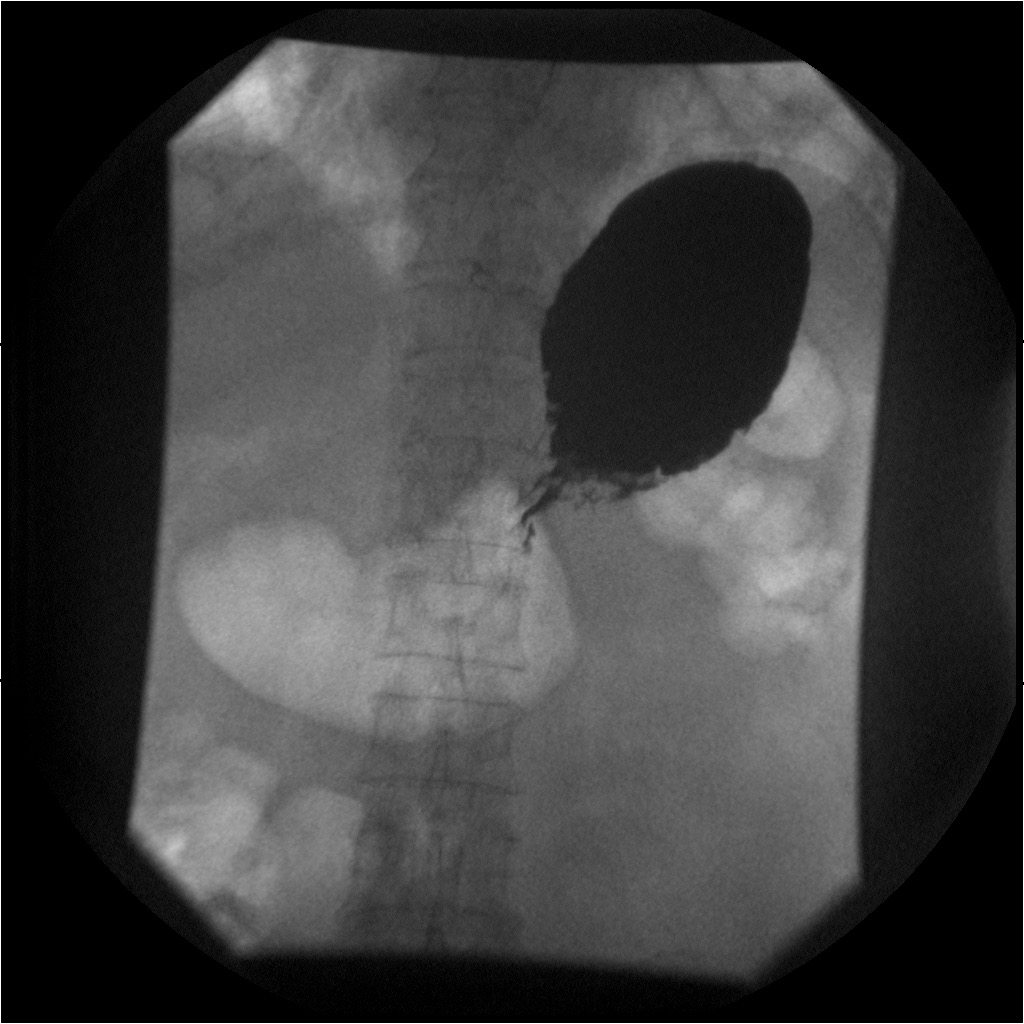
Gastric Carcinoma: Infiltrative Hourglass appearance
Obstruction has occurred as very little barium is passing through the narrowing

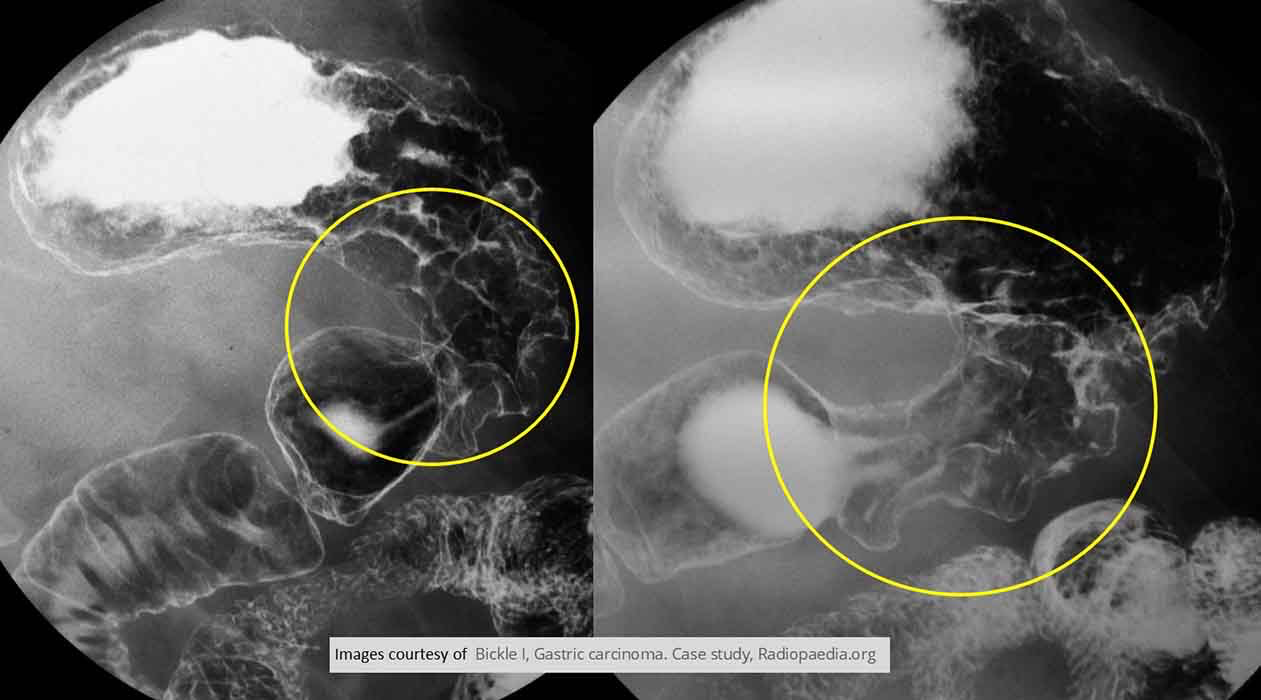
Gastric Carcinoma: Infiltrative In the pylorus area
Overall narrowing of the lumen
Irregular appearance at the rugal folds
Gives impression the tumor is extending proximally

Gastric Carcinoma: Infiltrative Total involvement of the stomach
Lack of any rugae

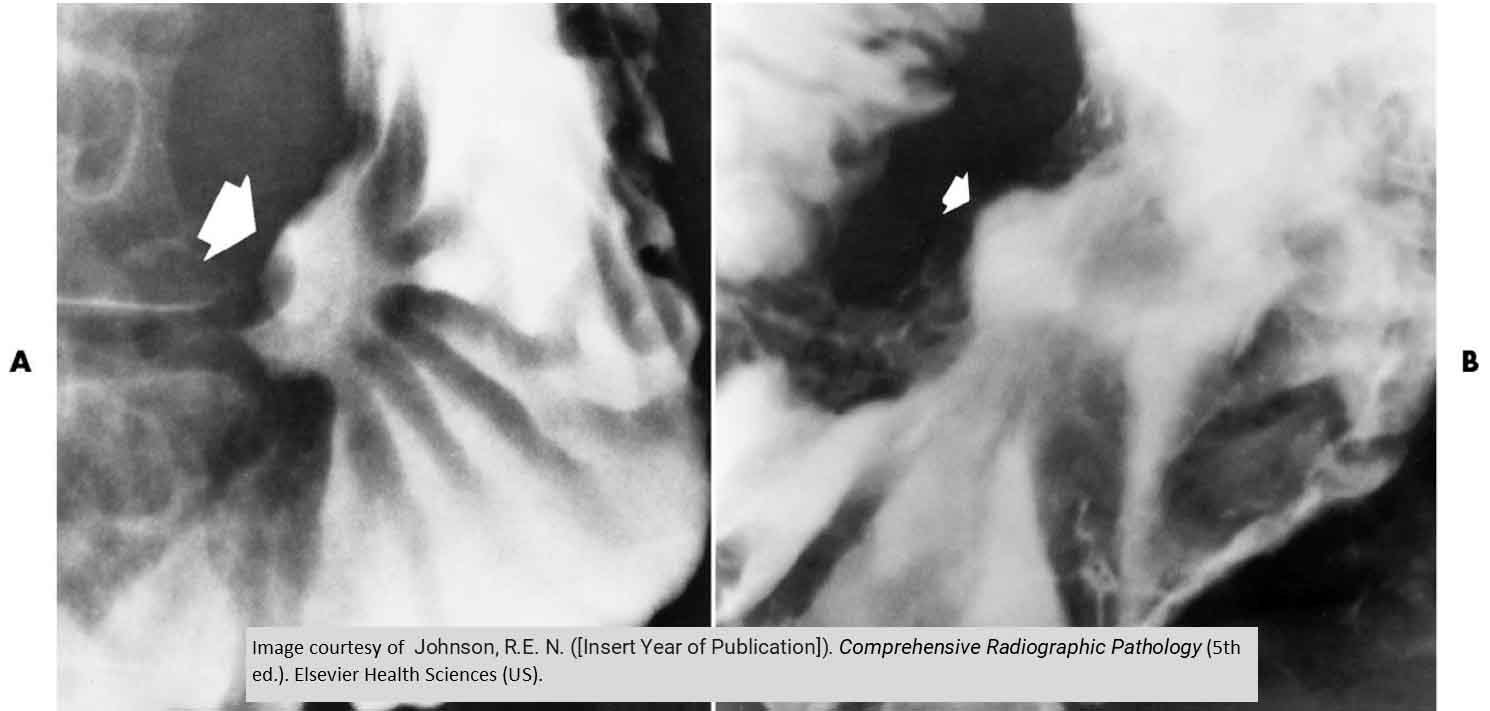
Gastric Carcinoma: Proliferating
Gastric Carcinoma: Proliferating Polypoid mass
Almost occluding the pyloric sphincter
Very little contrast getting through

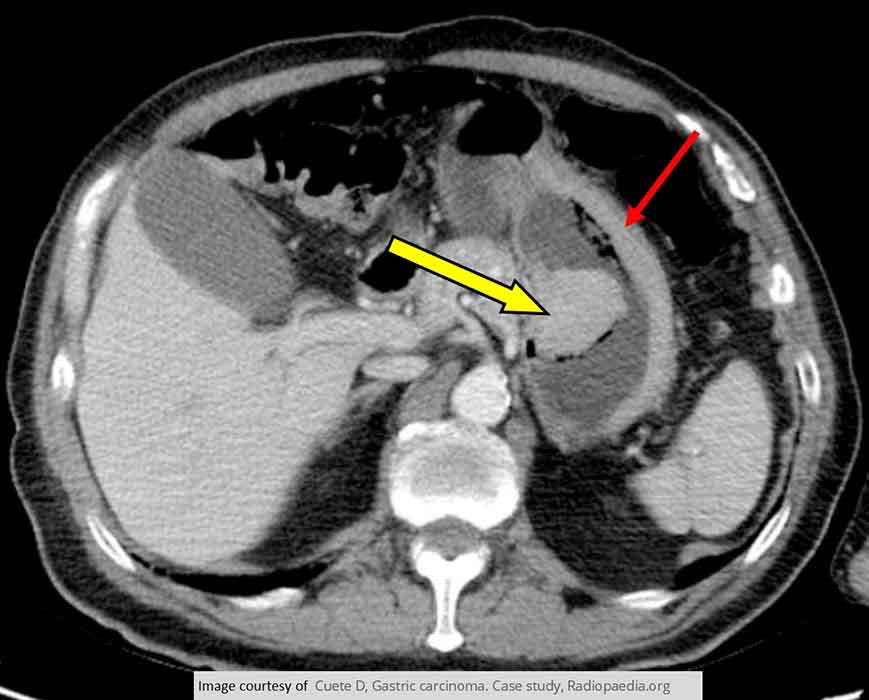
Gastric Carcinoma: Proliferating Yellow arrow showing 2polypoid mass
Red arrow showing tumor growth surrounding the entire stomach

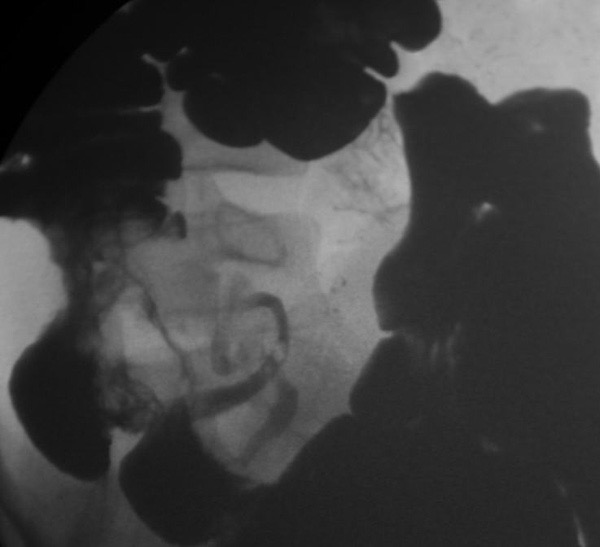
Chron’s: Narrowing of the terminal ileum
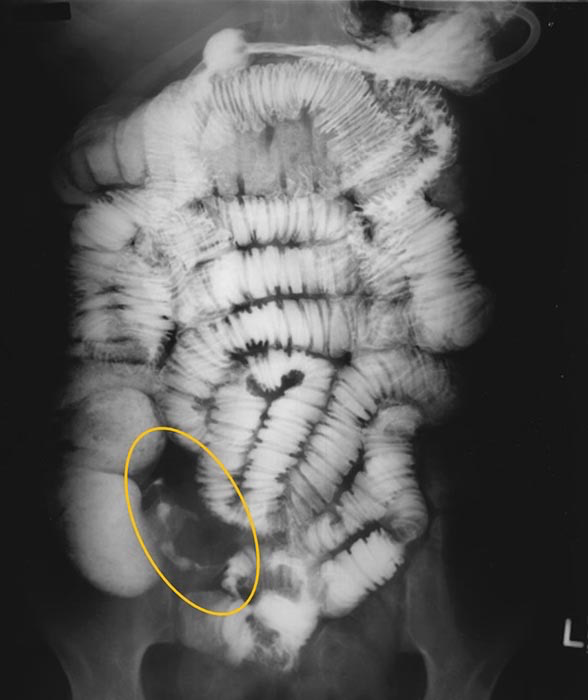
Chron’s: Narrowing of the terminal ileum

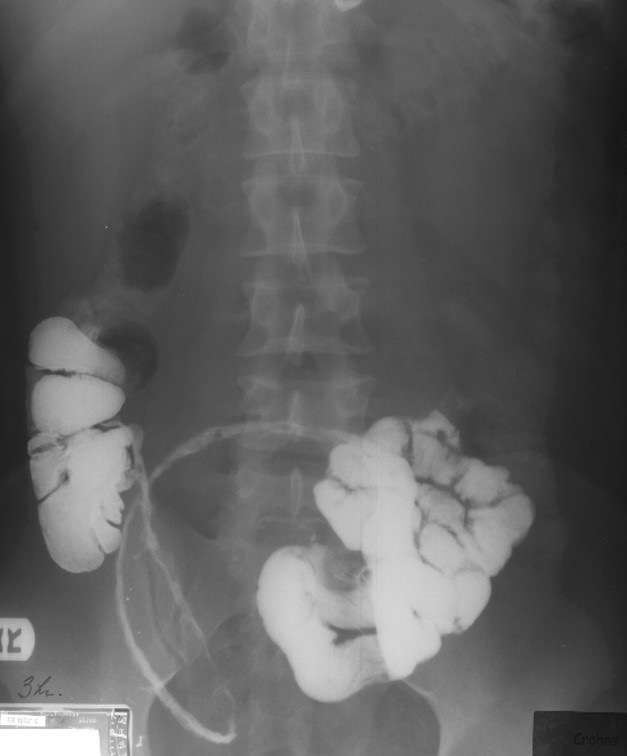
Chron’s: Large section of the terminal portion of the ileum w/ narrowing

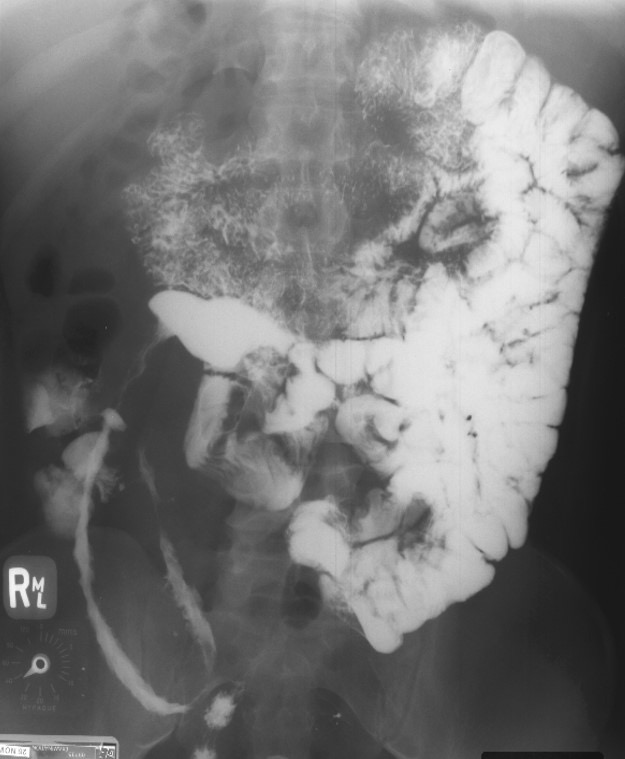
Chron’s: Large section of the ileum affected

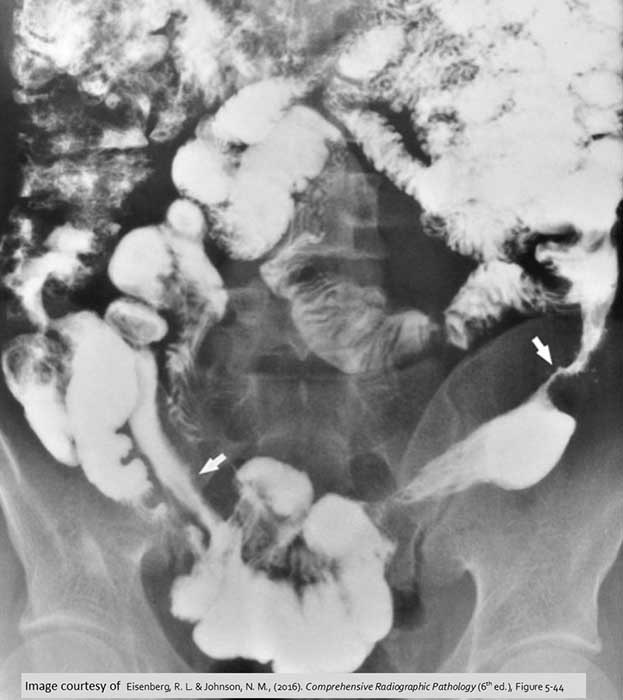
Chron’s: Skip lesions (white arrows)
Common in Chron's Disease, inflamed area of the bowel will be interspersed w/ normal non-affected areas of bowel

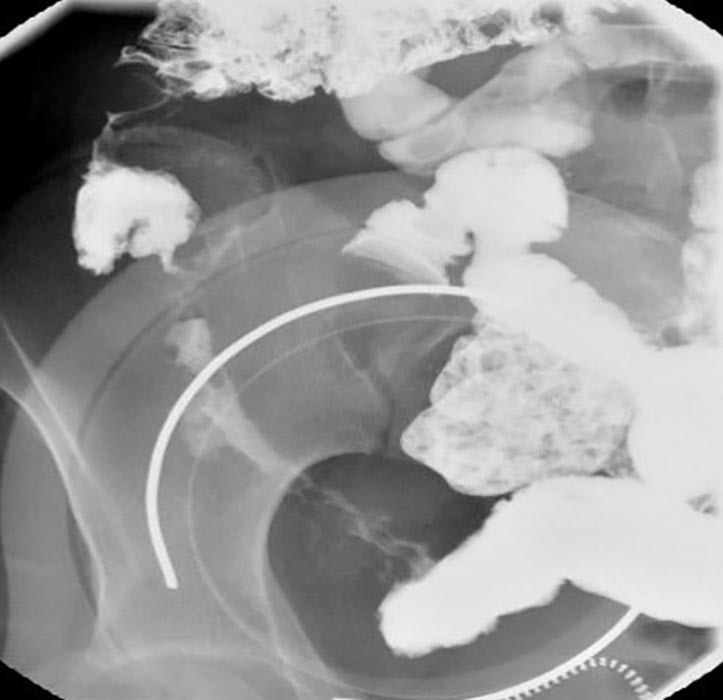
Chron’s: Narrowed area of bowel w/ a cobblestone appearance
Cobblestone look represents areas of ulceration within the bowel wall

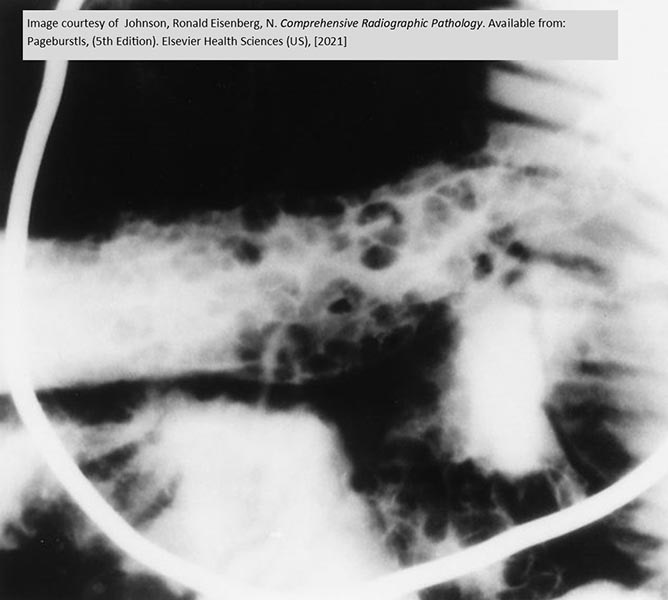
Chron’s: Areas of ulceration of the wall of the small bowel

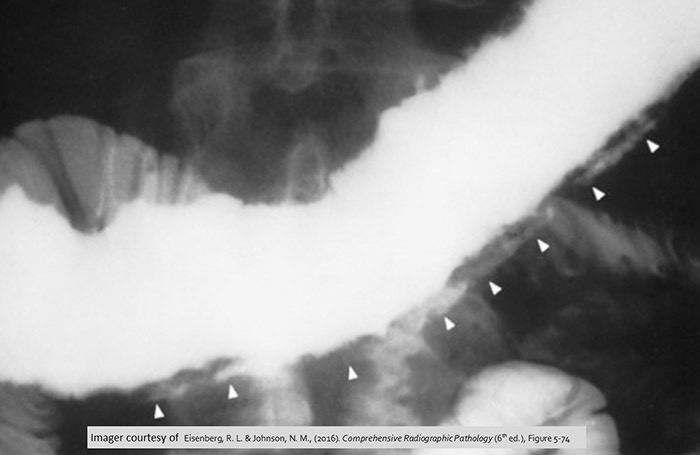
Chron’s: Arrows indicating a massive fistula within the transverse colon wall

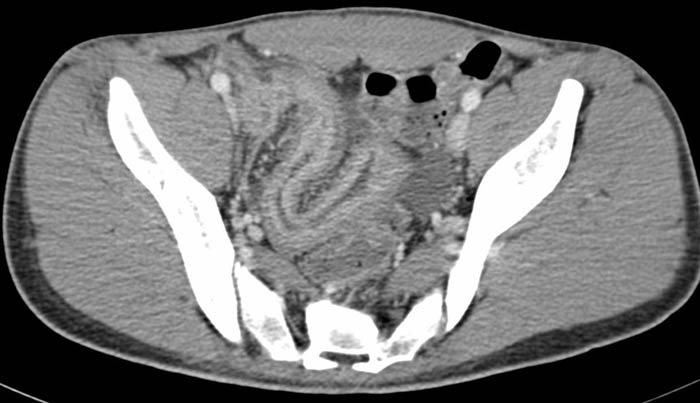
Chron’s: Demonstrating thicken small bowel walls

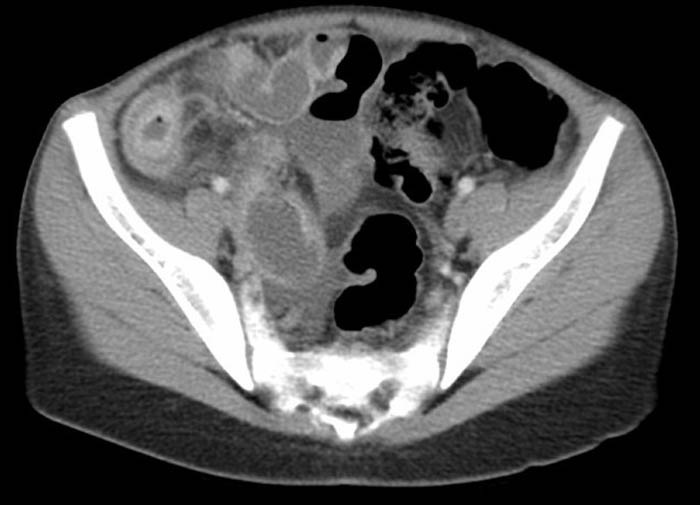
Chron’s: Demonstrating multiple areas of inflammation of the bowel wall

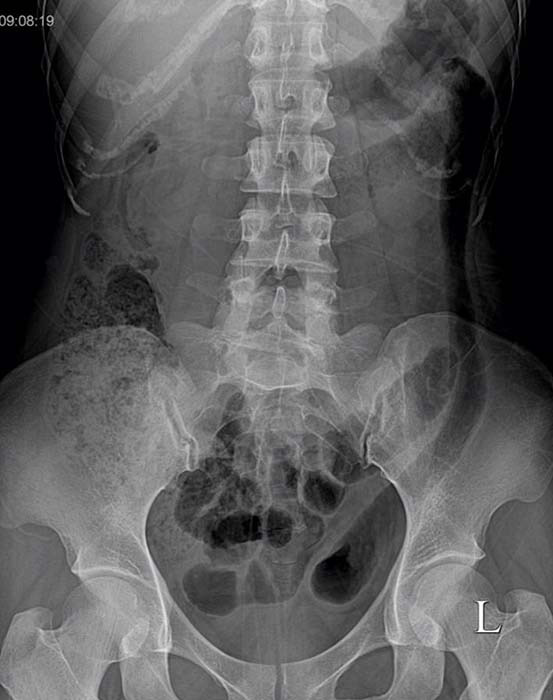
Ulcerative Colitis:Stove Pipe appearance of descending and sigmoid regions of the large bowel

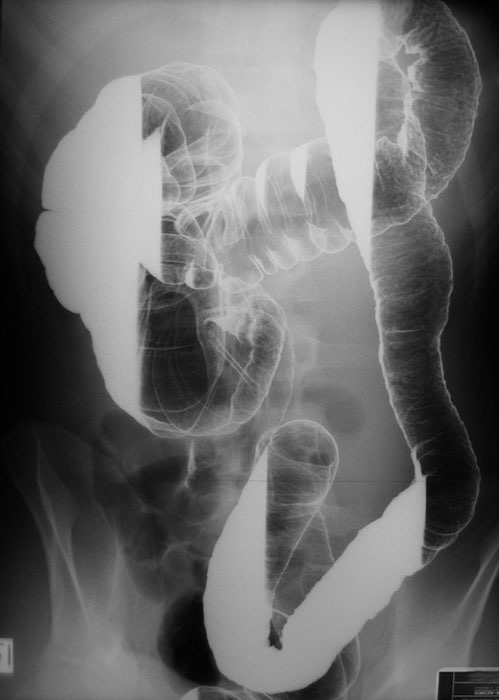
Ulcerative Colitis: Stove Pipe appearance in this double contrast decub

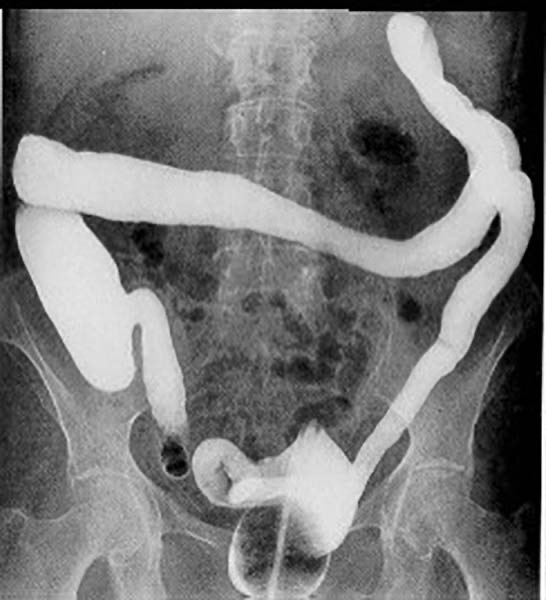
Ulcerative Colitis: Involvement of the entire large bowel is demonstrated (Pancolitis)

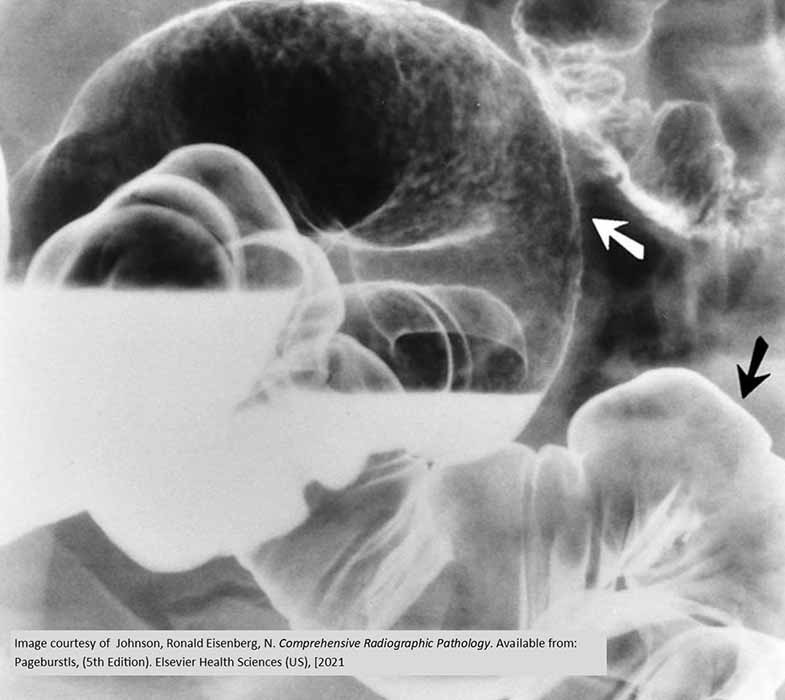
Ulcerative Colitis: White arrow shows the irregular appearance of an area of UC as compared w/ normal bowel wall (black arrow)

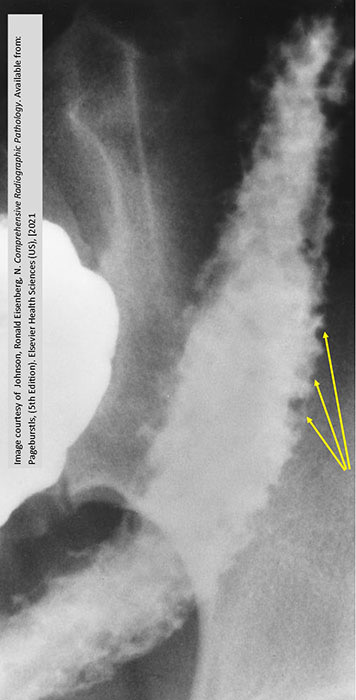
Ulcerative Colitis: "Collar button" appearance of damaged mucosa

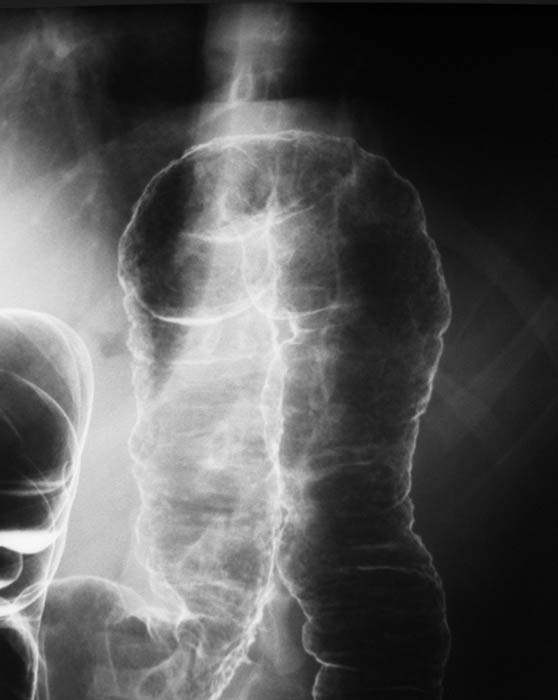
Ulcerative Colitis: Ulcerated mucosal lining at the splenic flexure

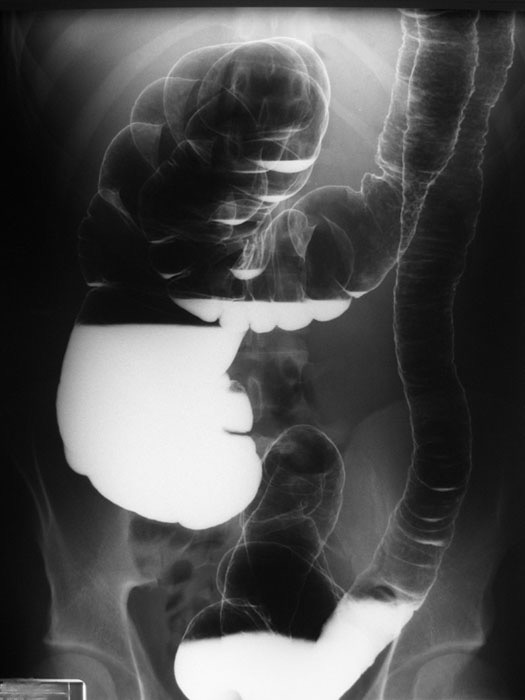
Ulcerative Colitis: Disease has progressed into the transverse colon

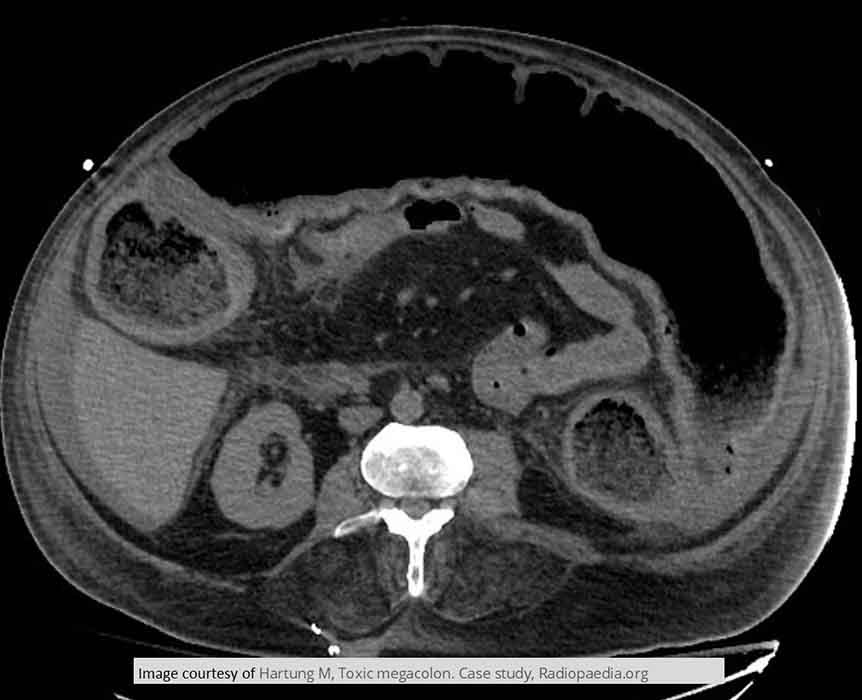
Toxic Megacolon: CT image of an UC PT w/ Toxic Megacolon who tested positive for C-dif infection

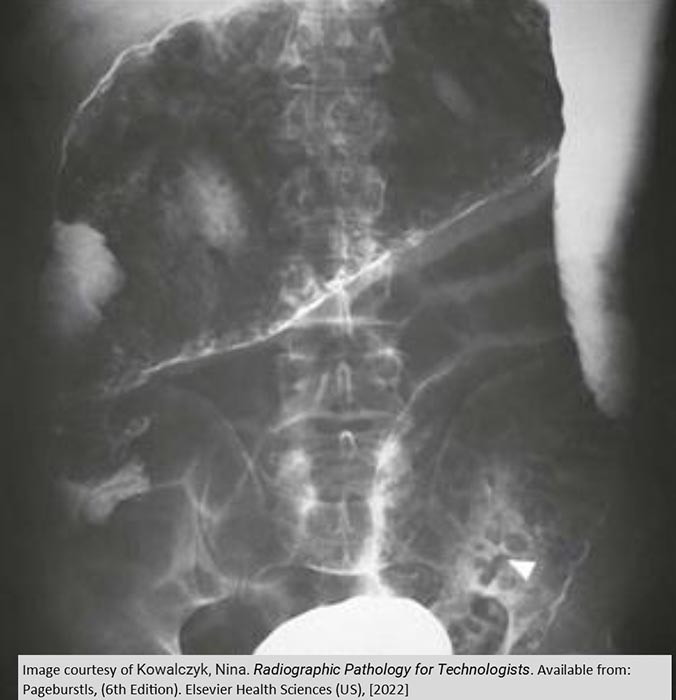
Toxic Megacolon: Grossly distended transverse colon of an Ulcerative Colitis PT w/ Toxic Megacolon

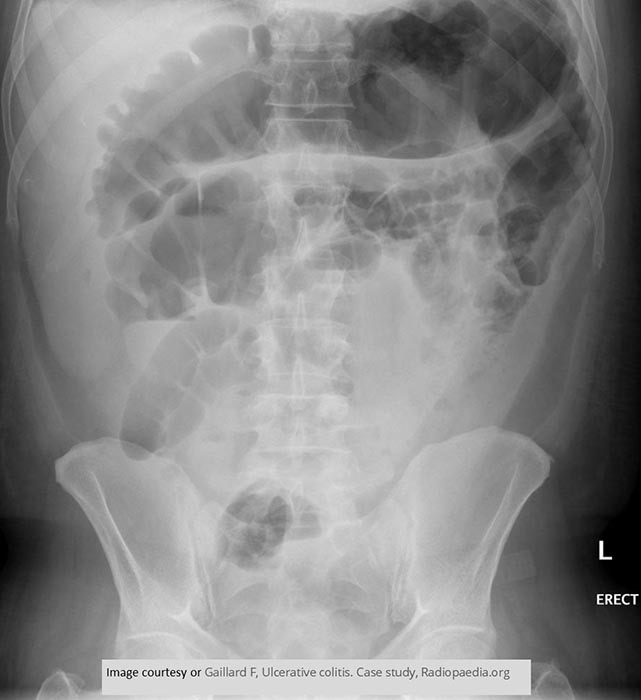

Toxic Megacolon: Dilation of the transverse colon measures 9 cm
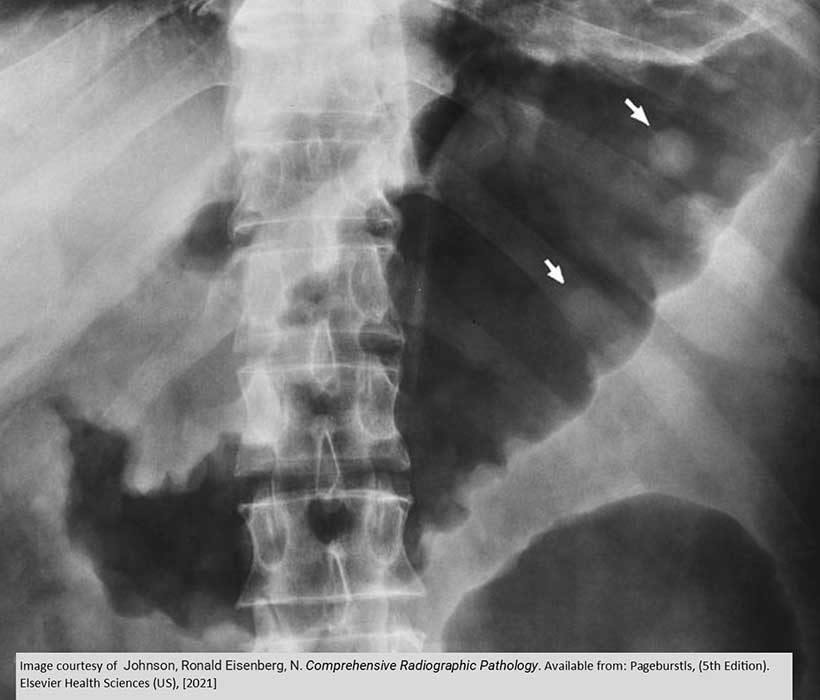
Toxic Megacolon: Toxic Megacolon - pseudo polyps as indicated by the arrows

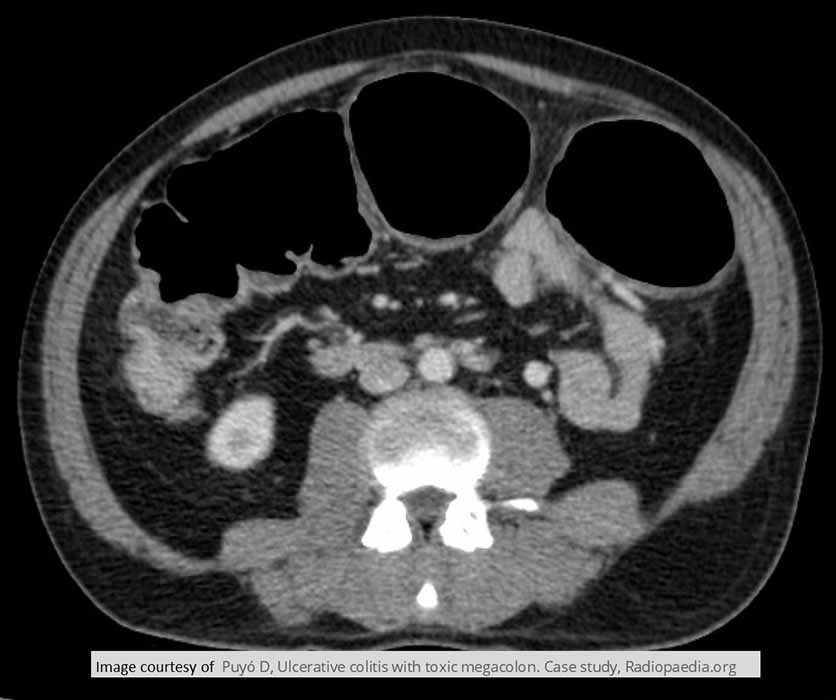
Toxic Megacolon: CT image of Toxic Megacolon w/ dilation measured at 8.4 cm in the large bowel

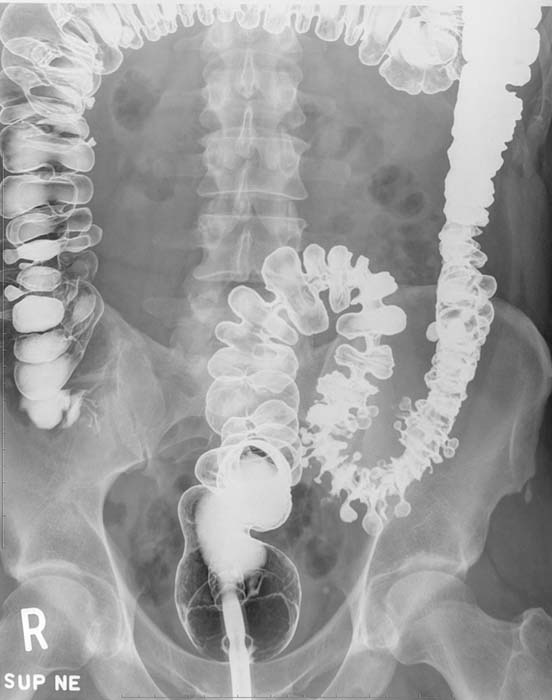
Diverticular Disease: "Saw-tooth" appearance

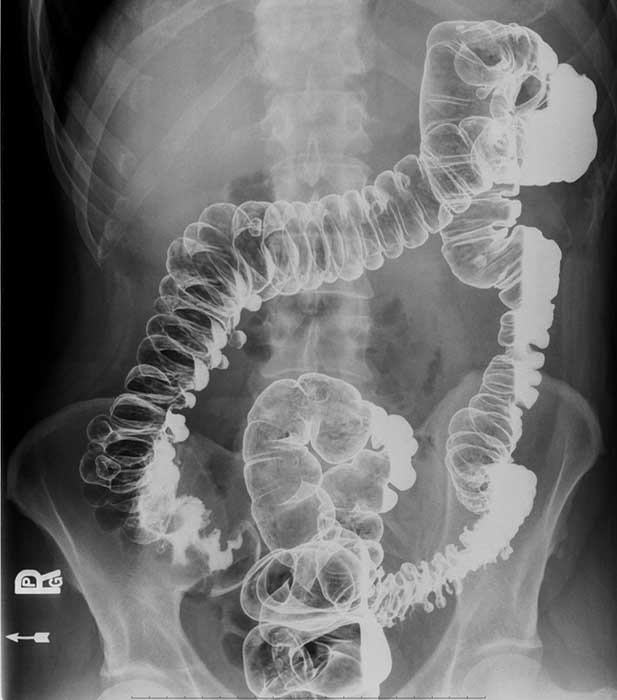
Diverticular Disease: "Saw tooth" appearance of the bowel in the distal portion of the descending colon

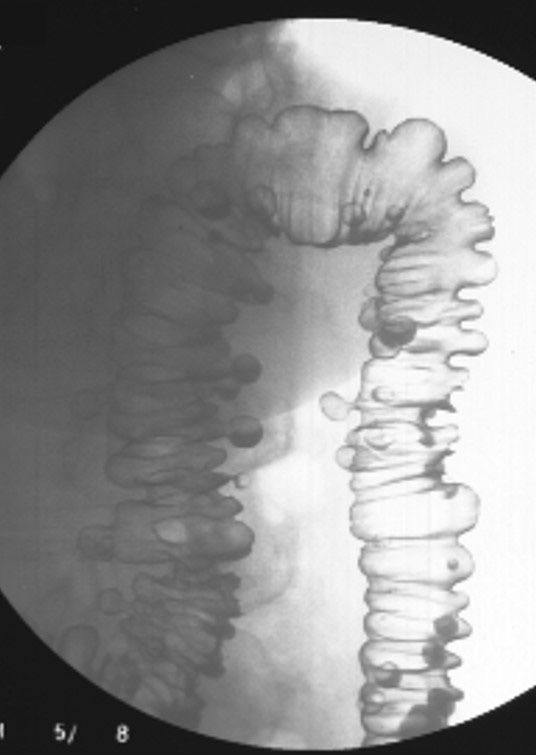
Diverticular Disease: Splenic flexure shown demonstrating diverticula in descending and transverse colon

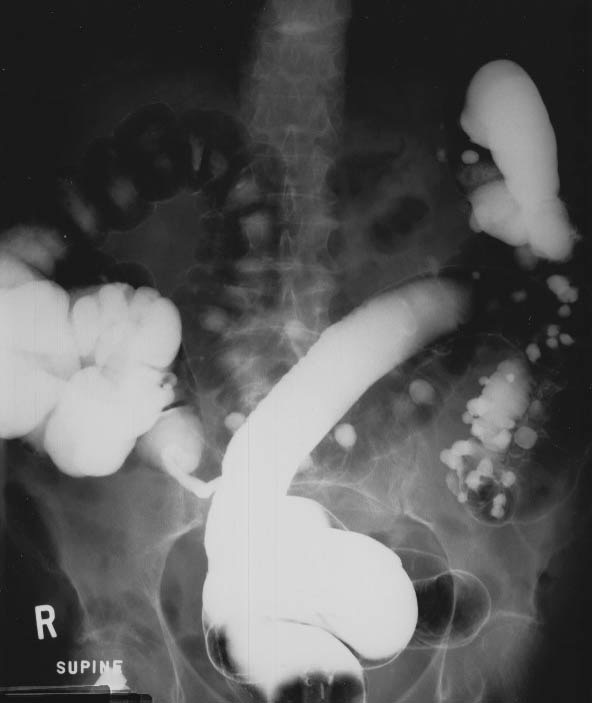
Diverticular Disease: Multiple areas of diverticula

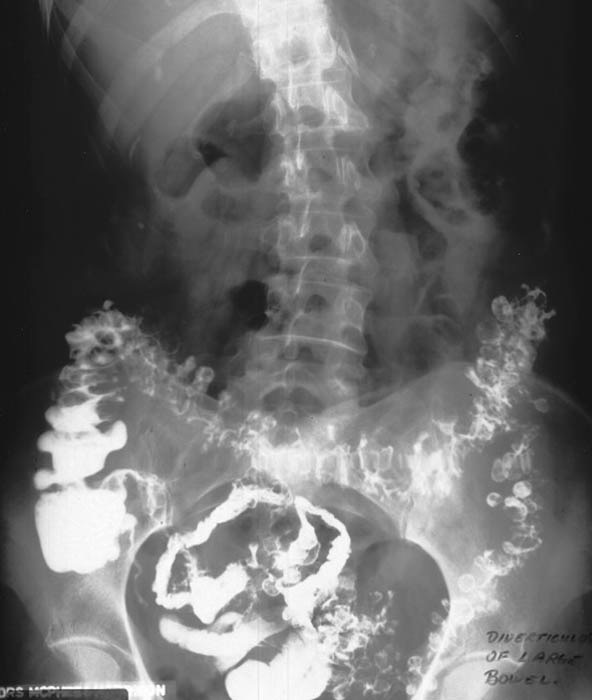
Diverticular Disease: Remnants of contrast within the diverticula

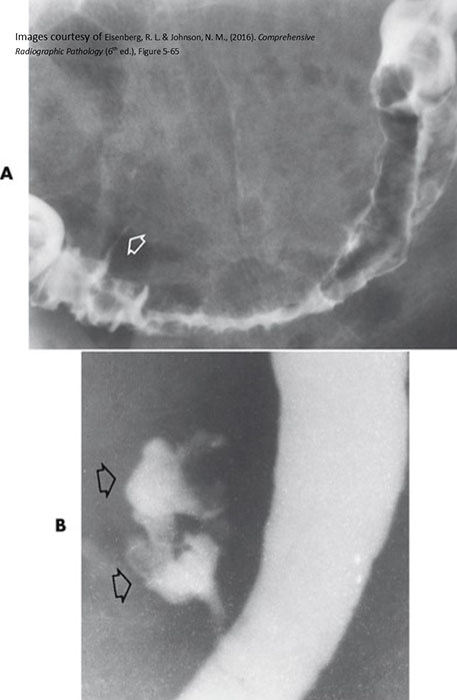
Diverticular Disease: Active diverticulitis

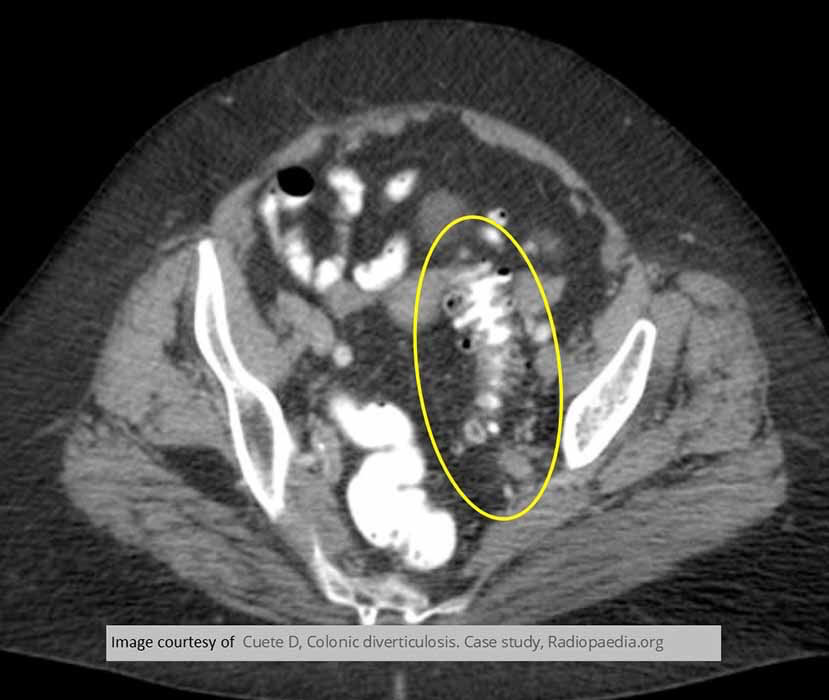
Diverticular Disease: CT AXIAL SLICE "saw tooth" appearance

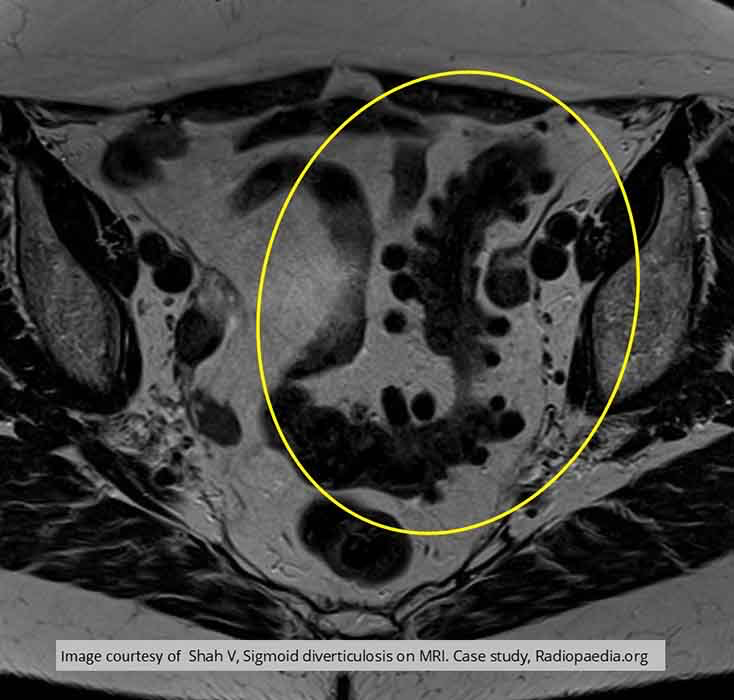
Diverticular Disease:
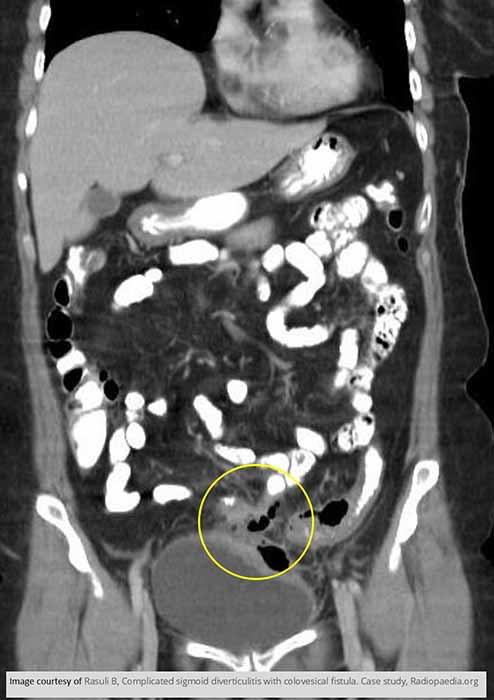
Diverticular Disease: Demonstrates a colovesical fistula b/w the sigmoid colon and the bladder due to diverticulitis

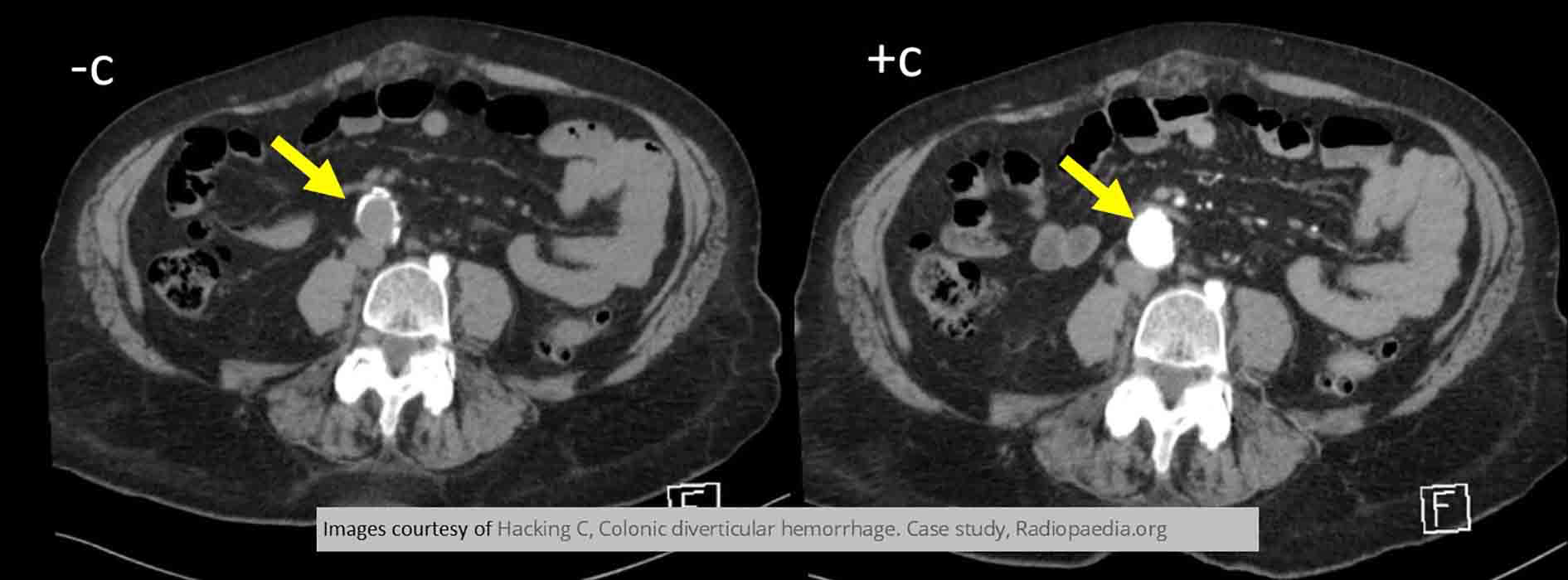
Diverticular Disease:Inflamed bleeding diverticulum

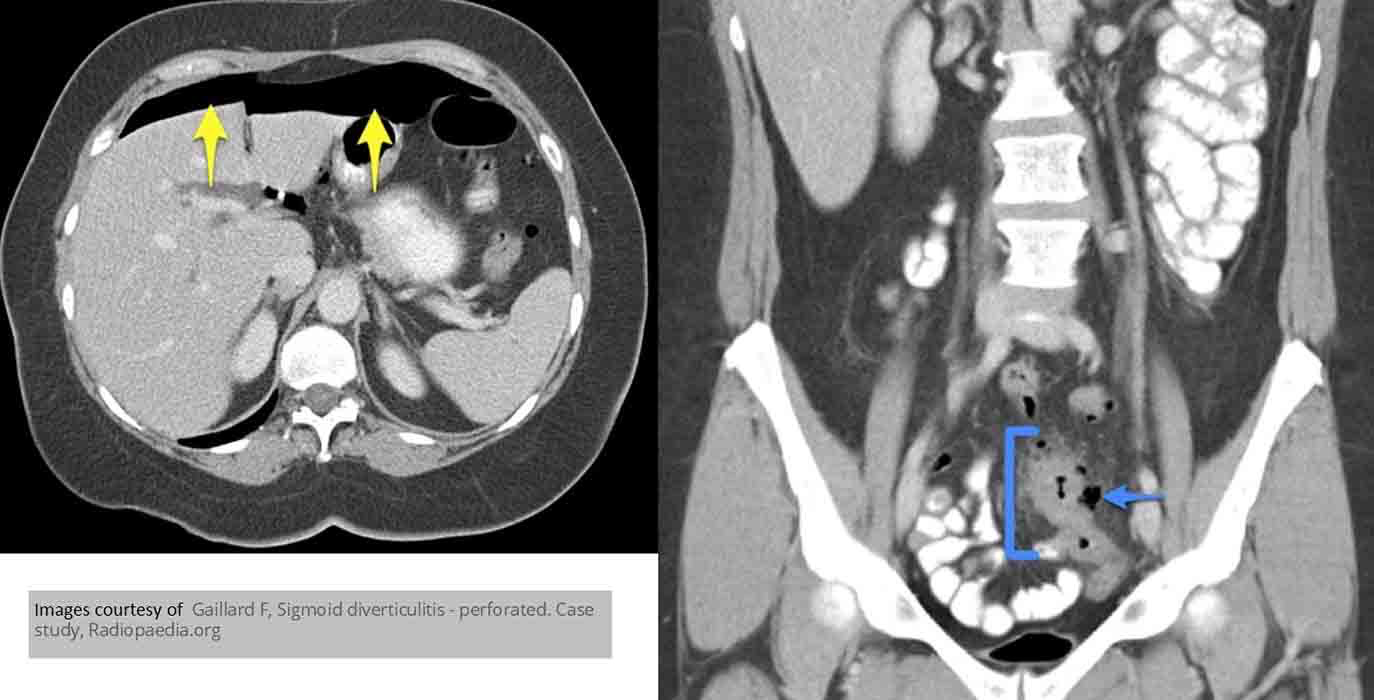
Diverticular Disease: Blue represents diverticulum which in turn has caused a pneumoperitoneum (yellow arrows)

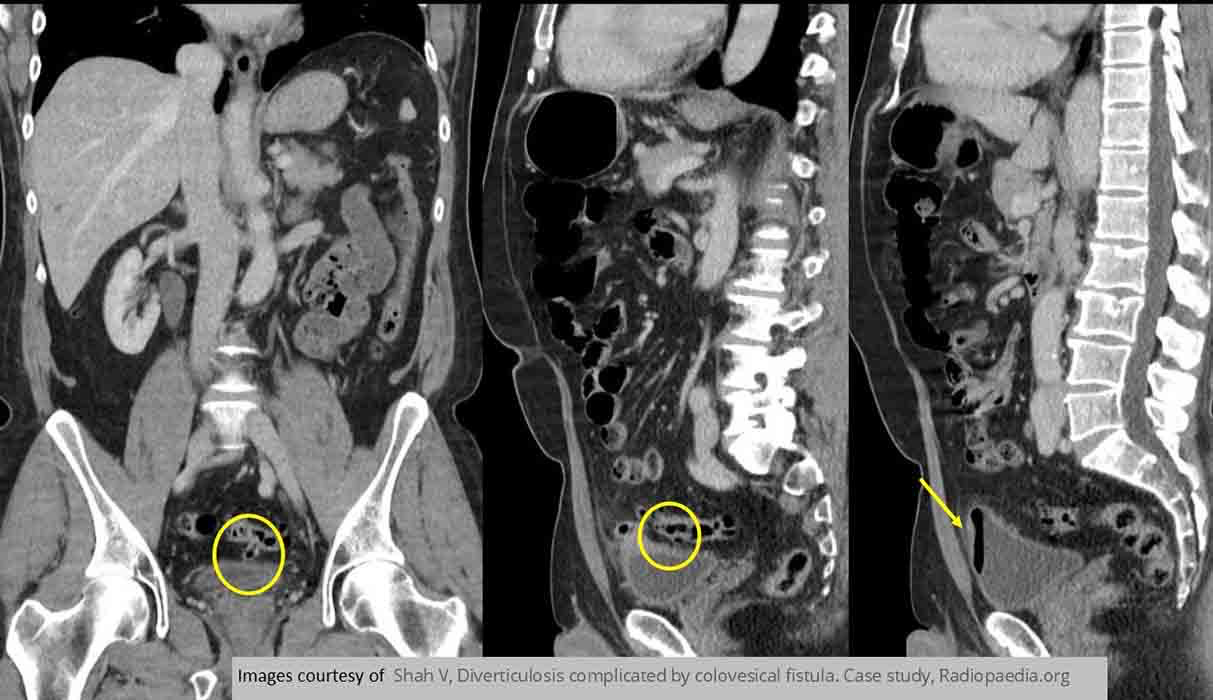
Diverticular Disease:
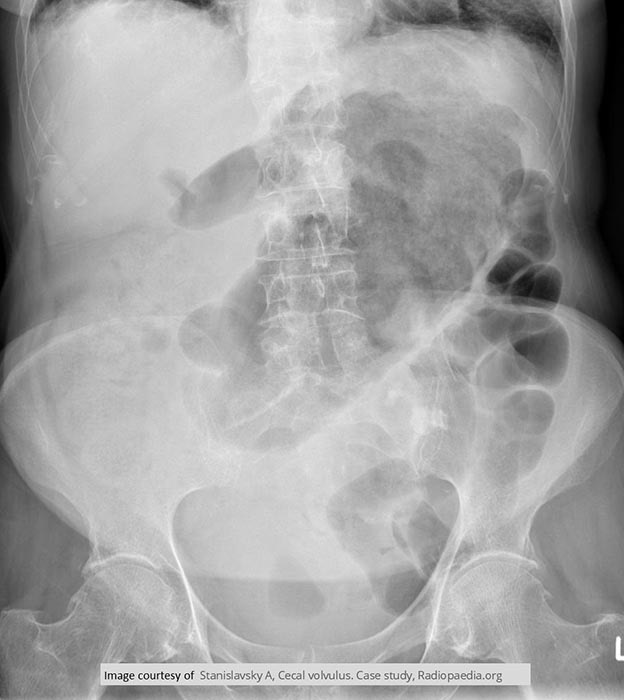
Volvulus: Cecal volvulus

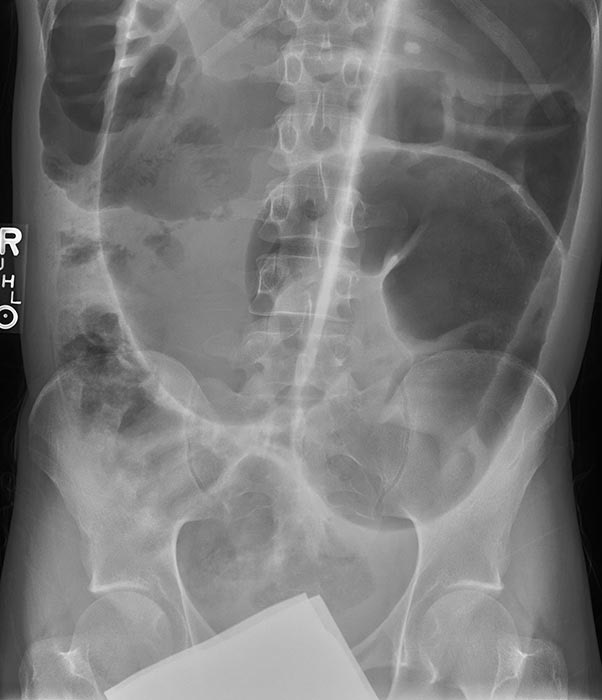
Volvulus: Sigmoid volvulus
