Exam 6 physio UC PA cohort 2027 (ENDO 520S) 17 SLIDES
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
respond to specific signals by synthesizing and releasing hormones into the circulation
The endocrine glands
Functions of Endocrine system
Differentiation
stimulation
coordination
maintenance
initiation
∙Hormones Operation Within Feedback Systems
Maintains an optimal internal environment
Positive Feedback
Negative Feedback
Mechanism of hormones
•Steroid Hormone Excretion
•Excreted directly by the kidneys
•Metabolized (conjugated) by the liver which inactivates them and renders the hormone more water soluble for renal excretion
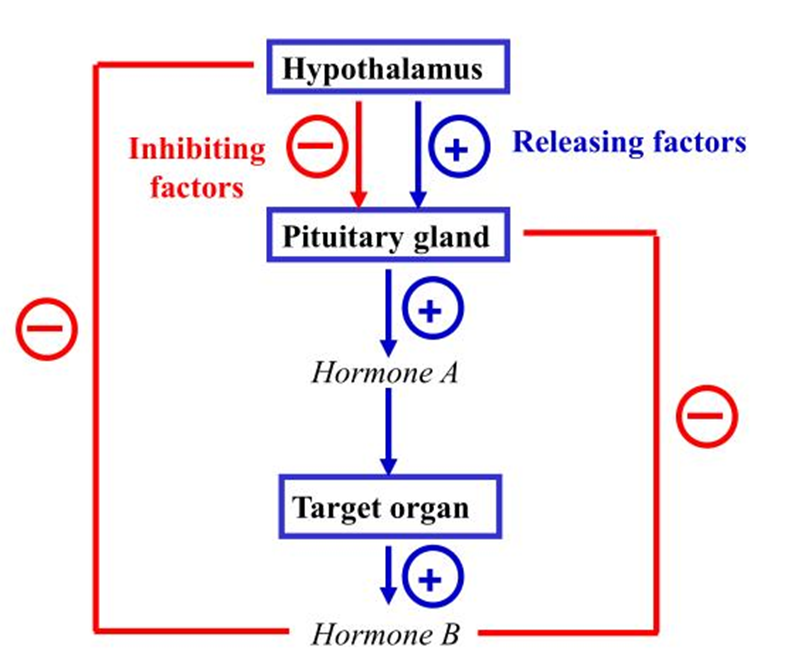
EXplain the feedback
Examples of Hrs glycoproteins
FSH-LH-Tyroid stimulating hr-
Hormones affect only
Cells with appropriated receptors
Poplypeptides
adenocorticotropes-antidiuretic Hrs-Calcitonin-Endorphins-glucagon-Hypothalamiv Hr-Lipotropins Melanocytes stimulating hrs-Oxytocin-Somastostain-Thymosin-Thyrotorpinrelaesing Hr
Hormones water soluble are
Peptides -Glycoproteins -Polypeptides-Amines
Hormones lipid soluble
Thyroxine -steroides -derivatives of arachnoic acid
Examples of Peptides
GH-INSULIN-LETPTIN-PTH-PROLACTINE
Amines hrs examples
Epinephrine- Norepinephrines
Thyroxine hrs
T4-T3,Estrogens
Steroids( Cholesterols is a precursor for all steroids)
glucocorticoids- mineralocorticoids-progestins-testosterone-leukotrienes-
Derivatives of arachidonic ( autocrine or paracine
Prostaglandins-prostacyclins-thromboxanes
•Hormones are released
•In response to an alteration in the cellular environment
•To maintain a regulated level of certain substances or other hormones
Hormone release is regulated by
•Chemical factors (blood glucose or calcium levels)
•Endocrine factors (a hormone from one gland controlling another endocrine gland)
•Neural control (stress-induced release of catecholamines from adrenal medulla)
Communicate by autocrine (within cells), paracrine (between local cells), and endocrine (between remote cells)
Communications between hormones
Explain the negative feedback loop of TSH
∙Products of a cycle act upon its gland of origin to shut off secretion (as a means to prevent excess secretion)
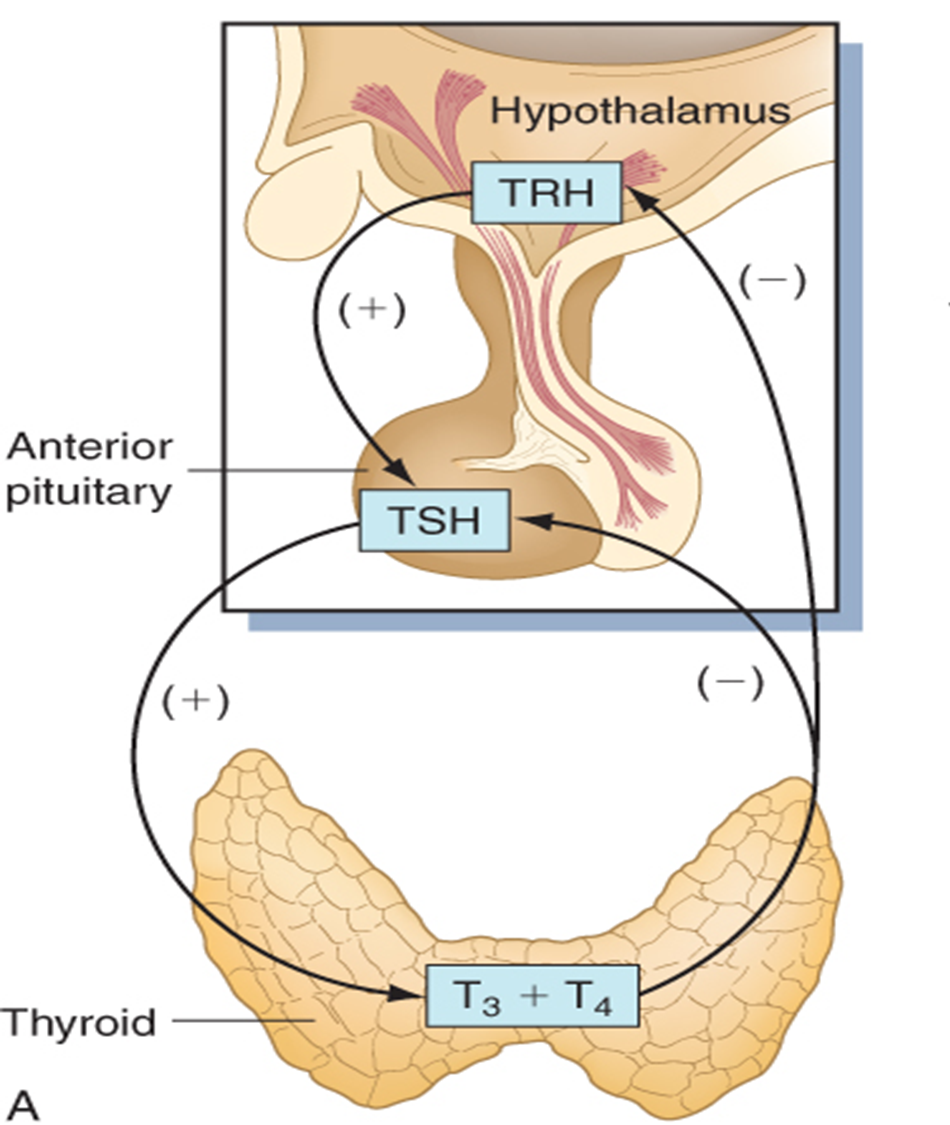
Hormones that have other endocrine glands as their target.
Trophic Hormones
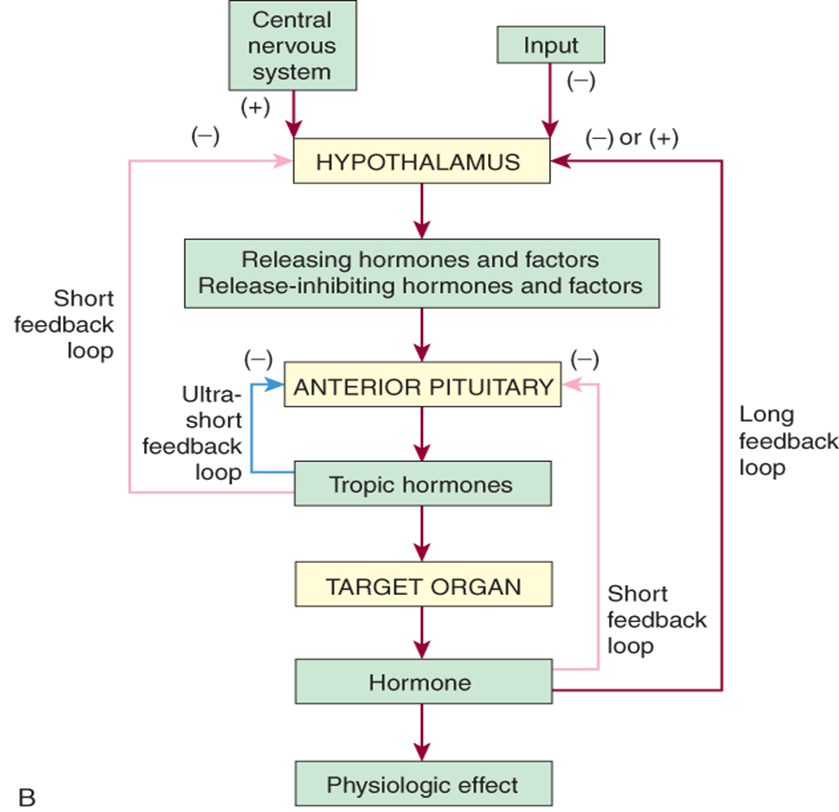
Three levels of negatives feedback
oTarget organ (ultrashort)
oAnterior pituitary (short)
oHypothalamus (long)
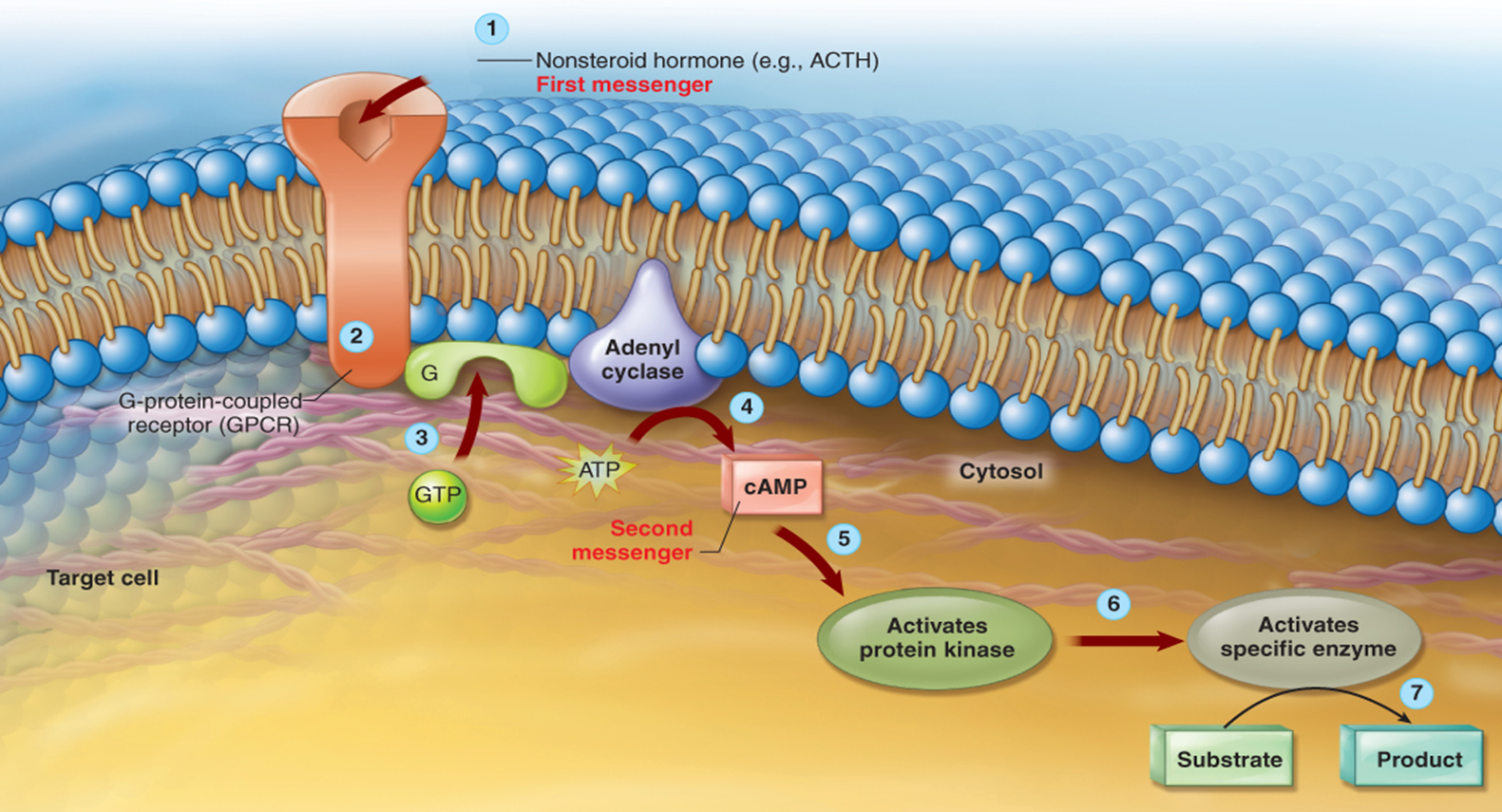
First Messenger
Hormones that carries the message to the target cell.
•Process by which this message is communicated into the target cell
•Involves several steps
Signal Transduction
Step of Signal transduction
∙A hormone is the first messenger that is secreted into bloodstream
∙Receptor activation or binding of a hormone to its receptor
∙Activation of a G protein (transducer) and membrane-associated enzyme (effector enzyme)
∙Production of a second messenger
∙Activation of an intracellular enzyme, such as protein kinase A or C
∙Alterations in gene transcription and the resulting target cell response to the hormone
G protein is consider as
Transducer
Membrane associated enzyme is considered as
Effector enzyme
Response to the cell the target cell is the result of ?
Alteration in gene transcription
initial link between the first signal and the inside of the cell
Second messengers
Identify each step
Example of second messenger
cAMP-cGMP-Ca2++
•Binds with calmodulin, a regulatory protein
calcium
•Is activated by the enzyme guanylyl cyclase
cGMP
•Must activate adenylyl cyclase.
cAMP
•Androgens, estrogens, progestins, glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, thyroid, vitamin D, retinoid
Liposoluble hrs
Differences between liposolubles and water solubles
•Diffuse across the plasma membrane and bind to cytoplasmic or nuclear receptors.
where do Cholesterol (liposolubles ) activated
•Ribonucleic acid (RNA) polymerase
•Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) transcription
Name the major glands of endocrine system ,hrs ( liposolubles or water solubles)
Hypothalamus = secretory hrs and inhibitory hrs( somatostatin and prolactin inhibitor hrs)
Pituitary= anthyphophsis( ACTH,TSH,GH,PRL,FSH,LH) + ADH, OXT)
Thyroid= T4&T3 ( Steroids hrs)
Pancreas= insulin+glugagon+PP+
Adrenals=mineralocorticoid+glycocorticoids+aldosterone+somastostain
Ovaries=Estrogen +progesterone +inhibin
Testes=Testosterone +inhibin