Geological Hazards and Their Warning Signs
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Geological Hazards
Natural phenomena causing significant global problems.
Landslide
Ground movement on sloping terrain due to gravity.
Soil Creep Landslide
Very slow downslope movement of weathered particles.
Slumping Landslide
Downward movement of rock debris from slope removal.
Debris Flow Landslide
Saturated slope triggers water-soaked mass movement.
Rock Fall Landslide
Sudden slide caused by heavy rain loosening rocks.
Sinkhole
Topographic depression from groundwater dissolving limestone.
Cover Collapse Sinkhole
Sudden development causing catastrophic damage.
Cover Subsidence Sinkhole
Gradual growth in permeable sediment areas.
Dissolution Sinkhole
Occurs where calcareous rock is exposed.
Artificial Sinkhole
Caused by human activities like groundwater pumping.
Landslide Warning Signs
Indicators predicting potential landslide occurrences.
Earlier Landslide Indicator
Frequent landslides suggest weak, unstable geology.
Tension Cracks
Cracks from stress in moving geologic materials.
Things Moving
Non-human caused deformation signals possible landslide.
Water Changes
Altered water flow indicates potential landslide risks.
Sinkhole Warning Signs
Indicators predicting potential sinkhole formation.
Tilting Trees
Trees leaning signals possible sinkhole activity.
Slanting Foundations
Foundations tilting indicate ground instability.
New Ponds
Unexpected ponds after rain suggest sinkhole risk.
Ground Cracks
Cracks in the ground indicate potential sinkholes.
Sudden Drainage
Rapid pond drainage signals possible sinkhole formation.
Depressions in Yard
New dips or slopes indicate ground instability.
Dead Vegetation
Wilting plants suggest underlying ground issues.
Neighborhood Sinkholes
Nearby sinkholes indicate regional geological instability.
Discolored Well Water
Contaminated water signals possible sinkhole activity.
Concrete Slab Cracking
Cracks in slabs indicate structural ground issues.
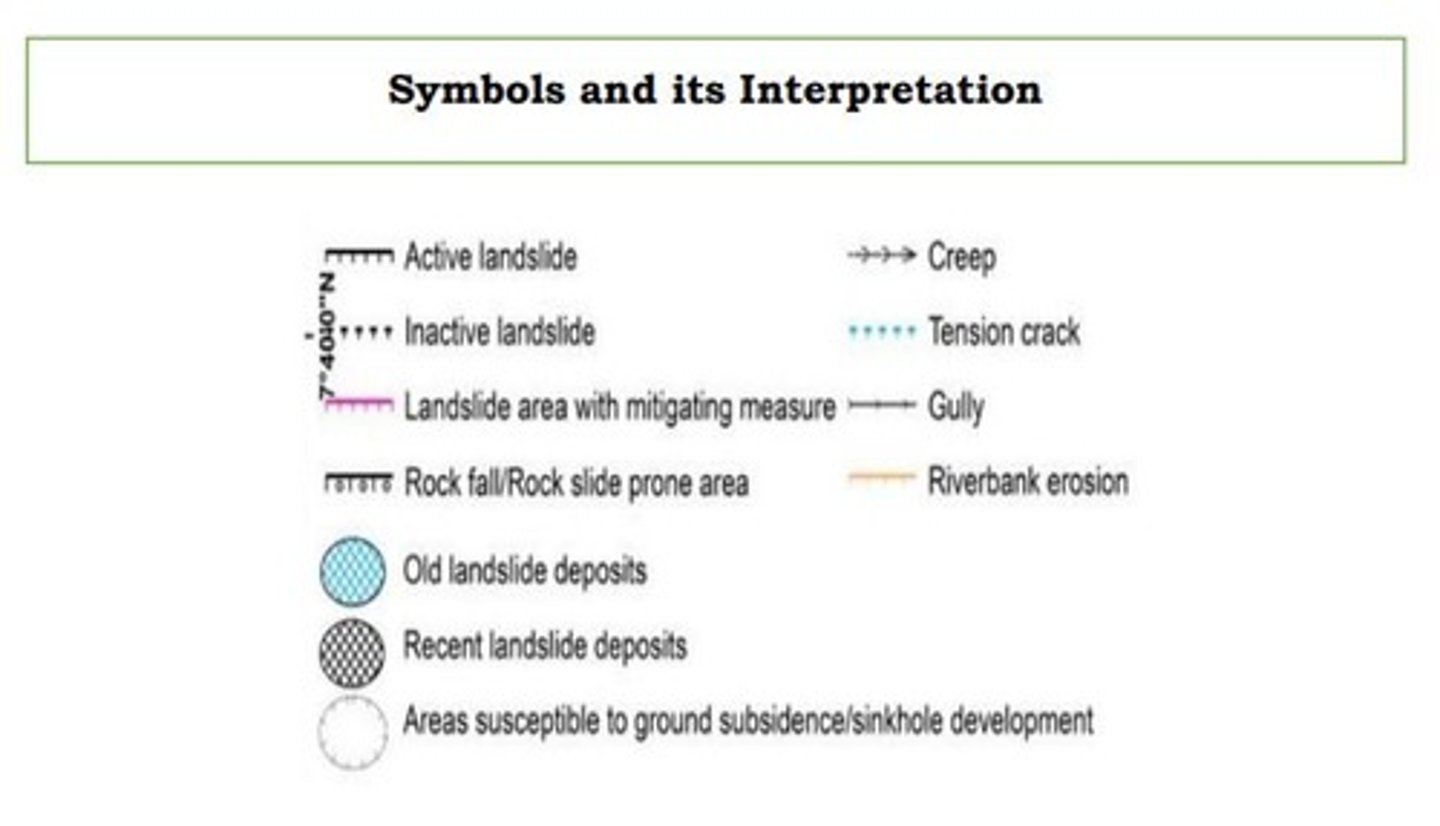
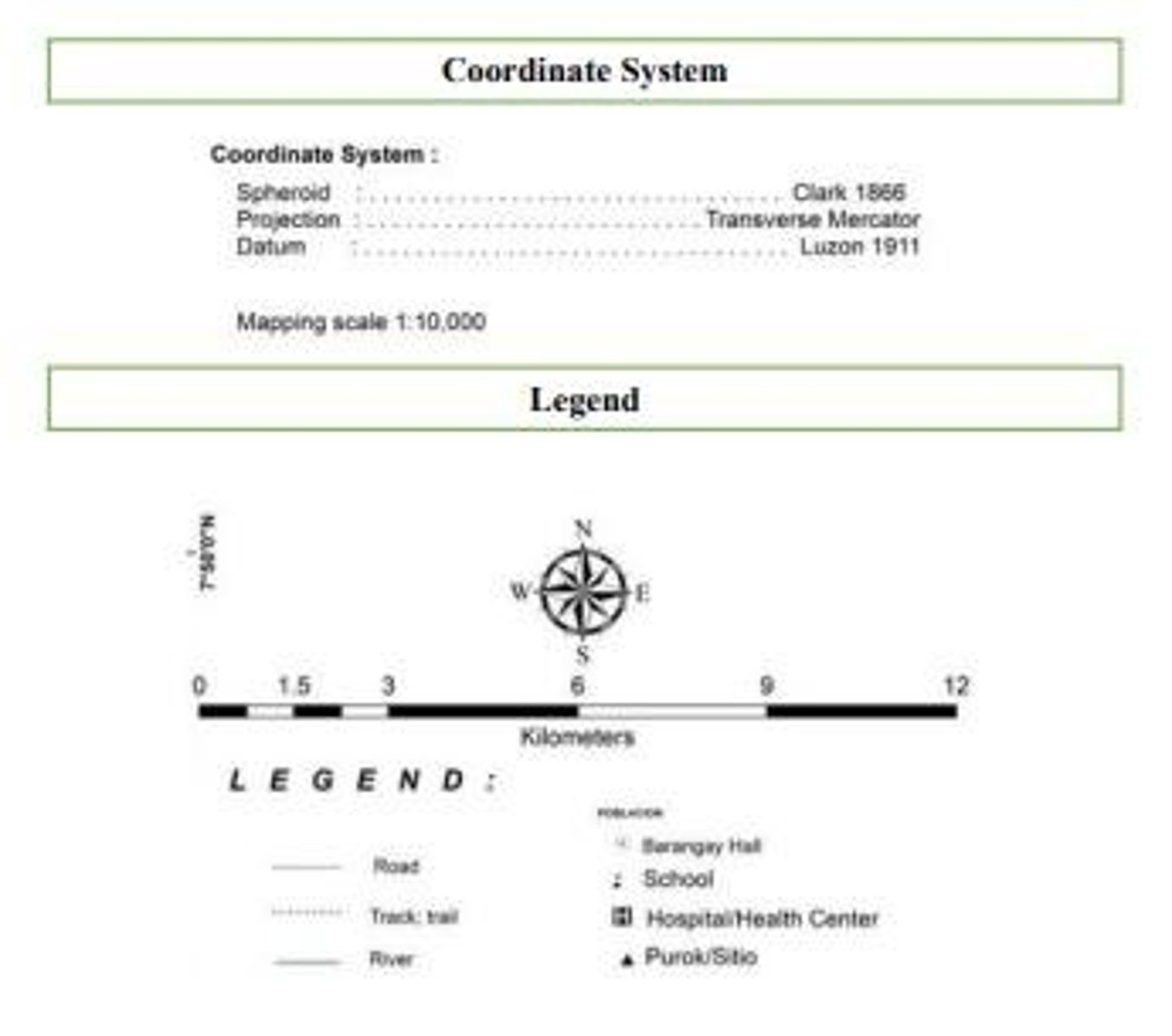
Geological Map
Map showing geological features and rock units.
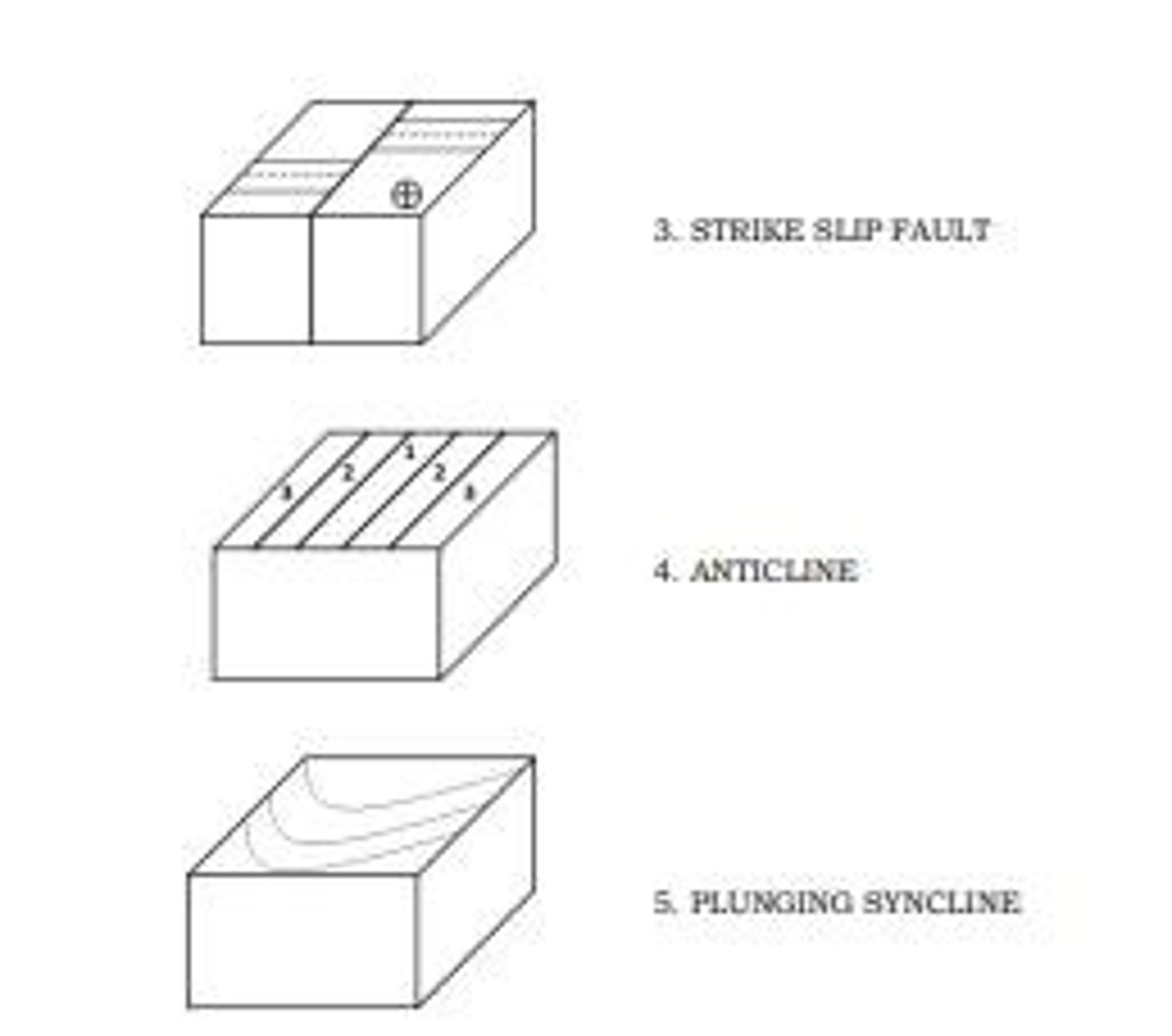
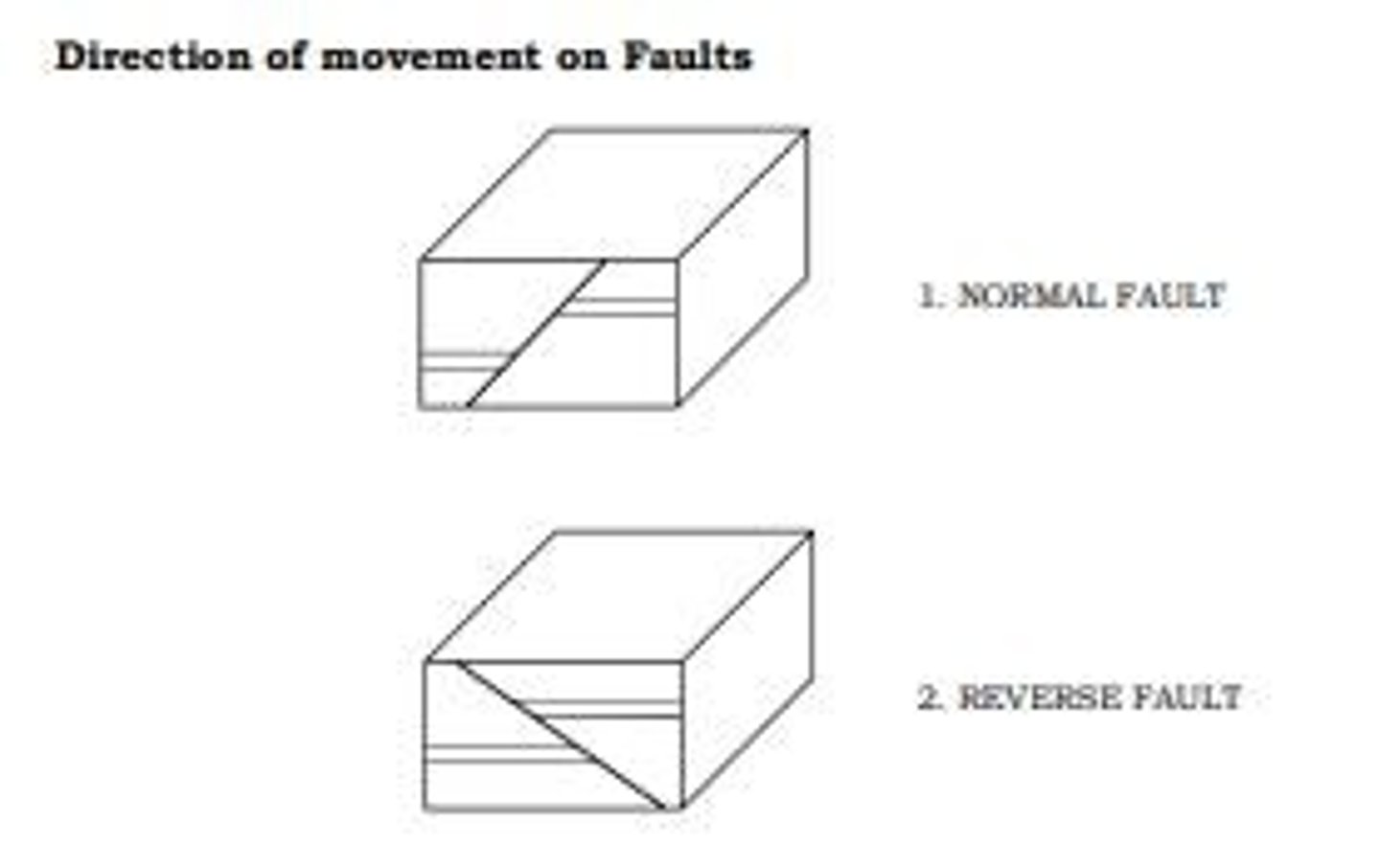
Geological Map Features
Includes faults, tilts, folds, and rock layers.
Geological Map Parts
Includes legend, interpretation, title, susceptibility, sources.
Geological Map Symbols
Colors and lines represent geological information.
Hydrometeorological Hazards
Hazards from extreme meteorological and climate events.
Temperature Measurement Tools
Instruments for measuring atmospheric temperature.
Thermometer
Measures the hotness or coldness of substances.
Thermograph
Records air temperature continuously on graph paper.
Mercurial Barometer
Measures atmospheric pressure using mercury column.
Aneroid Barometer
Pressure-sensitive sealed box expands or contracts.
Barograph
Records barometric pressure over time graphically.
Relative Humidity Measurement
Tools for measuring atmospheric moisture content.
Sling Psychrometer
Dry and wet-bulb thermometer for humidity measurement.
Hygrometer
Uses organic material to measure humidity changes.
Precipitation Measurement Tools
Instruments for measuring rainfall amounts.
8-inch Rain Gauge
Collects rain in a cylindrical measuring tube.
Tipping Bucket Rain Gauge
Measures rainfall by tipping small buckets.
Cloud Monitoring Tools
Instruments for assessing cloud conditions.
Ceiling Light Projector
Projects light beam to determine cloud height.
Ceiling Balloon
Meteorological balloon used to measure cloud base.
Pilot Balloon
Weather balloon used for atmospheric measurements.
Radiosonde
Airborne instrument measuring temperature and humidity.
Rawindsonde
Electronic tool for determining wind speed and direction.
Wind Finding Radar
Determines wind speed and direction using radar.
Weather Surveillance Radar
Tracks typhoons and cloud masses up to 400 km.