The Citric Acid Cycle
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
___________________ is the process where cells consume oxygen (O2) and produce carbon dioxide (CO2)
Cellular respiration
Cellular respiration provides energy (ATP) from glucose (more than ___________________)
glycolysis
Cellular respiration occurs in three major stages:
- acetyl CoA production
- acetyl CoA oxidation
- electron transfer and oxidative phosphorylation
Conversion of Pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA
- The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex includes three types of enzymes that collectively remove a ___________________ from pyruvate and produce ___________________
carboxylate group, acetyl-CoA and NADH.
Under aerobic conditions, the pyruvate is transported into the mitochondrial membrane. In the __________________, pyruvate is oxidatively decarboxylated by the ______________________ complex to form acetyl CoA
mitochondrial matrix, pyruvate dehydrogenase
The conversion of pyruvate into acetyl CoA consists of three steps
- Decarboxylation
- Oxidation
- Transfer acetyl group to CoA
the Mechanism of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase reaction is complicated. ______________________ participate
three enzymes and five coenzymes
the 5 Coenzymes in the Mechanism of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase reaction include
- Catalytic cofactors: thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP), lipoic acid, and FAD
- Stoichiometric cofactors: CoA and NAD+
Three enzymes of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
Pyruvate dehydrogenase (E1)
Dihydrolipoyl transacetylase (E2)
Dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase (E3)
step 1 of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
pyruvate dehydrogenase (E1) reaction
- pyruvate undergoes oxidative decarboxylation to form hydroxyethyl-thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP), with CO2 created as a byproduct
step 2 of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
dihydrolipoyl transacetylase (E2) reaction
- hydroxyethyl breaks away from TPP and transfers to lipoamide to form acetyl-dihydrolipoamide
step 3 of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
dihydrolipoyl transacetylase (E2) reaction
- acetyl breaks away from dihydrolipoamide and transfers to CoA to form acetyl CoA
step 4 of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase (E3) reaction
- dihydrolipoamide is reoxidized by FAD. NAD+ is reduced to NADH, which leads to the regeneration of the oxidized lipoamide
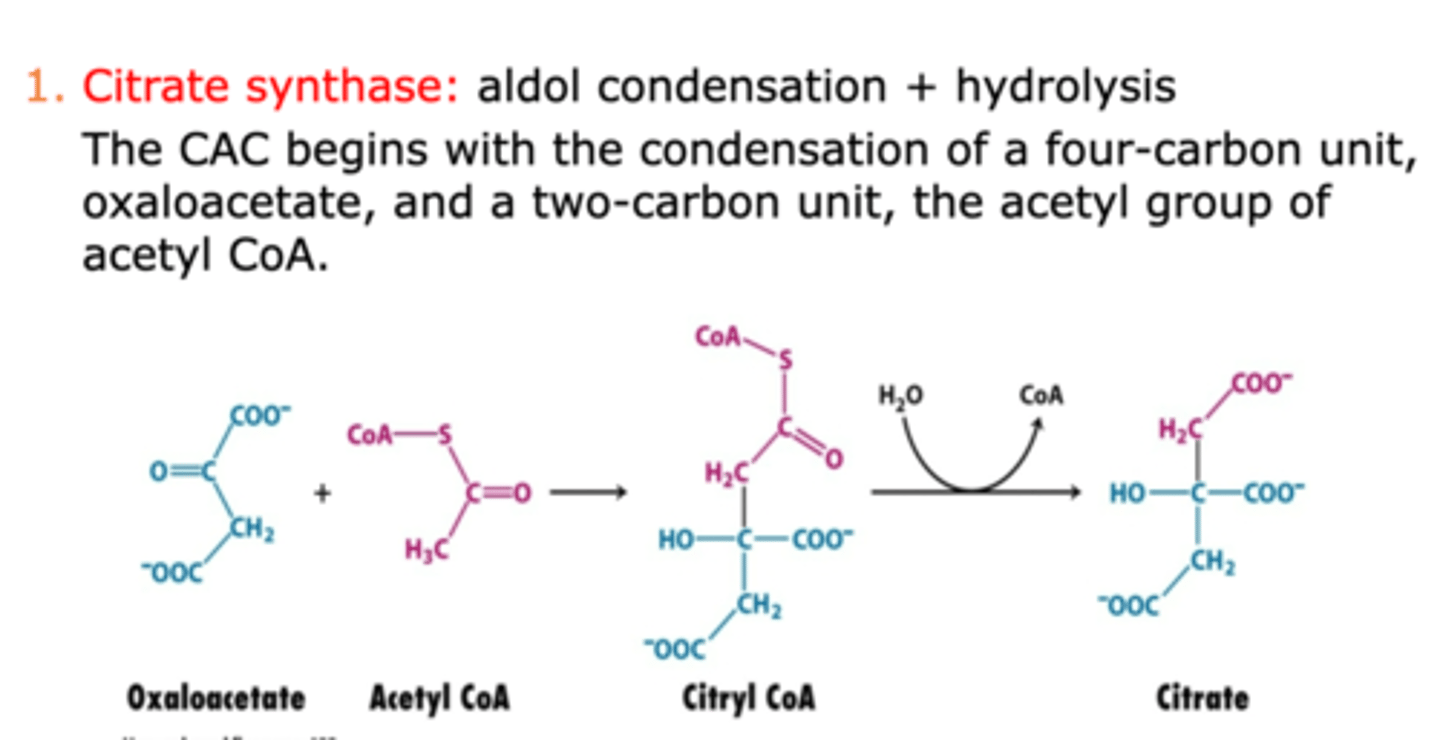
step 1 of citric acid cycle
Catalyzed by citrate synthase
- oxaloacetate and acetyl CoA undergo an aldol condensation to form citryl CoA, followed by a hydrolysis reaction to form citrate
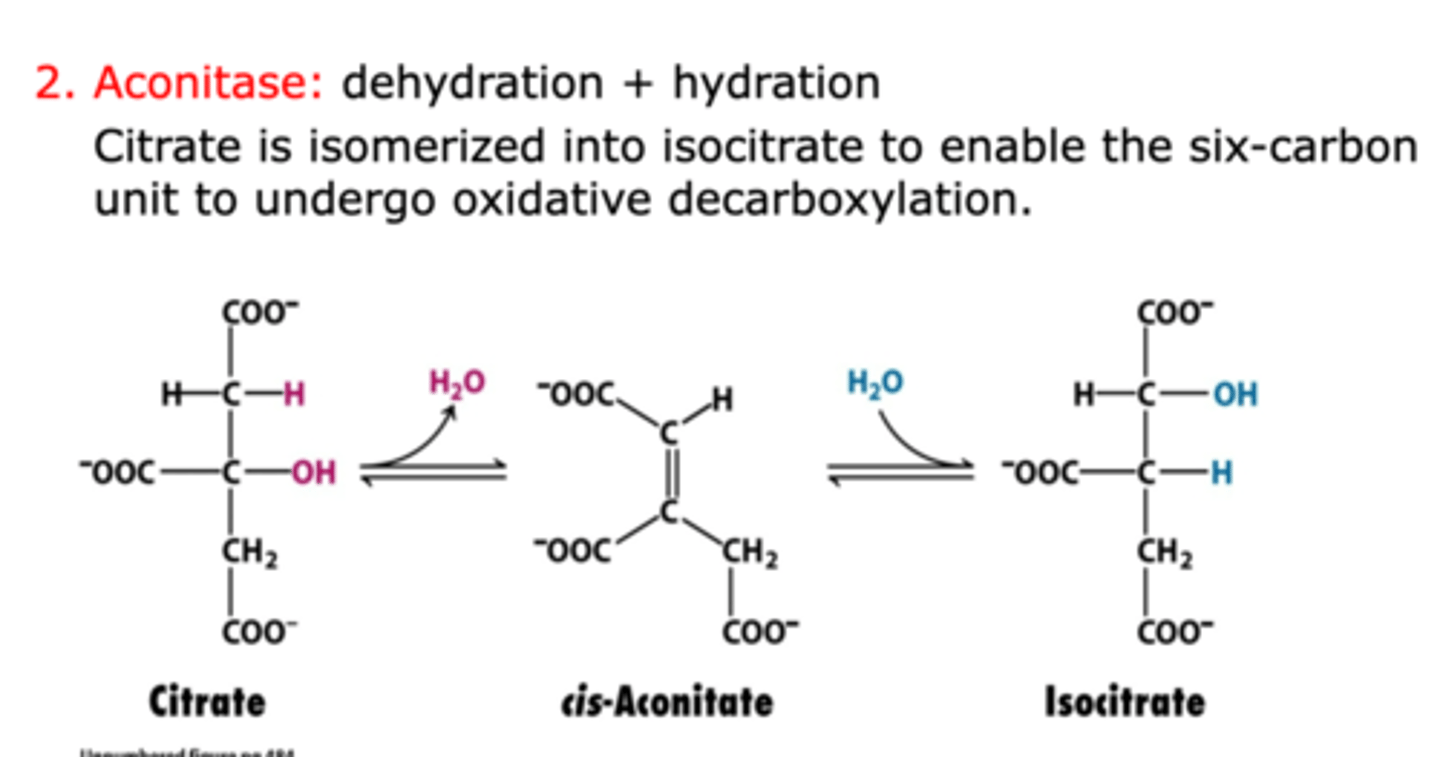
step 2 of citric acid cycle
Catalyzed by aconitase
- citrate undergoes dehydration to form cis-aconitate, followed by hydration to form isocitrate
step 3 of citric acid cycle
Catalyzed by isocitrate dehydrogenase
- an oxidative decarboxylation reaction with isocitrate and NAD+ as reactants and alpha-ketoglutarate, NADH, and CO2 as products

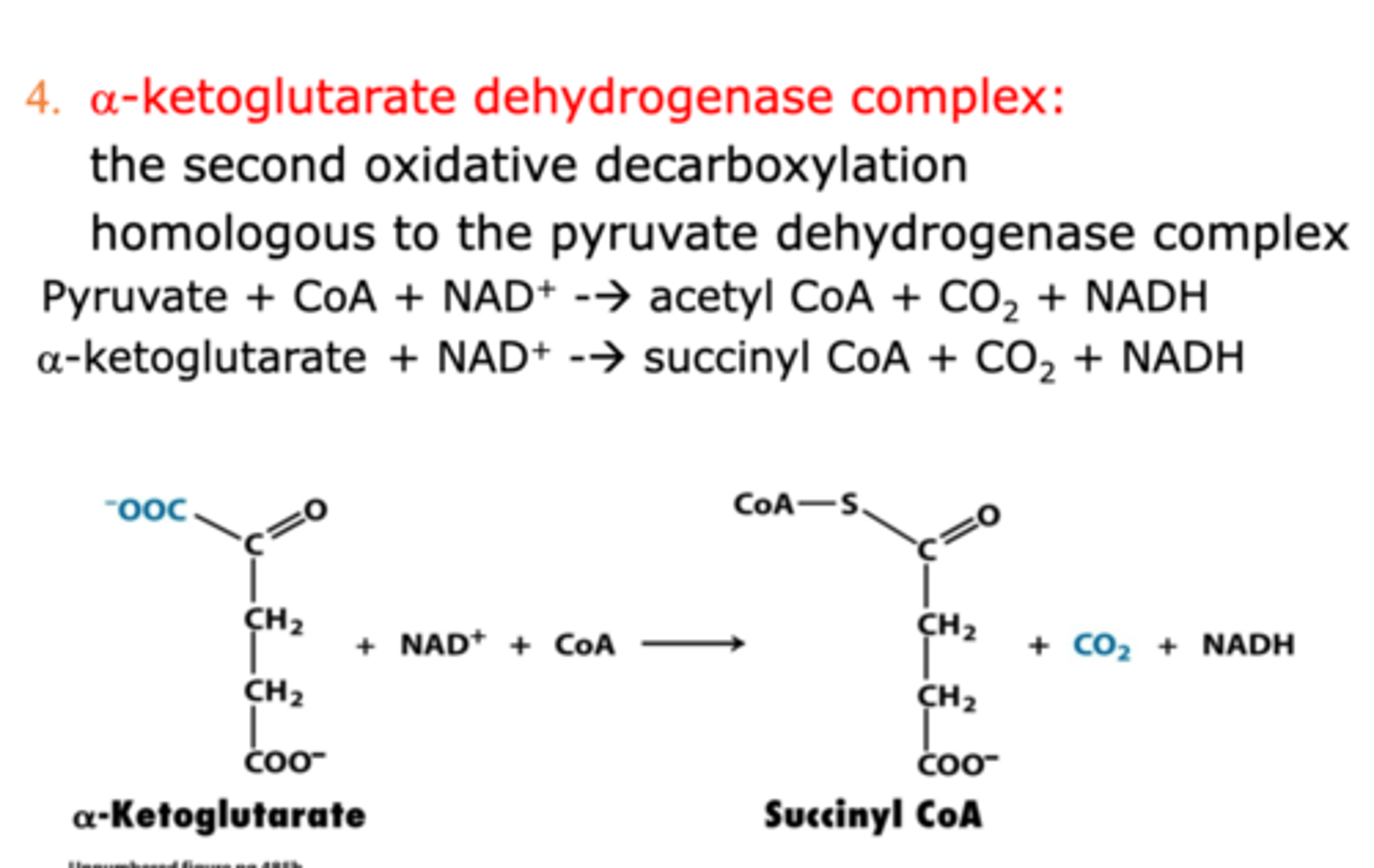
step 4 of citric acid cycle
Catalyzed by alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
- a second oxidative decarboxylation reaction with alpha-ketoglutarate and NAD+ as reactants and succinyl CoA, NADH, and CO2 as products
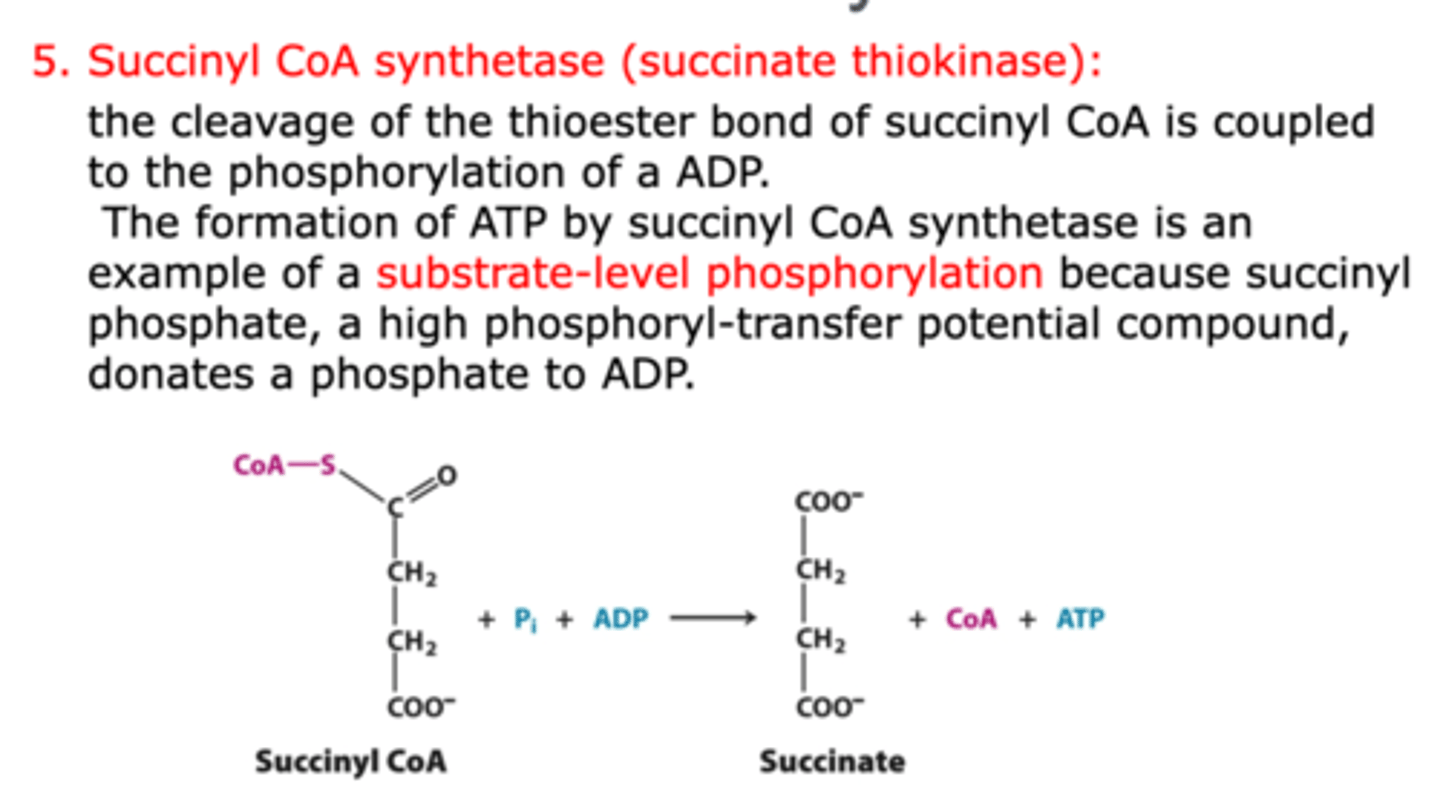
step 5 of citric acid cycle
Catalyzed by succinyl CoA synthetase (succinate thiokinase)
- example of substrate-level phosphorylation
- thioester bond of succinyl CoA gets cleaved
- succinyl CoA, ADP, and Pi are reactants and succinate, CoA, and ATP as products
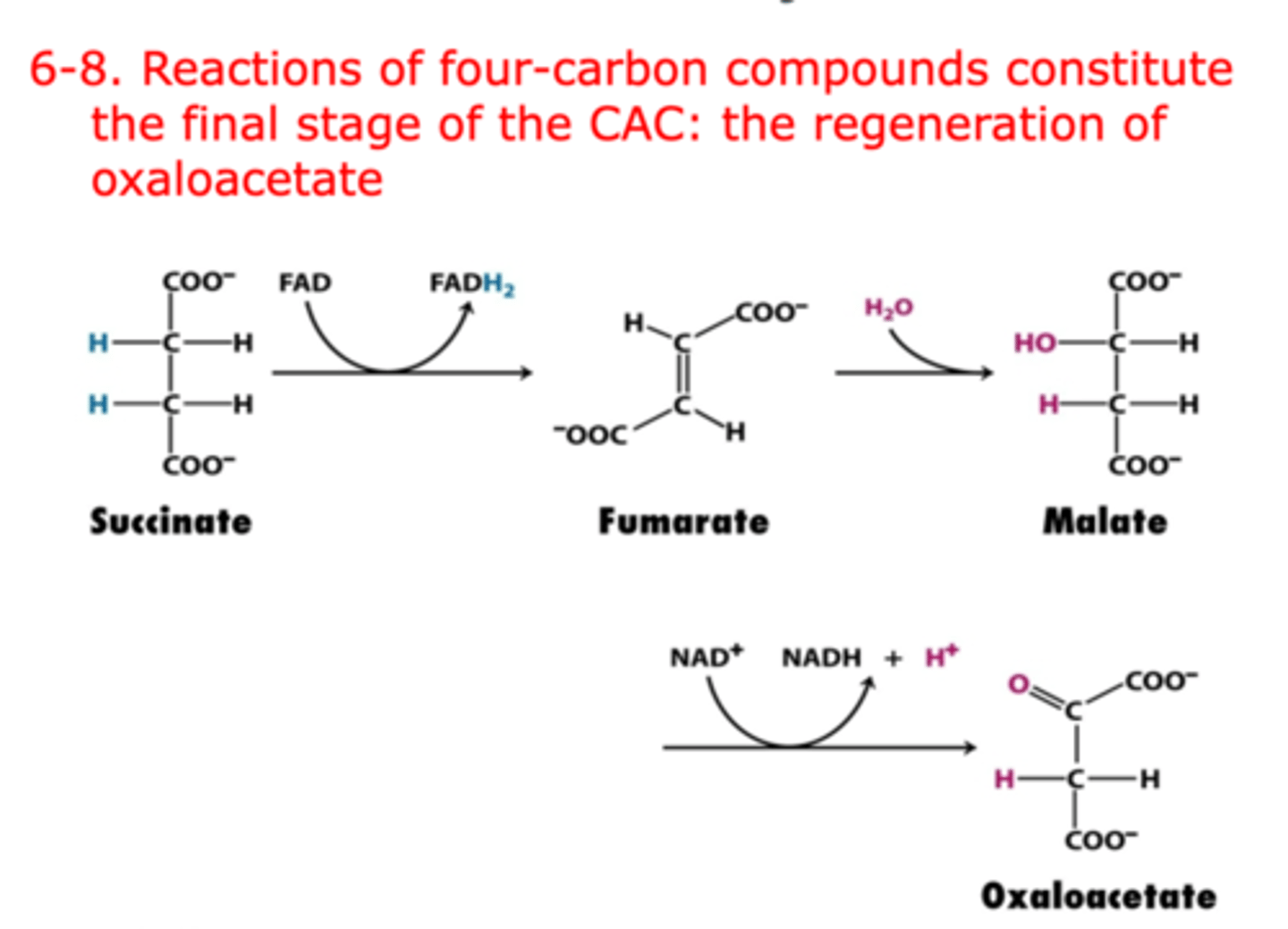
steps 6-8 of citric acid cycle
Step 6: Succinate is oxidized to fumarate, producing FADH2, catalyzed by succinate dehydrogenase.
Step 7: Fumarate is hydrated to malate, catalyzed by fumarase.
Step 8: Malate is oxidized to regenerate oxaloacetate, producing NADH, catalyzed by malate dehydrogenase
1 NADH = 2.5 ATP
1 FADH2 = 1.5 ATP
Each round of the citric acid cycle generates
three NADH, one FADH2, and one GTP or ATP.
Flux through the citric acid cycle is regulated primarily by ______________ at three steps.
feedback inhibition
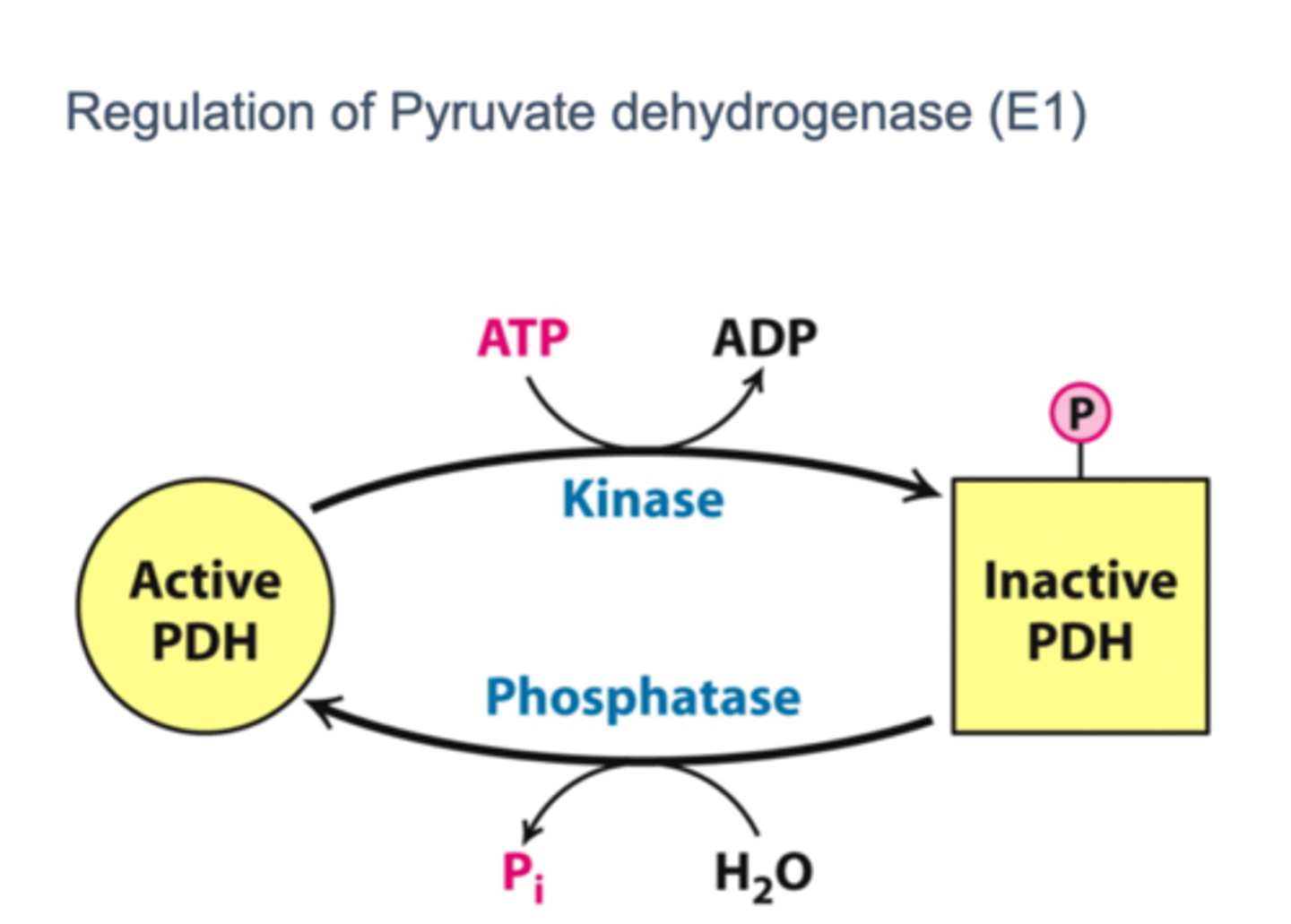
the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is regulated ______________ and by
allosterically, reversible phosphorylation
The formation of acetyl CoA from pyruvate is _________________ in animal cells.
irreversible
Acetyl CoA has two principle fates:
- metabolism by the citric acid cycle
- incorporation into fatty acids.
The key control points in the citric acid cycle are the reactions catalyzed by
isocitrate dehydrogenase and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
_________________ Functions of the Citric Acid Cycle
- The citric acid cycle supplies _________________ for the synthesis of other compounds, and, citric acid cycle intermediates can be replenished.
Amphibolic, precursors
__________________ Reactions: Citric acid cycle intermediates are precursors of other molecules.
Cataplerotic
An example of amino acid formation from a citric acid cycle intermediate. Glutamate is a precursor of the amino acids __________________
glutamine, arginine, and proline.
________________ reactions replenish citric acid cycle intermediates. Intermediates that are diverted to other pathways can be replenished.
Anaplerotic
In the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, covalent modification of E1, ______________________ leads to inactivation
phosphorylation