Intimate Relationships and Media Exam 2
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
General Premise of Attachment Theory
the most fundamental beliefs people hold about relationships are formed during infancy, based on experiences with a primary caregiver
two underlying dimensions of attachment
anxiety about abandonment
avoidance of intimacy
Anxiety about abandonment
the worry that others will find us unworthy and leave
avoidance of intimacy
the ease and trust with which we accept interdependent intimacy with others
What are the four attachment styles
secure, preoccupied, fearful, dismissing
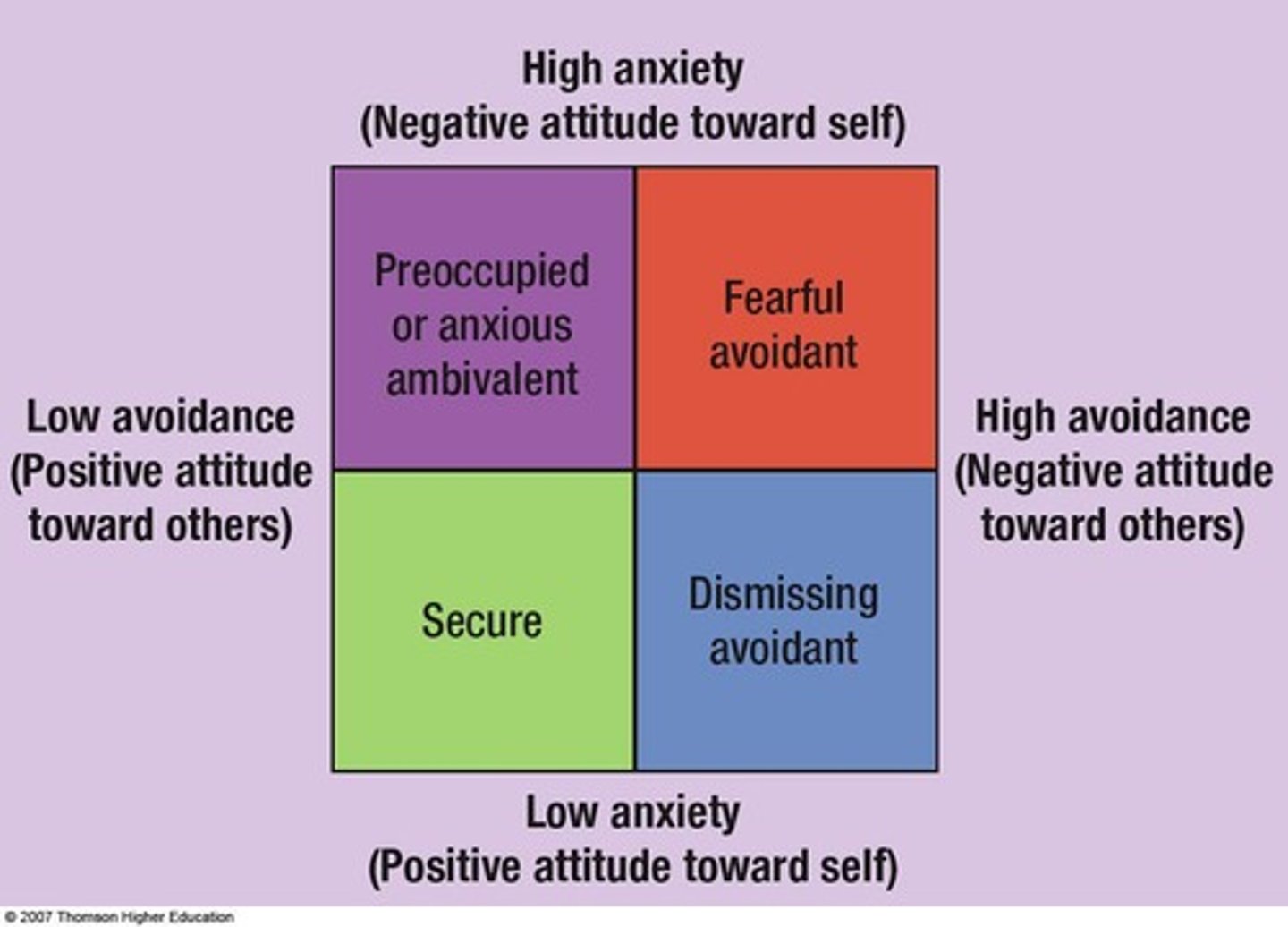
secure attachment style
comfortable with intimacy and interdependence; optimistic and socialable
preoccupied attachment style
Uneasy and vigilant toward any threat to the relationship; needy and jealous
fearful attachment style
fearful of rejection and mistrustful of others; suspicious and shy
dismissing attachment style
self-reliant and uninterested in intimacy; indifferent and independent
Attachment and DMC use
- Attachment anxiety is associated with online dating use
- Attachment avoidance is associated with less preference for face-to-face communication and greater preference for DMC
How attachment influences responses to romance media
- Avoidant attachment feels less enjoyment across all types of romance media
- Anxious attachment feels more enjoyment across all types of romance media
What cultivation theory predicts
Heavy media users develop worldviews similar to what they see in the media
The five dysfunctional relationship beliefs
- Disagreements are destructive
- partners cannot change
- mind-reading is expected
- sexual perfectionism
- the sexes are different
Dysfunctional relationship beliefs and Media use
Using media supports dysfunctional beliefs
Six love styles
1. Eros- strong physical component
2. Ludus- love as an uncommitted game
3. Storge- emphasizes friendship
4. Mania- demanding and possessive
5. Agape- altruistic, selfless, and dutiful
6. Pragma- practical, careful, and logical
Love styles and entertainment media
Entertainment media and love styles are genre-specific
Four Romantic Ideals
- Love finds a way
- One and only
- Partner idealization
- Love at first sight
-Media heavily endorses these ideals
Social Comparison Theory
Individuals often assess how well they are doing by comparing themselves to others around them
-assimilative- self-evaluation in the same direction as the comparison
-contrastive- self-evaluation in the opposite direction of the comparison

Assimilative comparison- Social Comparison Theory
self-evaluation in the same direction as the comparison
Contrastive comparison - Social Comparison Theory
self-evaluation in the opposite direction of the comparison
Upward assimilative comparison
feeling hopeful and making more favorable evaluations of oneself
Downward Assimilative Comparison
feeling concerned and making less favorable evaluations of oneself
Upward Contrastive Comparison
feeling envious and making less favorable evaluations of oneself
Downward Contrastive Comparison
feeling superior and making more favorable evaluations of oneself
Comparison and Media
Research suggests that individuals compare themselves to what they see on social media
Impression Formation
The impressions we form are an important part of starting and maintaining a couple of relationships
-Some impressions are more important than others
-We form an impression of someone, and we maintain that impression
Primacy effect
First impressions are important
Receny effect
most recent impression becomes more important as time goes on
Confirmation Bias in Impression Maintenance
- once you don't like someone, it's difficult to change your mind
- you search for things about them to confirm your impression instead of things that could change it
Impression Management
people's efforts to control the impressions that others receive of them
Self-presentation
presenting the person we would like others to believe we are
Script Theory
People have mental representations of how specific social situations unfold that then inform their actions
Affordances of Technology and Self-Presentation
Affordances make it possible to misrepresent the self or lie
Impression Management in Online Dating
Online daters use affordances to present themselves in idealized ways
-who they could be rather than who they are
Who is most likely ot be the victim of catfishing
middle-aged women
Who is most likely to be the perpetrator of catfishing
callous, self-centered people who enjoy inflicting harm upon others
Effects of catfishing
- often traumatic
-victims still experience grief when the relationship ends
types of sexual content
Mainstream and Explicit
Social Cognitive Theory in Relation to Sex
People learn by observing others
Processes of observational (vicarious) learning
attention
retention
reproduction
motivation
Role of Media Based on Social Cognitive Theory
When media provides models of sexual behavior, consumers may learn from those models.
What do we mean by media as a "sexual super peer"
adolescents often turn to the media for information about sex that they lack from other sources. like parents, school, and peers
Behavioral effects associated with sexual content consumption
- mainstream media consumption = more permissive attitudes about sex
-explicit media consumption = lower sexual and relationship satisfaction amongst men, attitudes that are conducive to sexual aggression
Entertainment Overcoming Resistance Model
Entertainment may be more compelling than other persuasion tactics because it reduces our resistance through:
- The ways we relate to characters
- Transportation
- Enjoyment
Educational effects related to sex
Educational messages embedded in entertainment programs may increase:
- Safe sex intentions
- Positive attitudes toward birth control
- Likelihood of discussing sexual health with others
- Getting tested for sexually transmitted infections
- Intention not to have sex while intoxicated
Mood effects related to sex
Music is often tied to sex as a way to "set the mood," associated with higher sexual satisfaction
Sexting
the use of digital devices such as computers or mobile phones to create and exchange sexually explicit content
Non-consensual sexting
when someone is forced into making or sending sexual images, or when sexual images are shared without permission
Prevalence and Motivations for Sexting
Men are most likely to have both sent and received sexts
Positive outcomes of sexting
- Receiving affirmations, feeling better about yourself
- Boosting self-esteem
Negative outcomes of sexting
Feeling fear, shame, anxiety
Increased substance abuse
Risky sexual behavior
Why females more likely to experience negative consequences of sexting
Women are more likely to receive nonconsensual sexts
Definition of Conflict
An expressed struggle between at least two interdependent people who have, or think they have, incompatible interests
Three stages of conflict
- beginnings
- middle stages
- termination
Three conflict tactics
- integrative: concern for oneself and one's partner
- distributive: concern only for oneself
- avoidant: deny and avoid
Four conflict styles
- Avoidance: shrink from or evade conflict
- Validating: work toward mutual satisfaction
- Volatile: disagree passionate
- Hostile: demonstrate contempt
The roles of communication (DMC and entertainment) in instigating conflict
Differing expectations of DMC use lead to conflict like Phubbing
Technoference
the interference of technology on the interaction of two people
Phubbing
the act of snubbing someone in a social setting by looking at your phone instead of paying attention
Effects of technoference on relationships
- leads to lower levels of life satisfaction
- causes conflict in relationships
Television as an instigator of conflict
- 2/3 of women and 3/5 of men reported that something about watching TV with their partner was frustrating to them
- 87% of couples argue about TV at least once a week
Video games as an Instigator
Playing Multiplayer Online Role-Playing Games is related to conflict among married couples, especially when only one partner was a gamer
That DMC may not be harmful but it's less beneficial for conflict and why
go over this in the book
Aggression and its types
Aggression is the intention to harm
Types: verbal, physical, postural, relational
Television viewing and relationship conflict
- The more relationship program viewing a couple did, the more conflict there was in a relationship
- Viewing TV that's high in conflict is associated with being controlled in one's romantic relationship
-Negative conflict examples = negative outcomes
Celebrities and relationship conflict study
Participants used conflict tactics in their own relationship that they saw their favorite celebrity couple use
Definition of Jealousy
A complex of thoughts, feelings, and actions which follow threats to self-esteem and/or threats to the existence of quality of the relationship, when those threats are generated by the perception of a real or potential attraction between one's partner and a (perhaps imaginary) rival
Types of Jealousy
anxious, possessive, reactive, retroactive
anxious jealousy
Worry about one's partner finding someone else
possessive jealousy
wanting to prevent even innoquous contact between one's partner and one's rival
reactive jealousy
- in response to a particular scenario
- being upset when one's partner interacts with one's rival in a sexual way
Retroactive Jealousy
triggered by a partner's romantic or sexual past
Responses to Jealousy
Rival focused**related to lower relationship satisfaction
- protective strategies related to the rival
- Contacting the rival
Destructive **related to lower relationship satisfaction
- Aggression, negative communication, manipulation
- Counter jealousy
Constructive **associated with higher relationship satisfaction
- Behaviors that are working to maintain the relationship
Avoidant
- Staying silent on the matter, not addressing the jealousy at all
The combination of type and response to jealousy that are most frequent in romantic movies
reactive strategies/ responses are most common
Why scholars investigate social media and jealousy
Numerous studies have shown that more time spent on social media is associated with greater romantic jealousy
Who is more likely to experience social media jealousy
Women
Anxiously attached
Lower in self-esteem
Higher in need for popularity
Viewing a rival known to them online only
Based on research, which platform encourages more jealousy: Facebook or Snapchat and why
Snapchat because it's less visible and more exclusive
Three types of cyberstalking
Passive
Invasive
Duplicitous
The association between jealousy and cyberstalking
mutually reinforcing, cyclical relationship
The definition of infidelity
An emotional or sexual act that is outside of the primary relationship and constitutes a breach of trust or agreed-upon boundaries of that relationship
Deception
The conscious attempt to create or perpetuate false impressions among other communicators
The two areas of deception research
Deception production
Deception detection
Three features related to deception
Synchronity- is it happening in real time
recordability- is there a record of it
distributed- is physical space being shared
Uses and gratifications approach
a perspective on media use that emphasizes the active role users play in selecting the media to which they are exposed
Parasocial Interaction
the relationship we feel we have with people we know only through the media
-considered normal part of the human experience
Parasocial relationships
"relationships" established with media characters and personalities
Parasocial Contact Hypothesis
exposure to media figures who are different from oneself may reduce stereotyping, prejudice, and discrimination
Paracouple relationships
Having an attachment to a couple you see in the media
Enduring interest in the couple
Liking and admiring the couple
Using the couples as an example for one's own romantic life
The amount of deception that seems to be the norm
Moderate amounts of deception are becoming more of a societal norm as opposed to our honesty and/or rampant amounts of dishonesty