AQA Physics paper 1 keyword megaset
1/170
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
171 Terms
activity
the number of unstable atoms that decay per second in a radioactive source
alpha radiation (α)
alpha particles, each composed of two protons and two neutrons, emitted by unstable nuclei
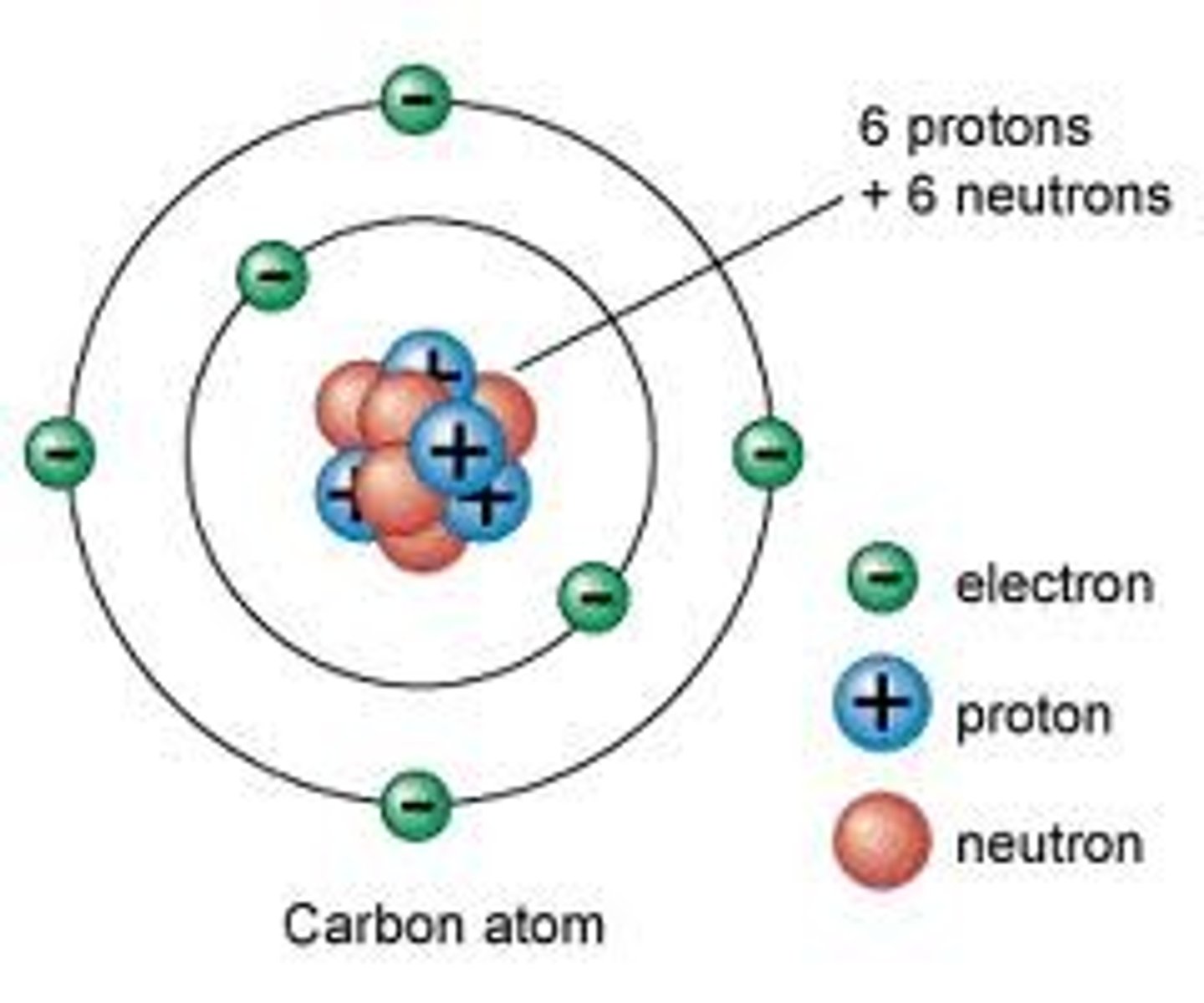
atomic number
the number of protons (which equals the number of electrons) in an atom. It is sometimes called the proton number
beta radiation (β)
beta particles that are high energy electrons created in, and emitted from, unstable nuclei
chain reaction
reactions in which one reaction causes further reactions, which in turn cause further reactions, etc.
count rate
the number of counts per second detected by a Geiger counter
gamma radiation (γ)
electromagnetic radiation emitted from unstable nuclei in radioactive substances
half-life
average time taken for the number of nuclei of the isotope (or mass of the isotope) in a sample to halve
ionisation
any process in which atoms become charged
irradiated
an object that has been exposed to ionising radiation
isotopes
atoms with the same number of protons and different numbers of neutrons
mass number
the number of proton and neutrons in a nucleus
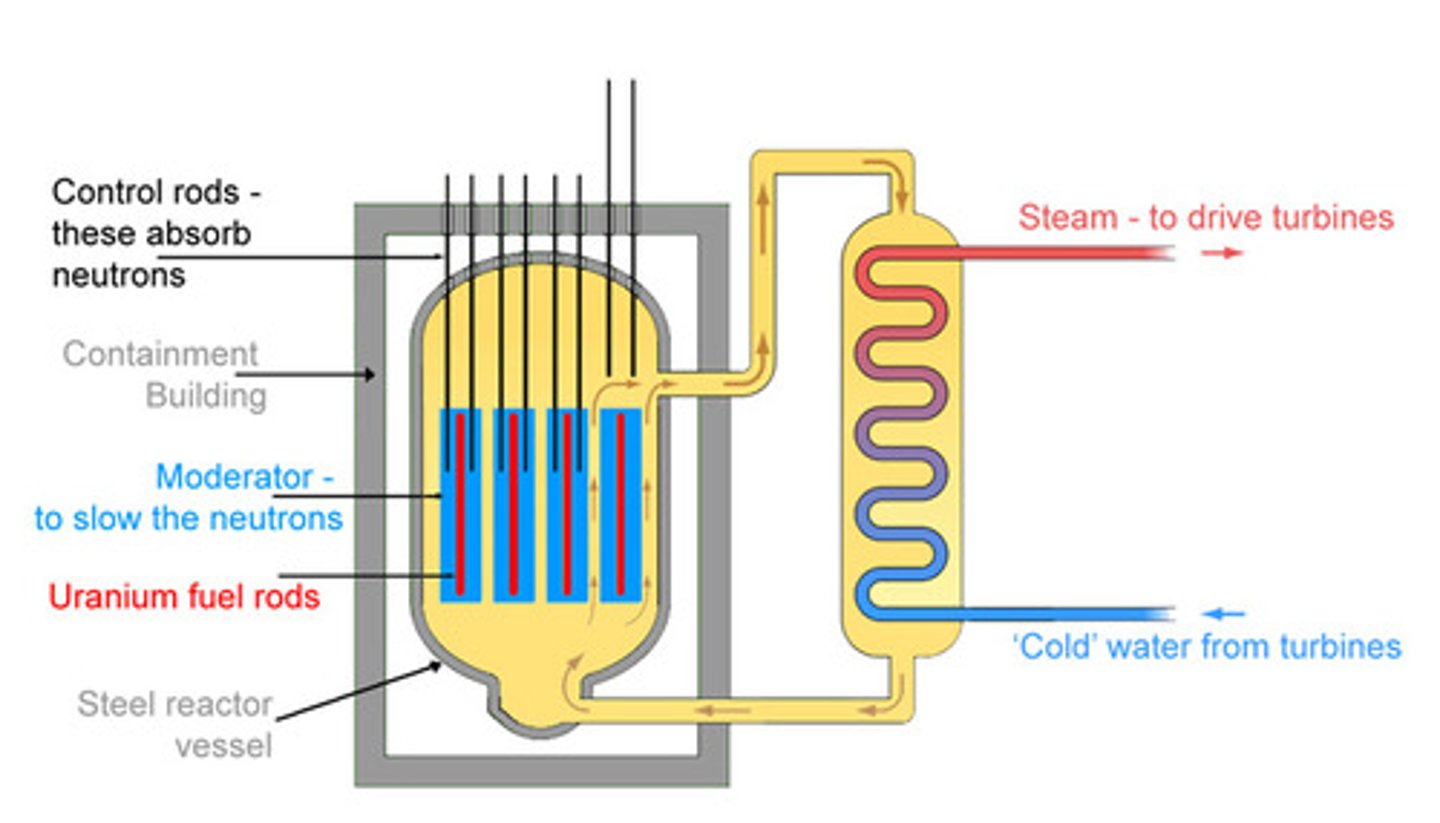
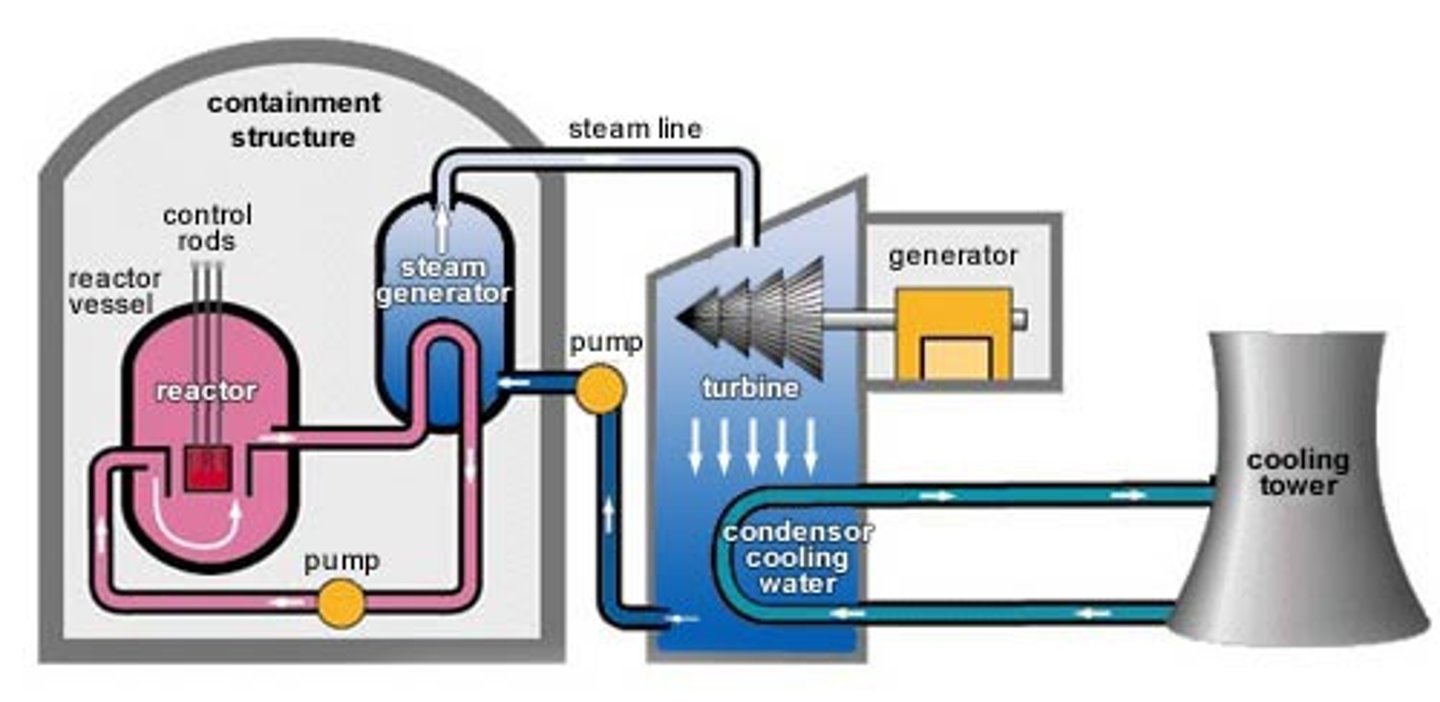
moderator
substance in a nuclear reactor that slows down fission neutrons
nuclear fission
the process in which certain nuclei (uranium-235 and plutonium-239) split into two fragments, releasing energy and two or three neutrons as a result
nuclear fission reactor
reactors that release energy steadily due to the fission of a suitable isotope, such as uranium-235
nuclear fusion
the process where small nuclei are forced together to fuse and form a larger nucleus
radioactive contamination
the unwanted presence of materials containing radioactive atoms on other materials
reactor core
the thick steel vessel used to contain fuel rods, control rods and the moderator in a nuclear fission reactor
boiling point
temperature at which a pure substance boils or condenses
melting point
temperature at which a substance melts or solidifies
Boyle's Law
for a fixed mass of gas at constant temperature, its pressure multiplied by its volume is constant
density
mass per unit volume of a substance
freezing point
the temperature at which a pure substance freezes
internal energy
the energy of the particles of a substance due to their individual motion and positions
latent heat
the energy transferred to or from a substance when it changes its state
melting point
temperature at which a pure substance melts or freezes (solidifies)
physical change
a change in which no new substances are produced
pressure
force per unit cross-sectional area for a force acting on a surface at right angles to the surface. The unit of pressure is the pascal (Pa) or newton per square metre (N/m2). p = F/A
specific latent heat of fusion Lf
energy needed to melt 1 kg of a substance with no change of temperature
specific latent heat of vaporisation Lv
energy needed to boil away 1 kg of a substance with no change of temperature
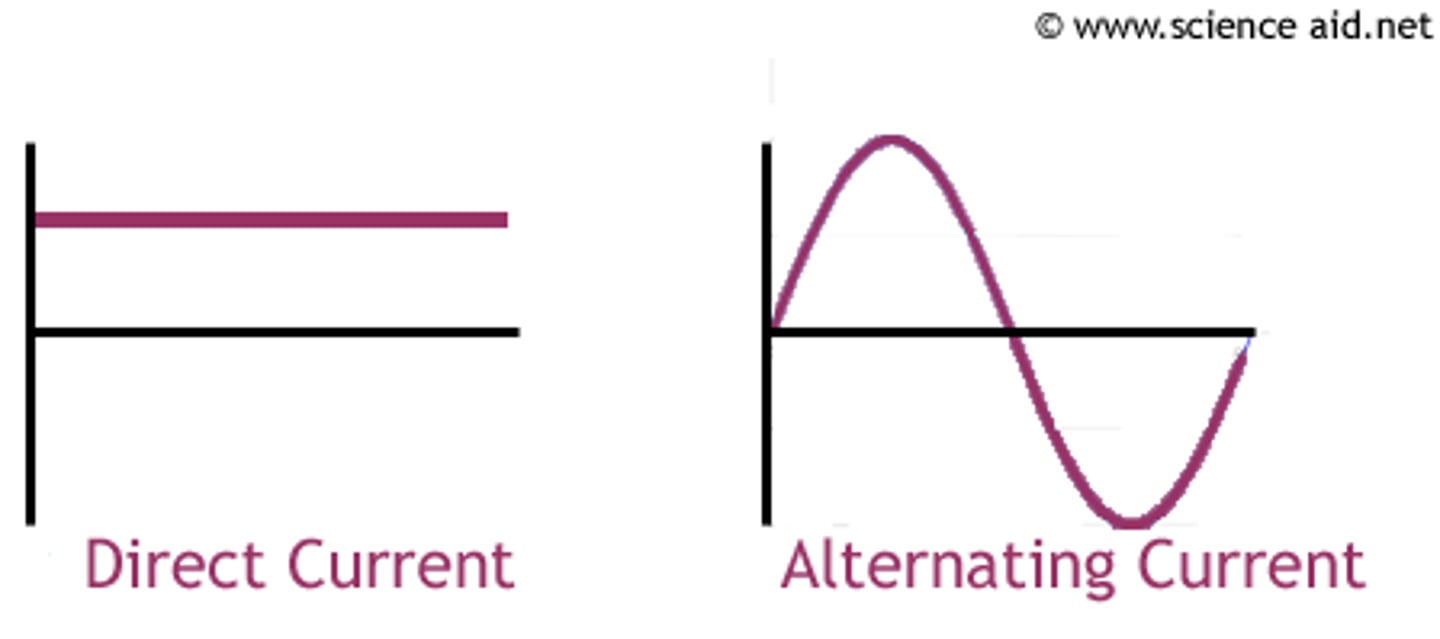
alternating current (a.c.)
electric current in a circuit that repeatedly reverses its direction
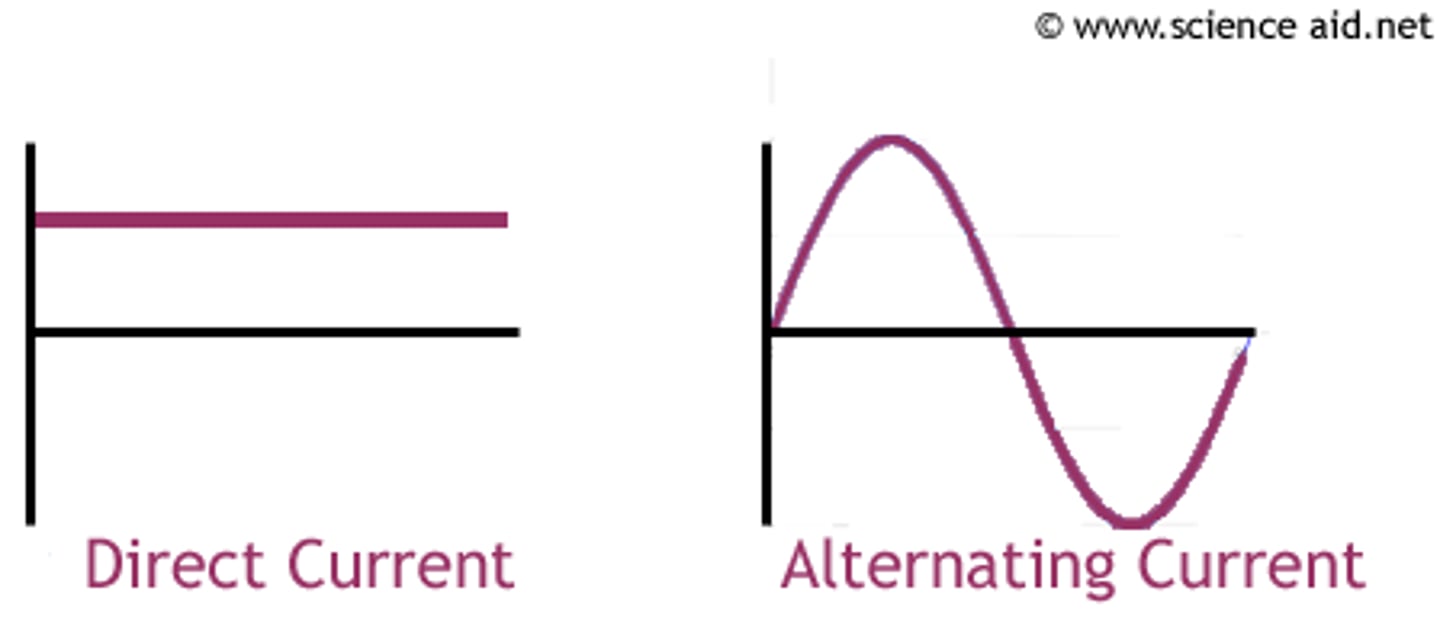
direct current (d.c.)
electric current in a circuit that is in one direction only
earth wire
the wire in a mains cable used to connect the metal case of an appliance to earth. Green and yellow
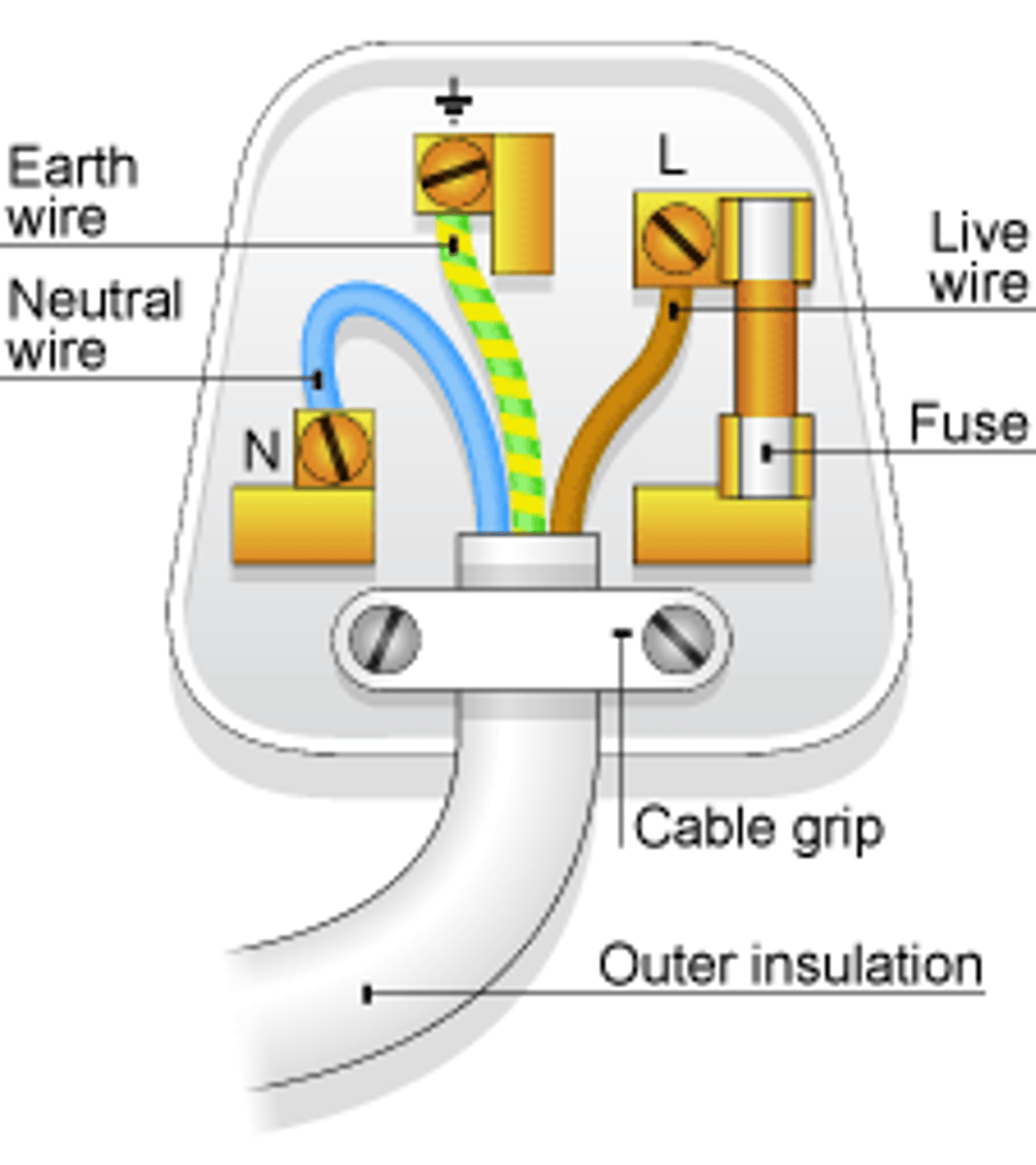
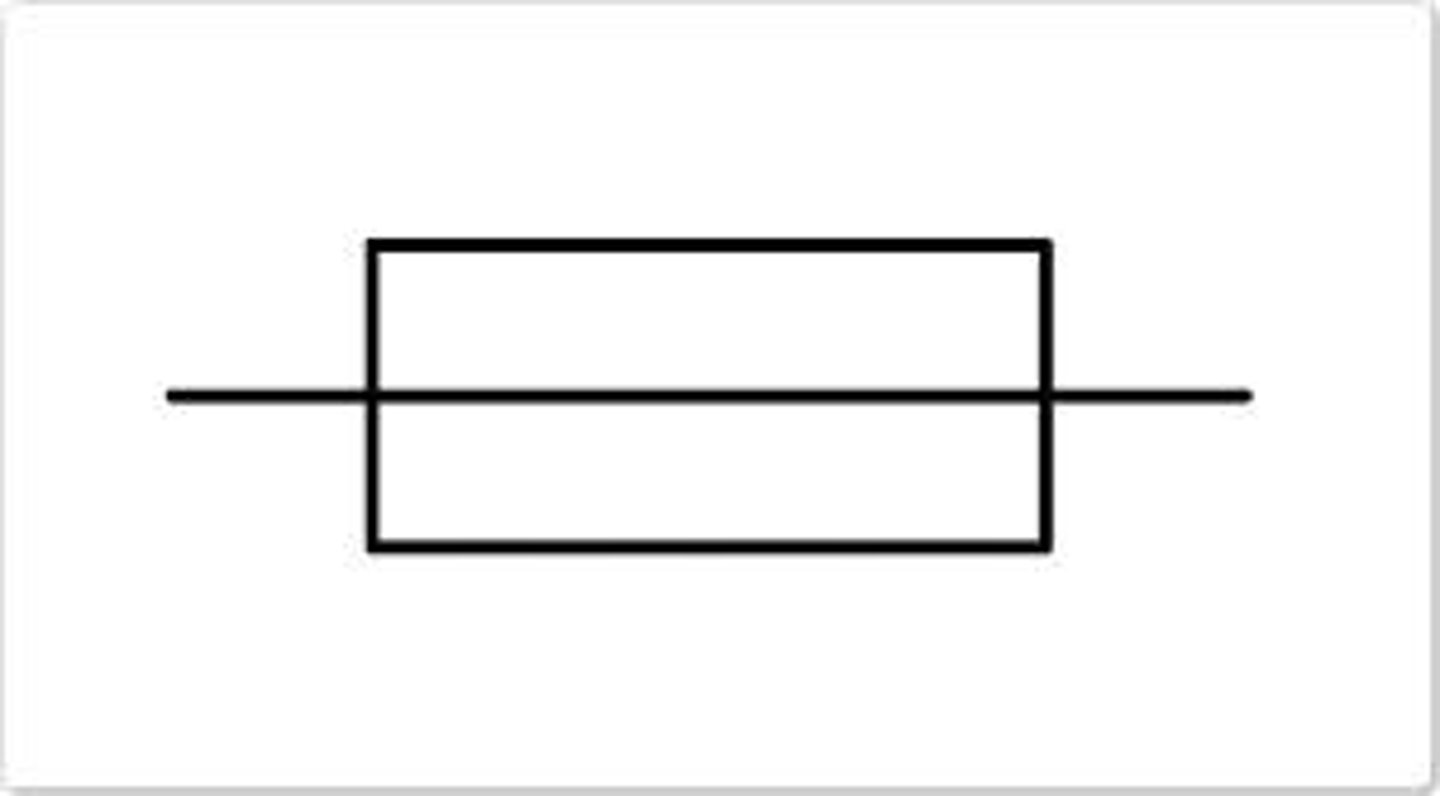
fuse
a fuse contains a thin wire that melts and cuts the current off if too much current passes through it
live wire
the mains wire that has a voltage that alternates in voltage (between +325 V and -325 V in Europe). Brown
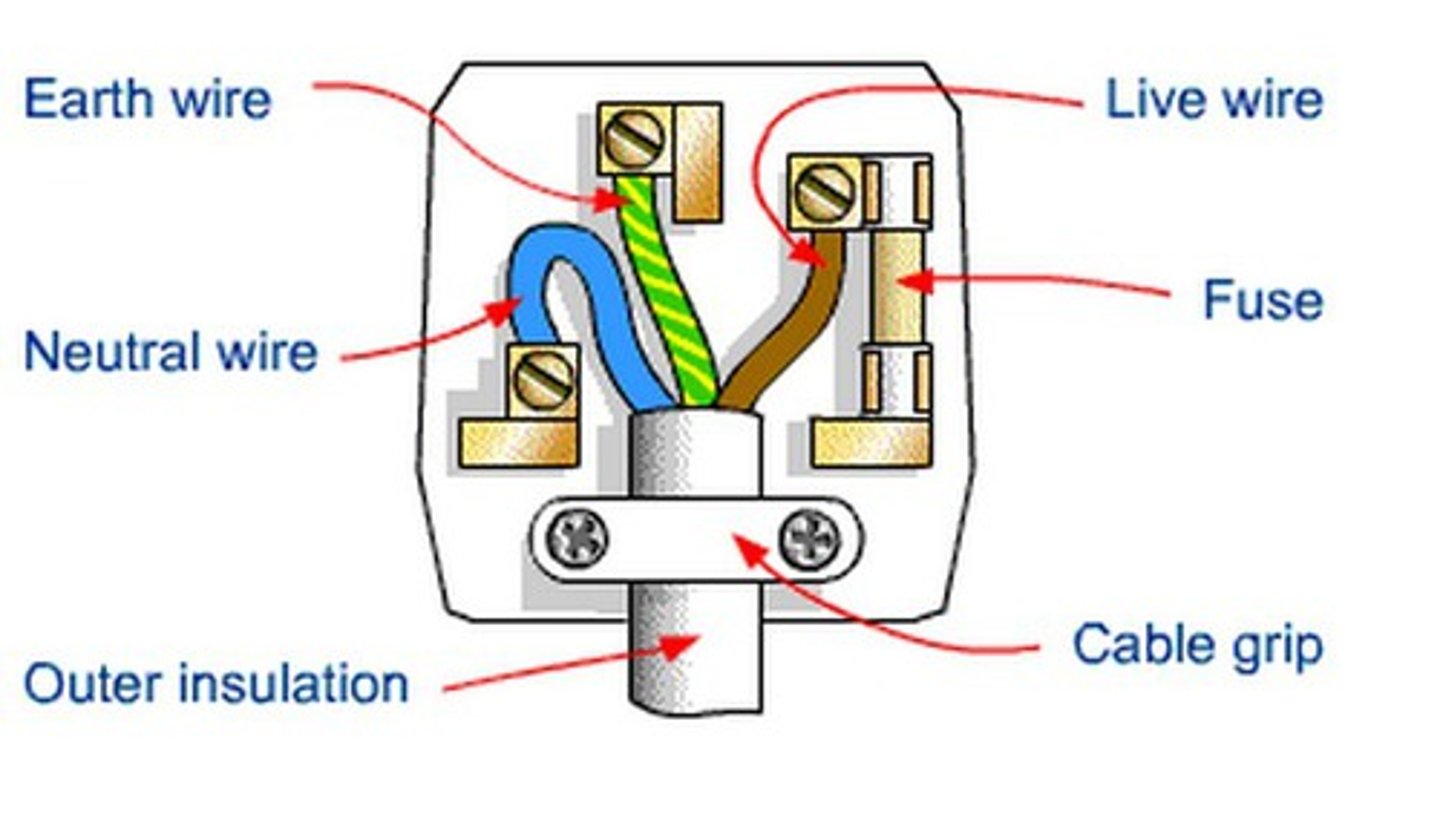
neutral wire
the wire of a mains circuit that is earthed at the local substation so its potential is close to zero Blue
oscilloscope
a device used to display the shape of an electrical wave
plugs
a plug has an insulated case and is used to connect the cable from an appliance to a socket
step-down transformers
electrical device used to step-down the size of an alternating potential difference
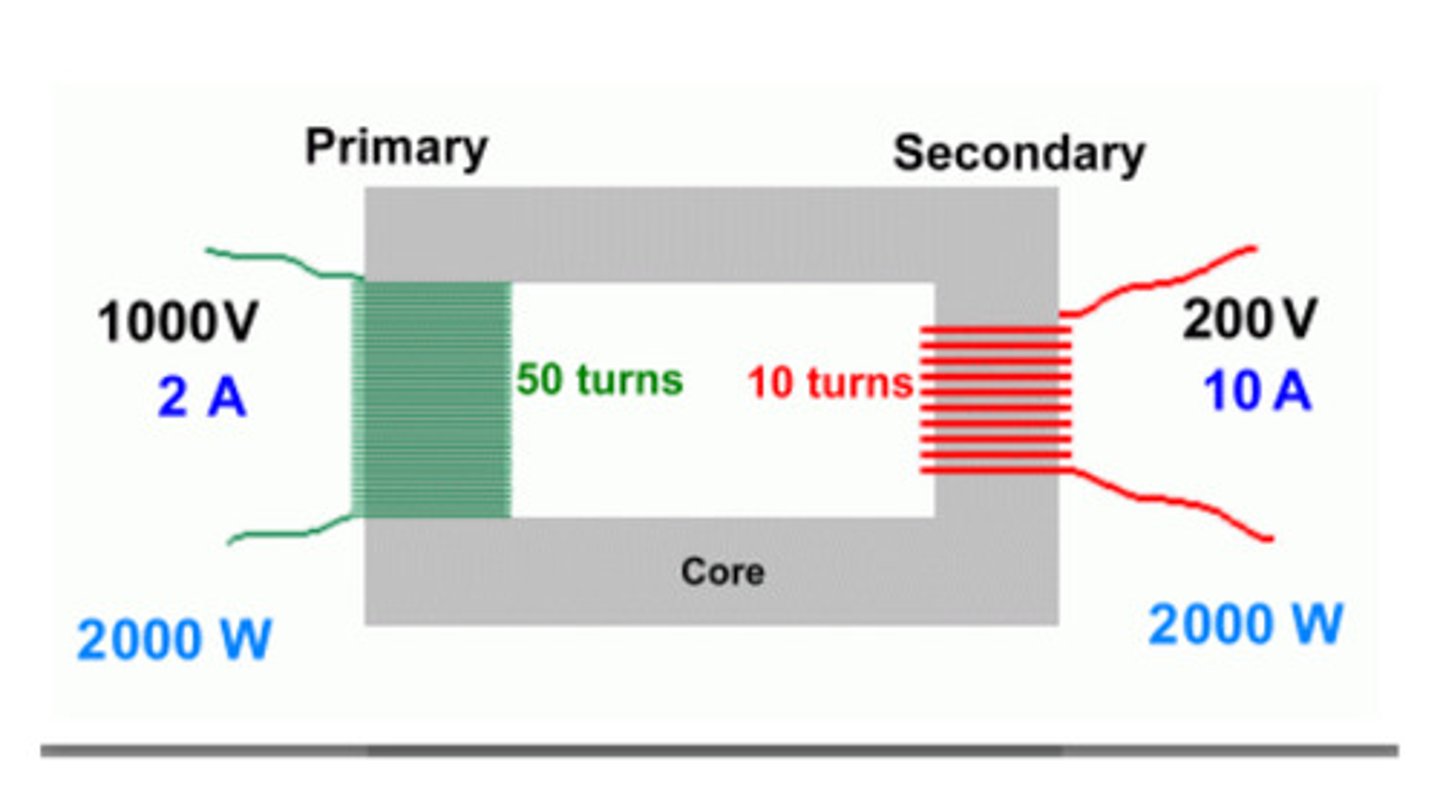
step-up transformers
electrical device used to step-up the size of an alternating potential difference
three-pin plug
a three-pin plug has a live pin, a neutral pin and an earth pin

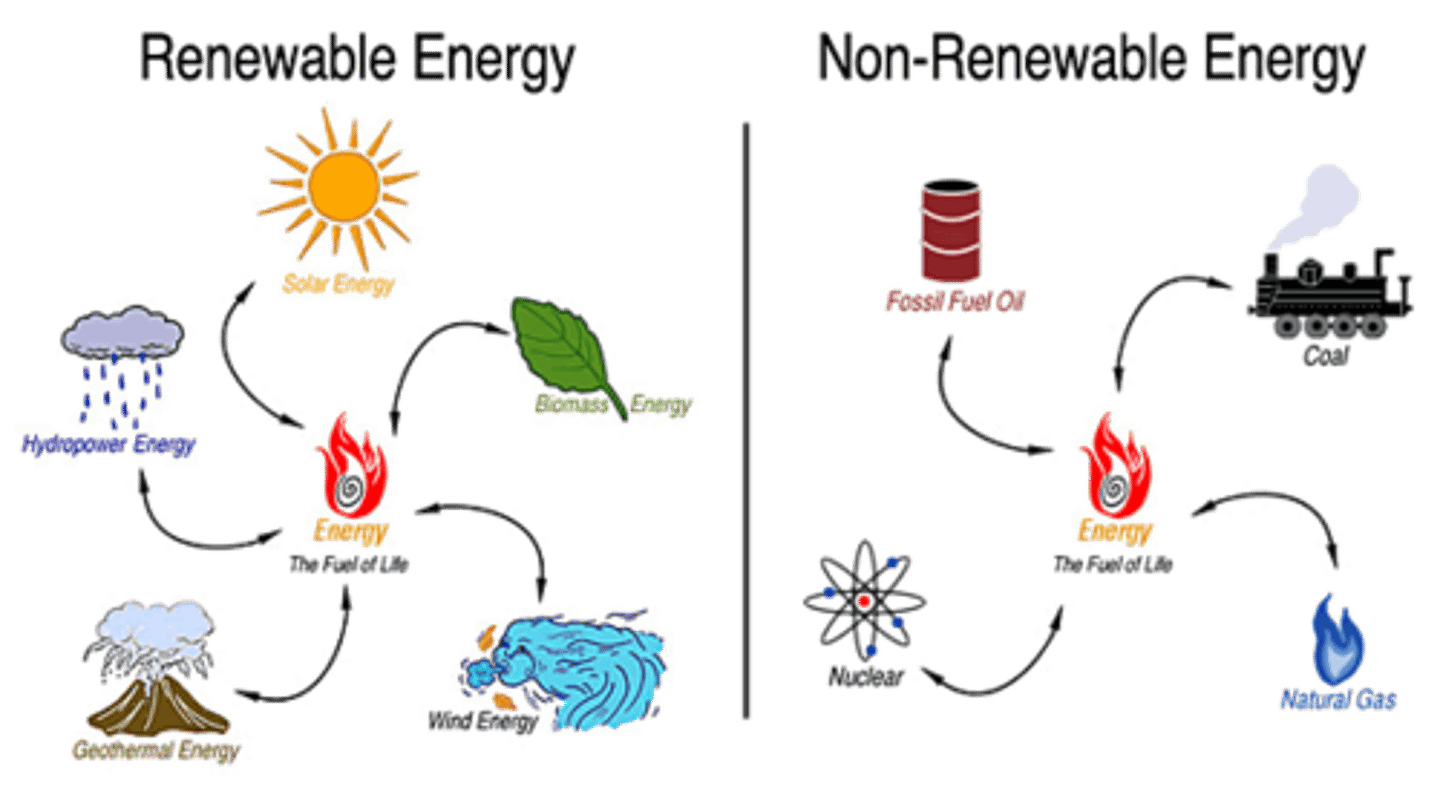
biofuel
any fuel taken from living or recently living materials, such as animal waste

carbon-neutral
a biofuel from a living organism that takes in as much carbon dioxide from the atmosphere as is released when the fuel is burned
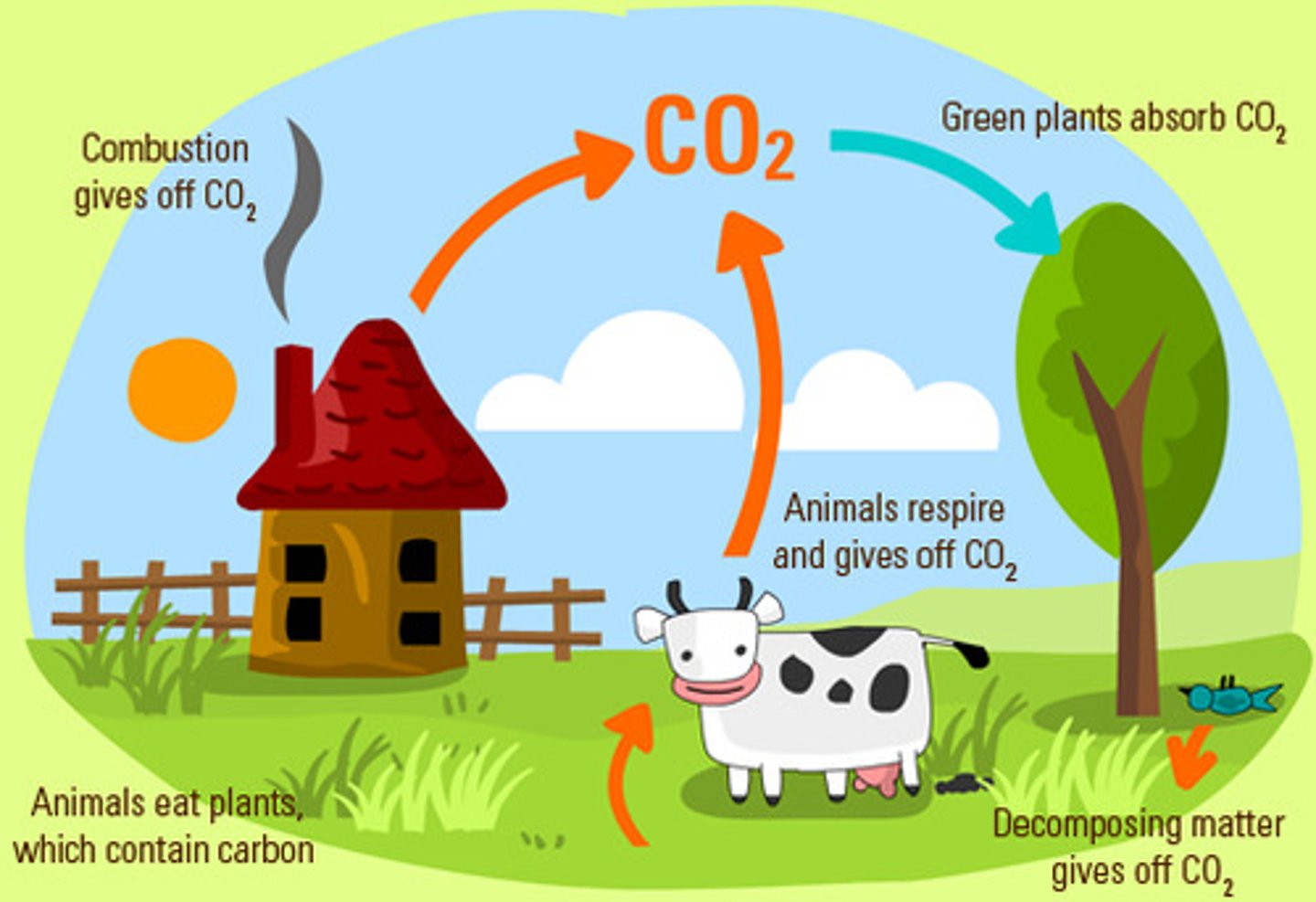
geothermal energy
energy released by radioactive substances deep within the Earth
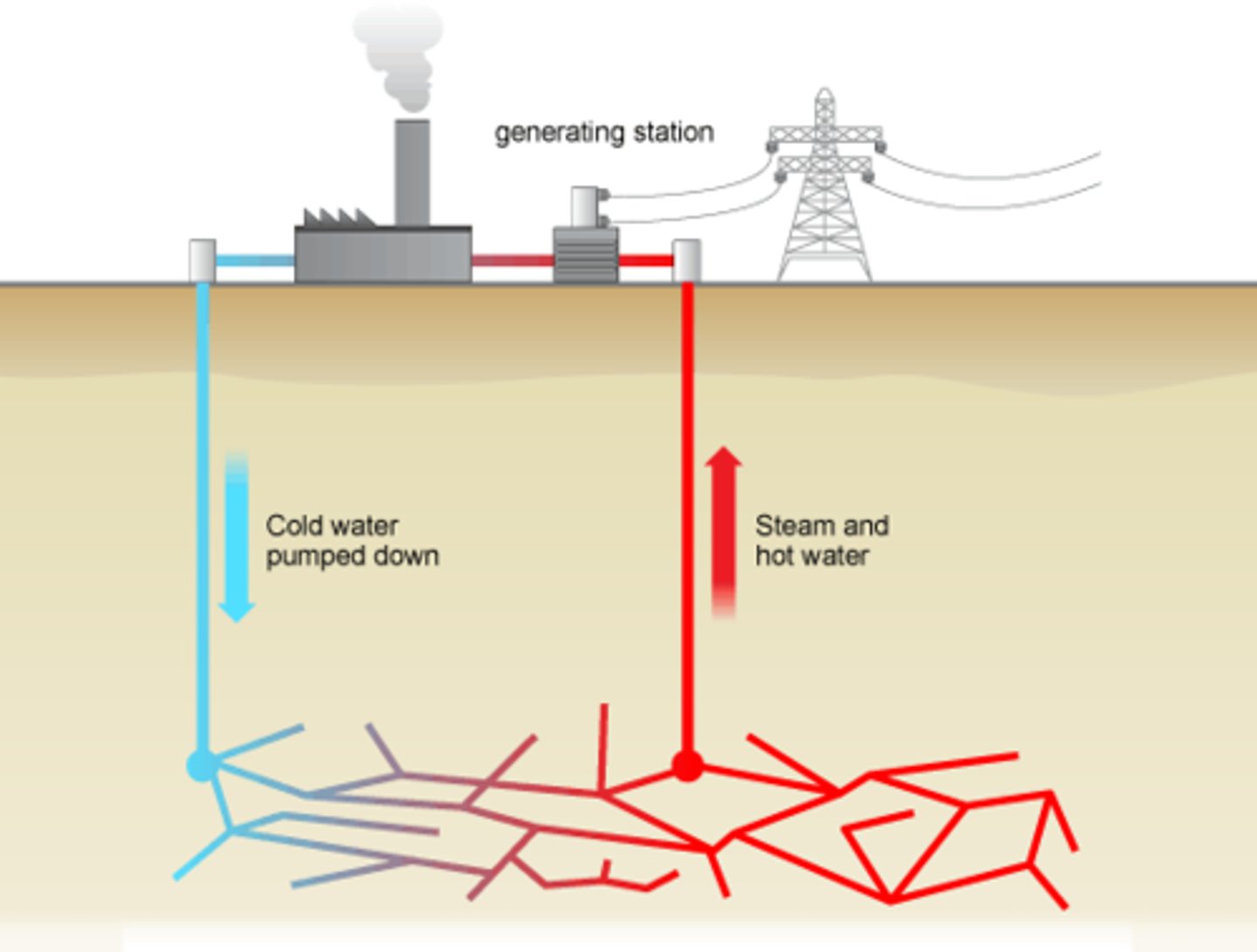
national grid
the network of cables and transformers used to transfer electricity from power stations to consumers (i.e., homes, shops, offices, factories etc.)
nuclear fuel
substance used in nuclear reactors that releases energy due to nuclear fission
nucleus
tiny positively charged object composed of protons and neutrons at the centre of every atom
reactor core
the thick steel vessel used to contain fuel rods, control rods and the moderator in a nuclear fission reactor
renewable energy
energy from natural sources that is always being replenished so it never runs out
the radiation emitted by a perfect black body (a body that absorbs all the radiation that hits it)
black body radiation
electromagnetic waves between visible light and microwaves in the electromagnetic spectrum
infrared radiation
energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 kg of a substance by 1 °C. Units are J/kgoC
specific heat capacity
property of a material that determines the energy transfer through it by conduction
thermal conductivity
Battery
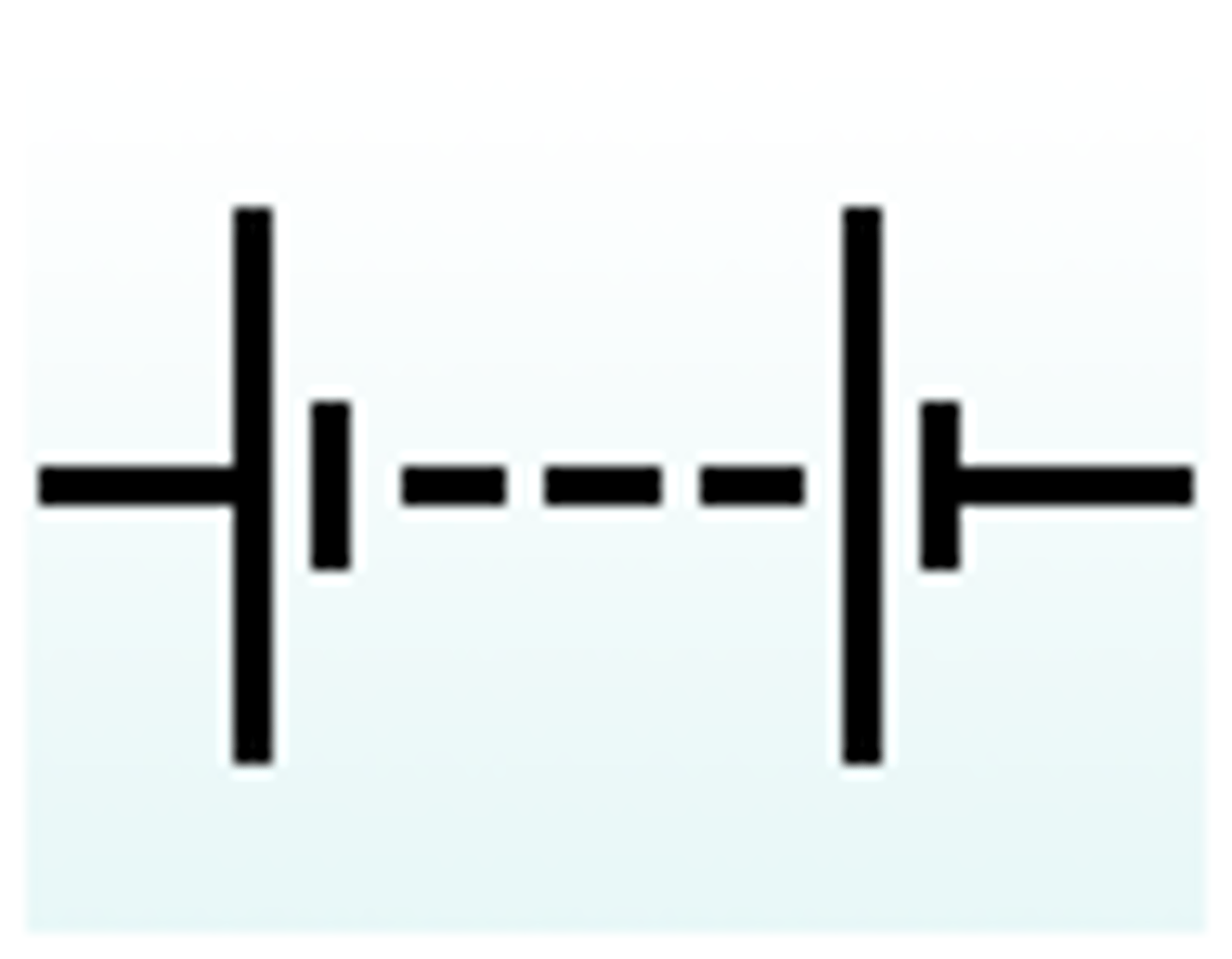
Switch open
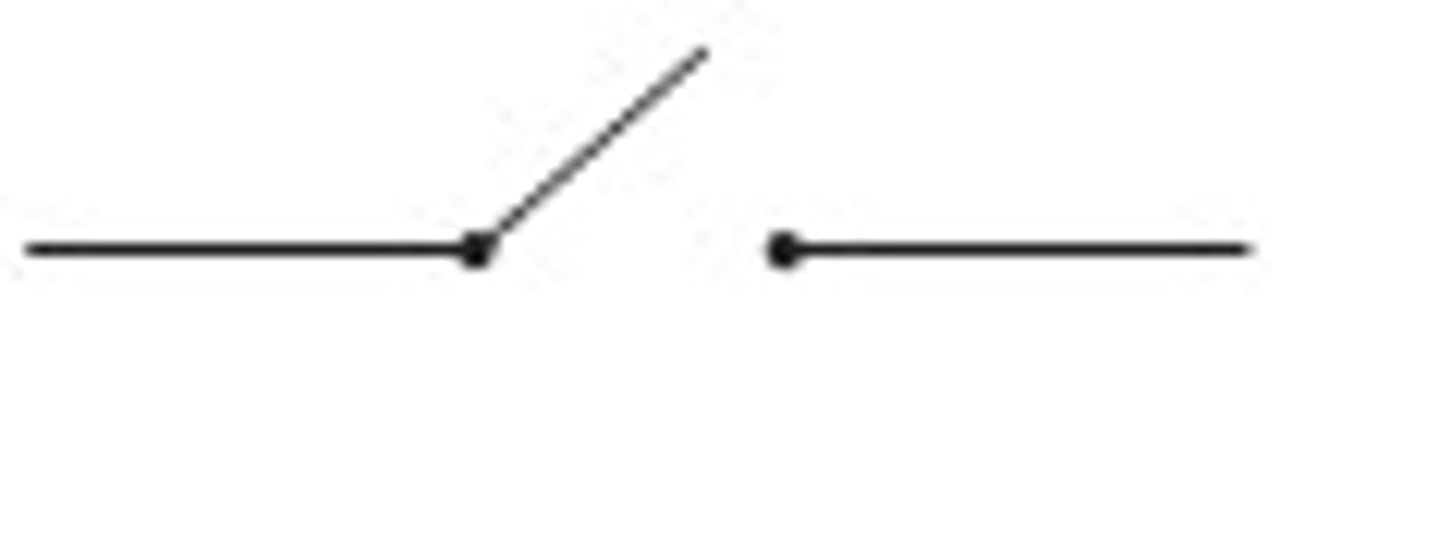
Switch closed

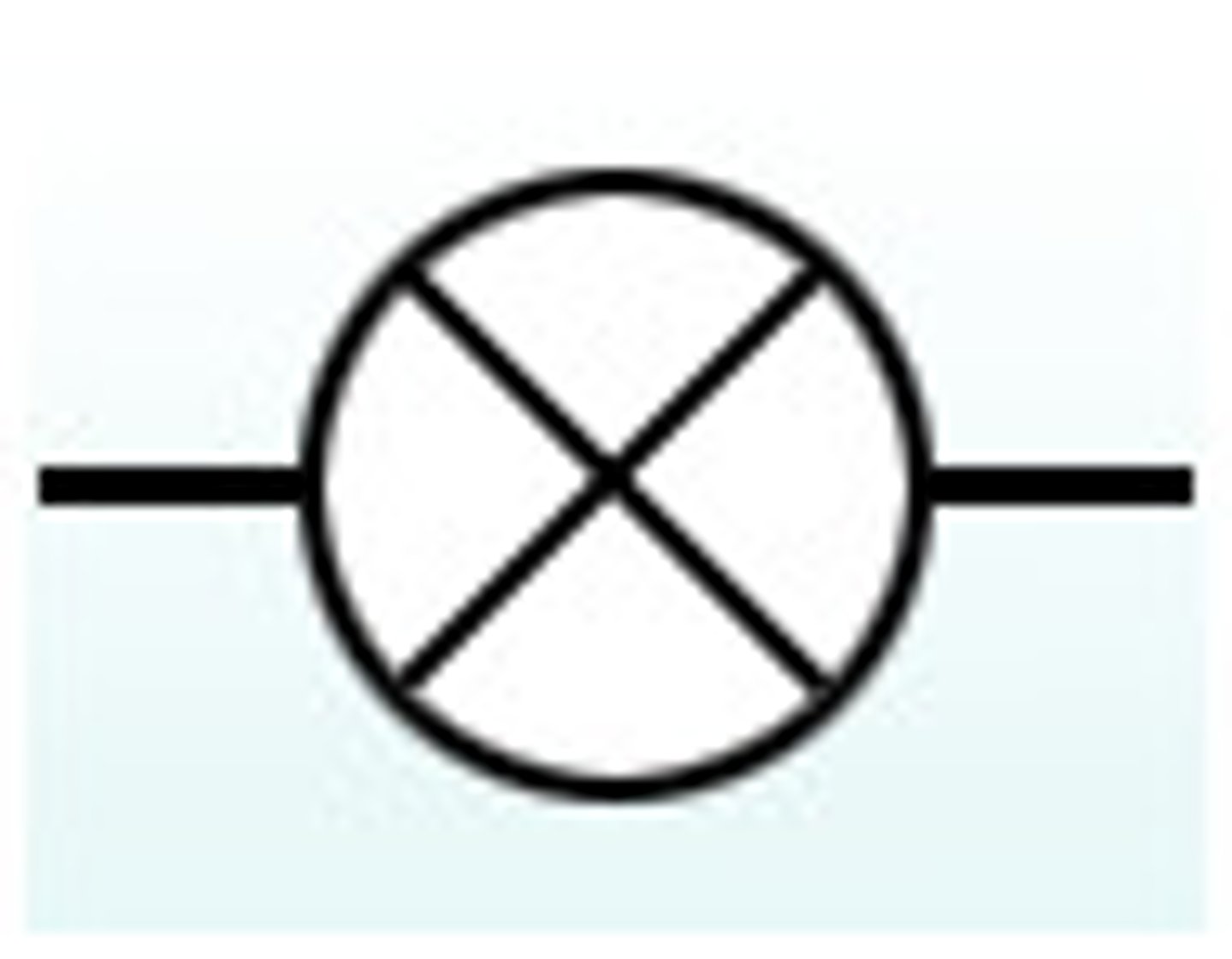
Filament bulb
Fuse
L.E.D
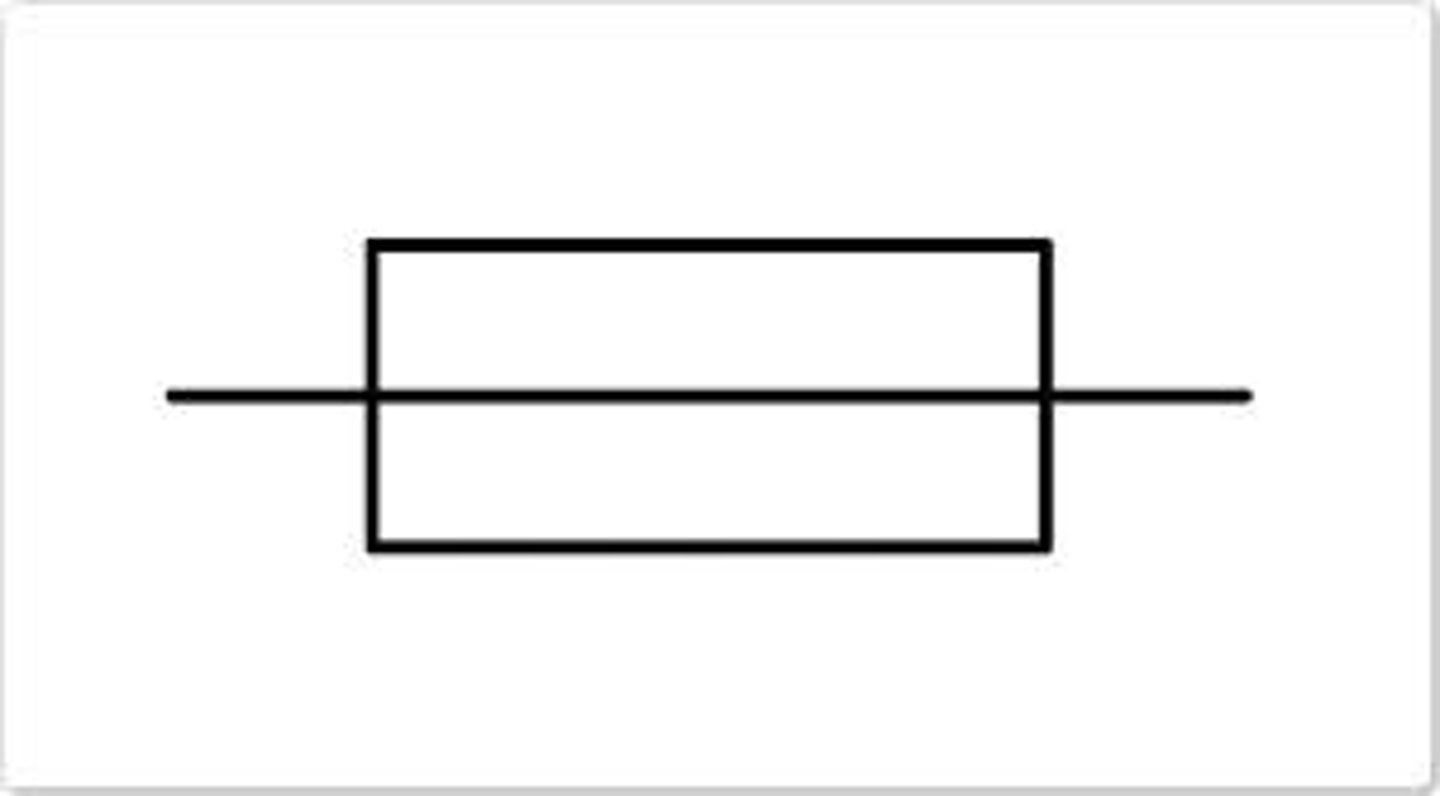
Resistor
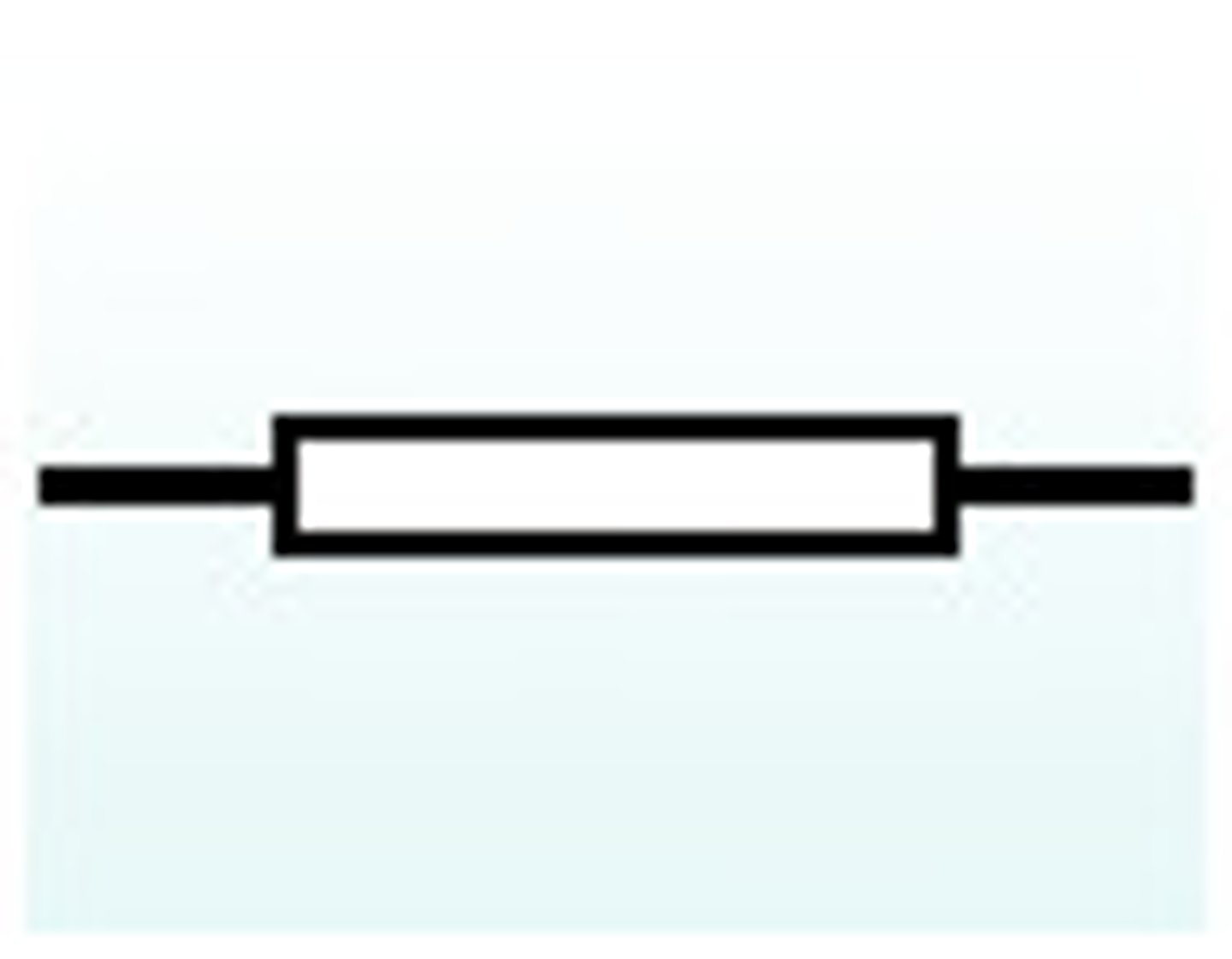
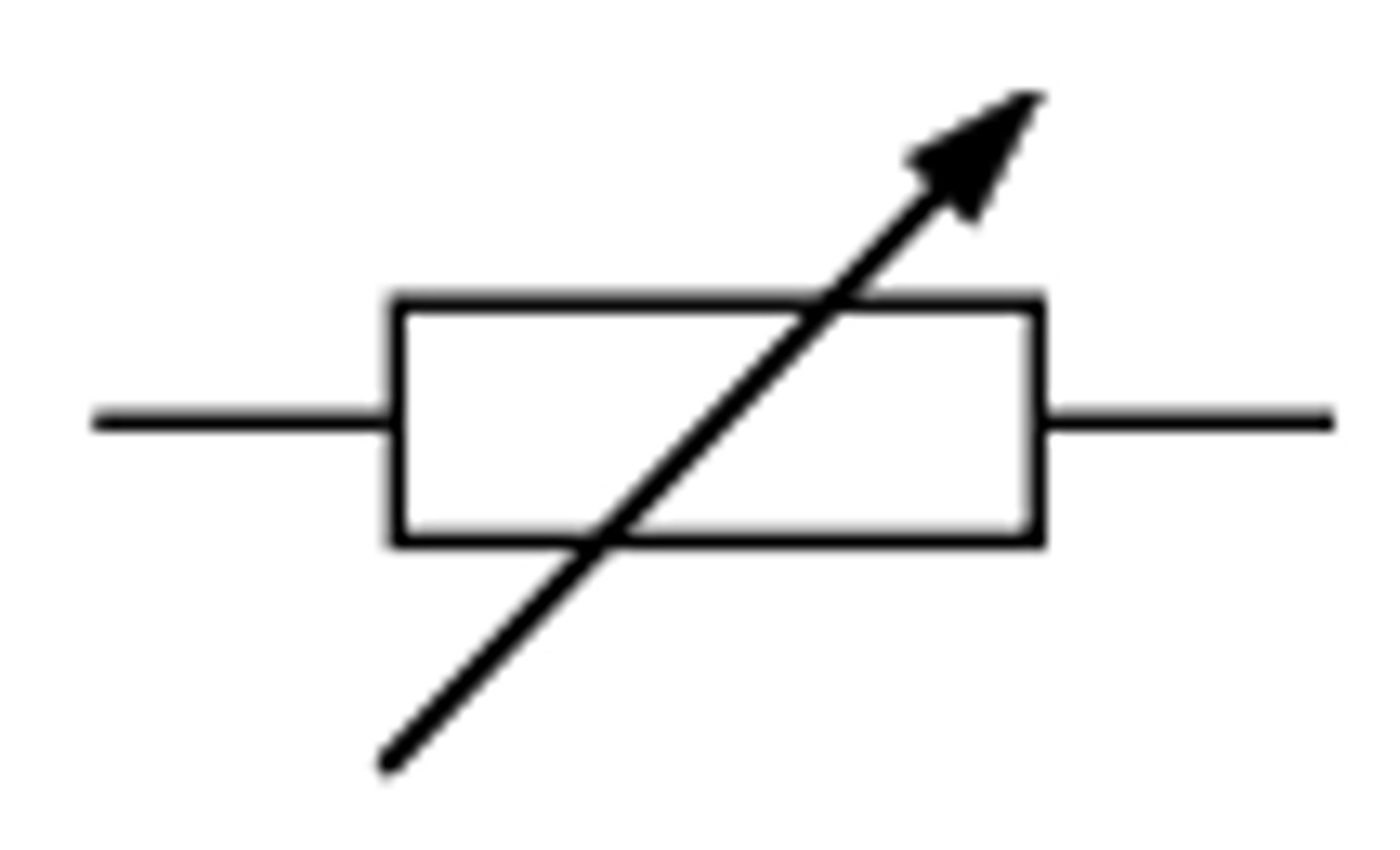
Variable Resistor
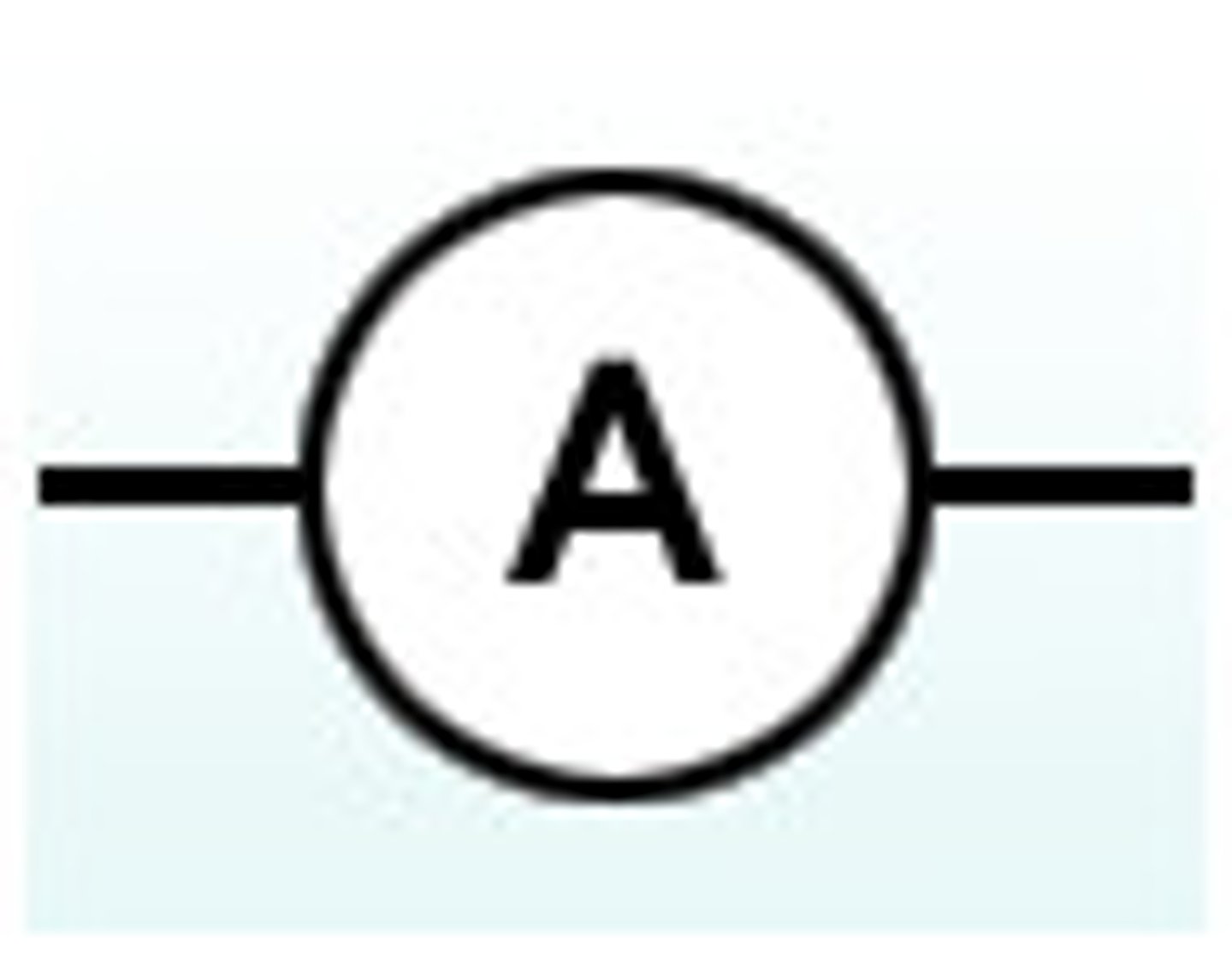
Ammeter
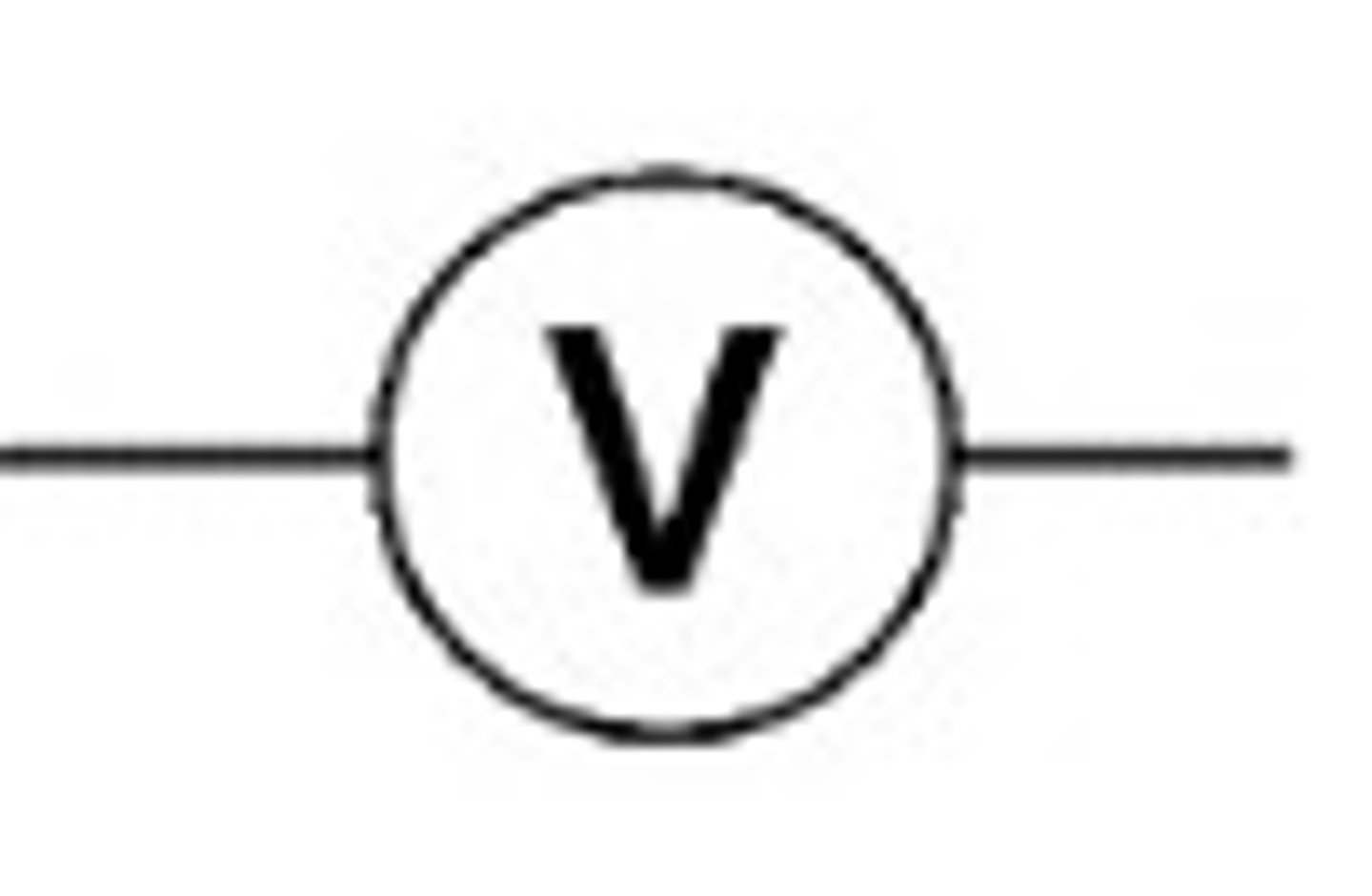
Volts
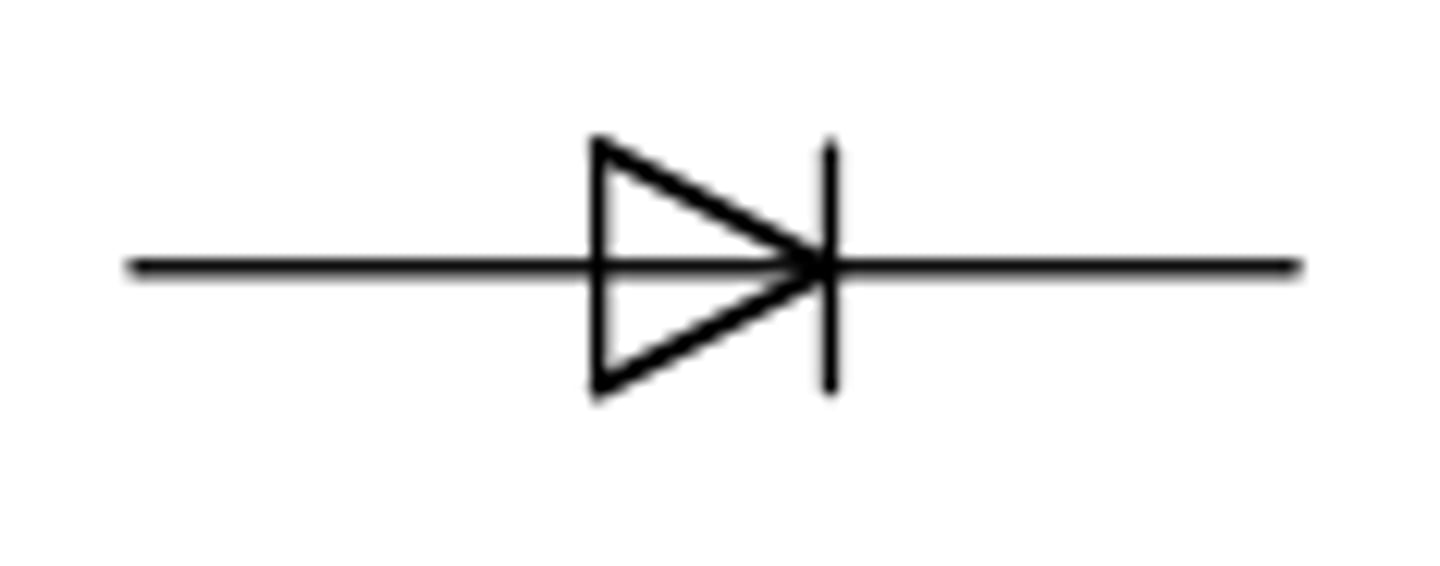
Diode
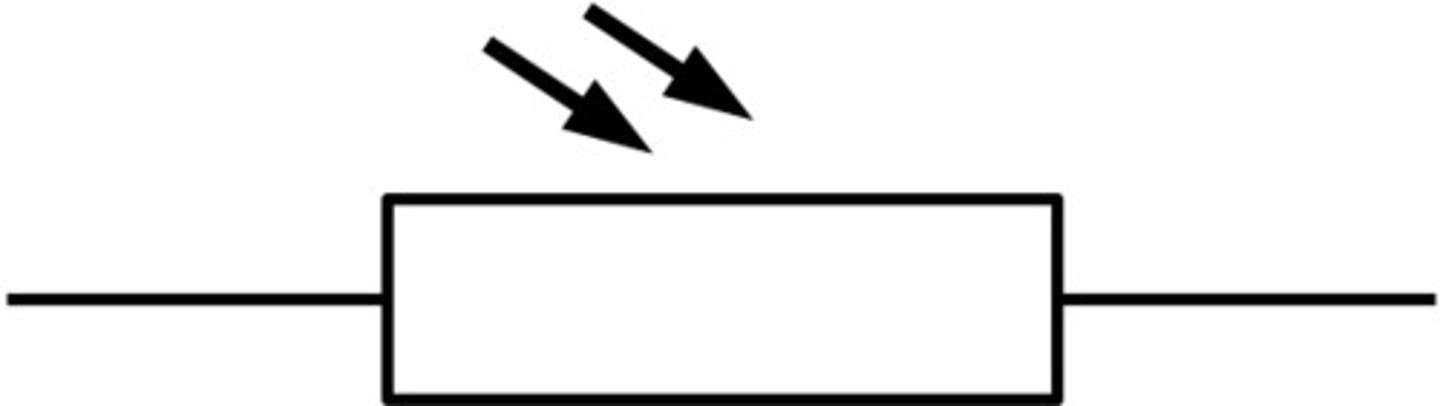
Light Dependent (L.D.R)
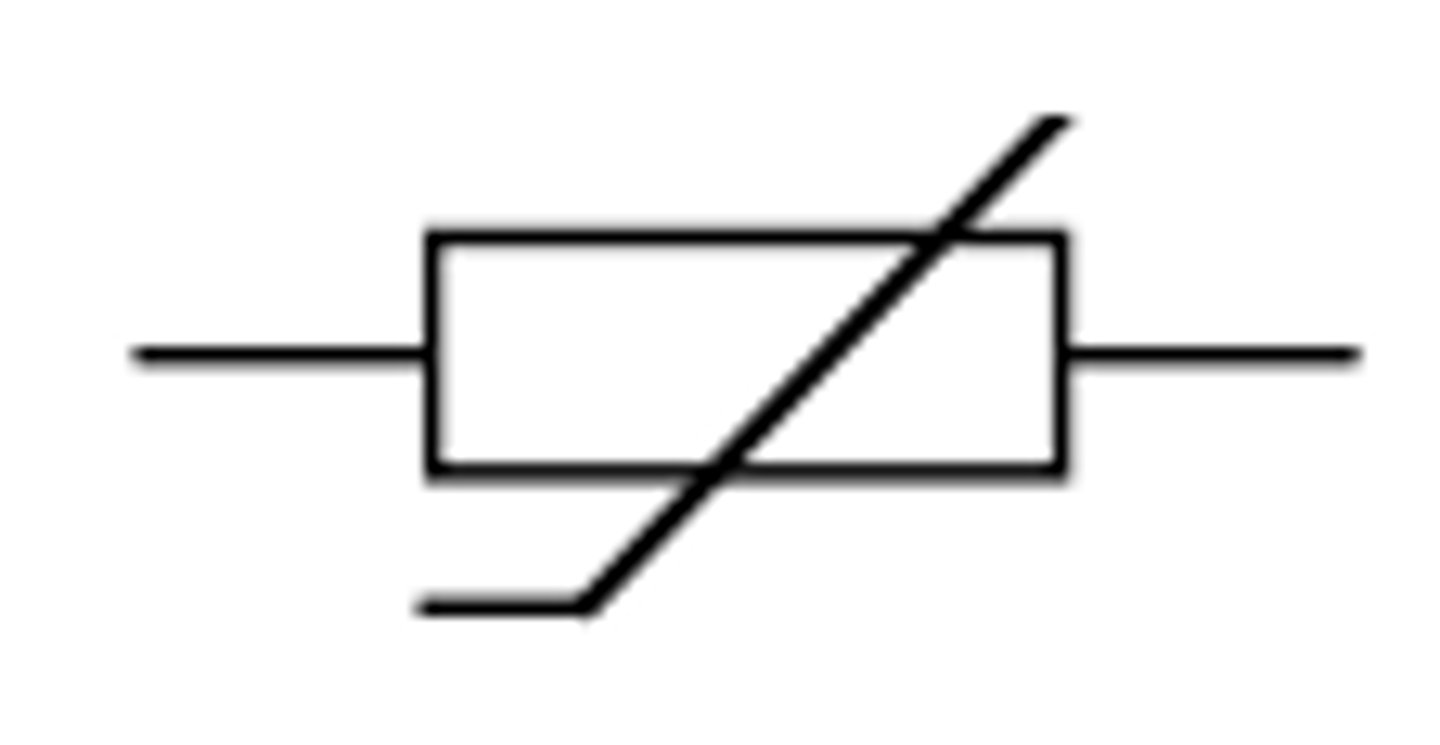
Thermistor
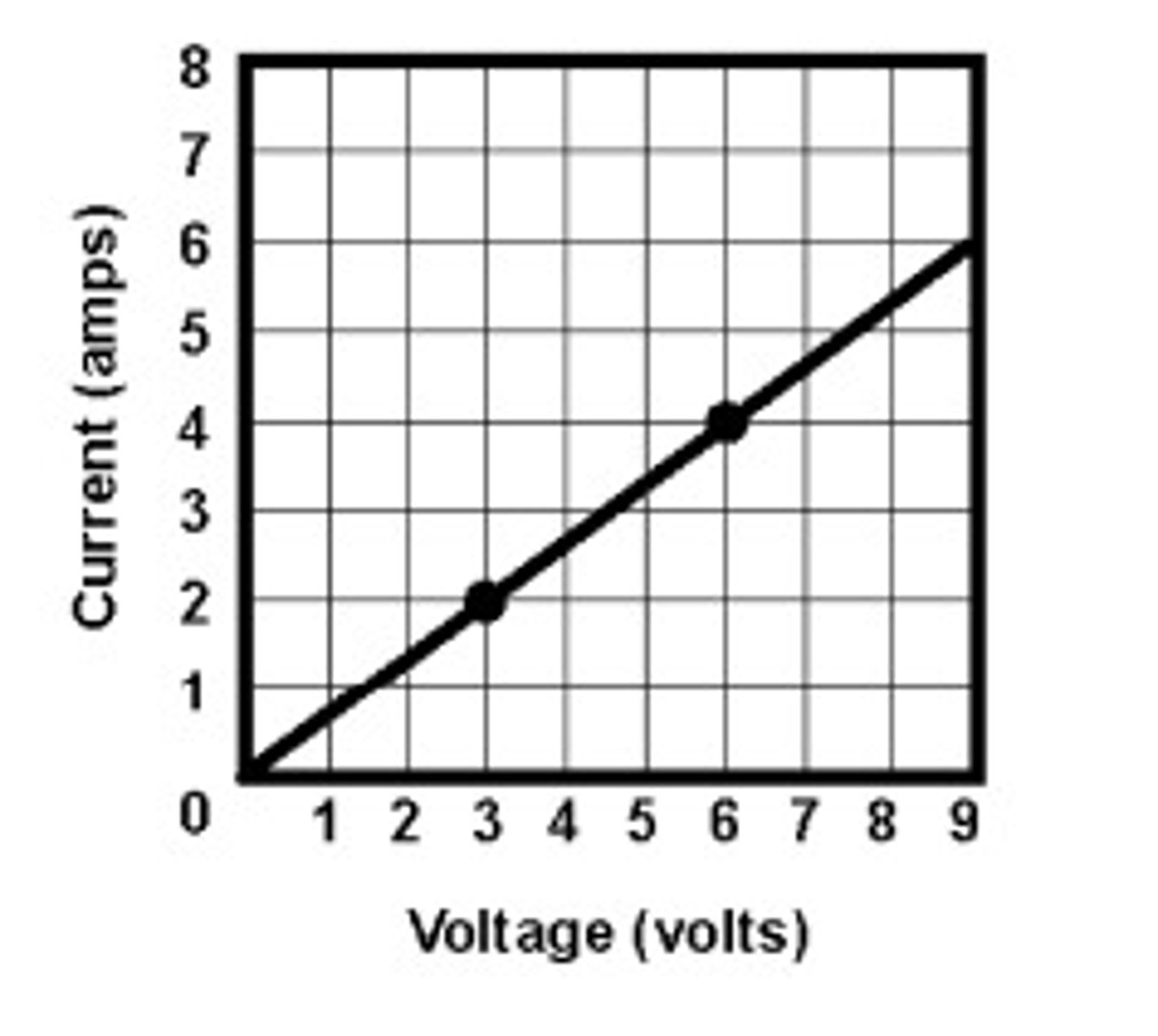
Electric Current (Amps)
The flow of an electric charge. The unit of this is ampere (A)
Potential difference (Voltage
Is the driving force that pushes the charge around. Measured in volts (V)
Resistance
Anything that slows down the flow of the current. Measured in ohms

Rate of the flow of charge
When current flows part a ceartin pointfor a ceartin lenght and time. Measured in coulombs (Q).
In the equation Q=current(I)XTime(t) in seconds
Ammeter
Measures the current in Amps. Must always be connected in the series.
Voltmeter
Measures the voltage in volts. Only able to measure the voltage when connected in a parallel.
Resistance
The longer the length of wire the higher the resistance goes up in solid line. Resistance all adds up
Filament light bulb
The higher the temperate the higher the resistance
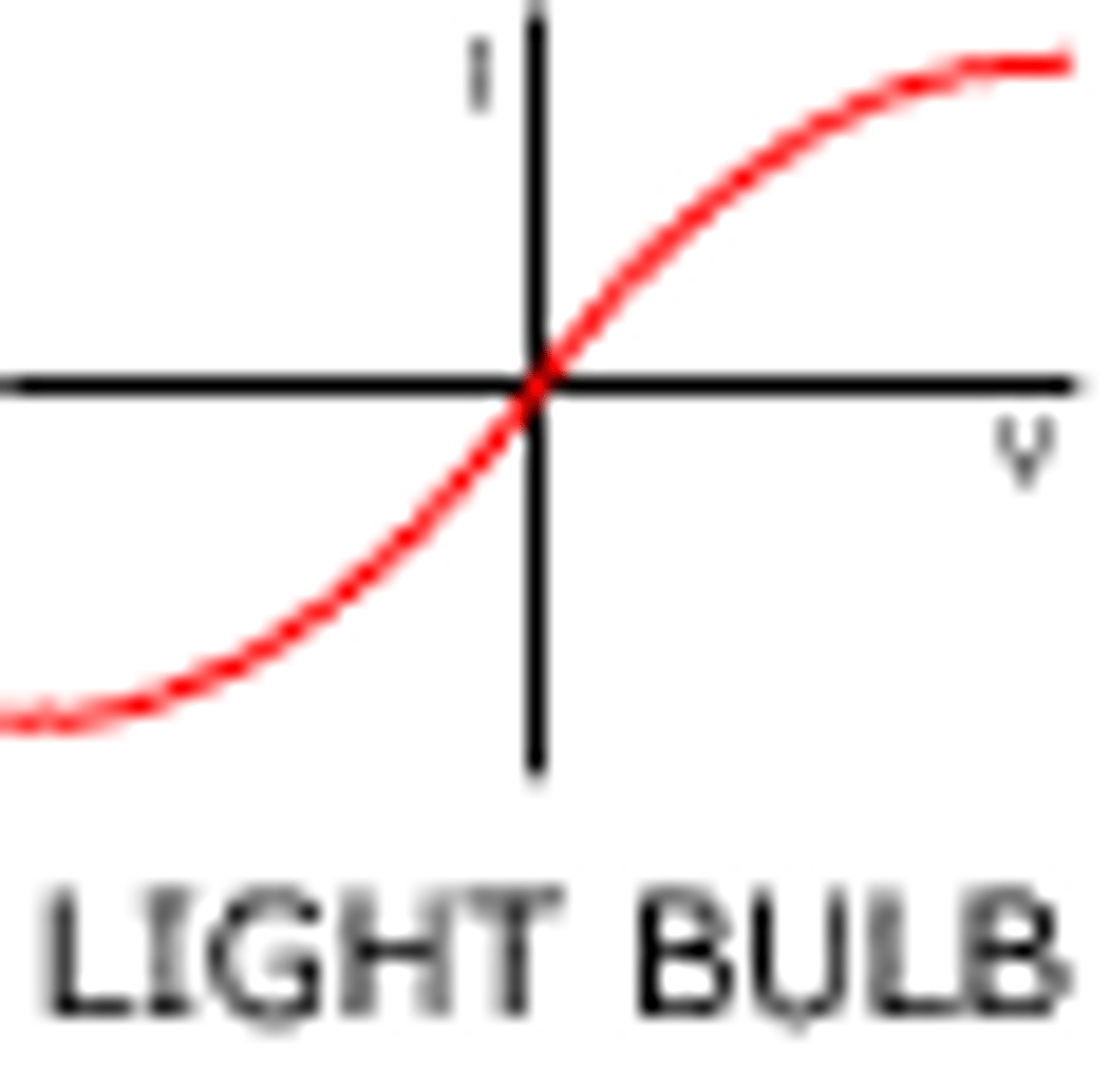
Diode
Flows fine in one way but has a very high resistance in the other
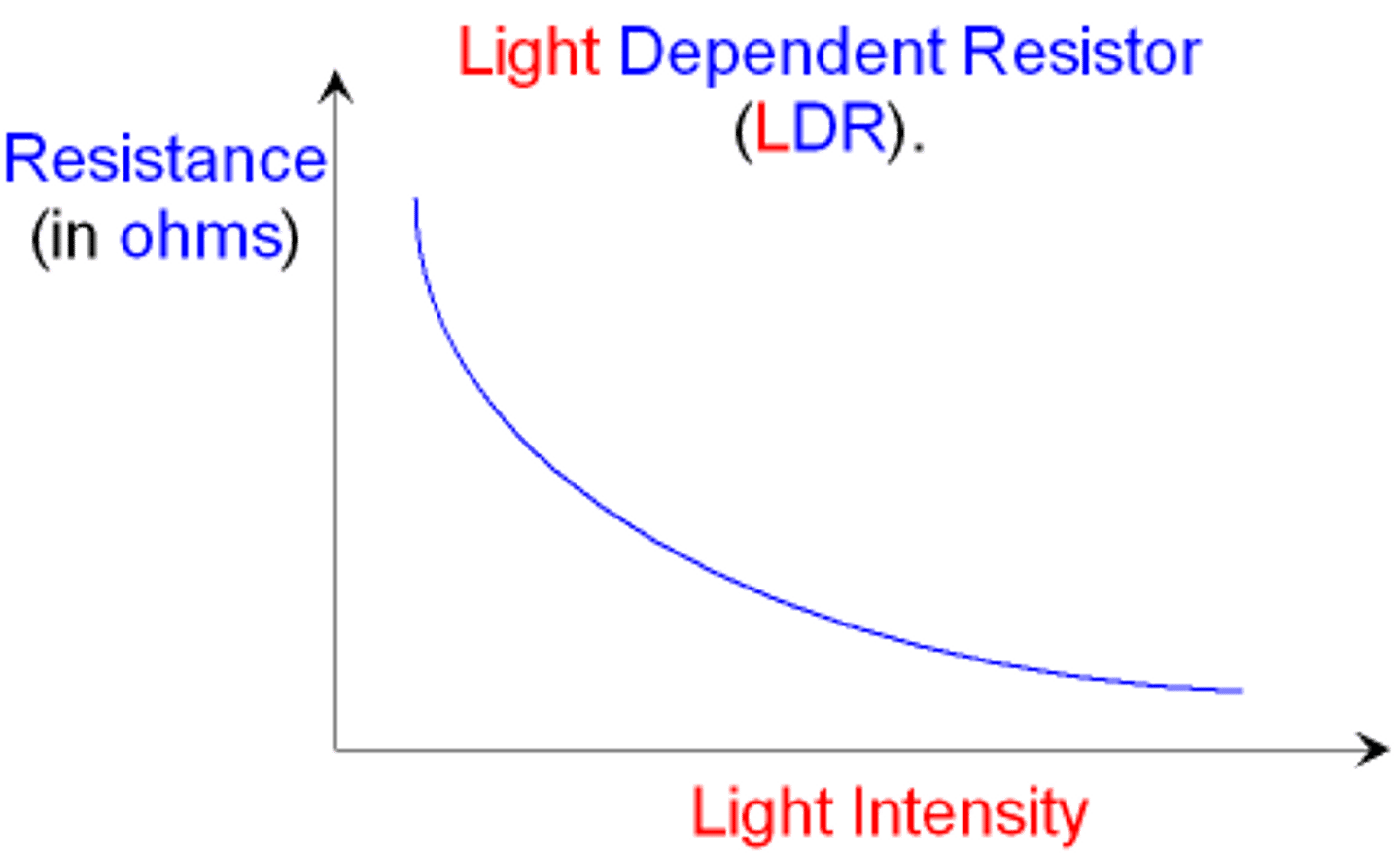
Light Dependent Resistor (L.D.R)
Dependent on the intensity of light. In bright light the resistance fall. In darkness the resistance increases
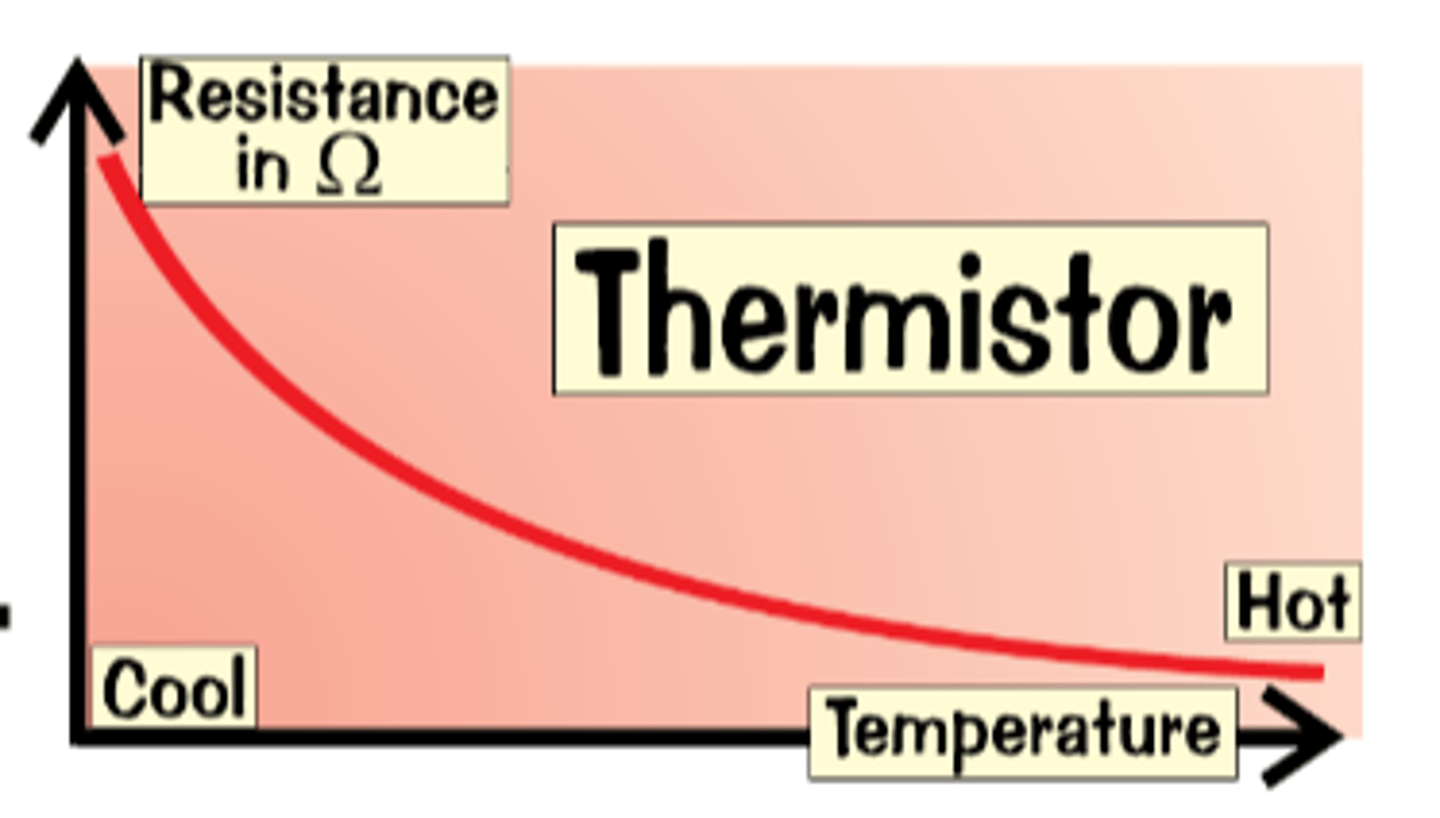
Thermistor
A temperature dependent resistor. In hot conditions, the resistance drops. In cool conditions the resistance rises. Useful in car engine sensors to turn the engine off if it reaches a certain point
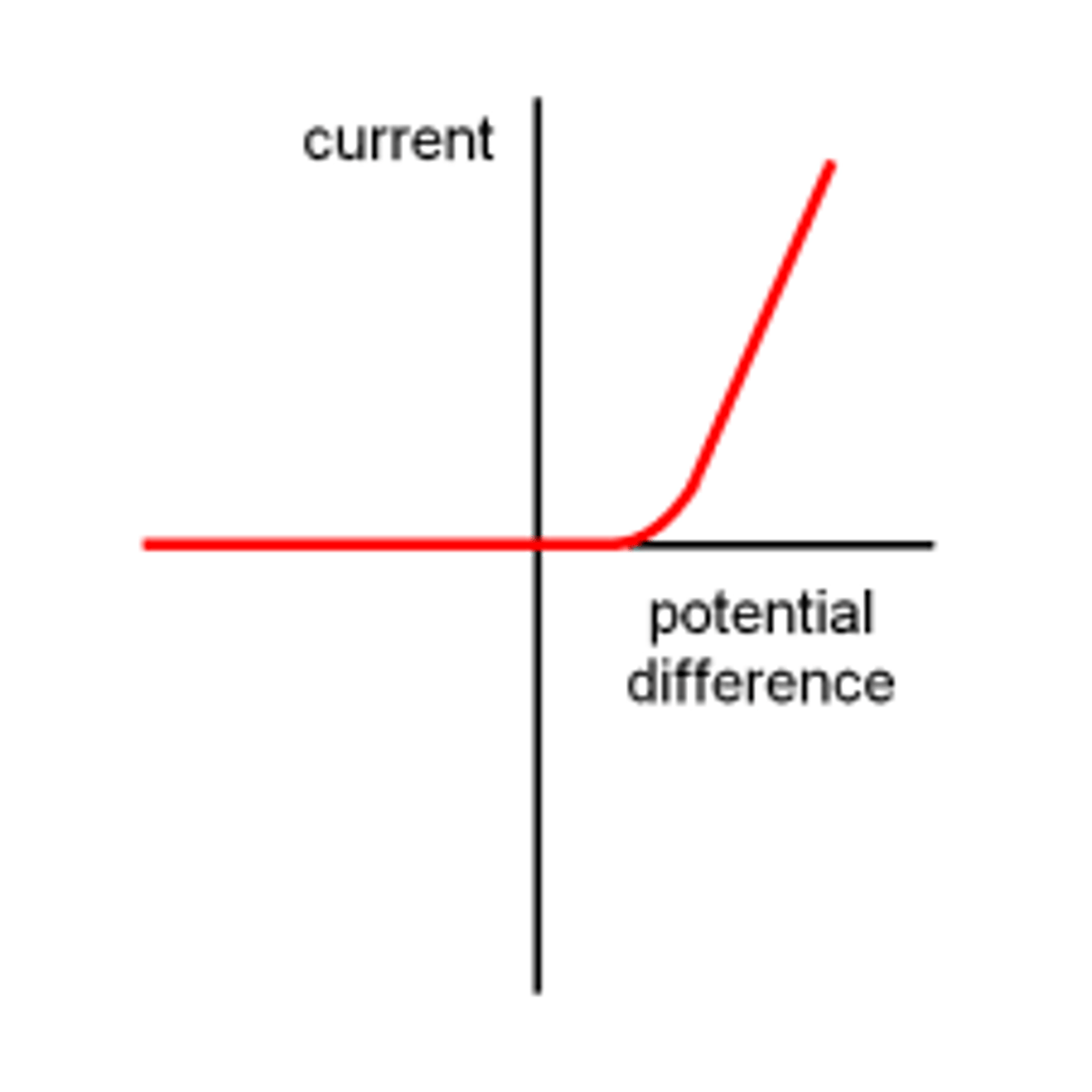
diode
a non-ohmic conductor that has a much higher resistance in one direction (its reverse direction) than in the other direction (its forward direction)
electric field
a charged object (X) creates an electric field around itself, which causes a non-contact force on any other charged object in the field
electrons
tiny negatively charged particles that move around the nucleus of an atom
ion
a charged atom or molecule
light-depending resistor (LDR)
a resistor whose resistance depends on the intensity of the light incident on it
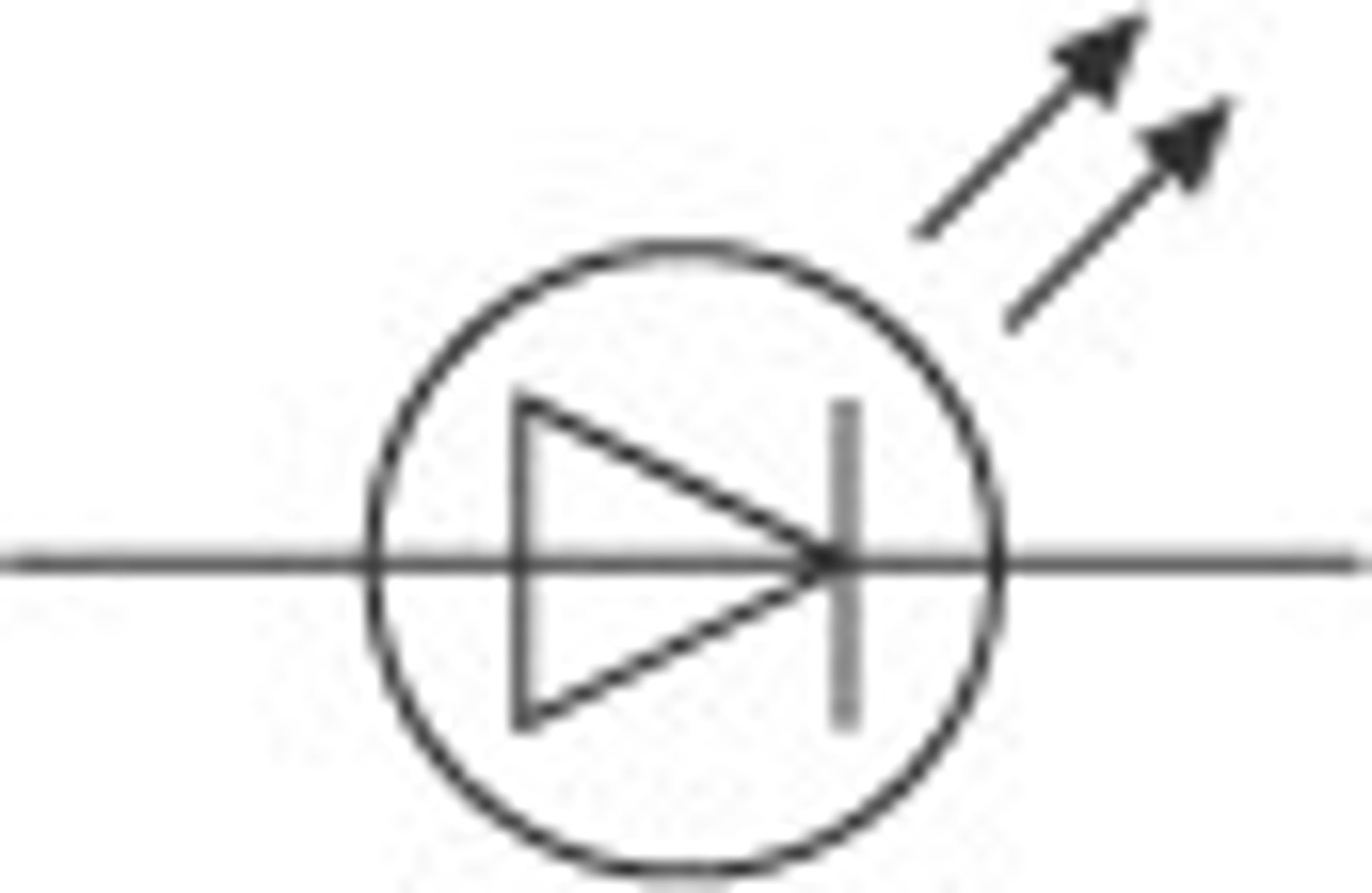
light-emitting diode (LED)
a diode that emits light when it conducts
line of force in an electric field
line along which a free positive charge moves long in an electric field
neutrons
uncharged particles of the same mass as protons. The nucleus of an atom consists of protons and neutrons
Ohm's law
the current through a resistor at constant temperature is directly proportional to the potential difference across the resistor
parallel
components connected in a circuit so that the potential difference is the same across each one
potential difference
a measure of the work done or energy transferred to the lamp by each coulomb of charge that passes through it. The unit of potential difference is the volt (V)
protons
positively charged particles with an equal and opposite charge to that of an electron
resistance
resistance (in ohms, Ω) = potential difference (in volts, V) ÷ current (in amperes, A), R = V/I
series
components connected in a circuit in such a way that the same current passes through them
static electricity
electric charge stored on insulated objects
thermistor
a resistor whose resistance depends on the temperature of the thermistor
Students should use numbers given in the question to work out the answer.
Calculate
Select from a range of alternatives.
Choose
This requires the student to describe the similarities and/or differences between things, not just write about one.
Compare
Answers should be written in the space provided, for example on a diagram, in spaces in a sentence, or in a table.
Complete
Specify the meaning of something.
Define
Students may be asked to recall some facts, events or process in an accurate way.
Describe
Set out how something will be done.
Design