1.1) External topography of the brain
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Phases of prenatal development
zygote, embryo, fetus
around week 9 what develops
the nervous system
at about 18 days after conception the embryo
begins to implant in the uterine wall
The uterine wall consists of three layers
- endoderm
- mesoderm
- ectoderm
thickening of the ectoderm leads to the development of
the neural plate
the neural groove begins to develop at
20 days
at 22 days the neural groove
closes along the length of the embryo making the neural tube
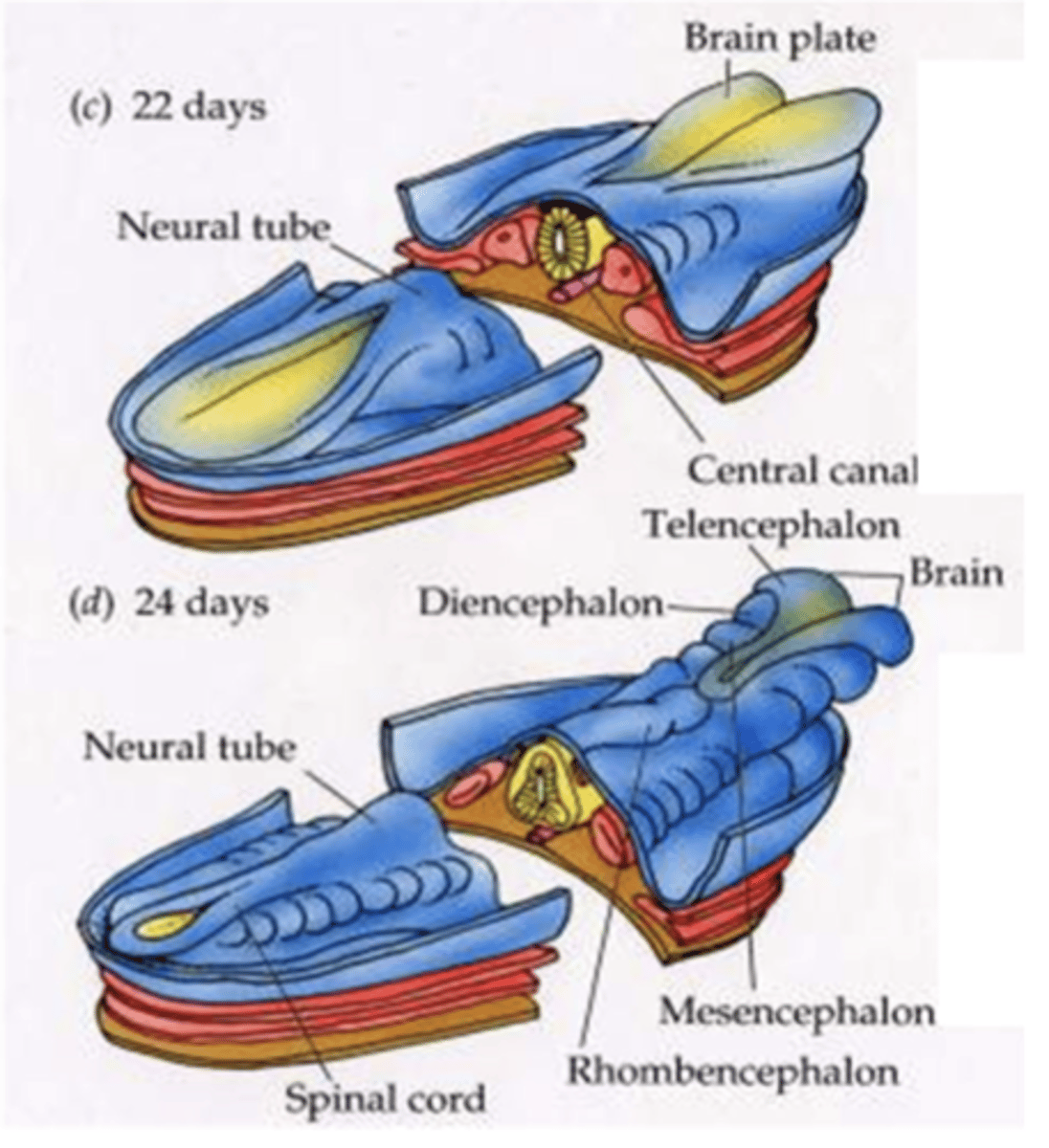
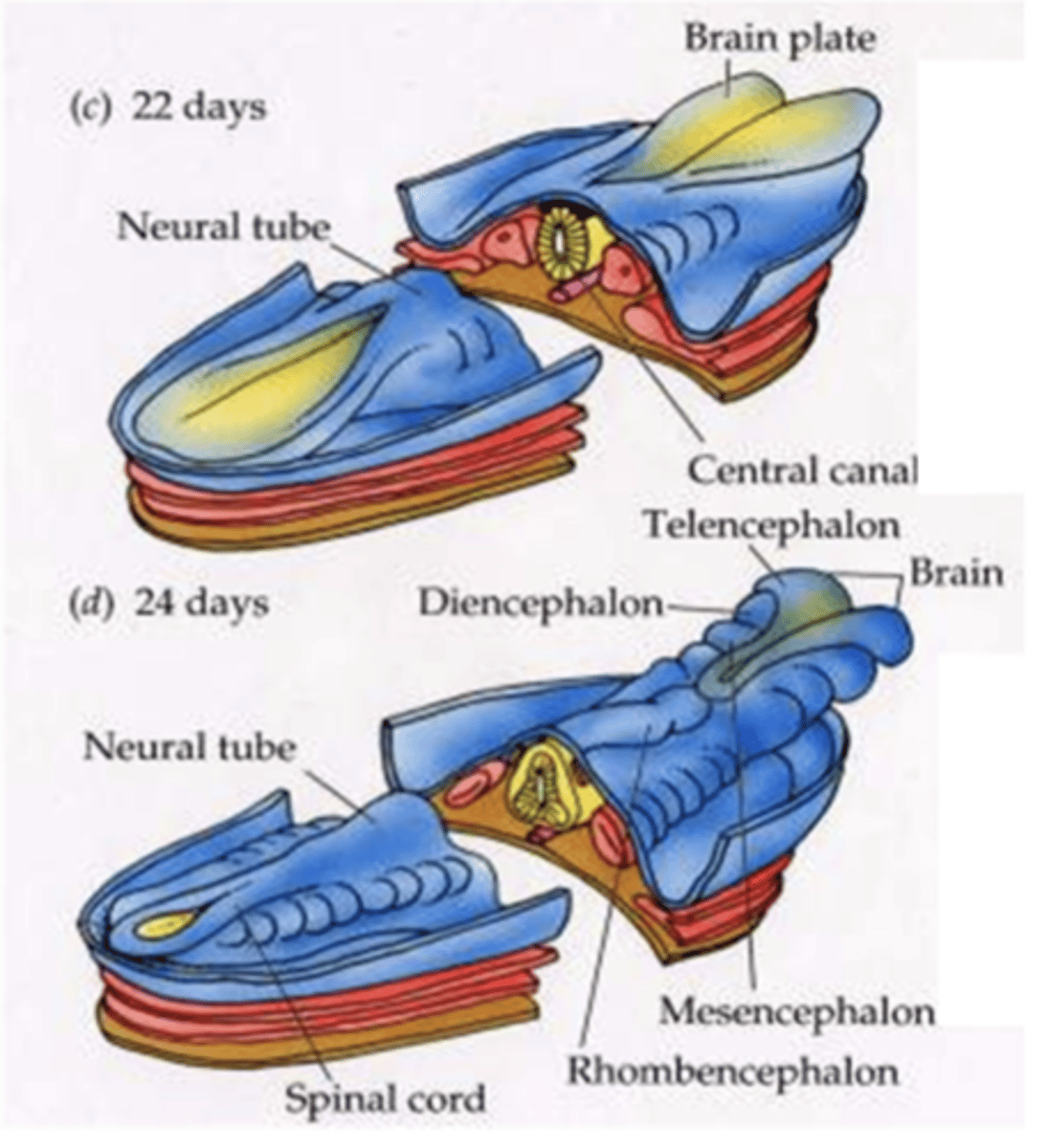
at around 24 days of development what is observed
the 4 major divisions of the brain
- telencephalon
- diencephalon
- mesencephalon
- rhombencephalon
4 subdivisions of the neural tube
prosencephalon
mesencephalon
rhombencephalon
spinal cord
at 5 weeks, prosencephalon divides into...
telencephalon and diencephalon
telencephalon becomes the
cerebral hemispheres
cerebral cortex
The mesencehpalon becomes the
midbrain
Diencephalon becomes the
thalamus
hypothalamus
epithalamus
at 5 weeks, rhombencephalon divides into...
metencephalon and myelencephalon
metencephalon becomes the
pons and cerebellum
myelencephalon becomes the
medulla
Cerebrum (telencephalon) has two hemispheres which contain
cerebral cortex
subcortical white matter
subcortical nuclei (basal ganglia)
ventricles (CSF filled spaces)
grey matter
Predominantly cell bodies
What is white matter primarily composed of?
Mostly myelinated axons
What is the function of white matter in the brain?
Allows different areas of the cerebral cortex to communicate with each other
Which structures does white matter connect with?
The brainstem and spinal cord
What is the surface of the cerebrum called?
Cerebral cortex (composed of grey matter)
What are groups of cell bodies embedded within the white matter of the cerebrum called?
Deep grey matter
names of the deep grey matter in the cerebrum
- basal ganglia
- basal forebrain nuclei
- claustrum
- amygdala
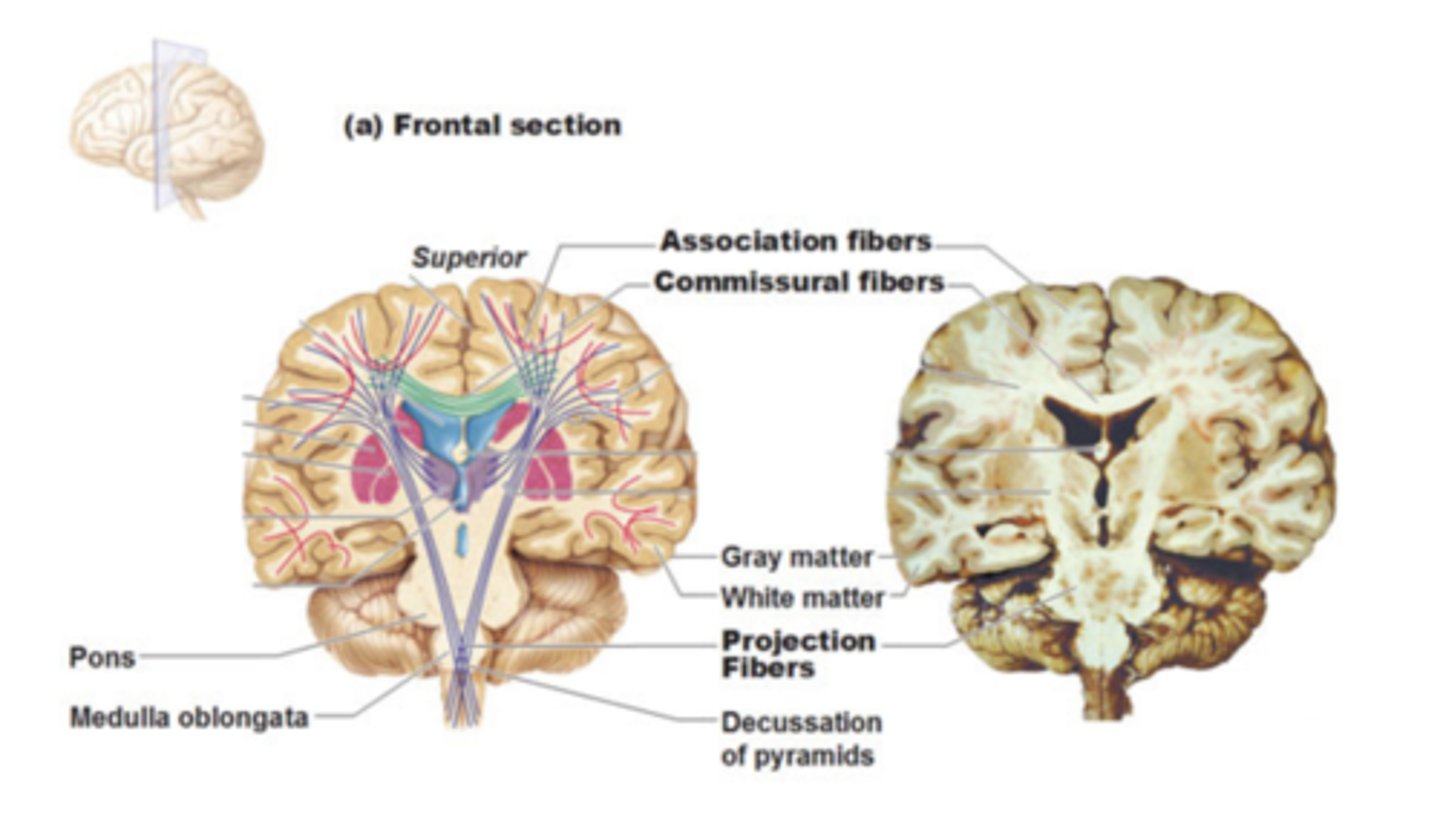
white matter of the cerebrum
-association fibers
-commissural fibers
-projection fibers
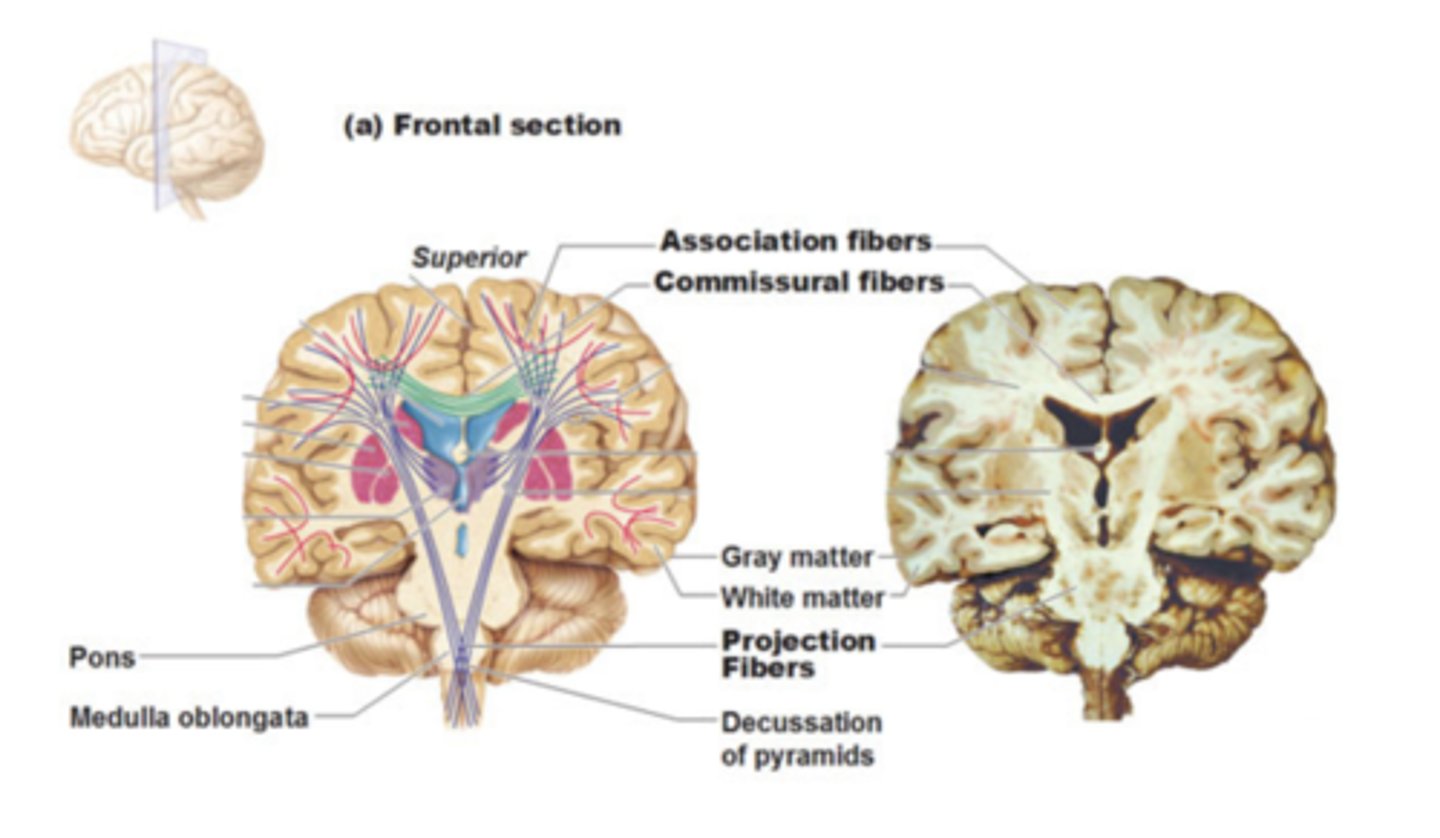
association fibers connect
different parts of the same hemisphere
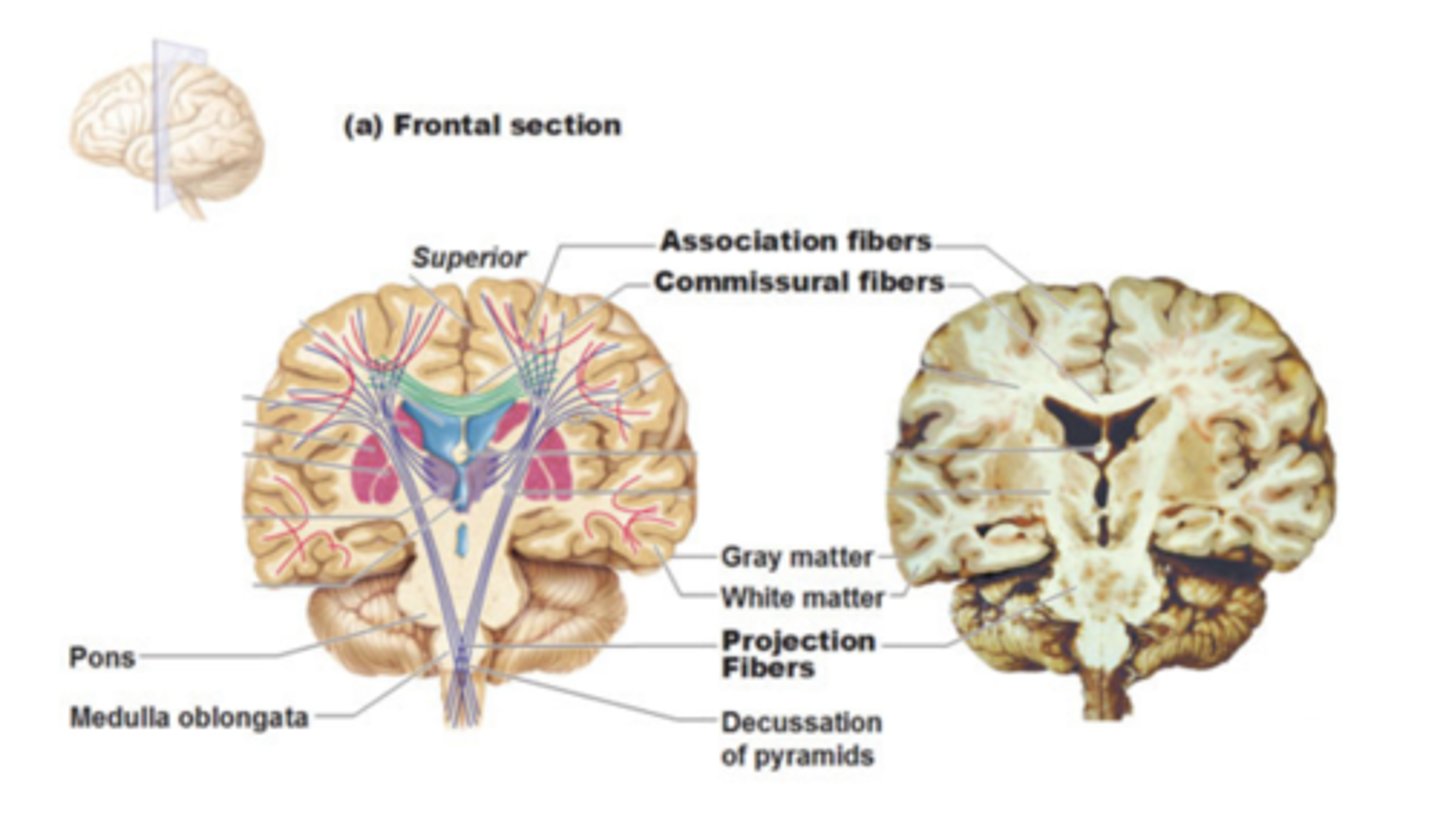
commissural fibers connect
cortical areas of right and left hemispheres
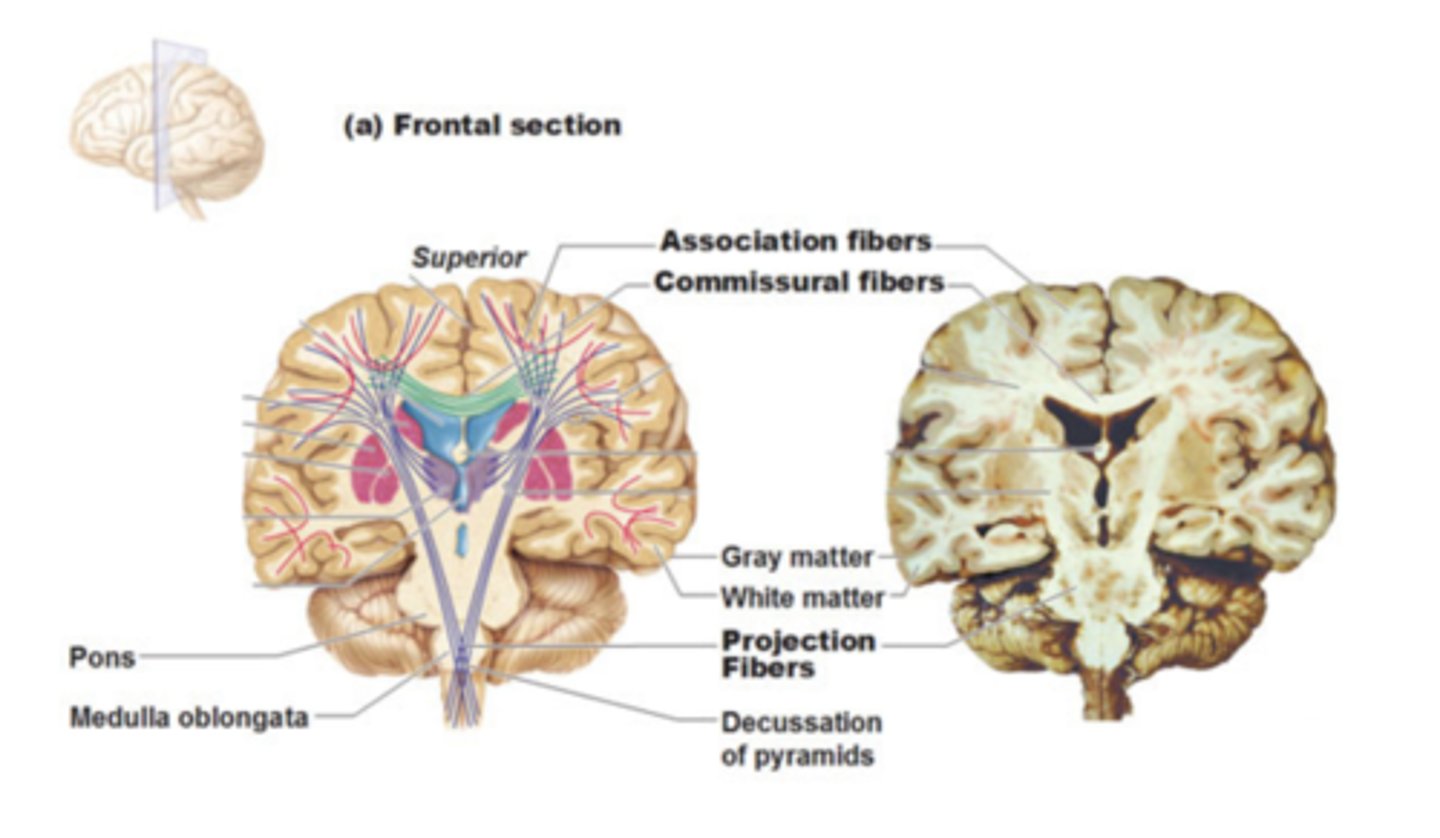
projection fibers run
vertically, ascending and descending to and from the spinal cord
falxi cerebri
the extension of the cranial dura mater between the hemispheres.
medial longitudinal fissure
separates hemispheres
corpus callosum function
connects left and right hemispheres of the brain
gyrus
hills of the cerebral cortex (made of grey matter)
sulcus
valley in the cerebral cortex (made of grey matter)
when a suclus is really deep it is called a
fissure
from the superolateral surface we can see
frontal lobe
parietal lobe
temporal lobe
occipital lobe
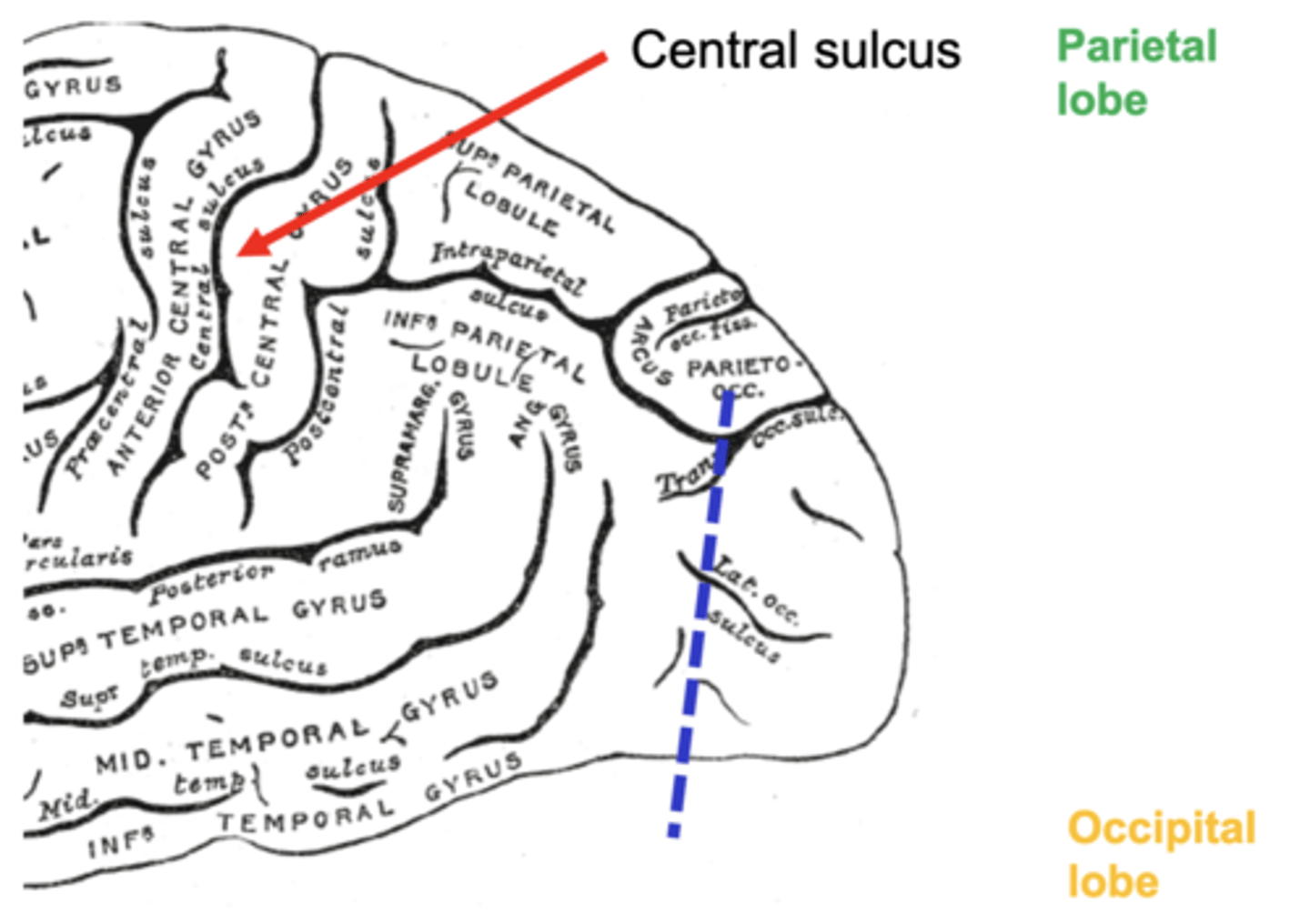
two main sulci that help us distinguish the 4 lobes of the brain
lateral sulcus
central sulcus
frontal lobe sucli
precentral sulcus
superior frontal sulcus
inferior frontal sulcus
superior frontal sulcus and inferior frontal sulcus help divide the frontal lobe into
superior frontal gyrus
middle frontal gyrus
inferior frontal gyrus
3 parts of the inferior frontal gyrus
orbital, opercular, triangular
sulci of the parietal lobe
postcentral sulcus
intraparietal sulcus
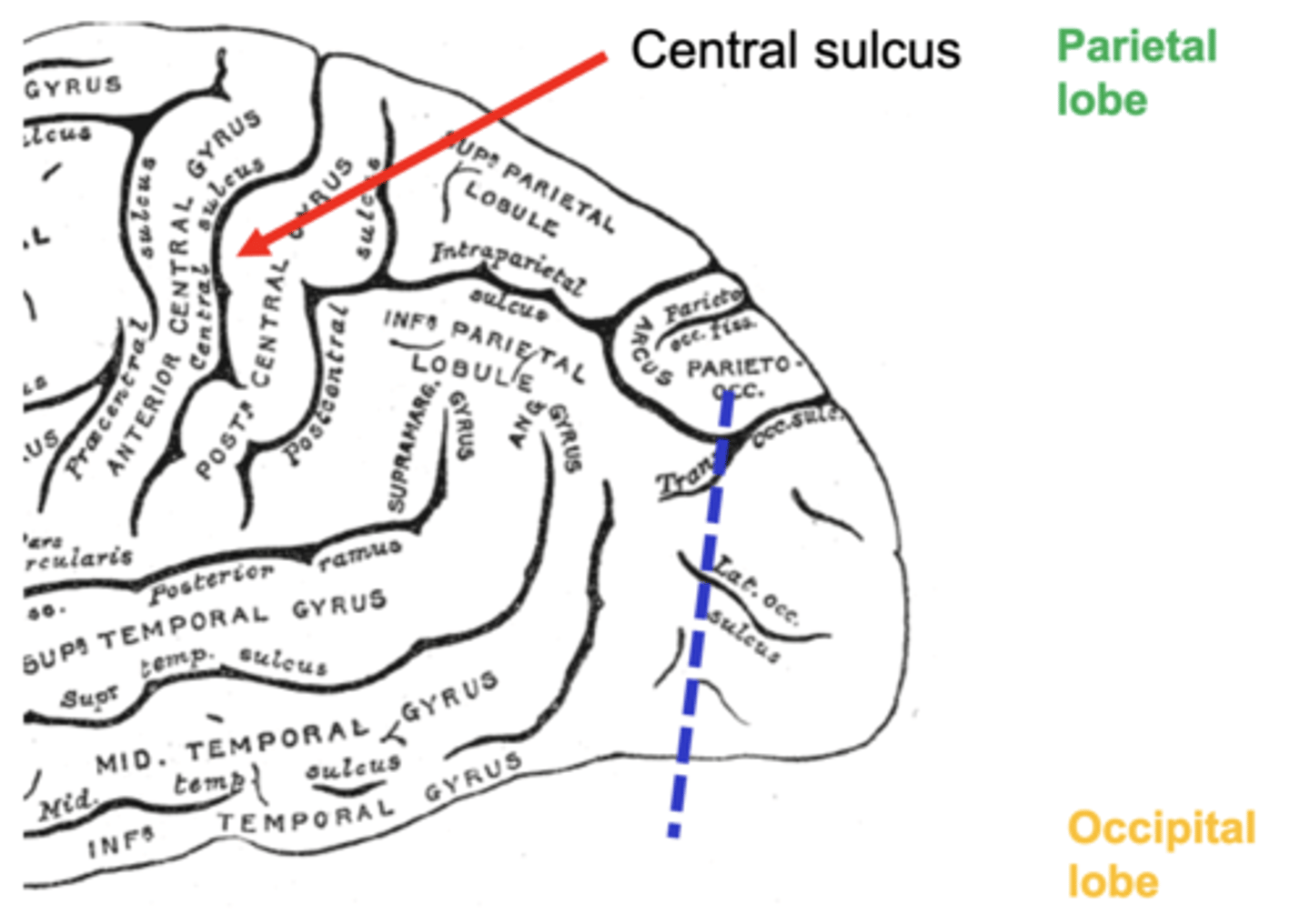
intraparietal sulcus divides the parietal lobe into
superior parietal lobule
inferior parietal lobule
gyri of the inferior parietal lobule
supramarginal gyrus and angular gyrus
main sulcus of the occipital lobe
lunate sulcus
tip of the occipital lobe is called the
occipital pole
2 main sulci of the temporal lobe
superior temporal sulcus
inferior temporal suclus
the sulci of the temporal lobe divide it into what gyri?
superior temporal gyrus
middle temporal gyrus
inferior temporal gyrus
when looking at the brain from the medial surface, we can see which gyrus and sulcus
cingulate gyrus
cingulate sulcus
midline structures of the diencephalon
hypothalamus
epithalamus
how many thalami do we have
2
- one on each side of brain
on the inferior surface we should focus on
parahippocampal gyrus
primary motor cortex function
voluntary control of skeletal muscles
primary somatosensory cortex function
registers and processes sensory information from receptors in the body
premotor cortex and SMA are in charge of
motor planning
damage to the area of broca leads to
Patient cannot speak
Damage to Wernicke's area
leads to difficulty in comprehending speech
cingulate sulcus is responsible for
emotional behavior
visual association area is responsible for
interpretation of visual stimulus
primary auditory cortex is responsible for
receiving auditory stimuli
parahippoccampal area is responsible for
memory