purification and analysis quick flashcards
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
what are primary metabolites
have metabolic functions essential for plant growth & development
carbs, lipids, amino acids, vitamins
compare primary and secondary metabolites
secondary metabolites don’t have apparent functions in growth and development
secondary metabolites aren’t produced in every plant
include terpenoids, special nitrogen metabolite non proteinogenic amino acids, amines, cyanogenic glycosides, glucosinolates and alkaloids and phenolics
what are some methods used in phytochemistey
TLC
gel chromatography
gas chromatography
mass spectrometry
nuclear magnetic resonance
x-ray crystallography
what is extraction based on
based on the different solubility of different molecules in organic solvents or aqeuous phases
explain the solubility of table salt in water
sodium cations and chloride anions become surrounded by water brining the salt in solution
what is the stationary phase
a solid or liquid that is fixed and interacts with the sample in TLC
eg silica gel and alumina
what is the mobile phase
a liquid or gas that carries the sample mixture through the system in TLC
what is the retention factor
distance traveled by sample/ distance traveled by solvent
what is the principle of TLC
compounds have different affinities for the mobile and stationary phases
this affects the speed at which it migrates
what does the speed of the compound travelling depend on
compound is soluble in solvent = travel further up TLC plate
if compound likes stationary phase = not move very far up TLC plate
what can we used for compounds which are not UV active in TLC
chemical stains
how do we purify compoudsn
using column chromatography we separate a chemical by passing it through a column filled with solid stationary phase and liquid mobile pahse
components of the sample based on their polarity and interactions with stationary phase travel through column at different rates and separate
how does mass spectrometry work
step 1: produciton of gas phase ions of compound, basically by electron ionization, molecular ion undergoes fragmentations
step 2-3: ions separated according to mass-to-charge ratio, are detected in proportion to their abundance
step 4: mass spectrum of the molecule is produced
example of mass spectrum
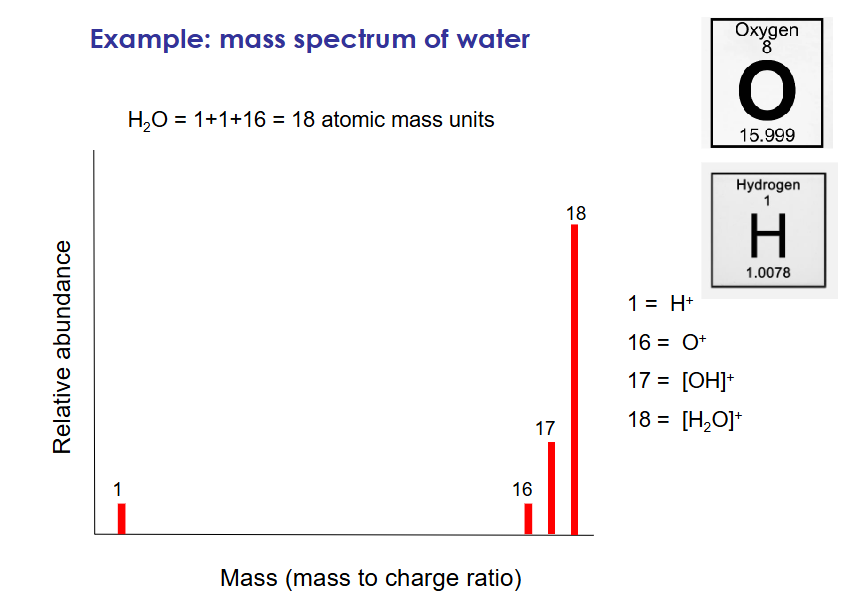
how is crystallography used
can get the structure
based on the analysis of the diffraction patterns that emerge from a sample targeted by a beam like an X-ray
how does crystallography work
X-rya beams shot through crystal of a molecule
crystal causes beam to diffract in a predictable pattern based on their crystal lattice structure
results in diffraction pattern
diffraction caused by electron clouds: higher atomic number = large electron clouds
what can X-ray crystallography be used for
stereochemistry
bond length
distance between atoms
CAN’T REVEAL WHAT ELEMENTS ARE PRESENT
what is infrared spectroscopy
based on absorption measurement of different IR frequenciess
used to detect presence of specific functional groups and other structure features from band poisitions and intensities
what is nuclear magnetic resonance
based on properties of certain nuclei when they’re in a strong magnetic field
information we get is related to atoms, their neighbouring atoms and interaction of atoms far away in a linear chain but brough close together if molecule is flexible
how does NMR work
when nucleus possess a magnetic moment (eg 1H or 13C) and is placed in a strong magnetic field, it spins
what information can we get from NRM
composition of atomic groups in the molecule
info about adjacent atoms
info on molecular dynamics
quantitative info eg atomic rations in a molecule