Introduction to Chemistry and Measurement Concepts
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Chemistry
Science of matter and its changes.
Matter
Anything with mass and occupies space.
Atom
Smallest particle retaining chemical identity.
Molecule
Two or more atoms bonded together.
Periodic Table
Arrangement of elements by atomic number.

Solid
Fixed shape and volume, incompressible.
Liquid
Fixed volume, no fixed shape, incompressible.
Gas
No fixed shape or volume, compressible.
Physical Change
Change in state without altering chemical identity.
Melting
Solid to liquid phase transition, requires energy.
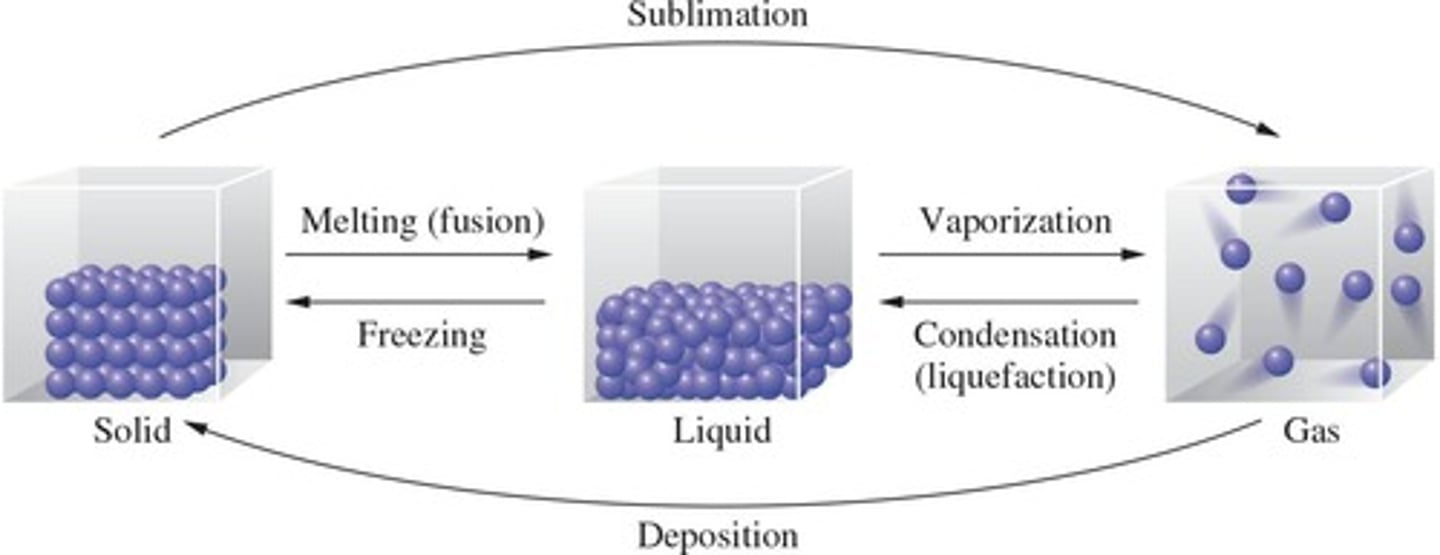
Vaporization
Liquid to gas phase transition, requires energy.
Sublimation
Solid to gas phase transition, requires energy.
Freezing
Liquid to solid phase transition, releases energy.
Condensation
Gas to liquid phase transition, releases energy.
Deposition
Gas to solid phase transition, releases energy.
Physical Properties
Observed without changing chemical identity.
Chemical Properties
Observed by changing chemical identity.
Extensive Property
Depends on amount of matter present.
Intensive Property
Independent of amount of matter present.
Substance
Matter with definite composition and distinct properties.
Element
Composed of one type of atom, cannot be broken down.
Compound
Substance formed from two or more elements chemically bonded.
Mixture
Combination of substances separable by physical means.
Heterogeneous Mixture
Composition is not uniform throughout the mixture.
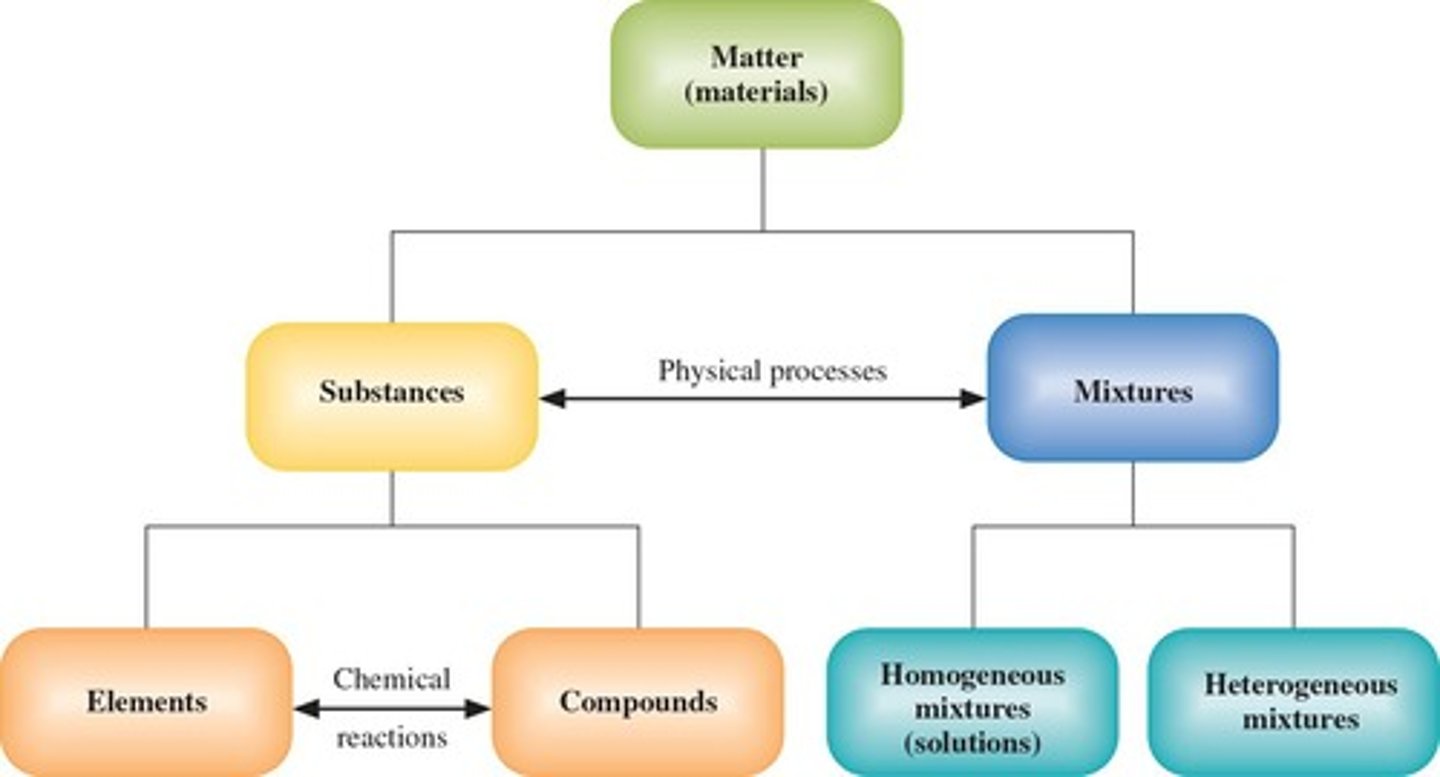
Homogeneous Mixture
Uniform blend of substances throughout the mixture.
Scientific Method
Systematic approach emphasizing observation and experimentation.
Hypothesis
Tentative explanation, often in 'If-then' format.
Experiment
Controlled observation of natural phenomena for reproducibility.
Theory
Broader explanation of widely observed natural phenomena.
Law
Concise statement about fundamental relationships in nature.
Law of Conservation of Mass
Mass is neither created nor destroyed in reactions.
Chemical Reaction
Process where reactants transform into products.
Electronic Balance
Device measuring mass or quantity of substances.
Scientific Notation
Method to express very large or small numbers.
General Expression of Scientific Notation
A × 10^n, where n is an integer.
Significant Figures
Digits in a measurement indicating precision and uncertainty.
Significant Figures Rule 1
All nonzero digits are significant.
Significant Figures Rule 2
Zeroes between nonzero digits are significant.
Significant Figures Rule 3
Placeholding zeroes are not significant.
Significant Figures Rule 4
Trailing zeroes after decimal are significant.
Addition/Subtraction Rule
Round to least decimal places in results.
Significant Figures in Calculations
Rules applied to maintain precision in results.
Precision
Agreement among repeated measurements of the same quantity.
Accuracy
How close a measurement is to the true value.
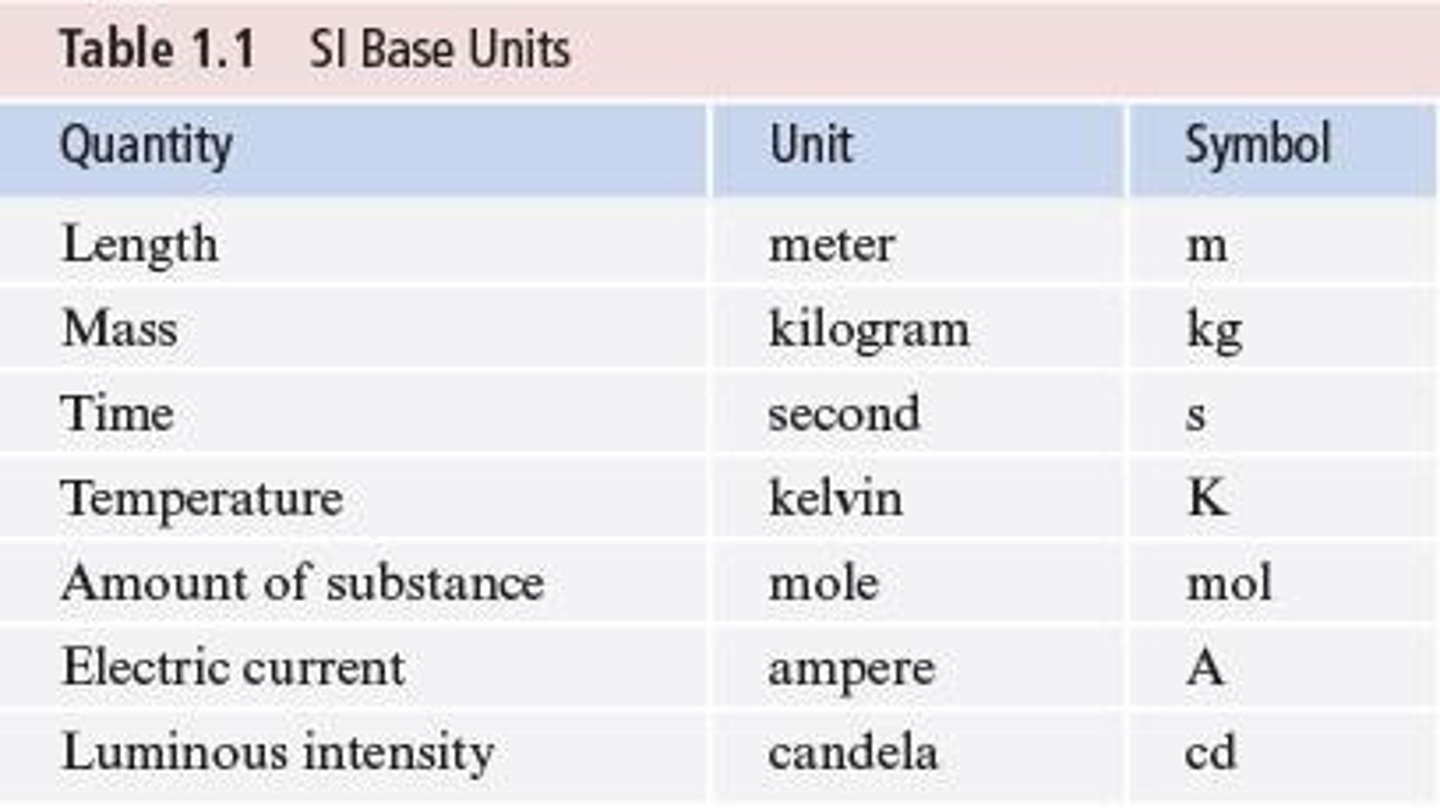
SI Units
International System of Units for scientific measurements.
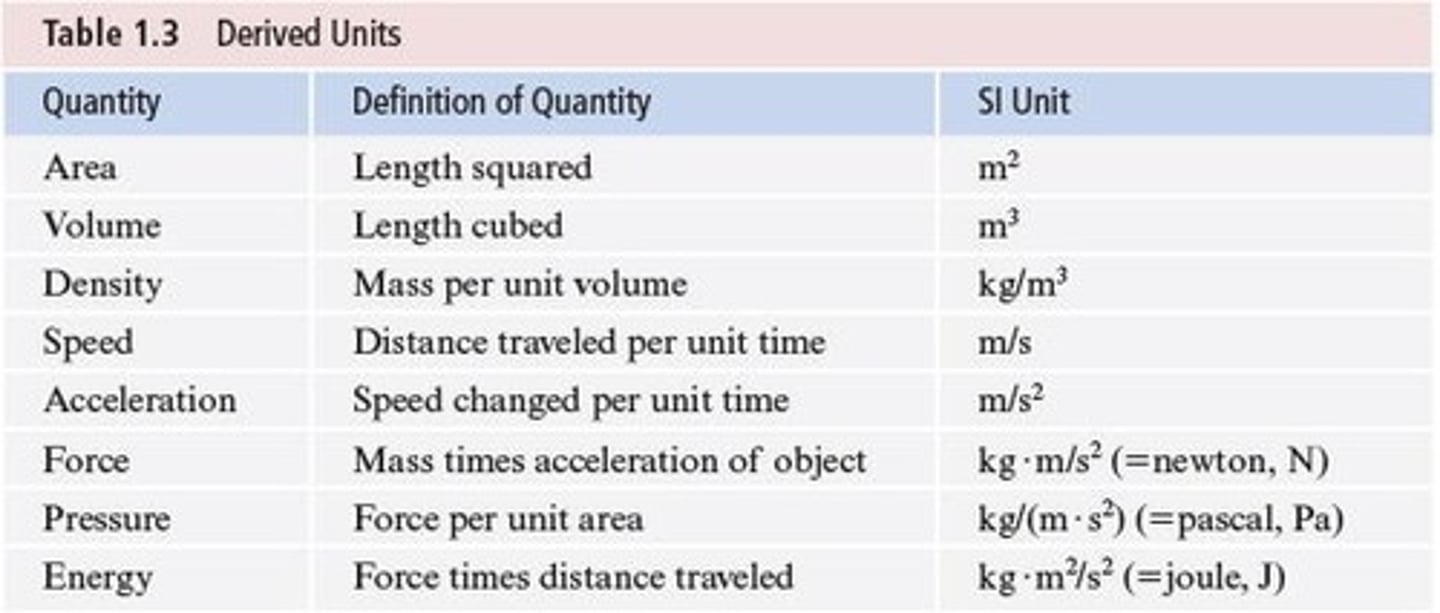
Derived Units
Units formed from base SI units, like density.
Dimensional Analysis
Method for converting units using conversion factors.
Conversion Factor
Exact ratio used to convert between units.
Density
Mass per unit volume, expressed as g/mL or kg/m3.
Volume of Metal
Calculated by water displacement method in a graduated cylinder.
Temperature
Quantitative measure of thermal energy in matter.
Celsius Scale
Temperature scale commonly used outside the USA.
Fahrenheit Scale
Temperature scale primarily used in the USA.
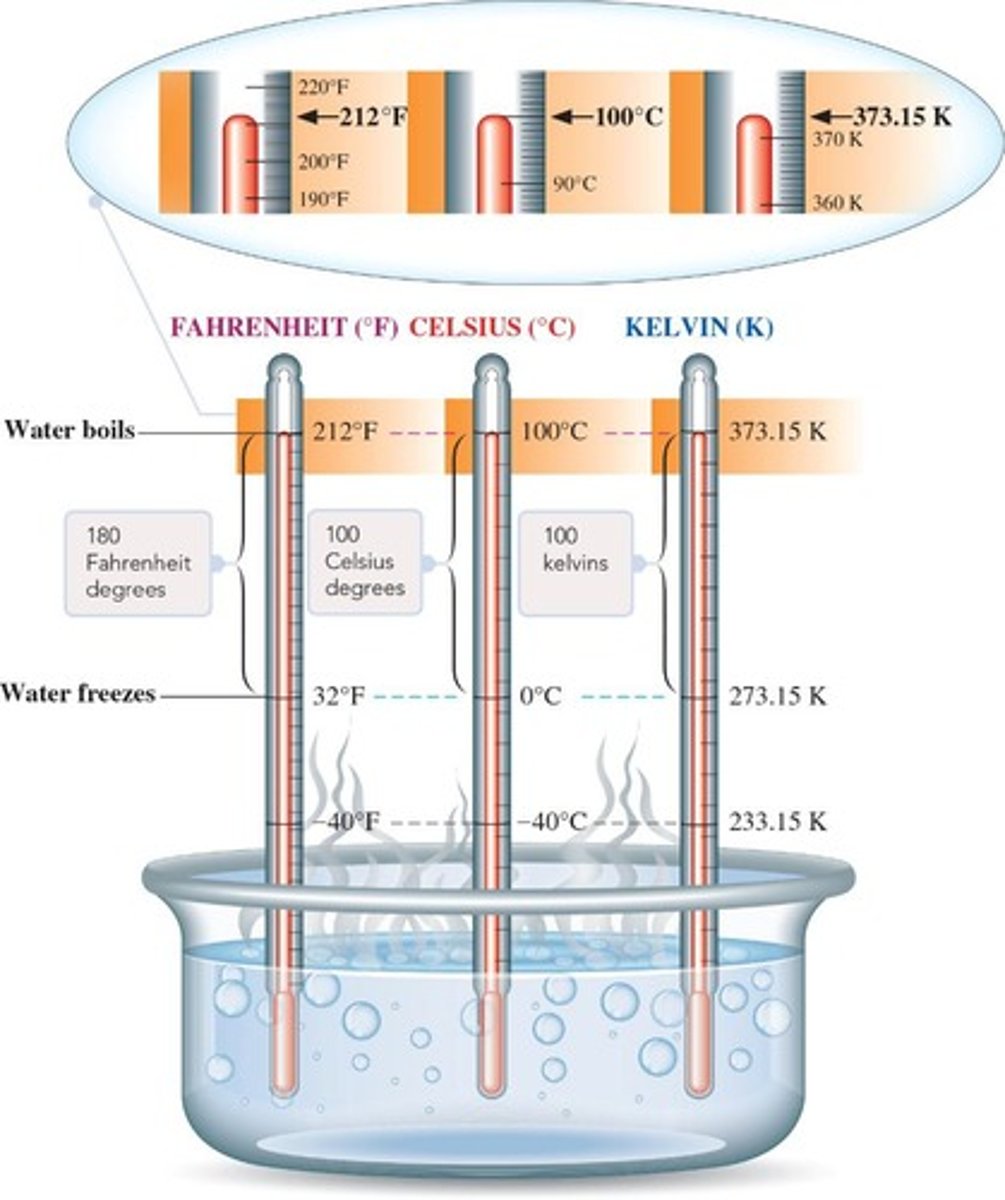
Kelvin Scale
Absolute temperature scale; 0 K is absolute zero.
Absolute Zero
Lowest possible temperature, 0 K or -273.15°C.
Multiplication Rule
Round to the least significant figures in multiplication.
Division Rule
Round to the least significant figures in division.
Mass of Sulfuric Acid
Calculated using density and volume of the liquid.
Temperature Conversion
Equations to convert between Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin.
Water Displacement
Method to measure volume by submerging an object.
Conversion from mL to cm3
1 mL equals 1 cm3, used in density calculations.
Exact Quantities
Numbers that have no uncertainty, used in conversions.