Plant Nutrition and Transport
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
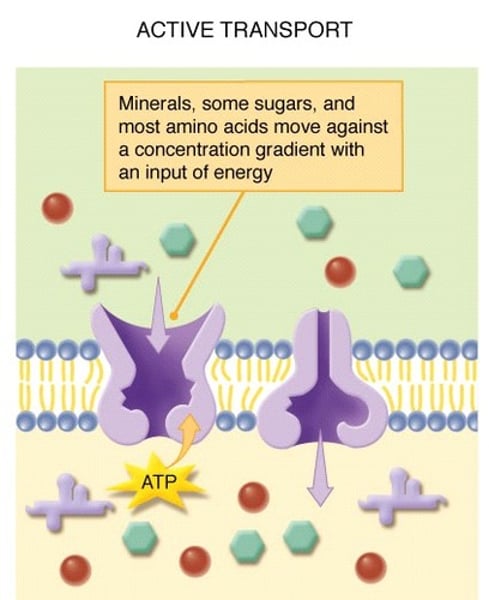
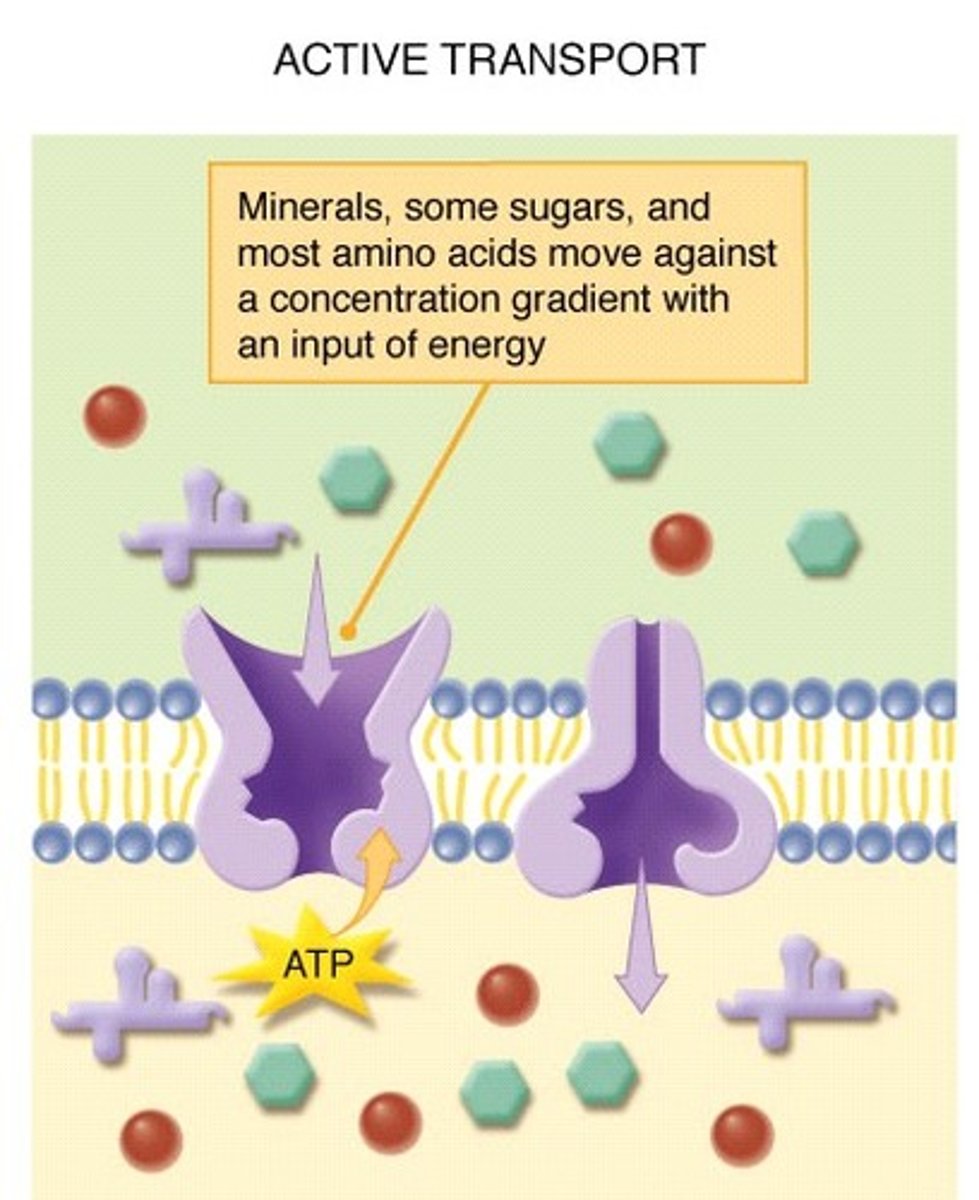
active transport
the movement of materials through a cell membrane using energy
chlorophyll
A green pigment found in the chloroplasts of plants, algae, and some bacteria
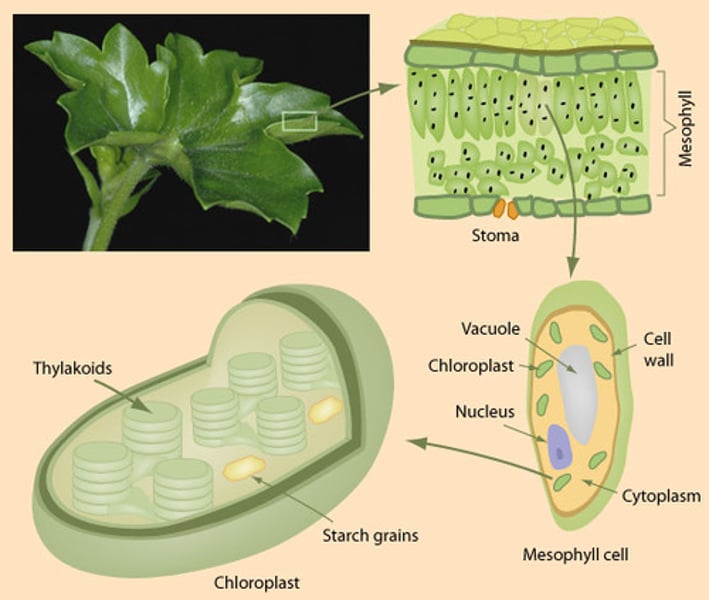
chloroplast
An organelle found in plant and algae cells where photosynthesis occurs
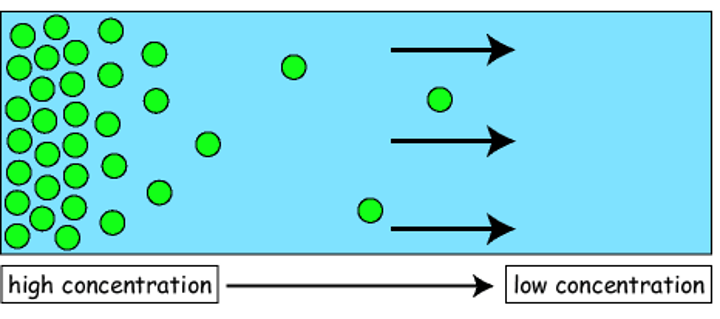
diffuse
When particles spread out from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration.
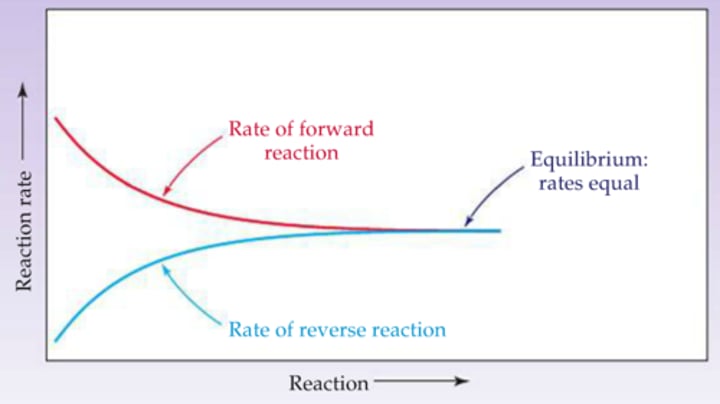
equilibrium
In chemical reactions, a situation where the forward and backward reactions happen at the same rate, and the concentrations of the substances stay the same.
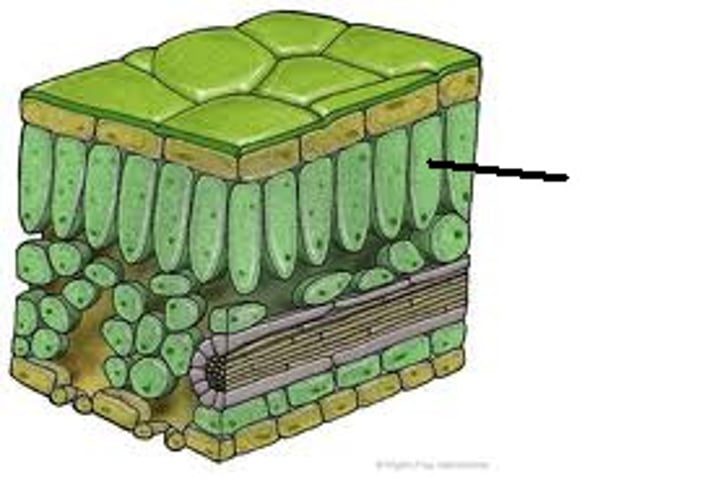
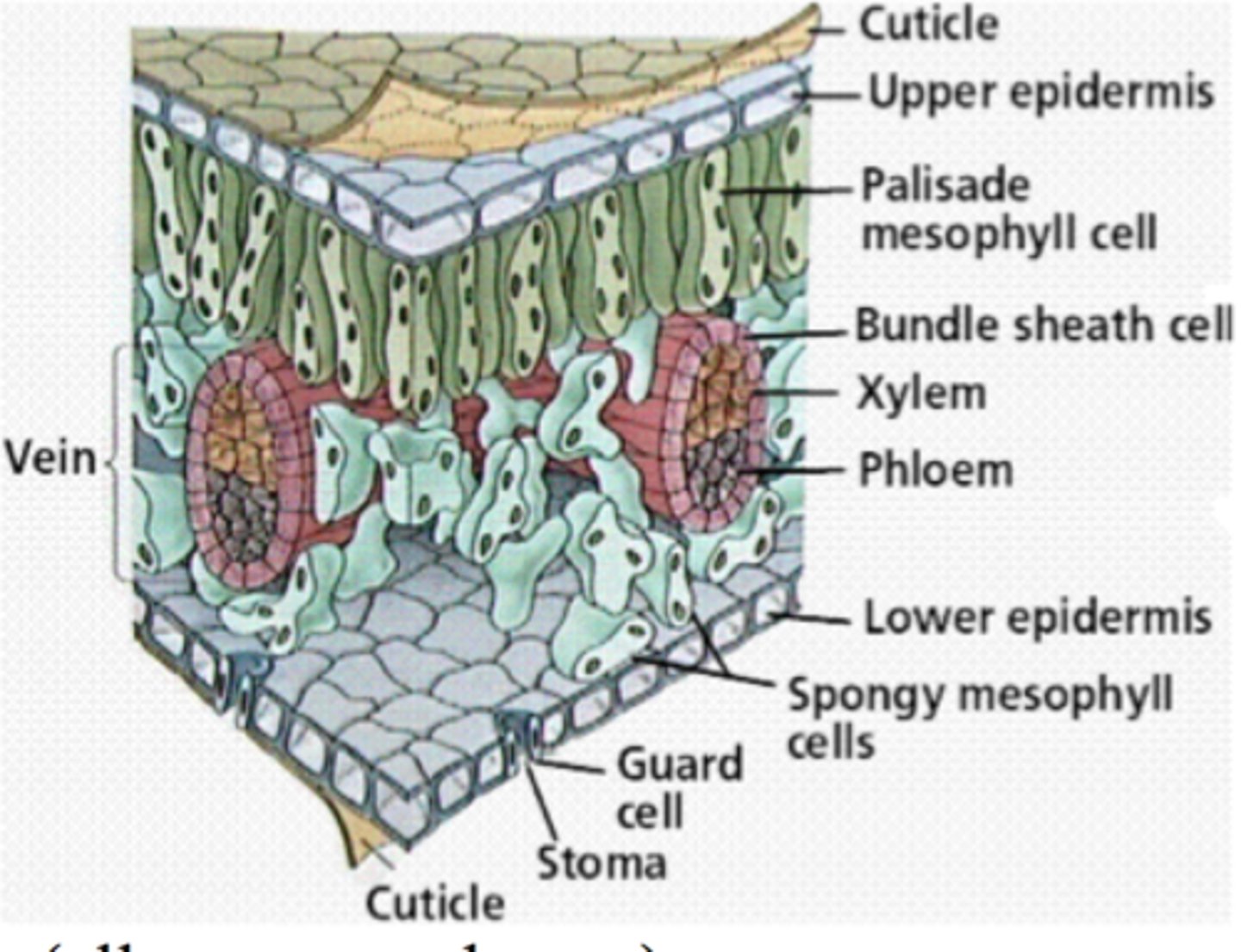
palisade mesophyll
Plant tissue containing closely packed cells in the upper layer of a leaf.
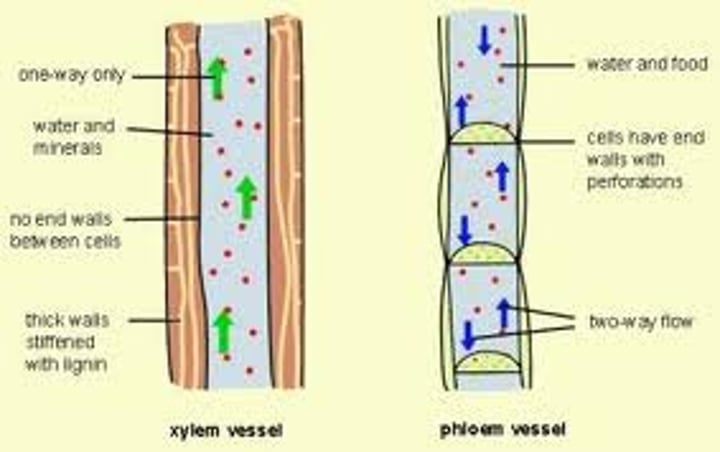
phloem
The tissue in plants that transports the products of photosynthesis, including sugars and amino acids.
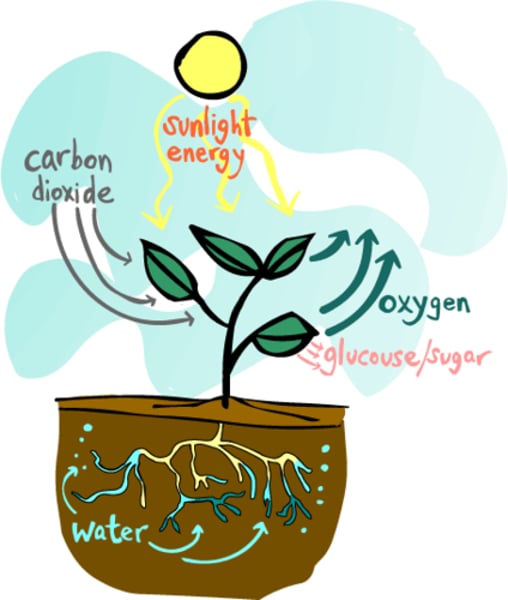
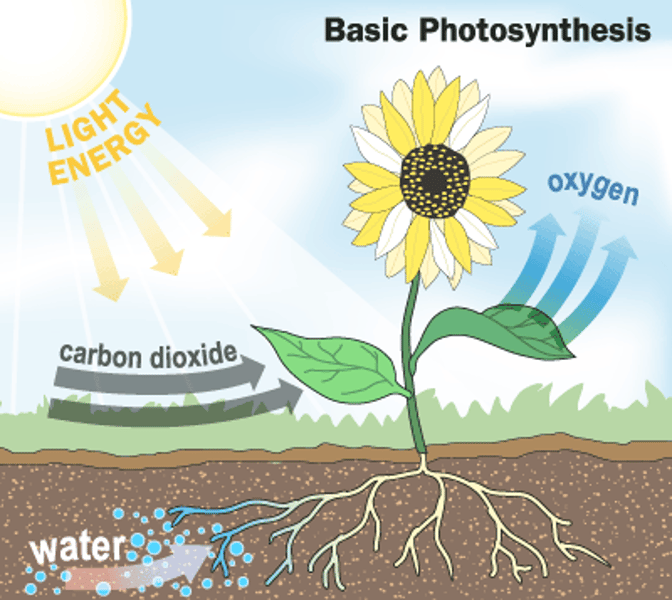
photosynthesis
A chemical process used by plants to make glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water, using light energy. Oxygen is produced as a by-product .
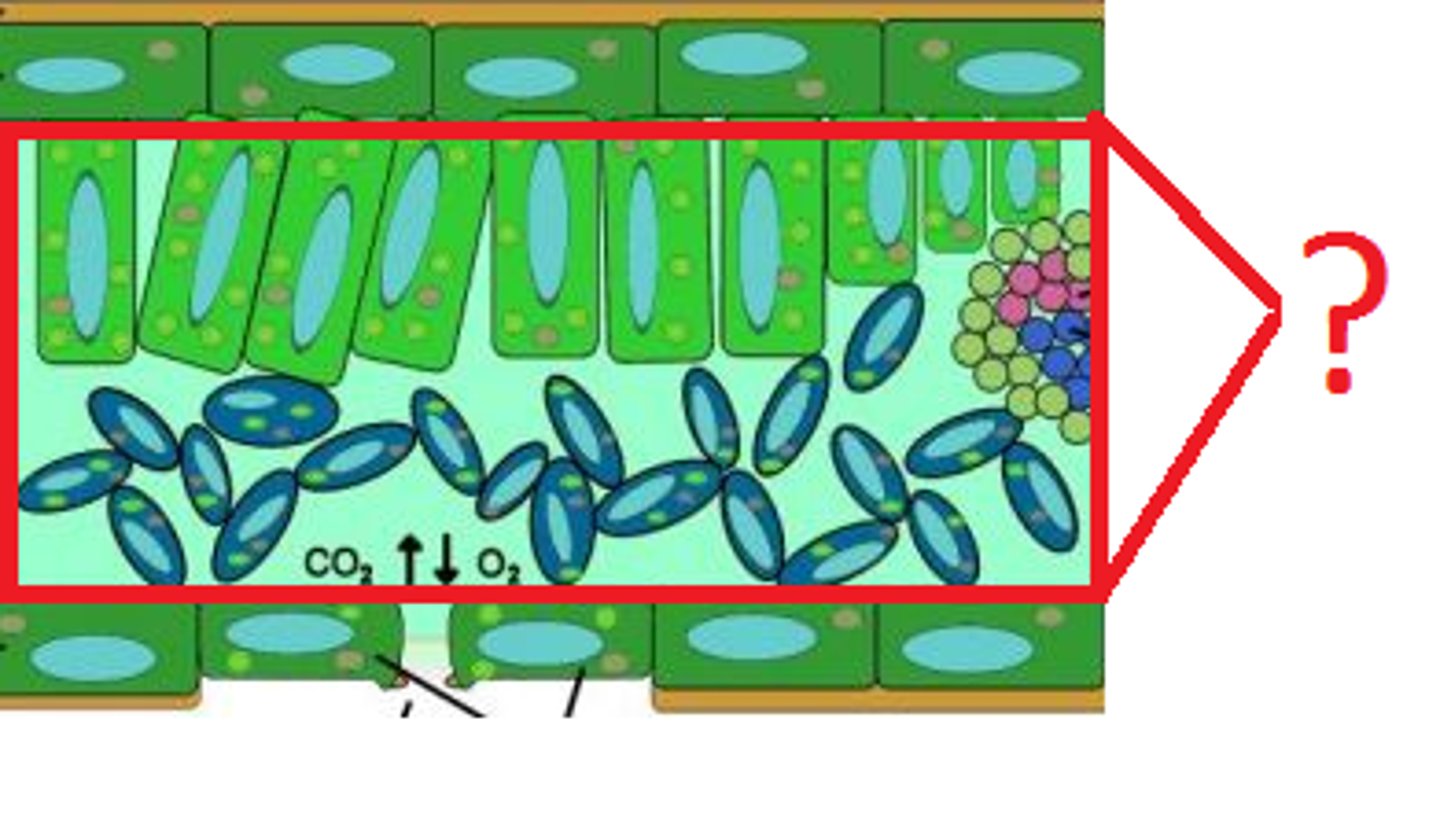
spongy mesophyll
The plant tissue in a leaf which has loosely packed cells and air spaces between them to allow gas exchange.
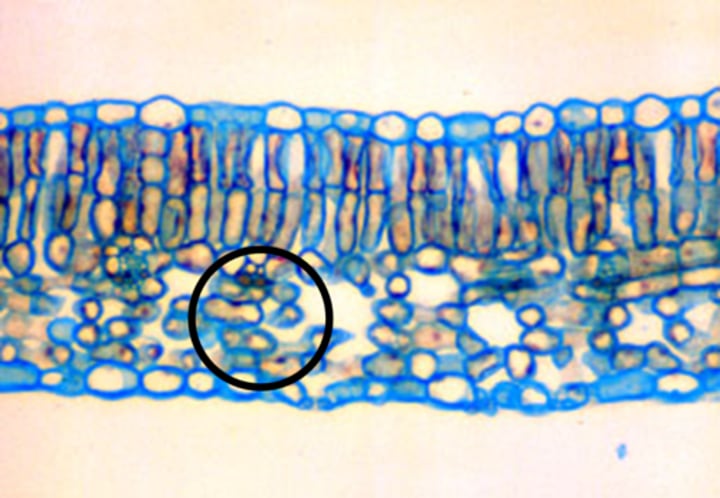
starch
A type of carbohydrate. Plants can turn the glucose produced in photosynthesis into starch for storage, and turn it back into glucose when it is needed for respiration.
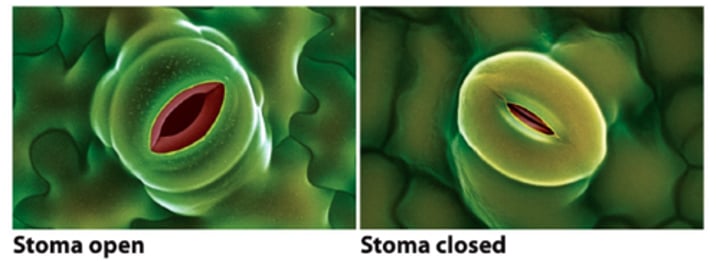
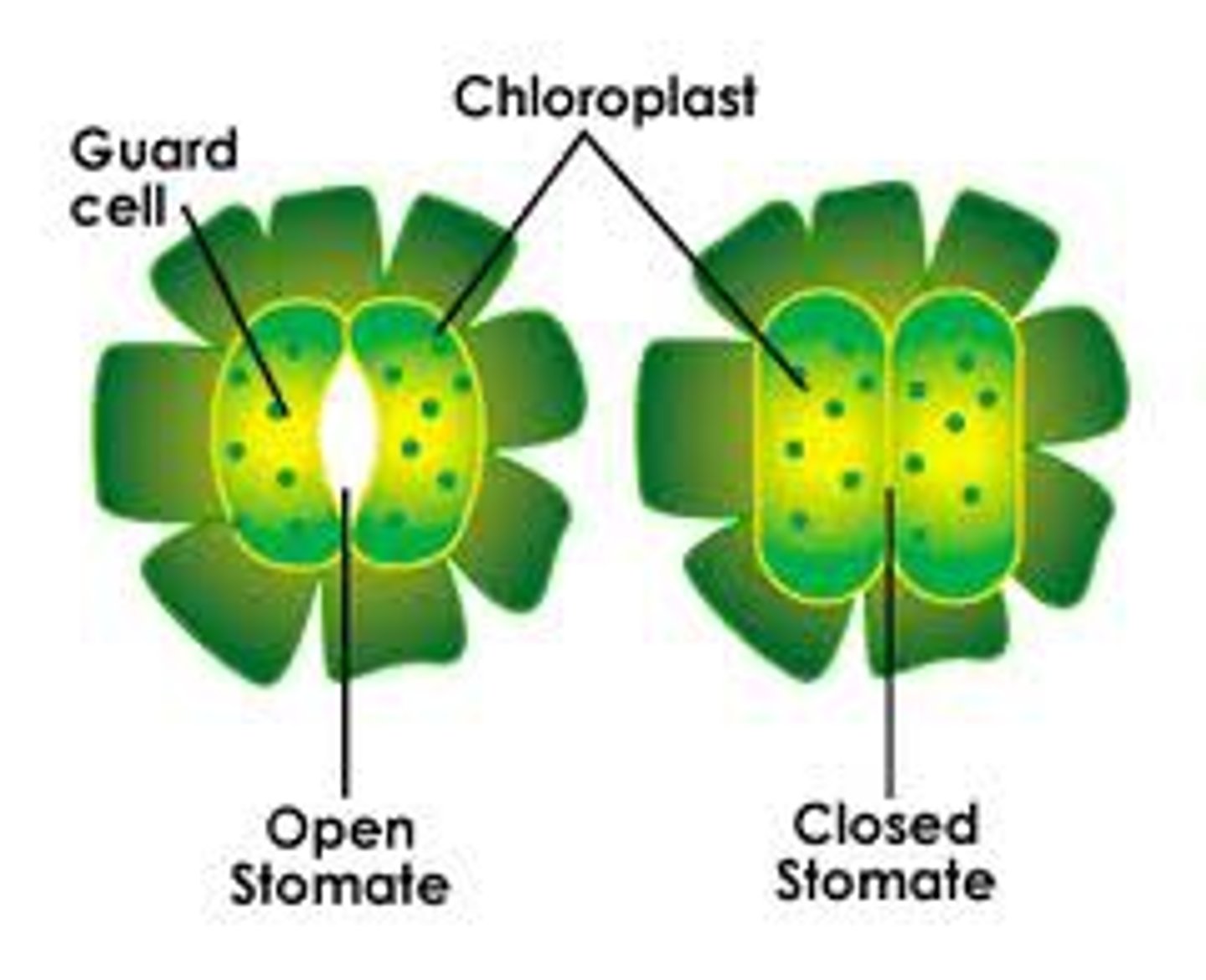
stomata
Tiny holes in the epidermis (skin) of a leaf. They control gas exchange by opening and closing and are involved in loss of water from leaves. Singular is stoma.
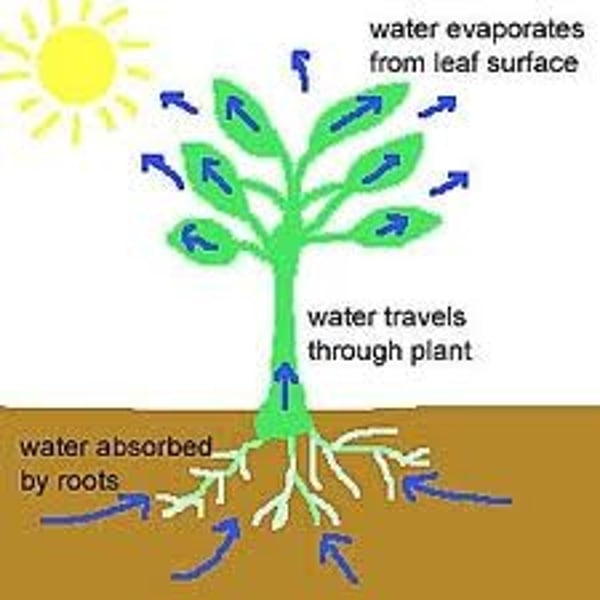
transpiration
The loss of water from leaves by evaporation through the stomata.
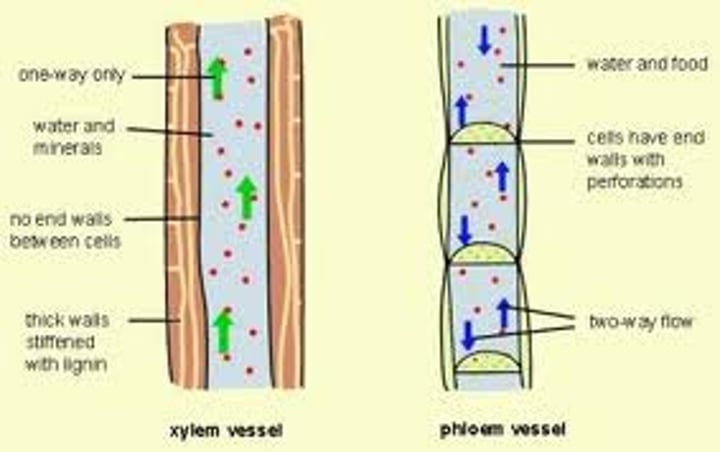
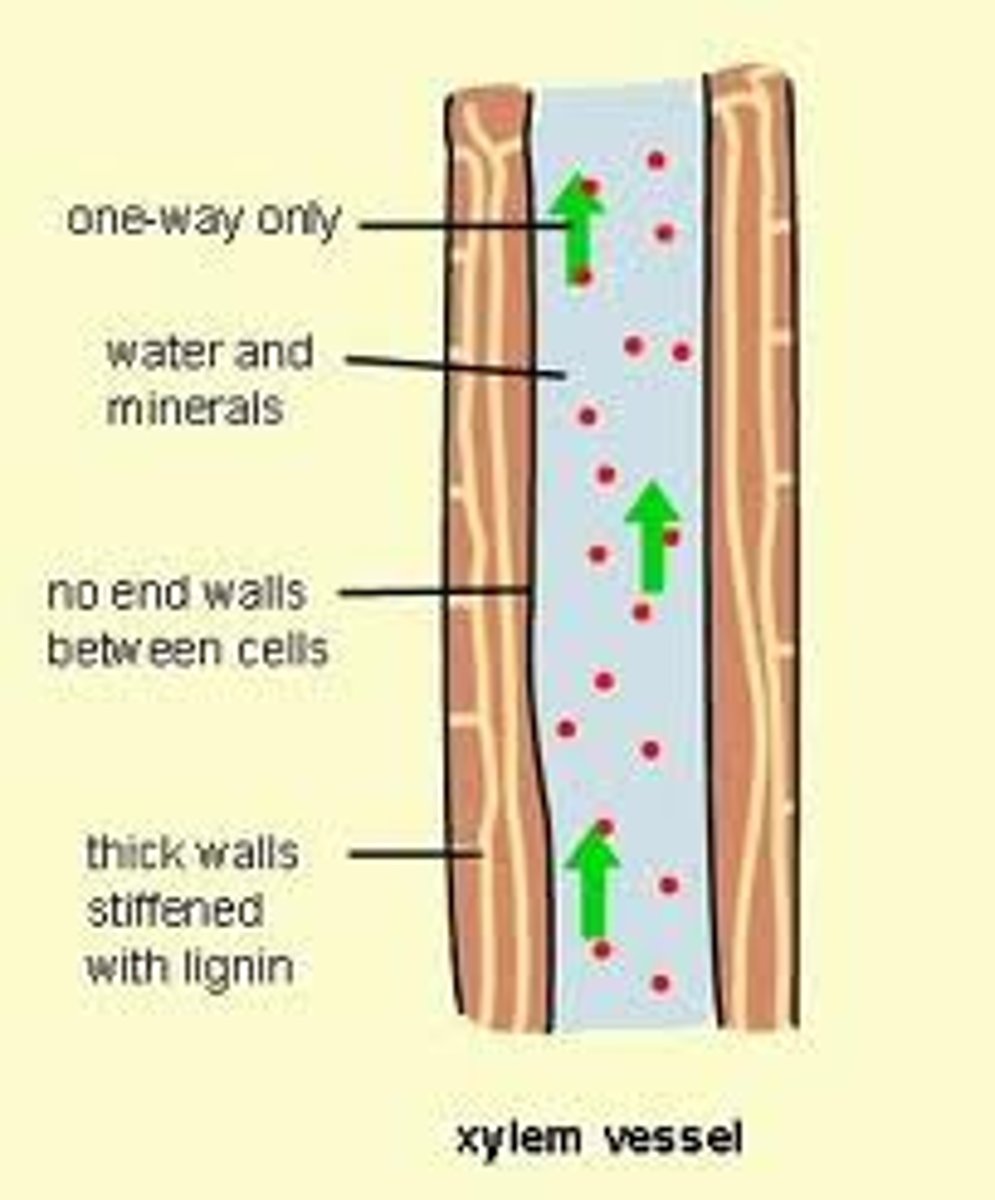
xylem vessels
Narrow, hollow, dead tubes with lignin, responsible for the transport of water and minerals in plants.
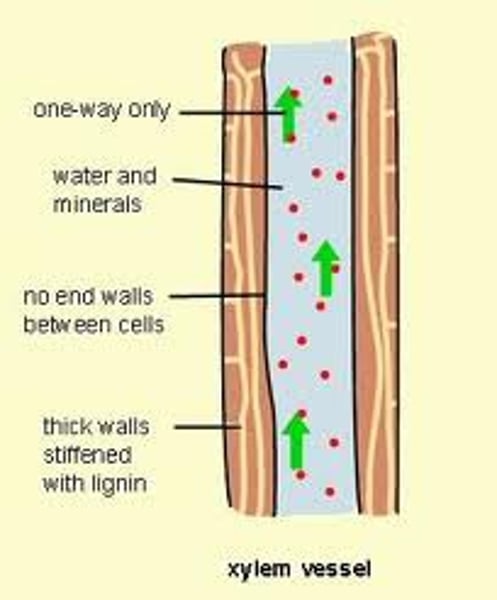
yield
The amount of crops harvested from a certain area.

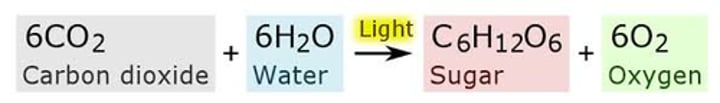
6CO2 + 6H2O → 6O2 + C6H12O6
Photosynthesis balanced equation
Glucose functions in the plant
- Respiration (making ATP)
- Stored as Starch
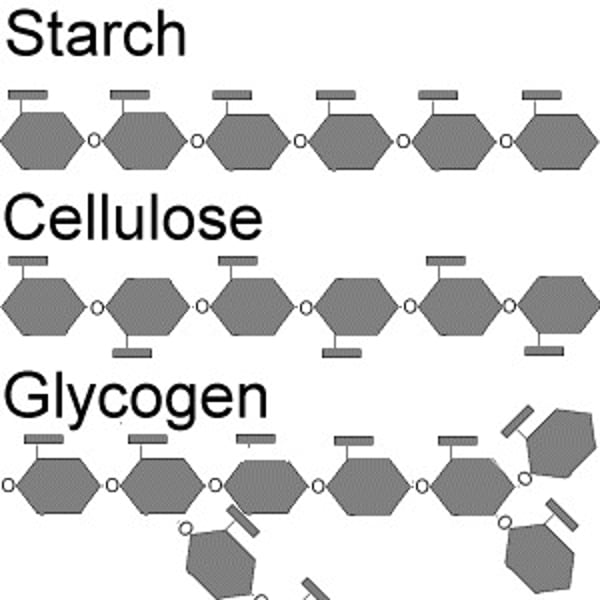
- Turned into Cellulose (cellulose is a polymer of glucose)
- Used to make fats and oils

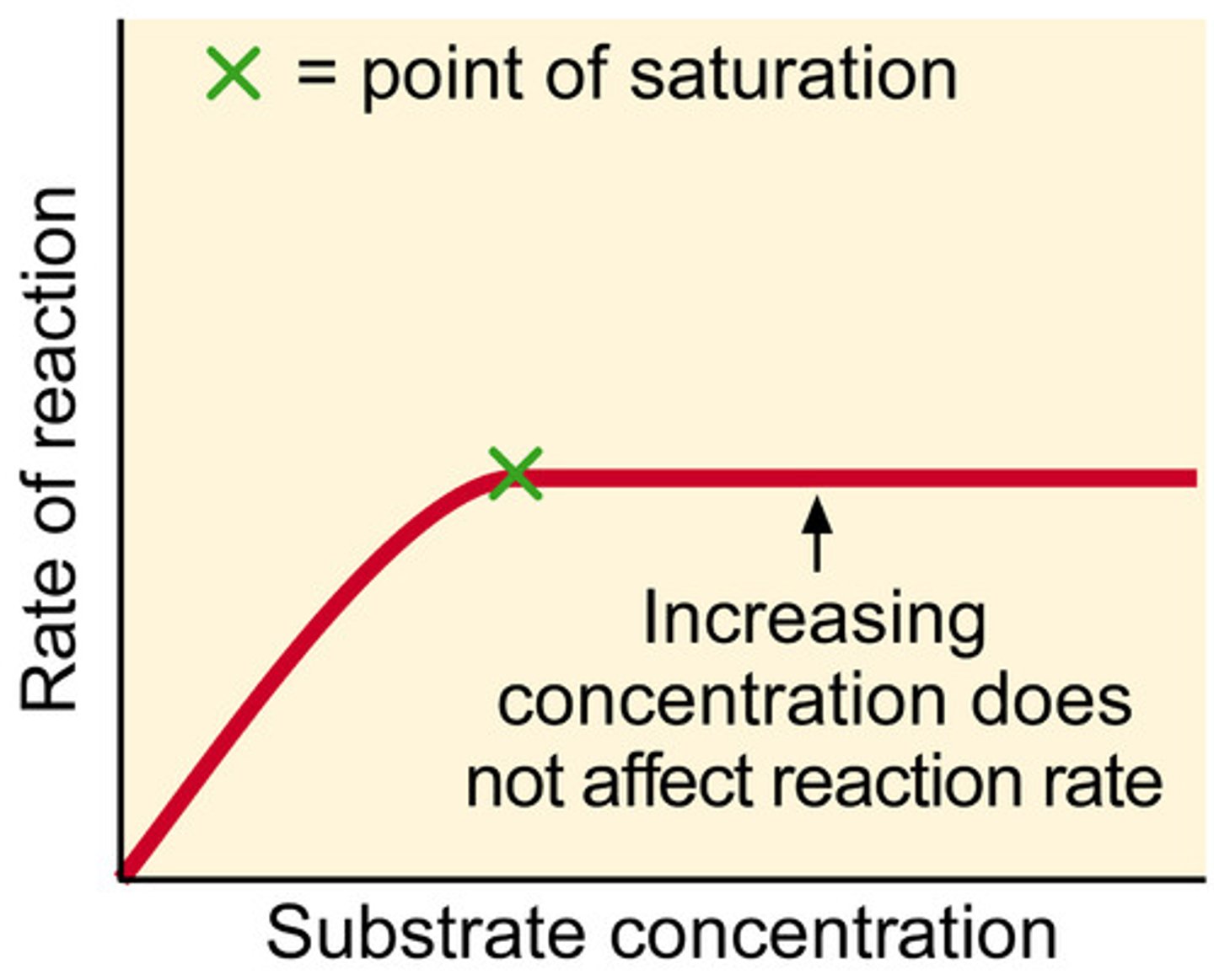
Photosynthesis limiting factors
Temperature, light intensity, carbon dioxide or chlorophyll availability
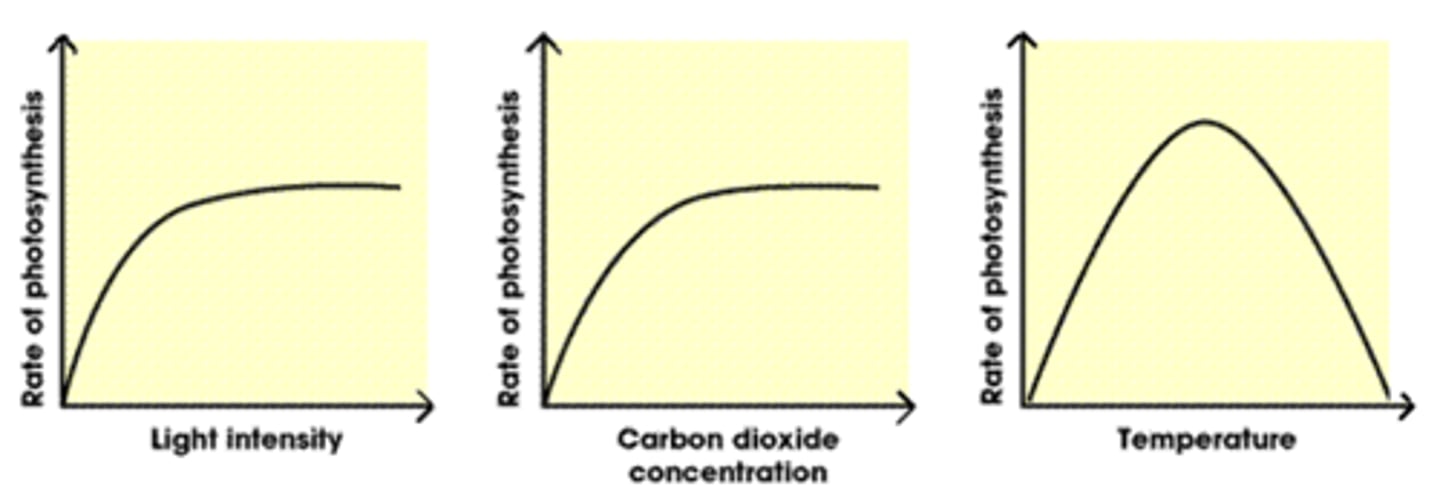
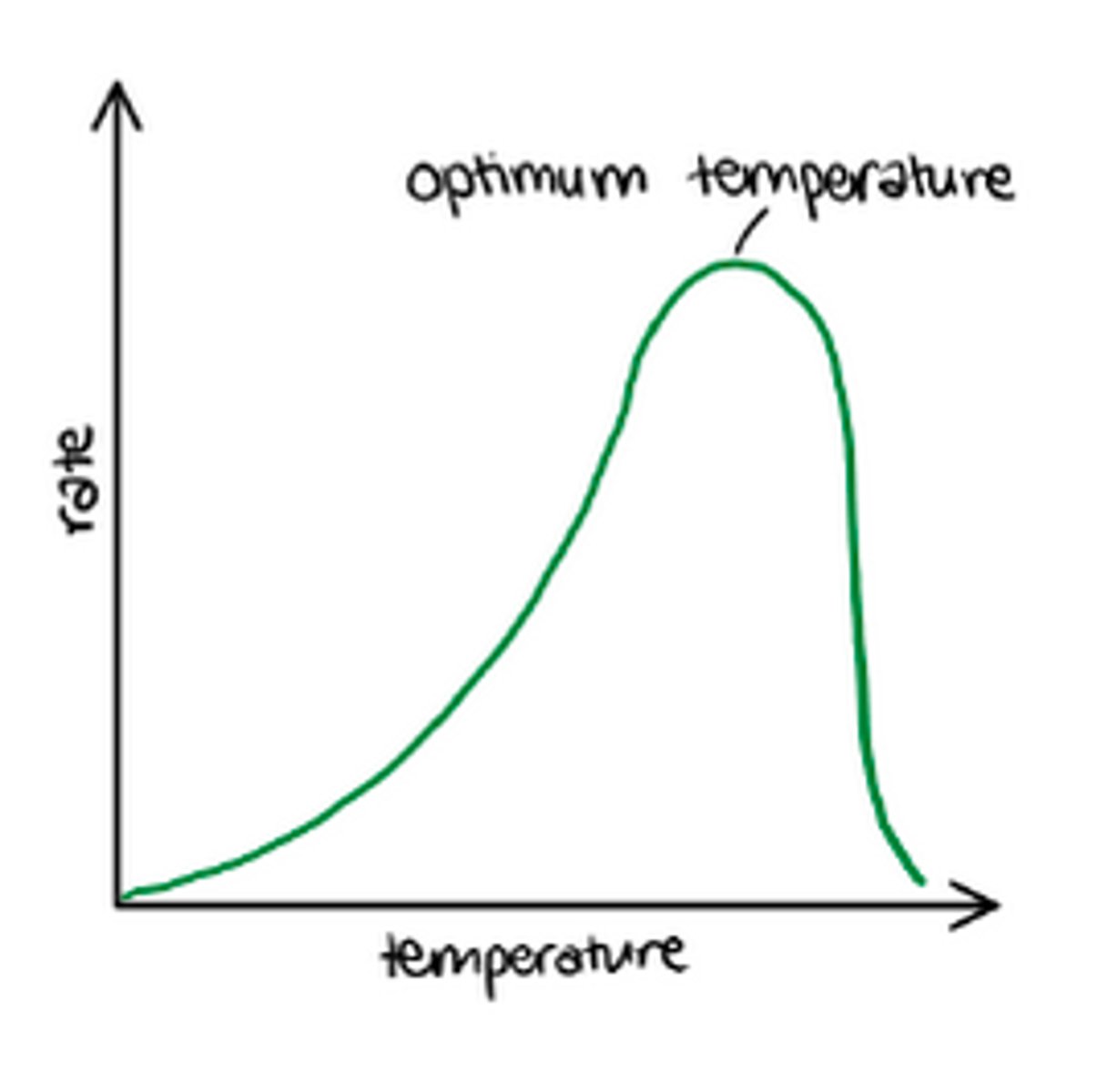
Optimum photosynthesis
Maximum rate of photosynthesis
plateau
When the graph line goes flat (horizontal), no increase in y.
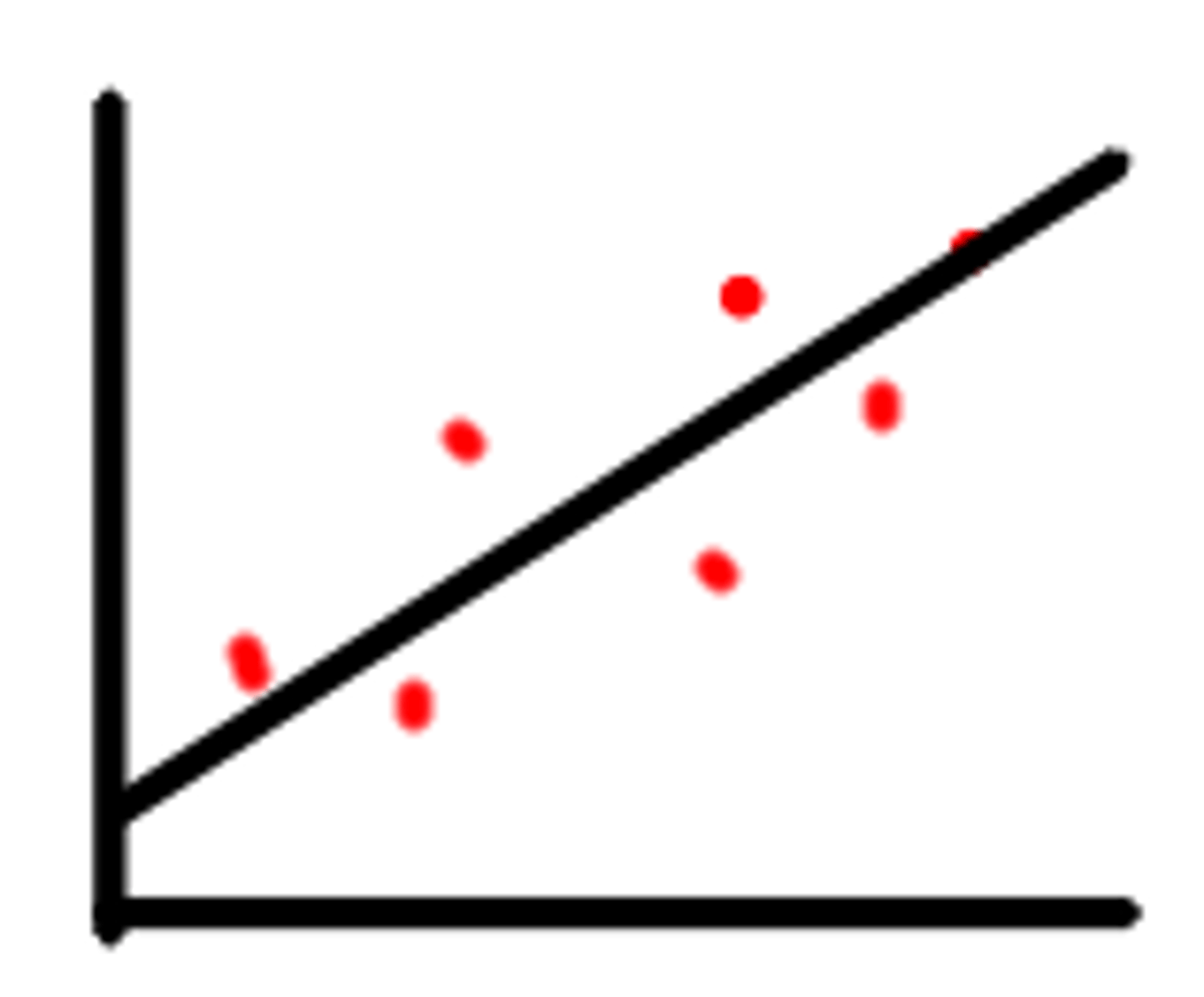
positive correlation
as one increases, the other increases
Cuticle
waxy layer on the outer surface of the epidermis of leaves and stems
guard cells
open and close stomata
Nitrate
used to make amino acids for use in plant proteins
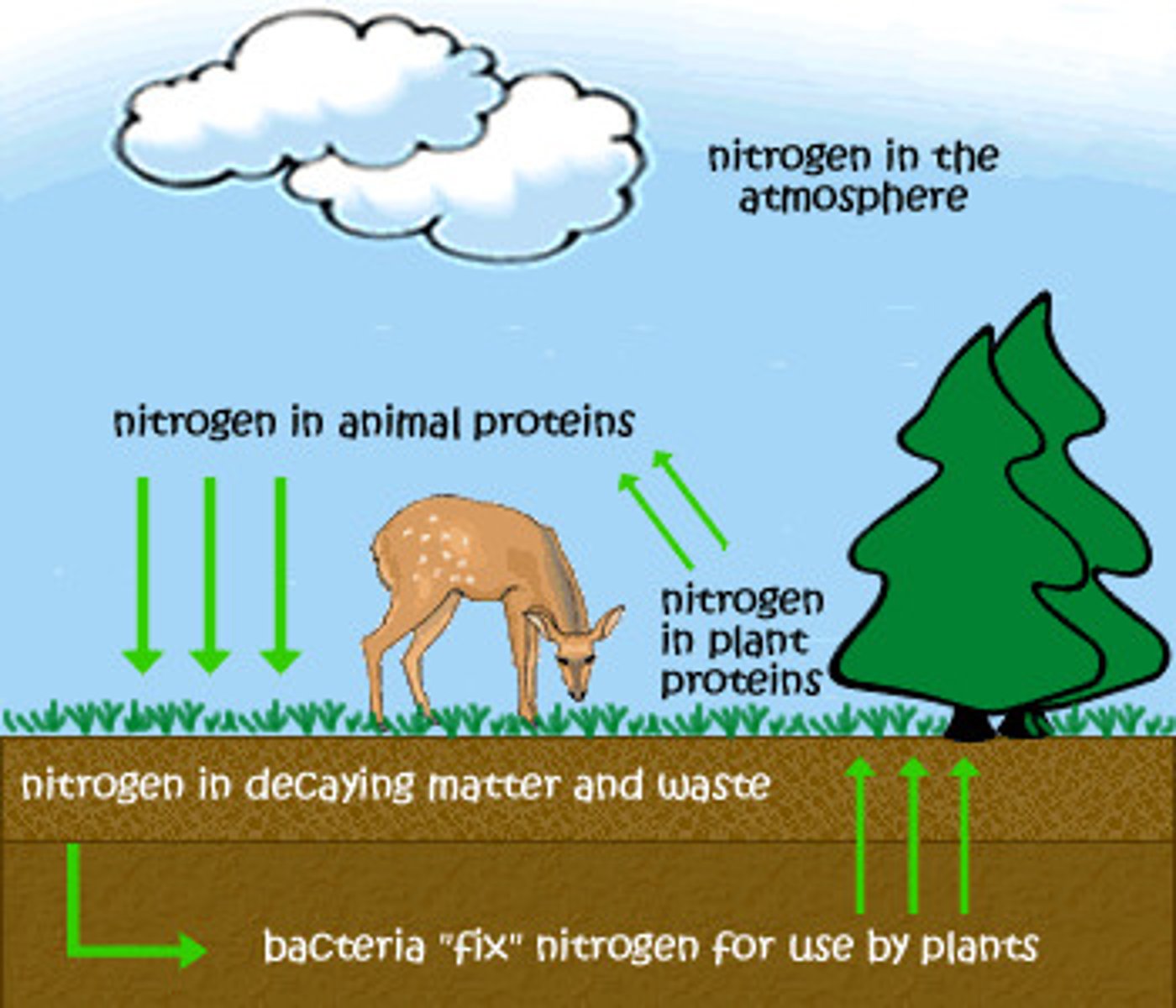
Magnesium
Forms part of the chlorophyll molecule
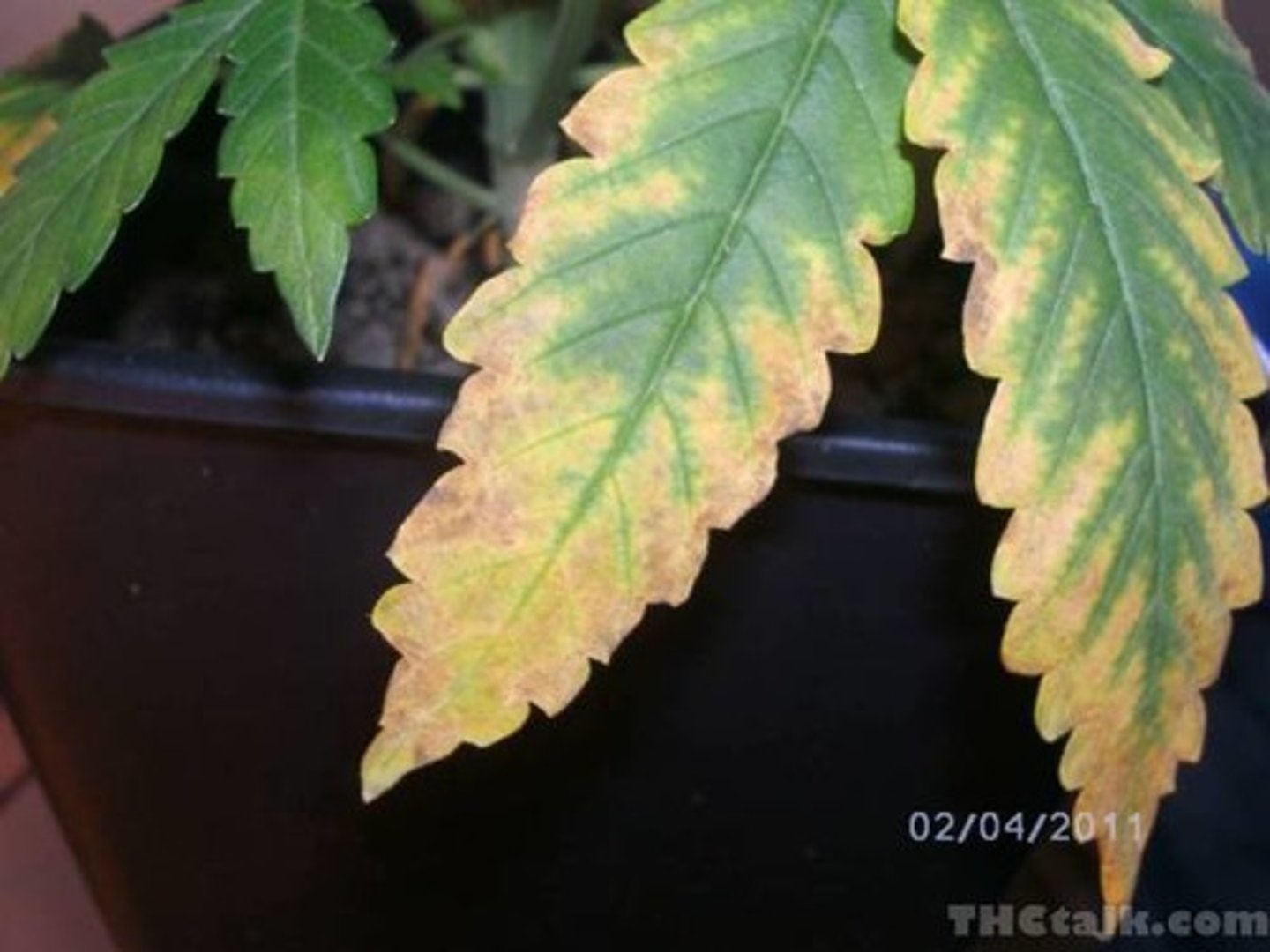

Potassium
Essential for cell membranes
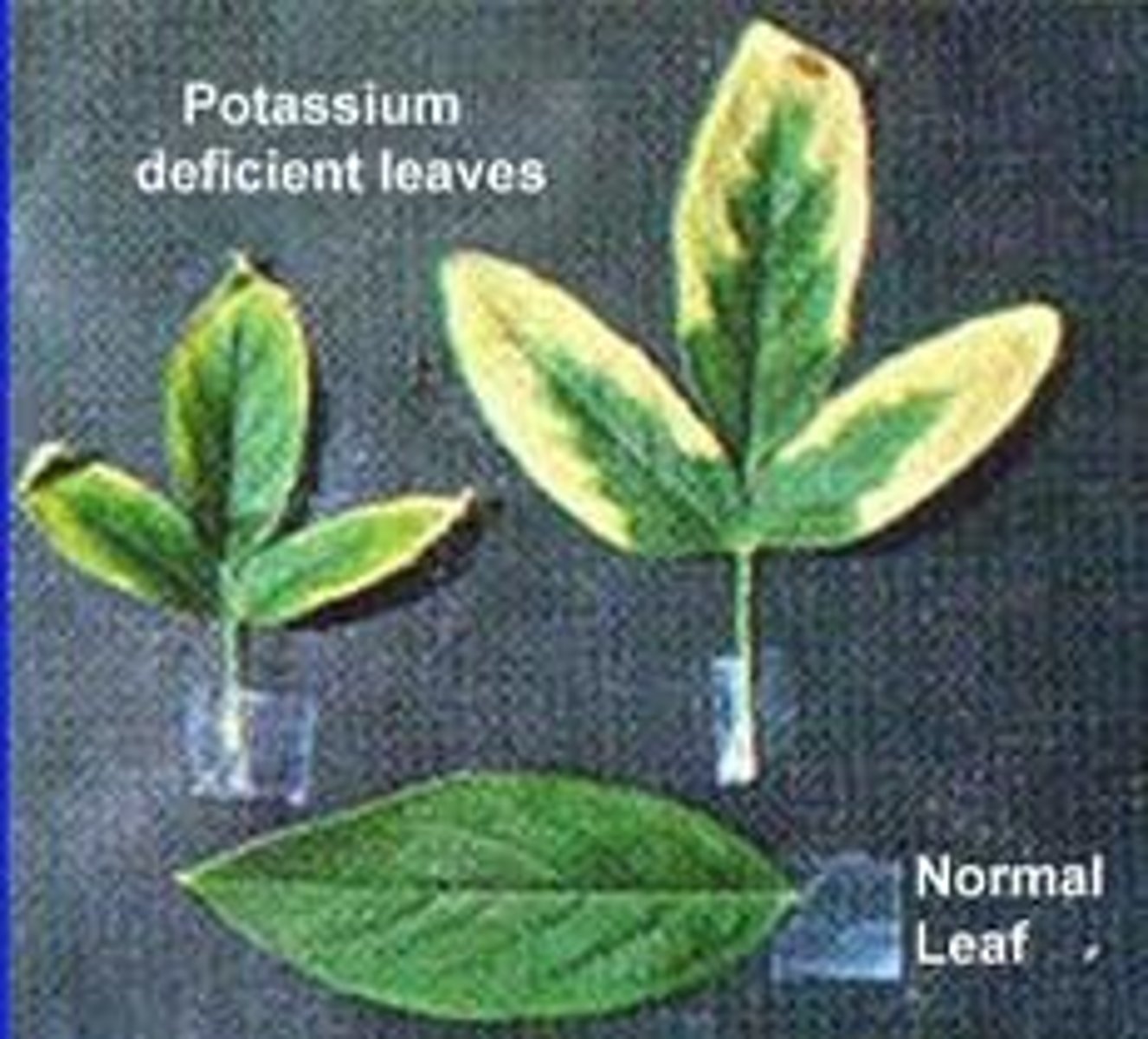

Phosphate
Essential part of DNA and cell membranes
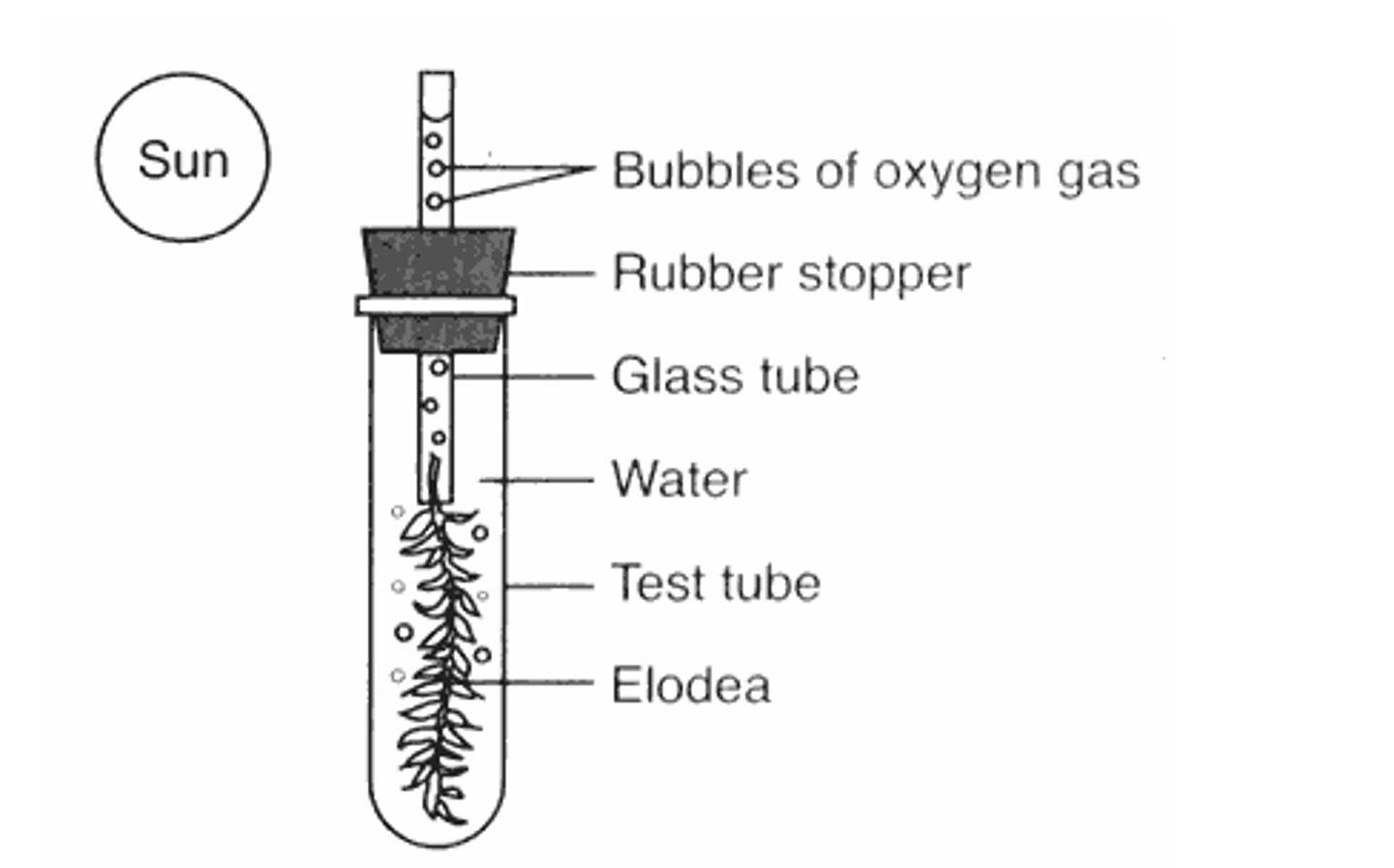
Oxygen bubbles
Can be collected or counted to indicate the speed of photosynthesis
Iodine
Test for starch, turns from brown to black.
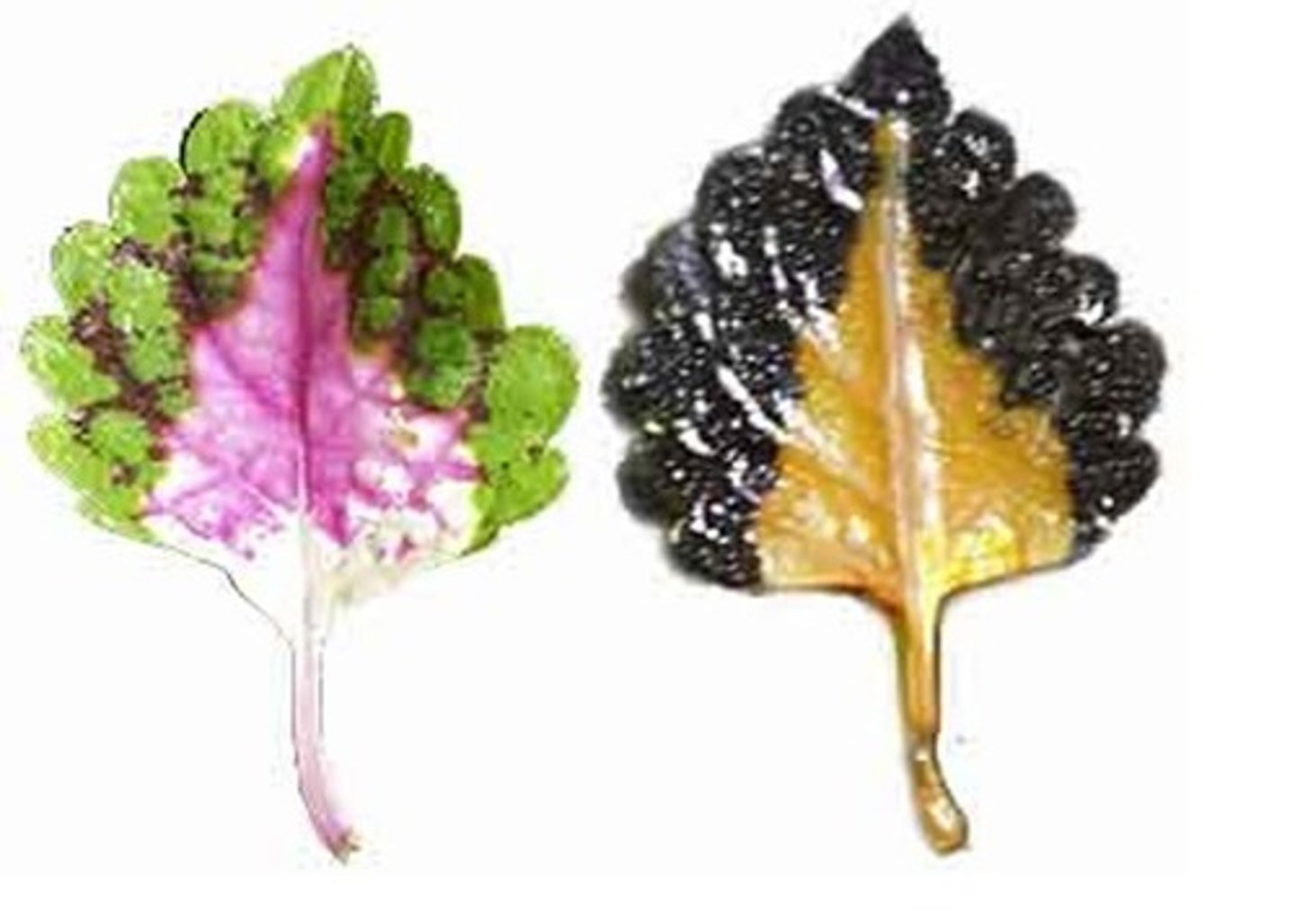

Ethanol
boil leaves in ethanol before conducting the iodine test

Limewater
A chemical that goes cloudy when carbon dioxide is bubbled through it.
diffusion distance
the greater the distance over which diffusion must occur, the longer it takes
Unicellular
Made of a single cell
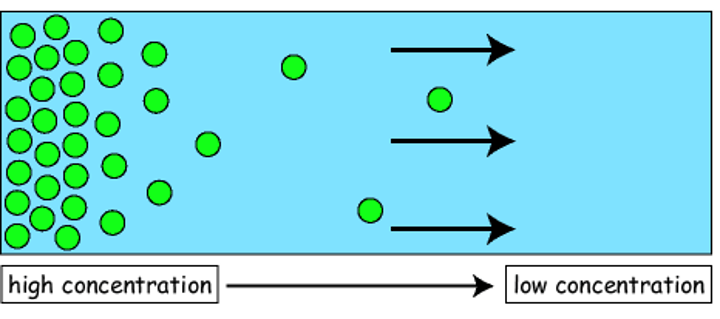
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Multicellular
Made up of more than one cell.

amino acids
The building blocks that make up a protein molecule.
capillary tube
Glass tubing which is very narrow inside.

cohesive
Able to stick together.

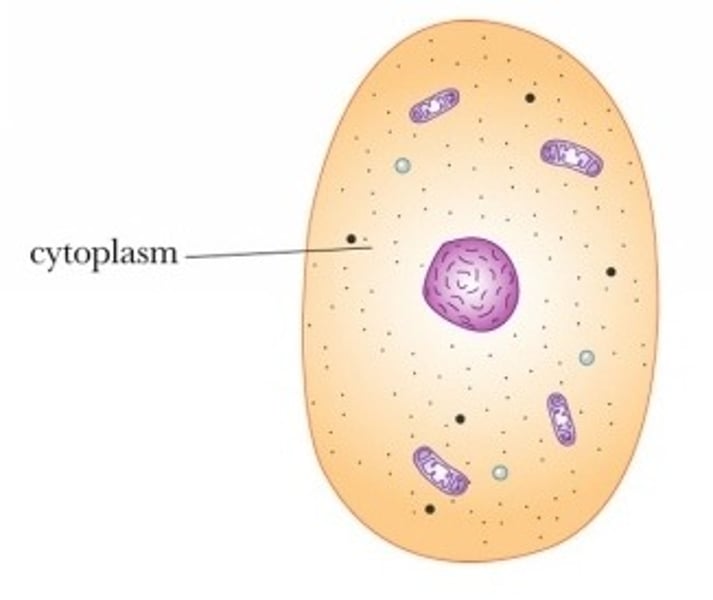
cytoplasm
The liquid and organelles (not including the nucleus).
evaporation
The process in which a liquid changes state and turns into a gas. This cools a surface.

impermeable
A substance which fluids are unable to pass through.

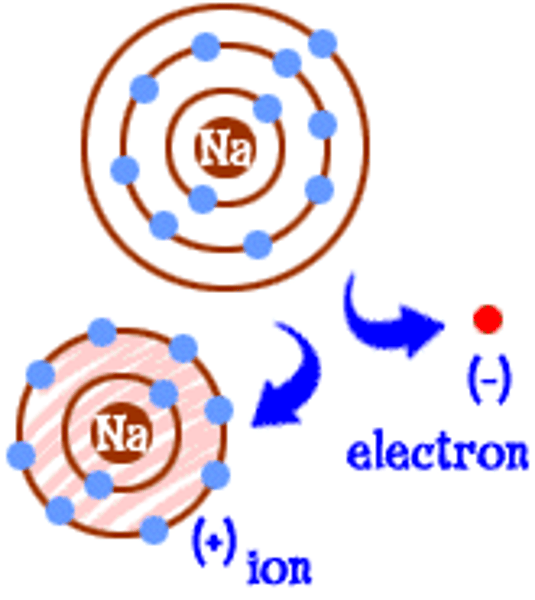
ion
Electrically charged particle, formed when an atom or molecule gains or loses electrons.
mass
The amount of matter an object contains. Mass is measured in kilograms (kg) or grams (g).

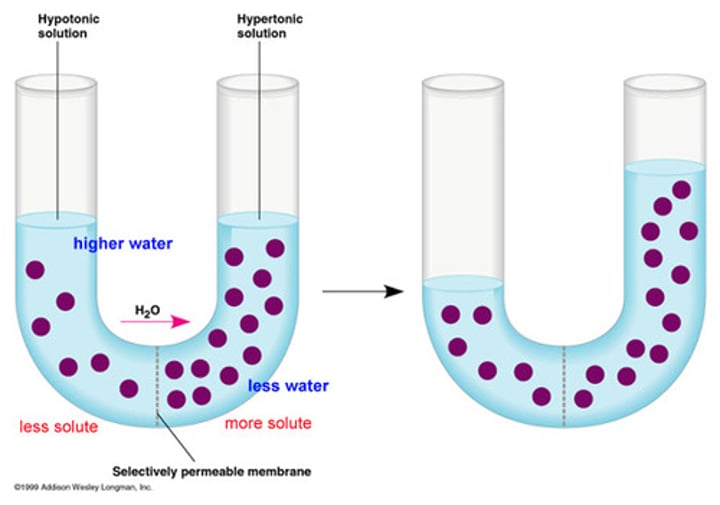
osmosis
The movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from a region of higher water concentration to a region of lower water concentration.
phloem
The tissue in plants that transports the products of photosynthesis, including sugars and amino acids.
photosynthesis
A chemical process used by plants to make glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water, using light energy. Oxygen is produced as a by-product of photosynthesis. Algae subsumed within plants and some bacteria are also photosynthetic.
water potential
Mmeasure of the tendency of water molecules to move from one place to another. During osmosis, water moves through a partially permeable membrane from high water potential (low solute concentration) to low water potential (high solute concentration).
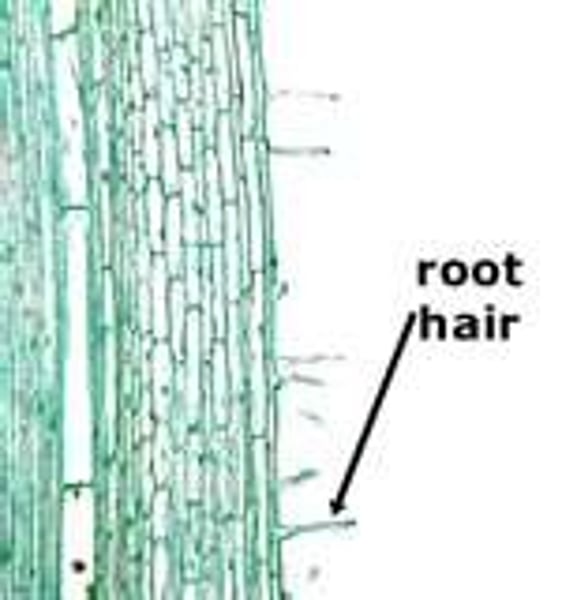
root hair cell
A specialised cell that increases the surface area of the root epidermis to improve the uptake of water and minerals.
stomata
Tiny holes in the epidermis (skin) of a leaf. They control gas exchange by opening and closing and are involved in loss of water from leaves. Singular is stoma.
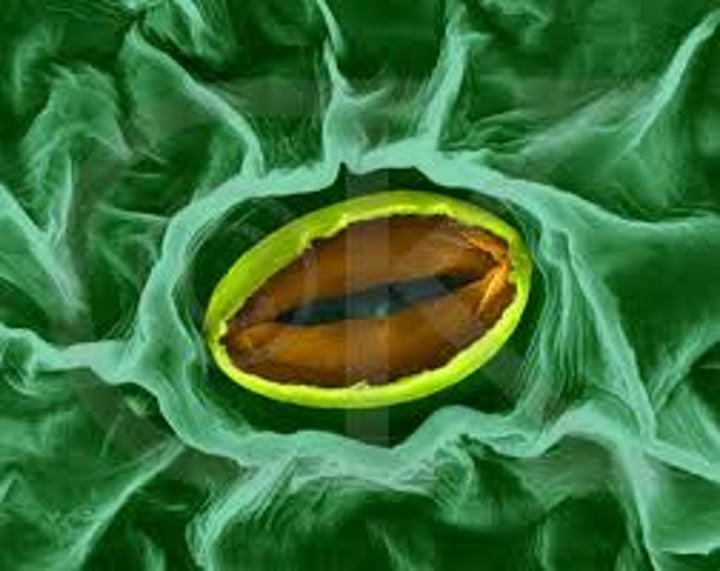
translocation
The transport of dissolved material within a plant.
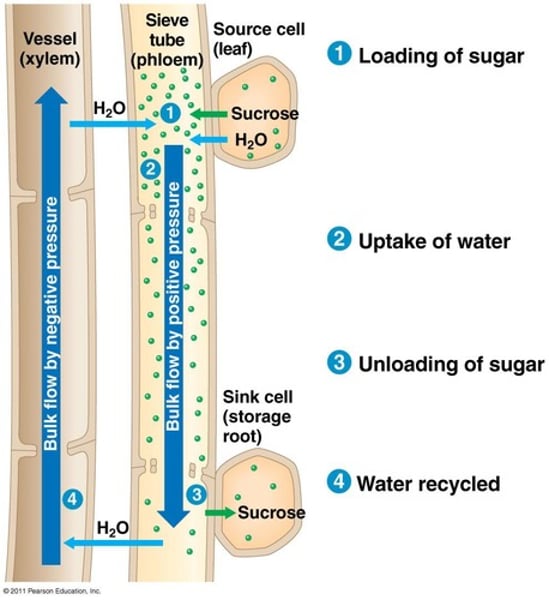
transpiration
The loss of water from leaves by evaporation through the stomata.
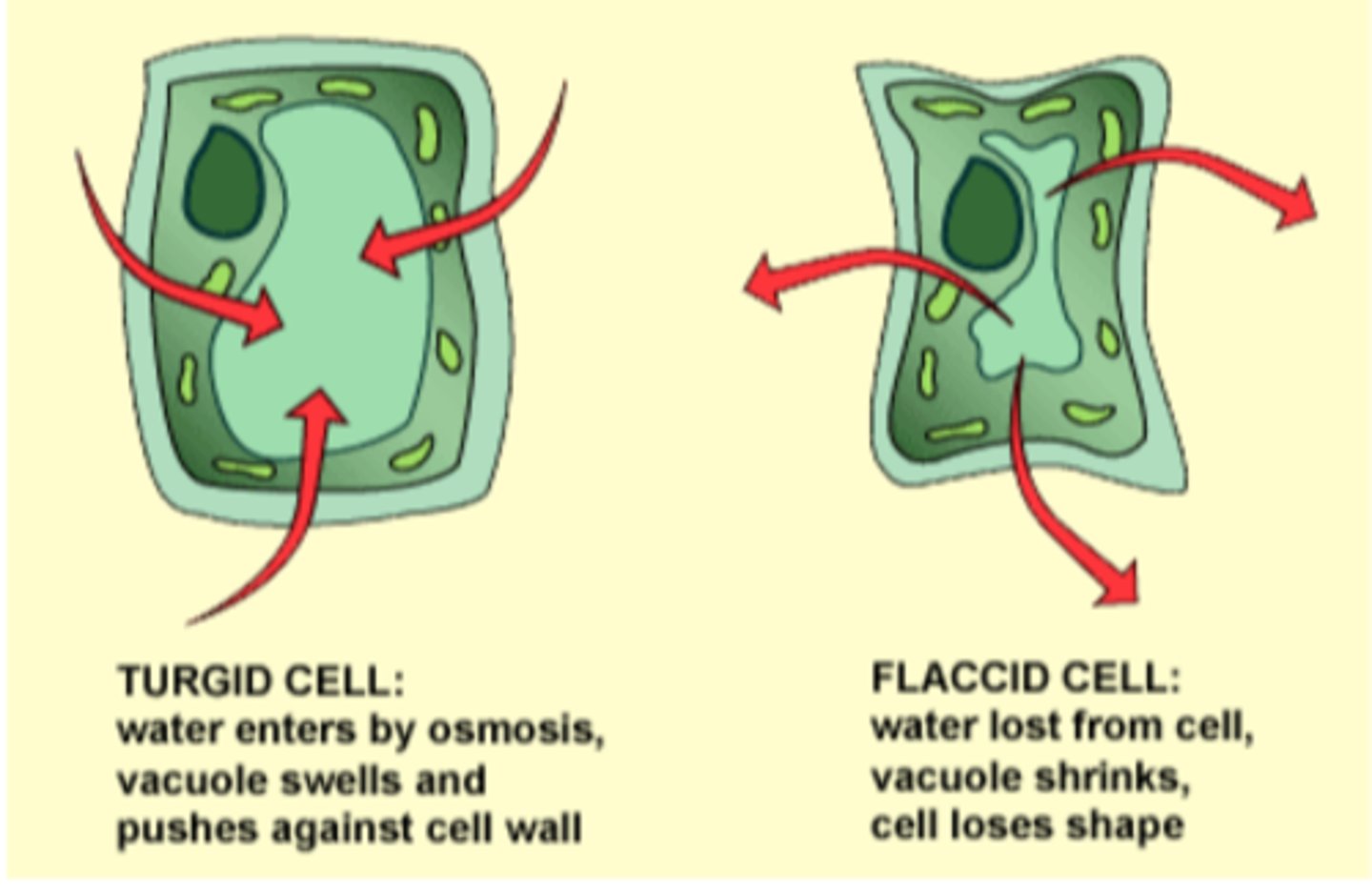
turgid
Enlarged and swollen with water. Having turgor. Description of a plant cell in which the vacuole has swollen due to water gain by osmosis
vascular bundles
Groups of xylem and phloem tissue in a plant.
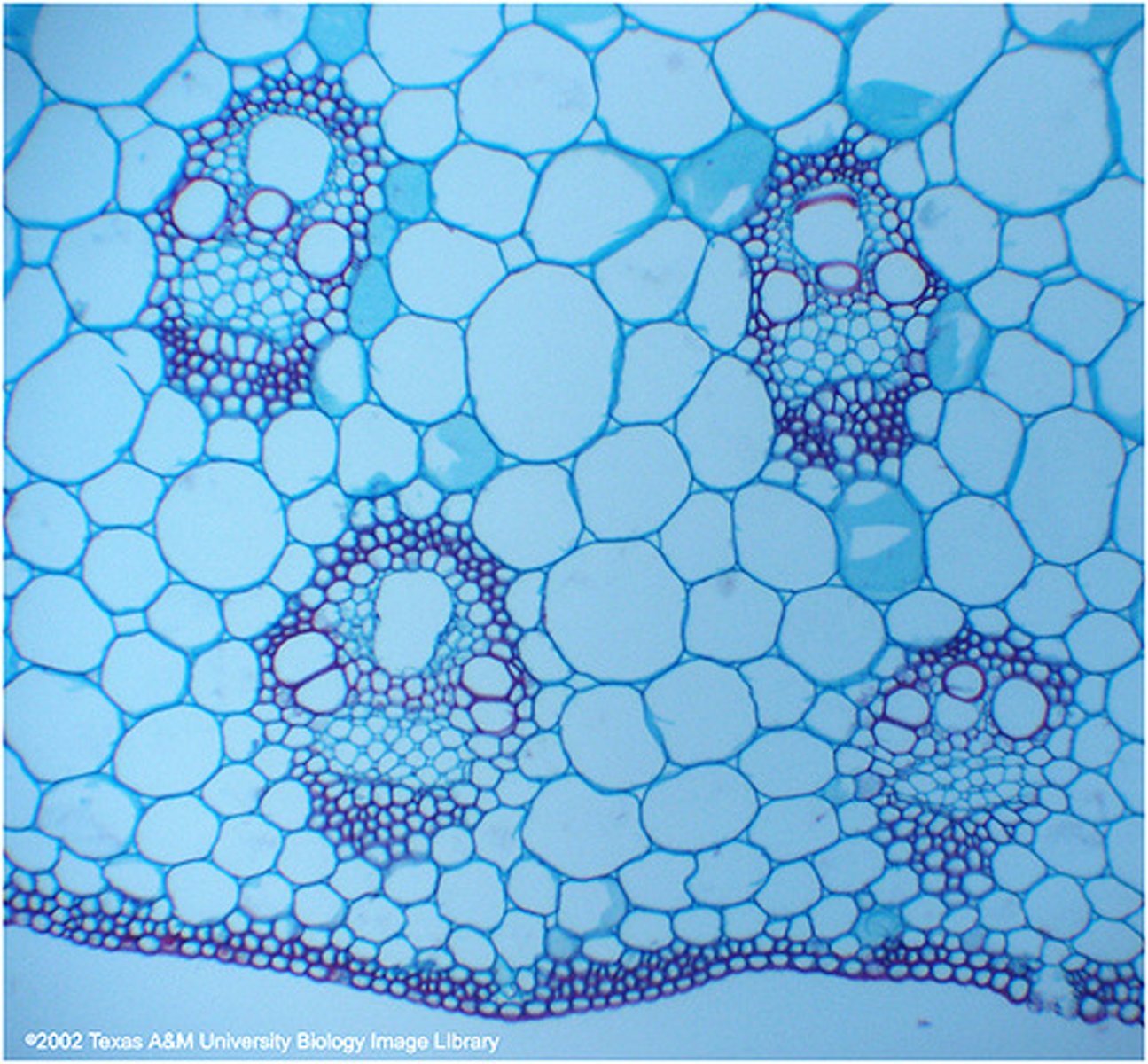
xylem vessels
Narrow, hollow, dead tubes with lignin, responsible for the transport of water and minerals in plants.
SA:Vol
Surface area to volume ratio. Needs to be a high number for good diffusion. (30:1 is better than 2:1)

active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference
mesophyll
Spongy tissue in the interior of the leaf where most chloroplasts are found.
evaporation
Liquid to gas

rate of transpiration
increased by environmental factors: warmer temperature, more wind and low humidity
Name and describe the process used by root cells to absorb mineral ions
active transport / active uptake; low to high conc. / against conc. gradient / eq;
Name the process by which a plant loses water
transpiration / evaporation / diffusion
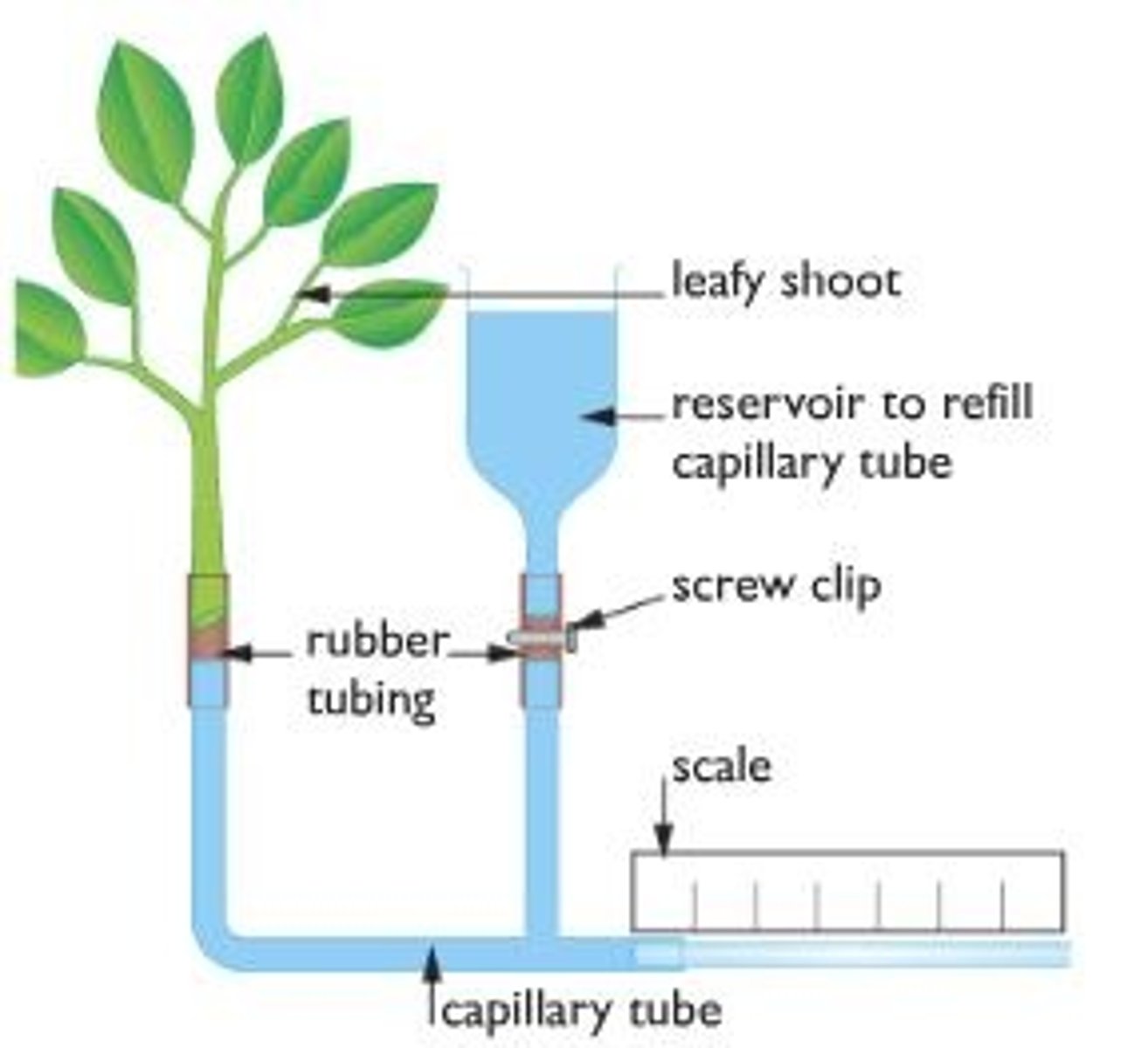
Describe how Steven should set up the potometer and how he should then use it to estimate the rate of water loss from the leafy shoot.
1 cut under water;
2 water tight / air tight / seal / eq; 3 how bubble introduced;
4 dry leaves / eq;
5 measure distance bubble moves / length of bubble eq;
6 scale / ruler / cm / eq;
7 time / second / minute / hour / day; 8 repeat;
Explain the change in water loss when wind was increased
blows water away / removes water / eq; (maintains) diffusion gradient / conc. gradient / eq;
Explain the change in water loss when light intensity was reduced
stomata close
Explain the change in water loss when half of the leaves where removed
less surface / area;
(fewer) idea of reduced number of stomata / pores;
What is meant by the term transpiration?
evaporation / loss of water / diffusion;
surface of plant / stomata / from leaves / from plant / eq;
Suggest why a polythene bag was put around the pot of soil
stop water loss (from soil) / stop evaporation (from soil) / water can only be lost through plant / eq;
Explain how the structure of the root hair cell is adapted to absorb water from the soil
1. large surface area;
2. permeable membrane;
3. osmosis / diffusion;
Explain how plants absorb water from the soil and transport the water to their leaves.
1. osmosis;
2. dilute solution to concentrated solution / eq; 3. root hair cells;
4. xylem;
5. transpiration / evaporation / diffusion of water
from leaves;
Some useful substances are dissolved in the water that is taken up by plants. Name one of these substances.
mineral / mineral ion / salt
Give two environmental conditions you could vary in the laboratory when investigating the rate of water uptake by a leafy shoot.
For each condition describe how you could obtain a range of different values.
1. wind + how varied / eq;; eg fan at high and low speed
2. light + how varied / eq;; eg lamp close and far
3. humidity + how varied / eq;; eg clear plastic bag
4. temp + how varied / eq;; eg air conditioning / room thermostat
Explain how the rate of transpiration is affected by changes in the environment
1. high humidity decreases rate; 2. reduced concentration
gradient / eq;
3. high wind increases rate ;
4. increased concentration gradient / eq;
5. high temperature increases rate ; 6. more (kinetic) energy /
more evaporation / eq;
7. high light increases rate ; 8. stomata open / eq;
Name two substances that are transported in the xylem
1. water;
2. minerals / ions / salts / named mineral ion / eq;
Plants obtain their food by the process of photosynthesis.
Explain how the structure of the leaf is adapted for its role as the organ of photosynthesis. (6)
large surface area;
thin (leaf);
upper epidermis / cuticle; transparent / lets light through; chloroplasts / chlorophyll; palisade (mesophyll);
close to surface;
absorb light;
spongy (mesophyll);
diffusion;
stomata / guard cells;
carbon dioxide;
xylem;
water; ignore if transpired
Describe how one named mineral ion helps plants to grow
named ion;
eg. nitrate / magnesium / phosphate / sulphate / iron / potassium / calcium
use of ion; - magnesium for chlorophyll production
Describe how magnesium ions are used to help trees to grow
chlorophyll / chloroplasts; photosynthesis / absorb light / eq
Describe how the structure of a leaf is adapted to absorb carbon dioxide
stomata / guard cells; spongy (mesophyll) / spongy (layer) / air spaces / eq; moist;
thin;
large surface area
A simple controlled experiment can be carried out to show that a plant leaf produces starch when exposed to light.
At the start of the experiment, all of the starch should be removed from the leaf. Suggest how this could be done.
dark for 12 hours plus;
Describe how you would test a leaf for starch.
Include the safety precautions you would take and the results you would expect to see.
boil/heat/warm in ethanol/alcohol
safety: water bath / no flame / eq; iodine;
blue black
Describe the role of chloroplasts in leaf cells
(trap/absorb) light / eq;
chlorophyll;
photosynthesis / starch / glucose / eq
Write the word equation for photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide + water = glucose + oxygen
Name four abiotic (non-living) factors likely to affect the rate of photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide
temperature / heat;
(sun)light / light intensity;
wavelength / colour;
water / rain;
minerals / ions / salts / named mineral / nutrients
What are magnesium ions used for in plants?
chlorophyll / chloroplast
What are nitrate ions used for in plants?
1. amino acids / protein / enzymes; 2. growth;
3. DNA / bases;
4. chlorophyll / eq;
Name two carbohydrates found in plants
1. starch; 2. glucose; 3. cellulose; 4. sucrose; 5. fructose
The production of tomatoes is affected by an insect pest called the tomato leaf miner. The photograph shows a tomato leaf that has been damaged by the tomato leaf miner.
The adult female leaf miner lays eggs on tomato leaves that develop into maggots (larvae). These maggots feed on leaf mesophyll tissue inside the leaf.
Explain how feeding on mesophyll tissue will affect tomato production.
1. lower production / fewer fruit / less growth / eq; 2. (fewer) chloroplasts / less chlorophyll;
3. (less) photosynthesis;
4. (less) carbohydrate / glucose / starch;
Name the gas given off during photosynthesis
Oxygen
How does upper epidermis help leaf with photosynthesis
transparent / lets light through / no chloroplasts
How does palisade layer help leaf with photosynthesis
idea of many / lots of chloroplasts;
densely packed / aligned vertically
absorb / take in / trap light
How does spongy mesophyll layer help with photosynthesis
Air spaces
Diffusion
Xylem/vascular bundle
Transport water
How do guard cells and stomata help with photosynthesis
Open/close
Let in carbon dioxide / water loss
Water lilies float on the surface of ponds. Guard cells are found on the upper surface of a water lily rather than the lower surface.
Suggest a reason for this adaptation
1. lower surface in water / upper surface exposed to air;
2. allows carbon dioxide in
3. allows transpiration / evaporation / water loss
Experiments can be done to demonstrate that light, chlorophyll and carbon dioxide are needed for photosynthesis.
Testing leaves for starch is the final step in these experiments.
Explain what other steps need to be taken to demonstrate that each of these factors is needed for photosynthesis.
(i) light
(ii) chlorophyll
(iii) carbon dioxide
i. 1. place one leaf in light / no cover of leaf;
2. place one leaf in dark / cover part of leaf;
ii. 1. use variegated leaf / eq;
2. draw pattern of chlorophyll and compare results / test white and green parts / eq;
iii. 1. NaOH / soda lime / KOH;
2. absorb / remove carbon dioxide