Biology 1: The cell
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
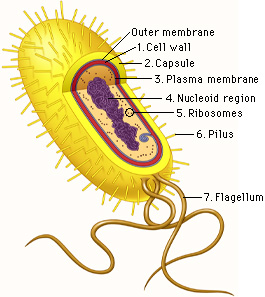
The nucleoid region is found in [eukaryotes or prokaryotes] and contains [...]
prokaryotes and contains DNA
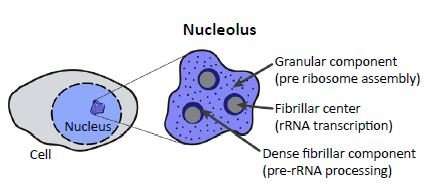
The nucleolus makes [...]
ribosomes
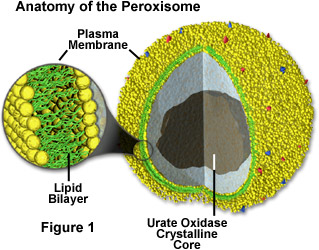
Peroxisomes [...] material
breakdown
The [smooth or rough] ER makes proteins from mRNA
rough ER
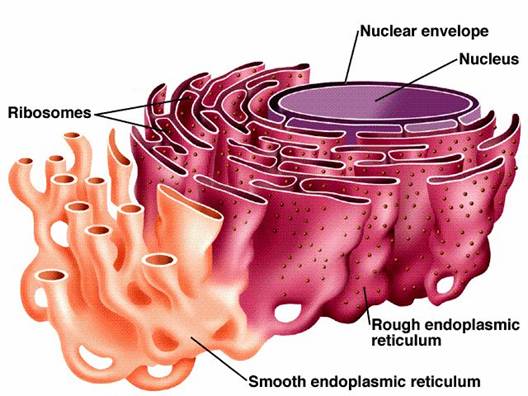
The [smooth or rough] ER is involved in detox and also in lipid formation
smooth ER
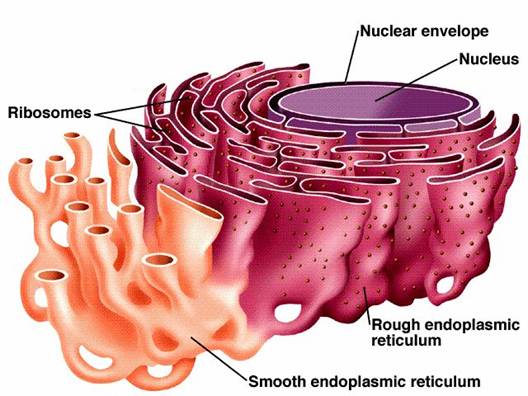
The [organelle] modifies and distributes proteins
Golgi apparatus
eukaryotes only

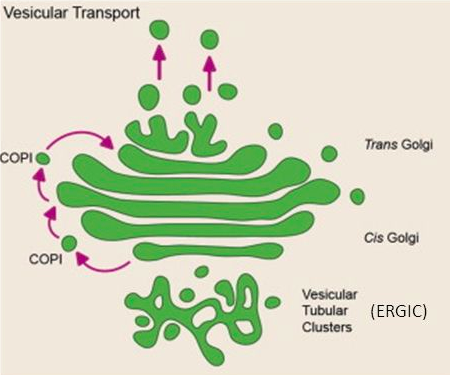
In the Vesicular Transport Model, the cis-, medial-, and trans-Golgi cisternae are [...] structures
static
the contents are physically shuttled from each cisterna to the next
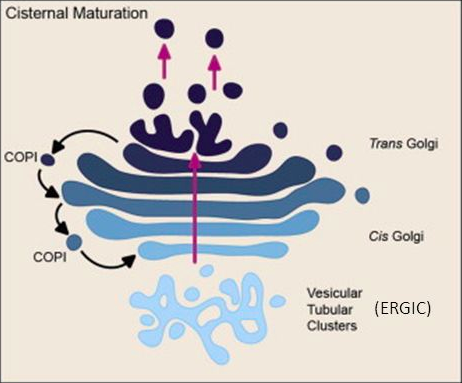
In the Cisternal Maturation Model, cisternae [...]
evolve and mature
this cis-golgi matures and becomes the medical-golgi, then eventually, the trans-golgi
vesicles move in retrograde motion
[...] are the demolition and recycling center
lysosomes
made by golgi
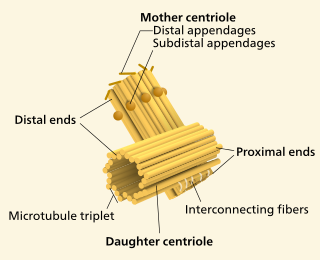
Centrioles contain 9 groups of [...] and they pull [...] apart
microtubules and they pull chromosomes apart
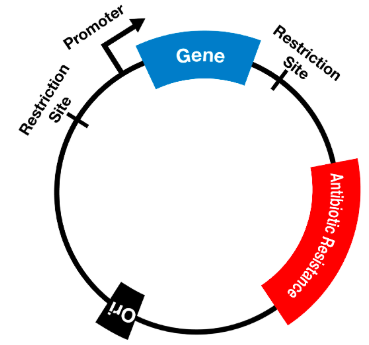
A/an [...] is a small prokaryotic DNA molecule separate from chromosomal DNA
plasmid
often the gene carried in plasmids provides bacteria with genetic advantages, such as antibiotic resistance
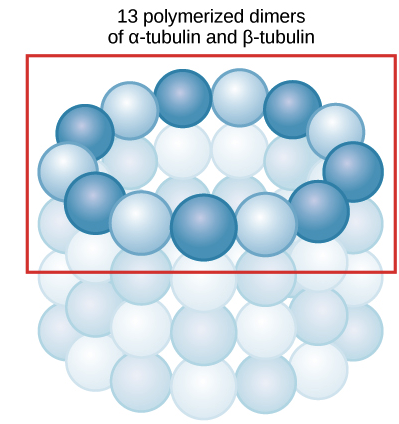
Microfilaments make up part of the cell's [...]
cytoskeleton
polymers of actin

Microtubules help the cell [...] compression forces
resits
made of tubulin proteins
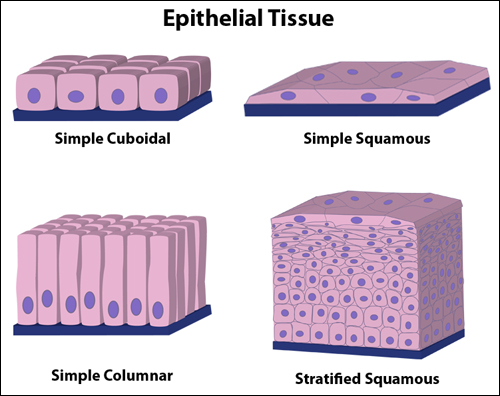
![<p><span>This is an example of </span><span style="color: mediumseagreen"><strong>[...]</strong></span><span> epithelial tissue</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e6fede19-cd20-4350-8153-842c474d6ca1.jpg)
This is an example of [...] epithelial tissue
simple squamous
![<p><span>This is an example of </span><span style="color: mediumseagreen"><strong>[...]</strong></span><span> epithelial tissue</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/de9f5bc2-493a-439e-bcd3-4cd3ec9a0ff7.jpg)
This is an example of [...] epithelial tissue
simple cuboidal
![<p><span>This is an example of </span><span style="color: mediumseagreen"><strong>[...]</strong></span><span> epithelial tissue</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/4a758534-8c2f-4f1f-8698-5c5a51250909.jpg)
This is an example of [...] epithelial tissue
simple columnat
![<p><span>This is an example of </span><span style="color: mediumseagreen"><strong>[...]</strong></span><span> epithelial tissue</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/0c2806f4-e7fb-489f-86ef-6d413a10b112.jpg)
This is an example of [...] epithelial tissue
pseudostratified columnar
![<p><span>This is an example of </span><span style="color: mediumseagreen"><strong>[...]</strong></span><span> epithelial tissue</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f91eb209-9c0b-41f9-82d0-6b2f6404e1cd.jpg)
This is an example of [...] epithelial tissue
stratified squamous
![<p><span>This is an example of </span><span style="color: mediumseagreen"><strong>[...]</strong></span><span> epithelial tissue</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/592e4756-438d-48a1-a1ab-0b4a3c3511ea.jpg)
This is an example of [...] epithelial tissue
stratified cuboidal
![<p><span>This is an example of </span><span style="color: mediumseagreen"><strong>[...]</strong></span><span> epithelial tissue</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/74e387d9-325d-489d-b358-269cd138ae9d.jpg)
This is an example of [...] epithelial tissue
stratified columnar
![<p><span>This is an example of </span><span style="color: mediumseagreen"><strong>[...]</strong></span><span> epithelial tissue</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/db1fe3a6-7f65-4dcd-a34e-f58a0ad38aa0.jpg)
This is an example of [...] epithelial tissue
transitional
Bone, cartilage, tendon, and blood are examples of [...] tissue
connective
Epithelial tissue covers [...] and [...] surfaces of the body
internal and external
![<p><span>This is an example of </span><span style="color: mediumseagreen"><strong>[shape]</strong></span><span> bacteria</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/46907918-53bb-4b94-b622-0151cc0bc67b.png)
This is an example of [shape] bacteria
bacilli (rod)
![<p><span>This is an example of </span><span style="color: mediumseagreen"><strong>[shape]</strong></span><span> bacteria</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/836ebc3f-d5d7-4c1a-8937-f31a108e9aff.png)
This is an example of [shape] bacteria
cocci (sphere)
![<p><span>This is an example of </span><span style="color: mediumseagreen"><strong>[shape]</strong></span><span> bacteria</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1f036751-f3c0-4483-b163-691c35a22572.png)
This is an example of [shape] bacteria
spirilla (spiral)
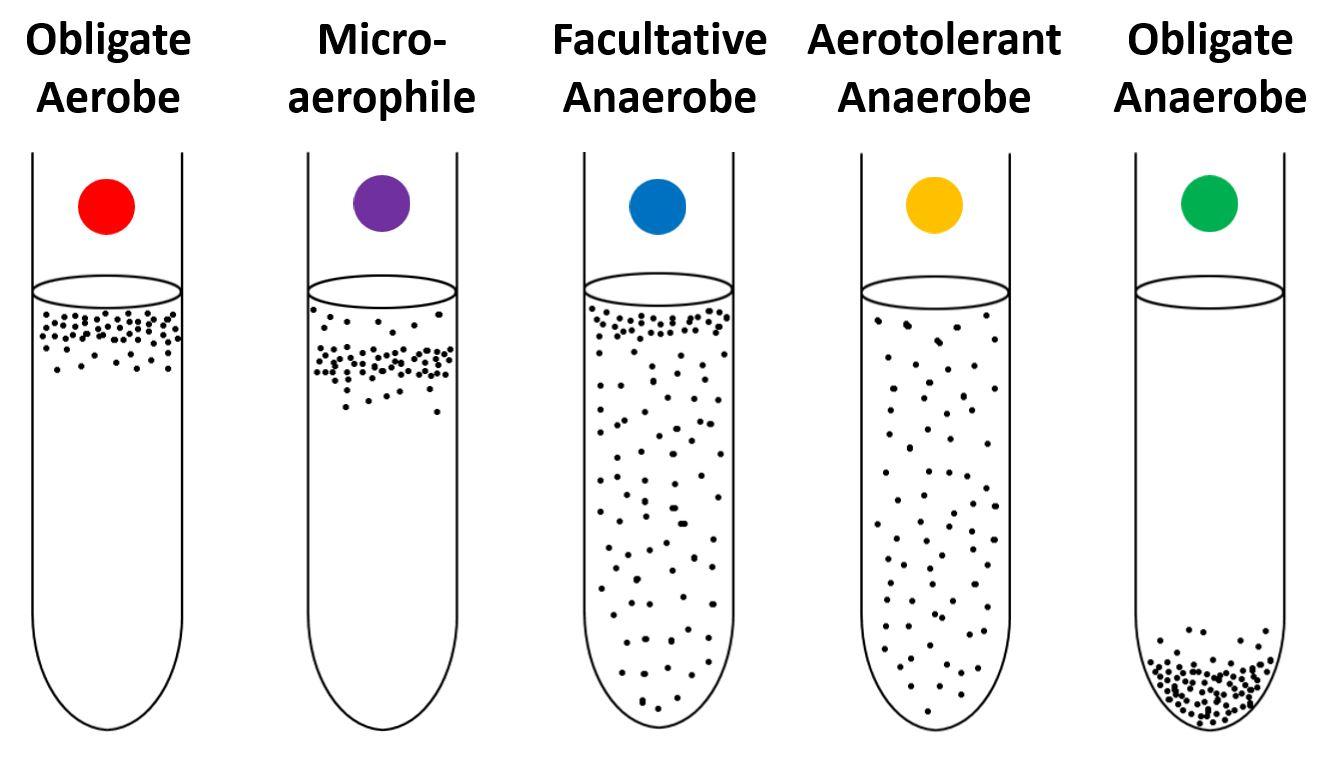
[type of microorganism] require O2
obligate aerobes
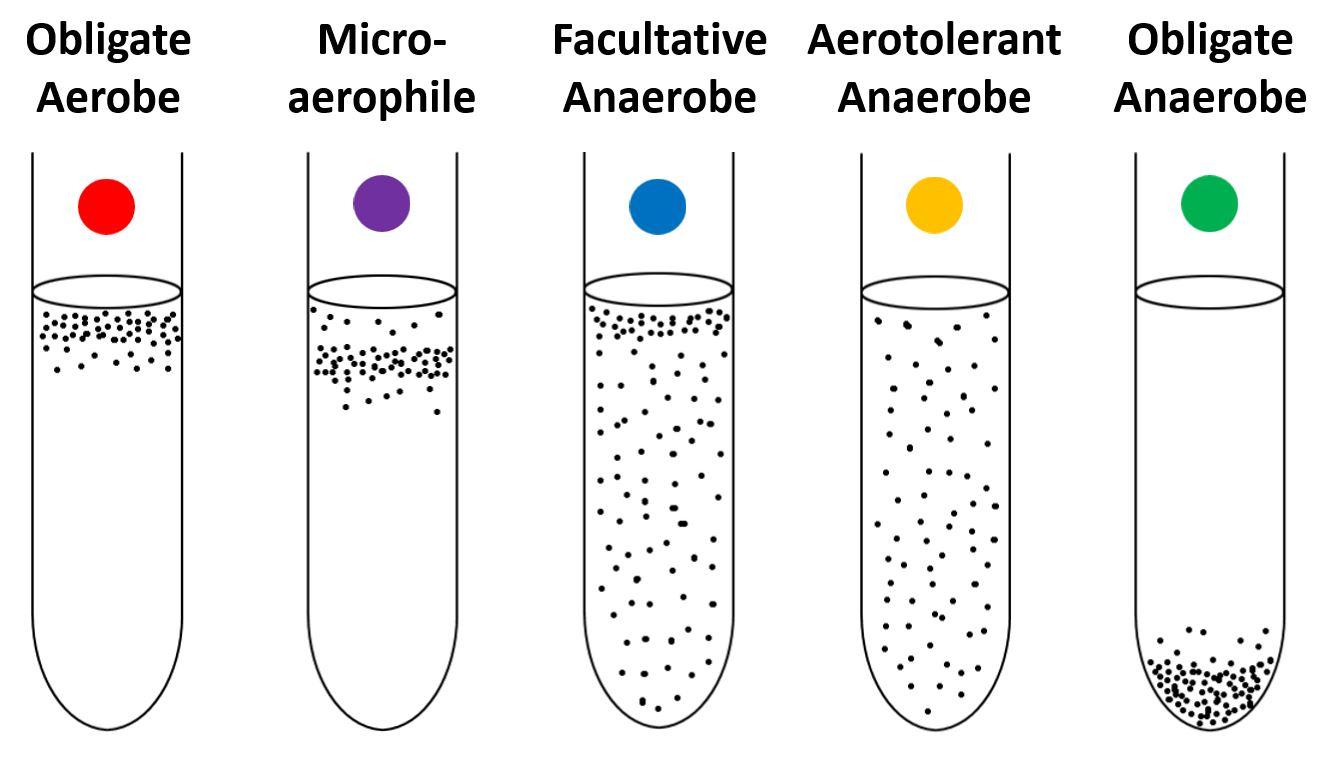
[type of microorganism] die in O2
obligate anaerobes
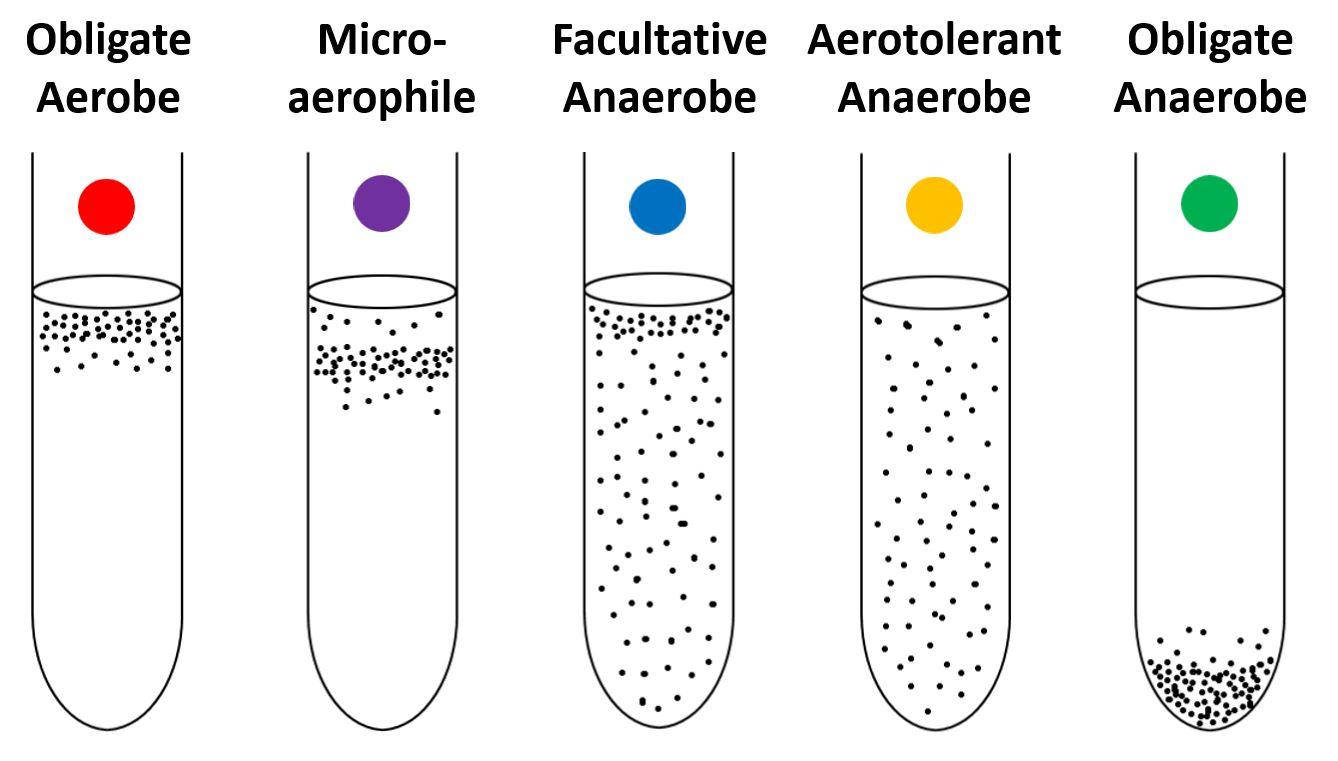
[type of microorganism] toggle between aerobic and anaerobic
facultative anaerobes
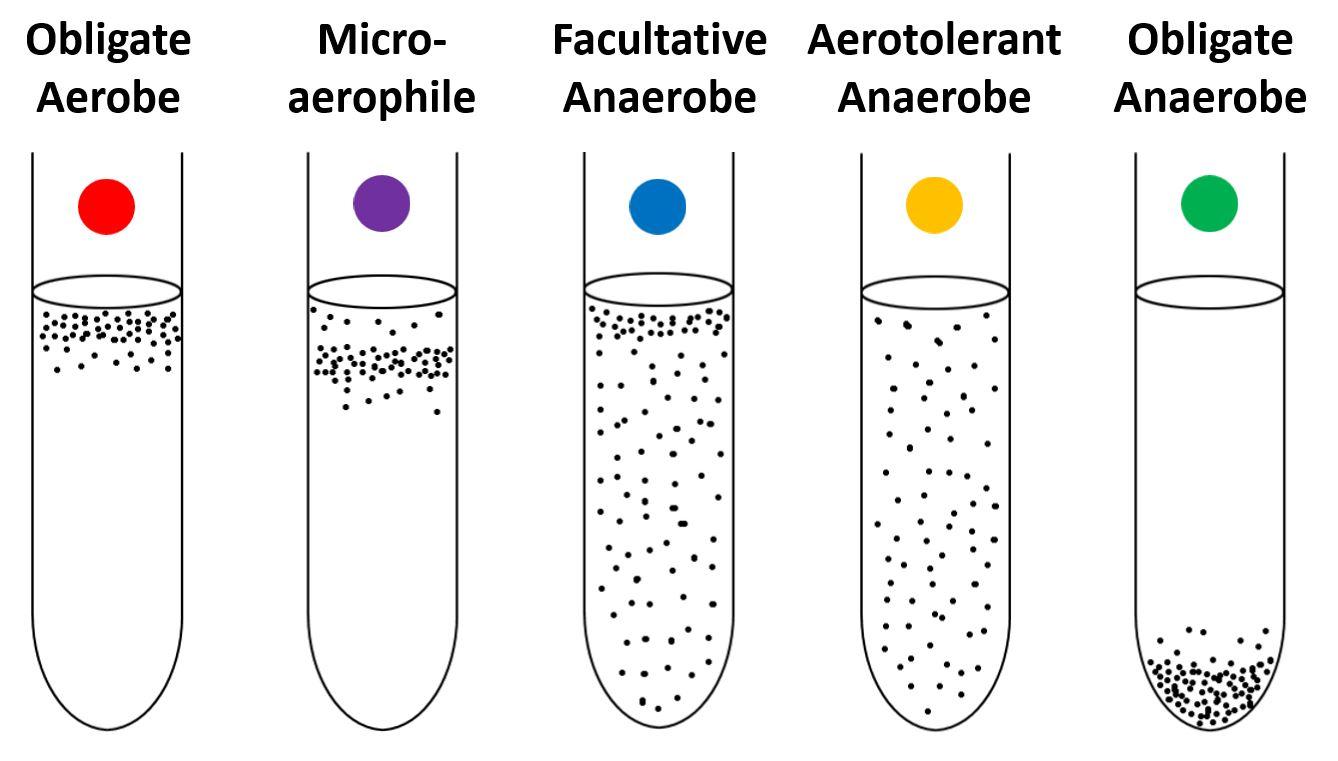
[type of microorganism]do not use O2 but tolerate it
aerotolerant anaerobes
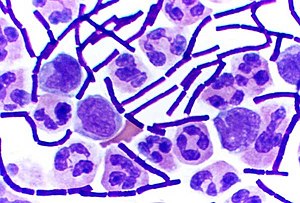
Gram + is [color] and has a [thick or thin] wall
purple and thick
wall is made of peptidoglycan lipoteichoic acid
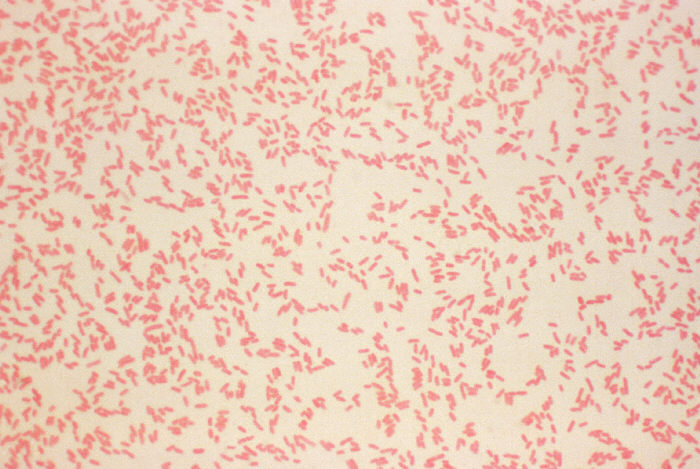
Gram - is [color] and has a [thick or thin] wall
pink thin
wall is made of peptidoglycan
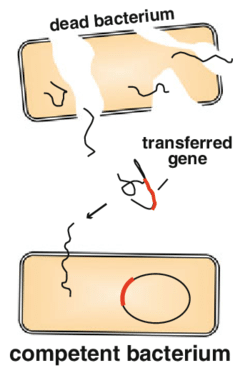
[...] is when bacteria gets genetic info from the environment
transformation
griffith experiment with mice (R strain safe, S strain deadly)
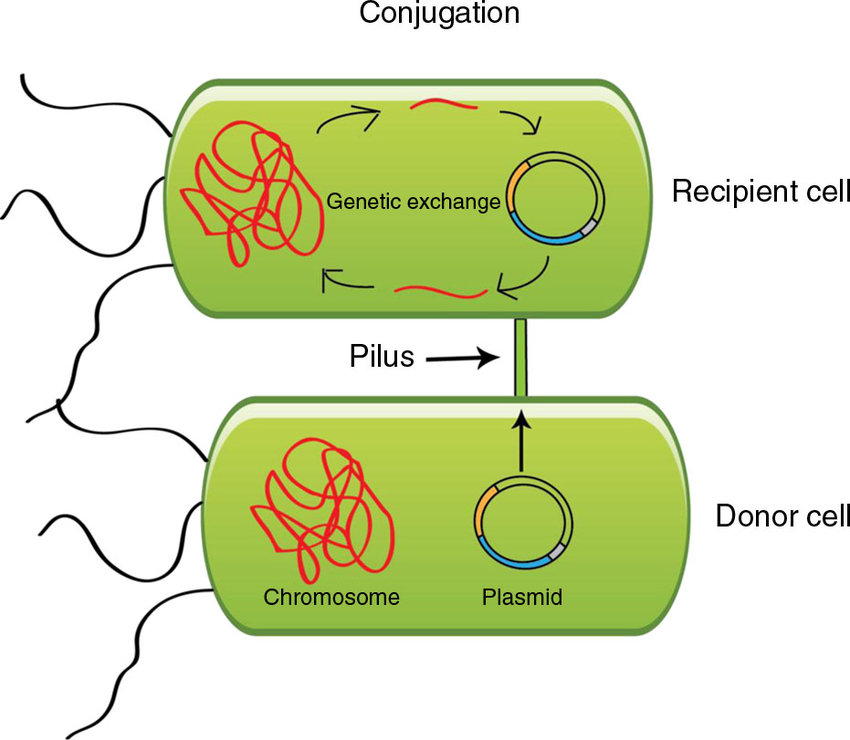
Conjugation is the transfer genetic info via a/an [...]
conjugation bridge
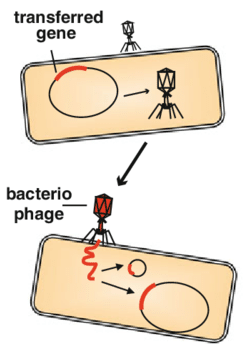
[...] is the transfer genetic material using a bacteriophage
transduction
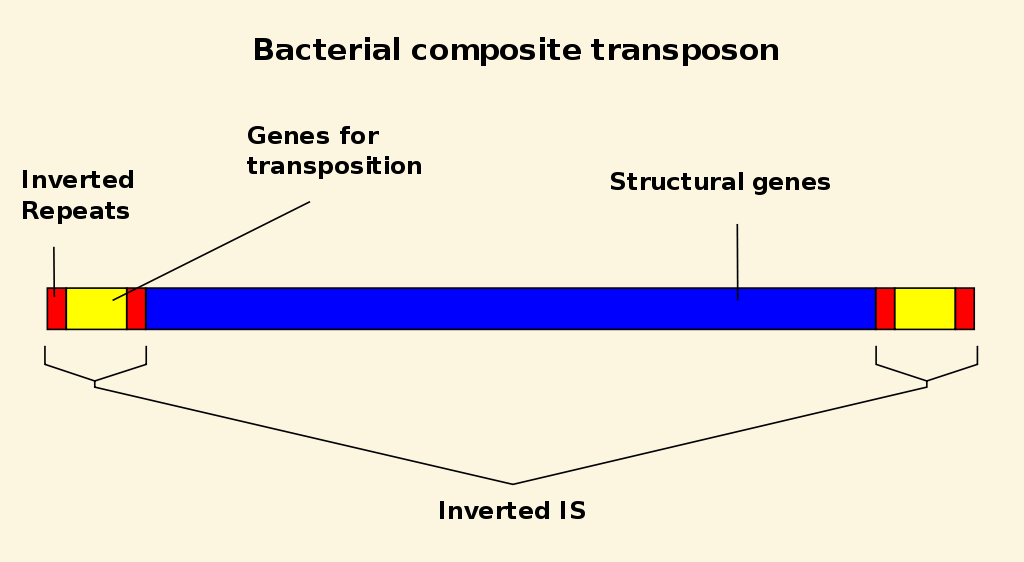
[...] are DNA sequences that can change their position within a genome
transposons
this sometimes create or reverse mutations
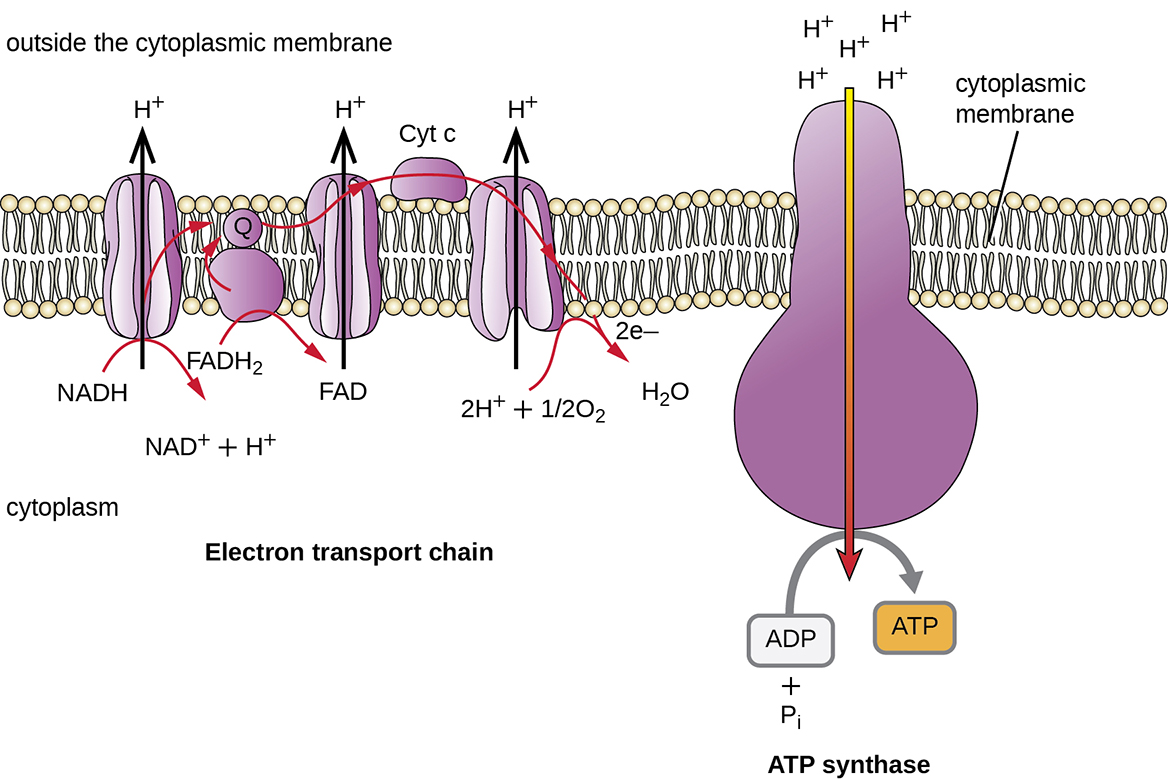
In eukaryotes, the electron transport chain takes place in the [cellular component]
inner mitochondrial membrane
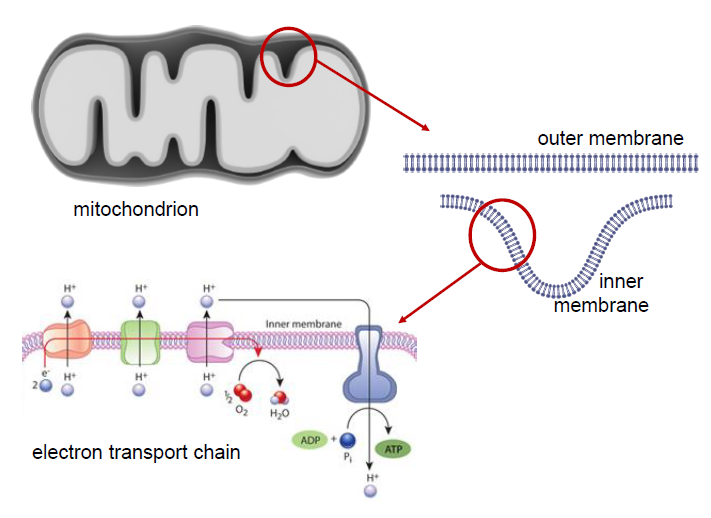
In prokaryotes, the electron transport chain takes place in the [cellular component]
cell membrane
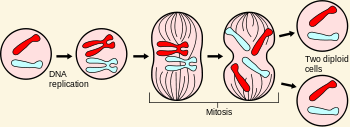
Eukaryotic cells reproduce via [...]
mitosis
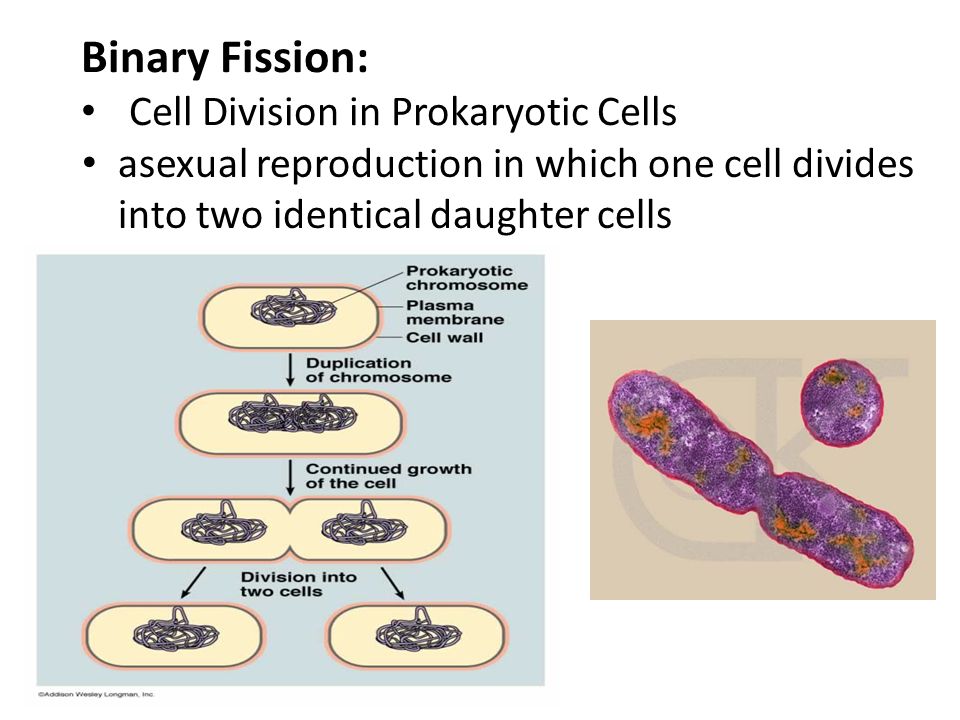
Prokaryotic cells reproduce via [...]
binary fission
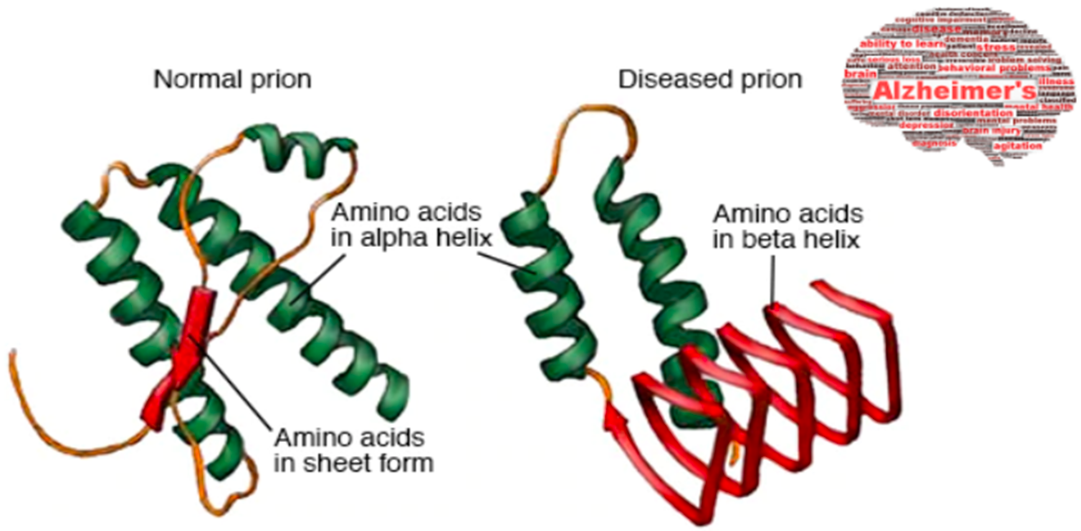
[...] are infectious proteins and can trigger misfolding
prions
creates creutzfeldt-jakob disease
alhemizer’s
...] are plant pathogens
viroids

[...] are bacteria viruses that use a tail sheath to inject DNA / RNA
bacteriophages
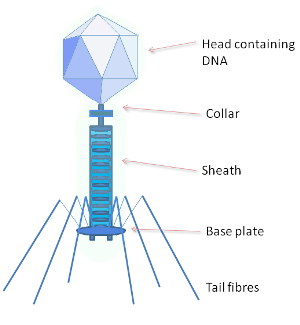
A/an [...] is the protein shell of a virus
capsid
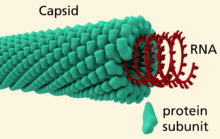
[...] are individual virus particles that are found extracellular
virions
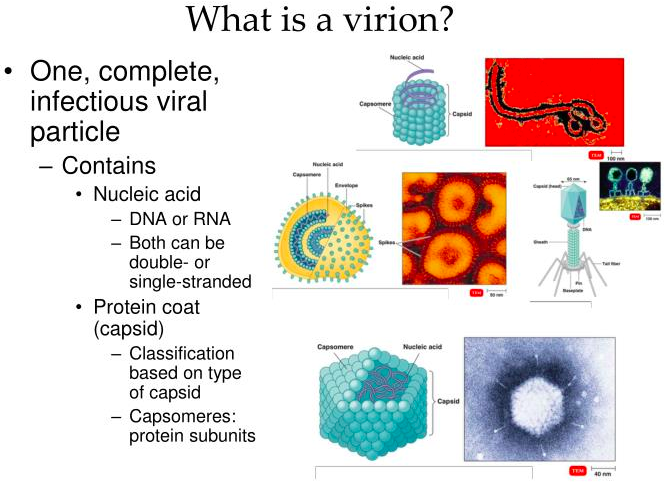
[...] genomes may be made of DNA or RNA and may be single or double stranded
viral
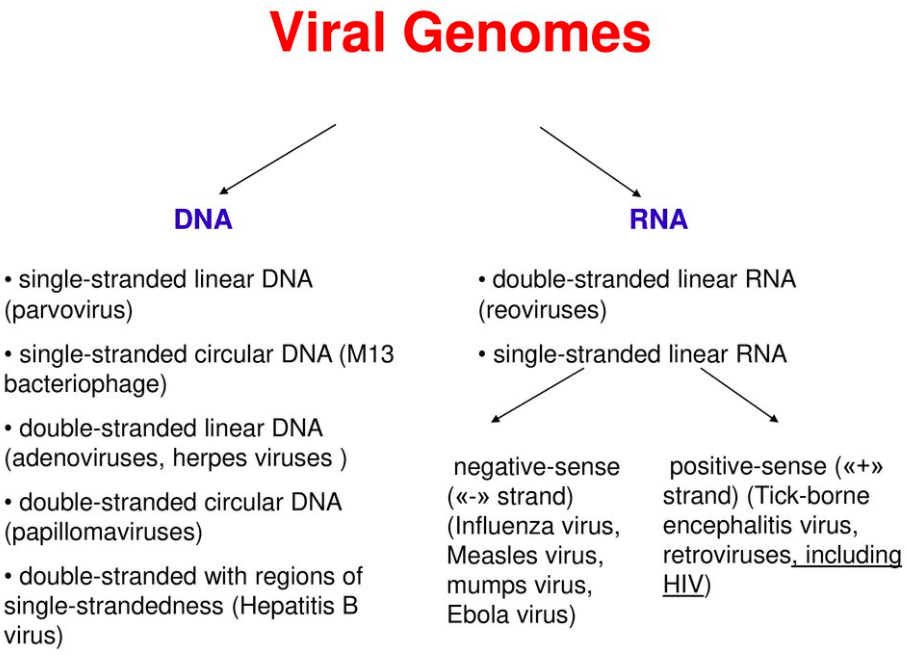
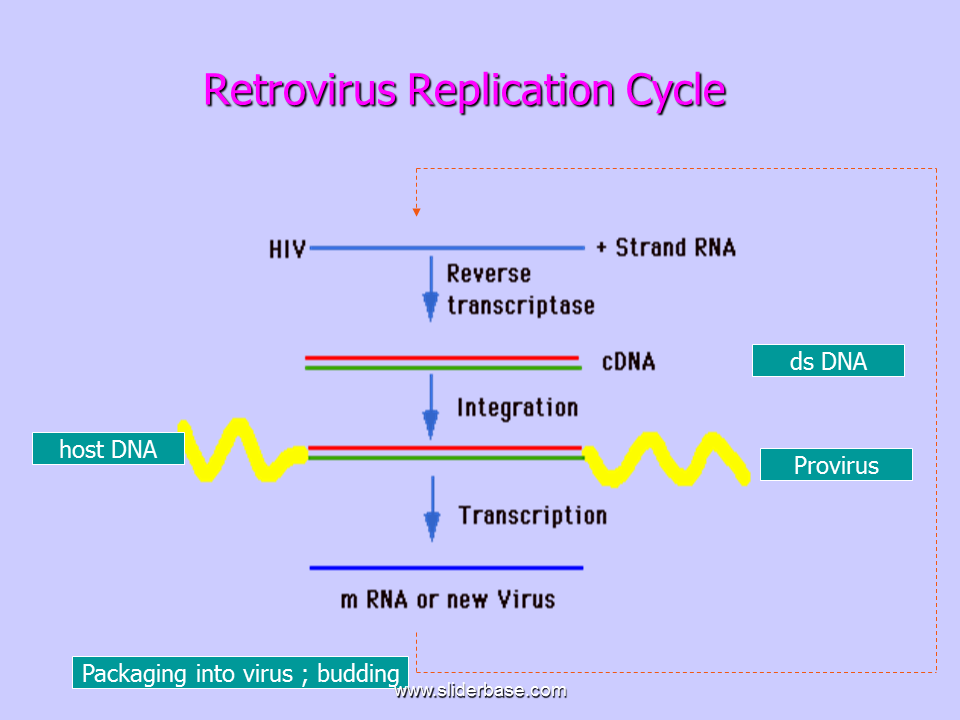
Retroviruses are single stranded [...]
RNA
reverse transcriptase is needed to make DNA
In a [...] bacteriophage life cycle, virions are made until the cell lyses
lytic - viruses enter cells and use the cell to make copies of themselves often destroying the cell in the process
