IB Biology HL - Ecology
5.0(4)
Card Sorting
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:04 AM on 4/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
1
New cards
Define a species.
A soecies is a group of organisms that can potentially interbreed to produce fertile, viable offspring.
2
New cards
What are hybrids?
Organisms resulting from cross-breeding of two different, but closely related species. They are reproductively sterile.
3
New cards
Define population.
A population is a group of organisms of the same species living in the same area at the same time
4
New cards
Define community.
Community is a group of populations living together and interacting with each other within a given area.
5
New cards
Define habitat.
Habitat is the environment in which a species normally lives, or the location of a living organism.
6
New cards
Define ecosystem.
Ecosystem is a community and its abiotic environment (habitat).
7
New cards
Define ecology.
Ecology is the study of the relationship between living organisms, or between living organisms and their environment.
8
New cards
Outline the modes of nutrition.
* ==autotrophs== - synthesize their own organic molecules from simple inorganic substances using energy derived from sunlight (==photosynthesis==) or oxidation (==chemosynthesis==); producers
\
* ==heterotrophs== - obtain organic molecules from other organisms
* ==consumers== - ingest organic molecules from living or recently killed organisms
* ==herbivores== - consume plant matter
* ==carnivores== - consume animal matter
* ==omnivores== - consume both plants and animals
* ==scavengers== - consume dead and decaying carcasses
* ==detritivores== - ingest organic molecules found in the non-living remnants of organisms (e.g. detritus, humus)
* ==saprotrophs== - release digestive enzymes and then absorb the external products of digestion (decomposers)
\
* ==mixotrophes== - some unicellular organisms ocassionally use both forms of nutrition, depending on the resource availability
\
* ==heterotrophs== - obtain organic molecules from other organisms
* ==consumers== - ingest organic molecules from living or recently killed organisms
* ==herbivores== - consume plant matter
* ==carnivores== - consume animal matter
* ==omnivores== - consume both plants and animals
* ==scavengers== - consume dead and decaying carcasses
* ==detritivores== - ingest organic molecules found in the non-living remnants of organisms (e.g. detritus, humus)
* ==saprotrophs== - release digestive enzymes and then absorb the external products of digestion (decomposers)
\
* ==mixotrophes== - some unicellular organisms ocassionally use both forms of nutrition, depending on the resource availability
9
New cards
Explain how nutrients cycle in the environment.
The supply of inorganic nutrients on Earth is finite, so the chemical elements are constantly recycled.
* autotrophs obtain inorganic nutrients from air, water and soil and convert them into organic compounds
* heterotrophs ingest the organic compounds and use them for growth and resporation, releasing inorganic byproducts
* when organisms die, saprotrophs decompose the remains and free inorganic materials into the soil
* the return of inorganic materials to the soil ensures the continual supply of raw materials for the autotrophs
* autotrophs obtain inorganic nutrients from air, water and soil and convert them into organic compounds
* heterotrophs ingest the organic compounds and use them for growth and resporation, releasing inorganic byproducts
* when organisms die, saprotrophs decompose the remains and free inorganic materials into the soil
* the return of inorganic materials to the soil ensures the continual supply of raw materials for the autotrophs
10
New cards
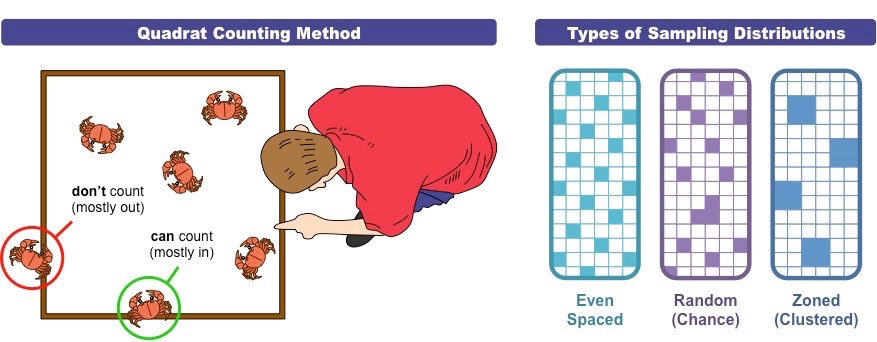
Outline the quadrat sampling method.
It is the method used to determine the presence of two species within a given environment.
A quadrat is a rectendular frame of known dimensions that can be used to establish population densities. Quadrats are placed inside a defined area, either in ==random== or ==designed== arrangement. The number of individuals of a given species is either counted or estimated via percentage coverage. The sampling process is repeated many times to gain the representative data set.
In each quadrat, the presence or absence of each species is identified, allowing for the number of quadrats where both species were present to be compared against the total number of quadrats.
It is an effective method to count plants and sessile animals, but not motile organisms.
==Chi square test== can be used to test for association between the presence of both species.
A quadrat is a rectendular frame of known dimensions that can be used to establish population densities. Quadrats are placed inside a defined area, either in ==random== or ==designed== arrangement. The number of individuals of a given species is either counted or estimated via percentage coverage. The sampling process is repeated many times to gain the representative data set.
In each quadrat, the presence or absence of each species is identified, allowing for the number of quadrats where both species were present to be compared against the total number of quadrats.
It is an effective method to count plants and sessile animals, but not motile organisms.
==Chi square test== can be used to test for association between the presence of both species.
11
New cards
What is the initial source of energy for almost all ecosystems?
Sunlight (in rare cases the producers are chemoautotrophic bacteria).
12
New cards
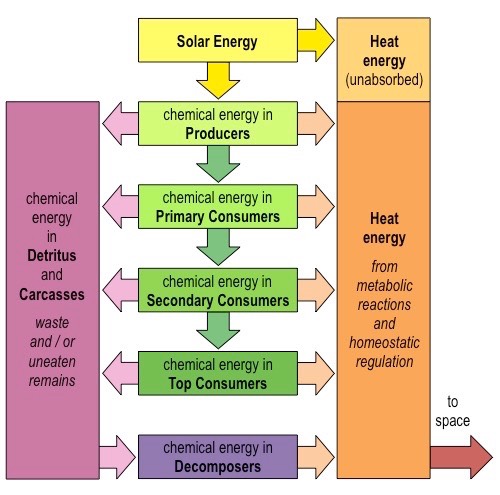
Describe the energy flows in the ecosystems.
1. Energy enters most ecosystems as sunlight and is converted into chemical energy by the producers in photosynthesis. This chemical energy is stired in carbon compounds (organic molecules) and is transferred to heterotrophs when they feed on plants (producers are the first trophic level)
2. Primary consumers feed on plants (second trophic level)
3. Further consumers may occupy subsequent trophic levels.
13
New cards
What is a trophic level?
The position that the organism occupies within a feeding sequence.
14
New cards
What is a food chain?
A graphical representation of the ==linear== feeding relationships between species in a community.
15
New cards
In what ways do organism lose energy?
Chemical energy produced by an organism can be converted into kinetic, electrical or even light energy, but it is accompanied by an energy loss in the form of evolved ==heat==.
Living organism ==cannot== turn the heat into other forms of usable energy, so it is lost from the ecosystem. That is why ecosystems require a continuous influx of energy from an external source, such as sun.
Living organism ==cannot== turn the heat into other forms of usable energy, so it is lost from the ecosystem. That is why ecosystems require a continuous influx of energy from an external source, such as sun.
16
New cards
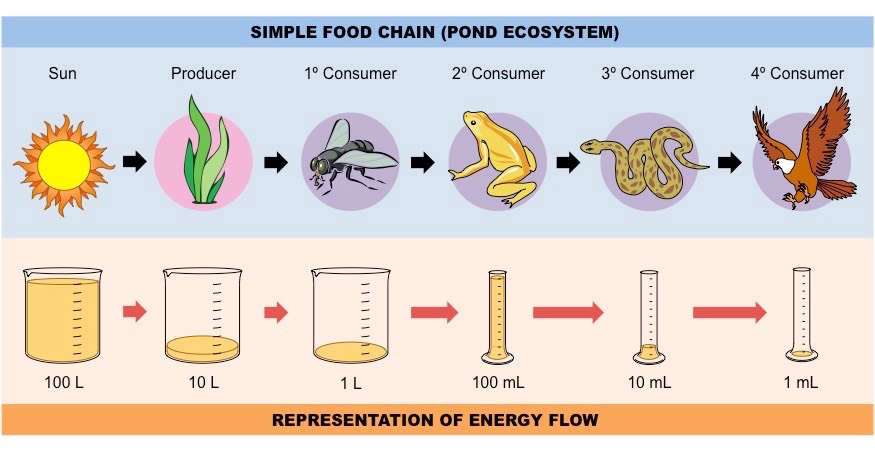
Comment on the efficiency of energy transfer between subsequent trophic levels.
Typically, energy transformations are \~10% efficient, with about 90% of available energy being lost between trophic levels (the exact values depend on the certain organism’s ability to efficiently capture and use energy).
Most energy is lost to the organism - either used in respiration, released as heat, excreted in faeces or unconsumed.
Consequently, hugher trophic levels strore less energy as carbon compounds and have less biomass. It is because the subsequent trophic levels receive less and less energy from feeding, so they have to eat more to obtain sufficient nutrients. It also causes them to expend more energy hunting for food. Eventually, when the energy required to hunt orey exceeds the energy available from the food eaten, the trophic level becomes unviable - this is why the number of trophic levels is limited.
Most energy is lost to the organism - either used in respiration, released as heat, excreted in faeces or unconsumed.
Consequently, hugher trophic levels strore less energy as carbon compounds and have less biomass. It is because the subsequent trophic levels receive less and less energy from feeding, so they have to eat more to obtain sufficient nutrients. It also causes them to expend more energy hunting for food. Eventually, when the energy required to hunt orey exceeds the energy available from the food eaten, the trophic level becomes unviable - this is why the number of trophic levels is limited.
17
New cards
What is biomass?
The tital mass of a group of organisms - consisting of the carbon compounds contained in cells and tissues.
18
New cards
What is a pyramid of energy?
A graphical representation of the amount of energy at each trophic level of a food chain, expressed in units of energy per area per time.
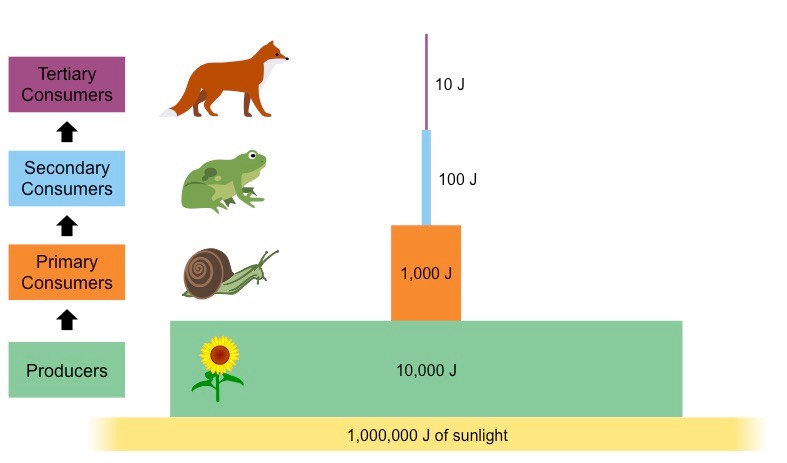
19
New cards
Construct a diagram of the carbon cycle.
The carbon cycle is a biogeological cycle whereby carbon is exchanged between the different spheres of the Earth (atmosphere, litosphere, hydrosphere and biosphere)
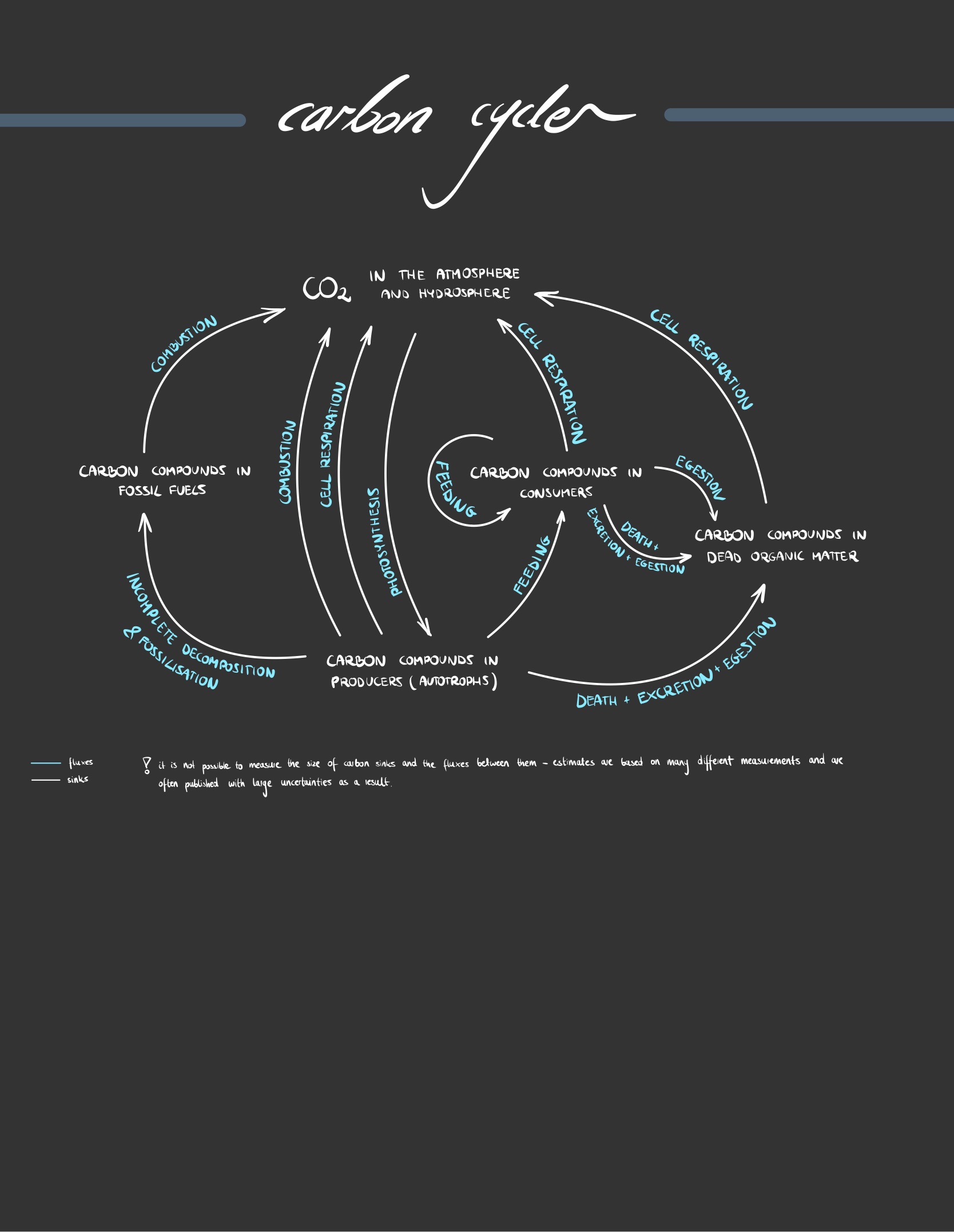
20
New cards
How is carbon present in aquatic ecosystems?
* carbon dioxide from the atmosphere dissolves in water
* some of it remains as dissolved gas, the remainder combines with water to form ==carbonic acid== (CO2 + H2O
* some of it remains as dissolved gas, the remainder combines with water to form ==carbonic acid== (CO2 + H2O
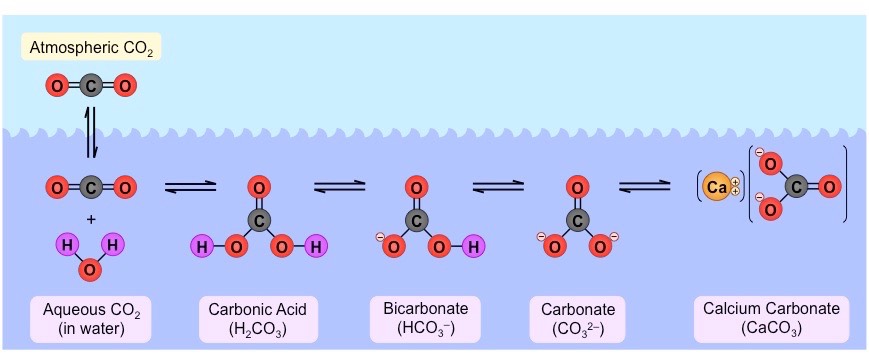
21
New cards
Outline the production of methane.
* methanogens are archaean microorganisms that produce methane (CH4) as a metabolic by-product in anaerobic conditions (wetlands, marine sediments, digestive tracts of ruminants animals
acetic acid —> methane + carbon dioxide
CH3COO- + H+ —> CH4 + 2H2O
carbon dioxide + hydrogen —> methane + water
CO2 + 4H2 —> CH4 + 2H2O
* Methane can either accumulate under the ground or diffuse into the atmosphere
* Mathane persists in the atmosphere for \~12 years and naturally oxidizes to form carbon dioxide and water
CH4 + 2O2 —> CO2 + 2H2O
This is why methane levels in the atmosphere are not very large, even though significant quantities are being produced
acetic acid —> methane + carbon dioxide
CH3COO- + H+ —> CH4 + 2H2O
carbon dioxide + hydrogen —> methane + water
CO2 + 4H2 —> CH4 + 2H2O
* Methane can either accumulate under the ground or diffuse into the atmosphere
* Mathane persists in the atmosphere for \~12 years and naturally oxidizes to form carbon dioxide and water
CH4 + 2O2 —> CO2 + 2H2O
This is why methane levels in the atmosphere are not very large, even though significant quantities are being produced
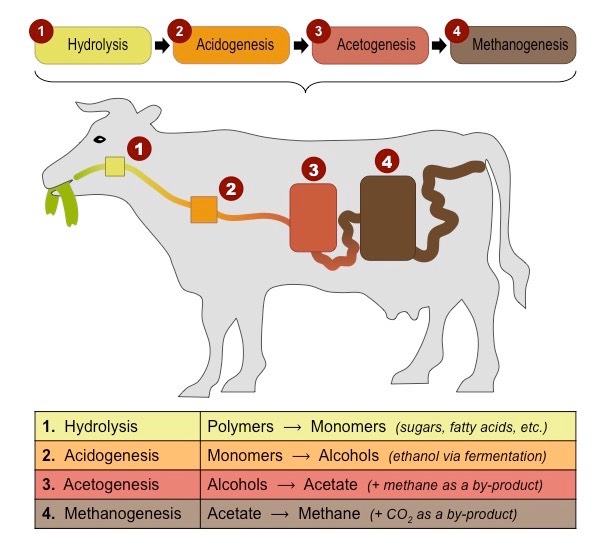
22
New cards
How are peat and coal formed?
* ==saprotrophic== bacteria in soil decompose dead organisms and return nutrients to the soil (this process ==requires oxygen==, as the cell resporation is meeded to fuel digestive reactions)
* ==waterlogged== regions lack oxigenated air spaces - ==anaerobic conditions==
* organic acids are produced in anaerobic respiration, resulting in ==acidic conditions==
* saprotrophs cannot function effectively on anaerobic/acidic conditions, preventing decomposition and forming ==peat==
* when deposits of peat are copressed under sediments, ==heat and pressure== force out impurities and remove moisture
* remaining material has a high carbon concentration and undergoes chemical transformation to produce ==coal==
* ==waterlogged== regions lack oxigenated air spaces - ==anaerobic conditions==
* organic acids are produced in anaerobic respiration, resulting in ==acidic conditions==
* saprotrophs cannot function effectively on anaerobic/acidic conditions, preventing decomposition and forming ==peat==
* when deposits of peat are copressed under sediments, ==heat and pressure== force out impurities and remove moisture
* remaining material has a high carbon concentration and undergoes chemical transformation to produce ==coal==
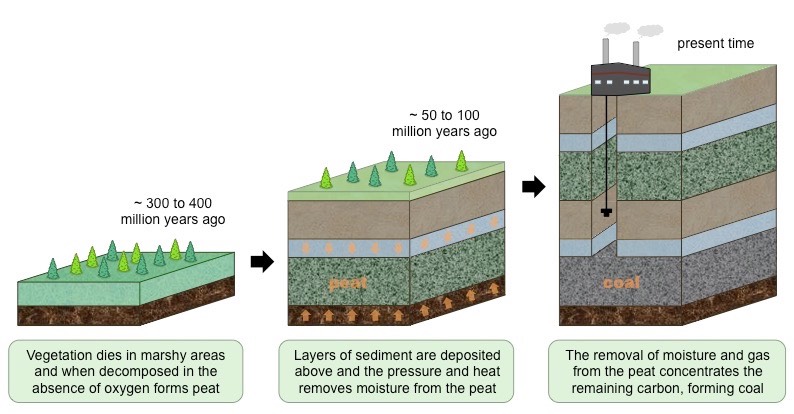
23
New cards
How are oil and natural gas produced?
* they are formed as the result of the decay of marine organisms on the ocean floor
* sediments (clay, mud) are deposited on top of the organic matter, creating anoxic conditions to prevent decomposition
* burial and compaction causes the organic material to be heated and hydrocarbons are formed
* hydrocarbons form oil and gas, which are forced out of the source rock and accumulate in porous rocks, such as sandstone
* this process takes millions of years
* sediments (clay, mud) are deposited on top of the organic matter, creating anoxic conditions to prevent decomposition
* burial and compaction causes the organic material to be heated and hydrocarbons are formed
* hydrocarbons form oil and gas, which are forced out of the source rock and accumulate in porous rocks, such as sandstone
* this process takes millions of years
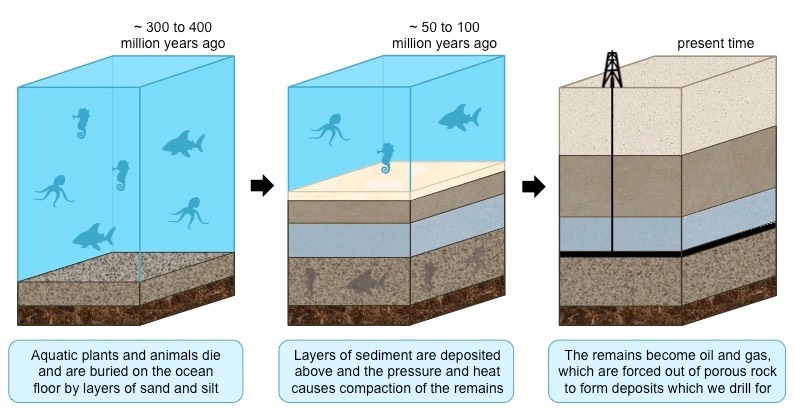
24
New cards
What are carbon fluxes?
Carbon fluxes describe the rate of exchange of carbon between various carbon sinks (litosphere - earth crust, hydrosphere - oceans, atmosphere - air, biosphere - organisms)
25
New cards
Is it possible to directly measure the size of carbon sinks and fluxes between them?
Nope. Estimations are made and usually they involve large uncertainties fur to variety of sources and the size of fluxes.
26
New cards
How can climat coditions, natural event and human activity affect the size of carbon fluxes?
1. Climate conditions
* rates of photosynthesis are highers in summer seasons (more daulight)
* oceanic temperatures determine how much carbon is stored in the water
* events like El Niño and La Niña change the rate of carbon flux between ocean and atmosphere
* melting of polar ice caps results in the decomposition of frozen detritus
2. Natural events
* forest fires release CO2 + loss of trees decreases the rate of photosynthesis
* vulcanic eruptions release CO2
3. Human activity
* deforestation
* increased numbers of ruminant lifestock (e.g. cows) = higher levels of methane
* burning fossil fuels
27
New cards
What are greenhouse gases?
Atmospheric gases that absorb and emit long-wave (infrared) radiation, thereby trapping and holding heat within the atmosphere. They collectively make up < 1% of the Earth’s atmosphere
* water vapour
* CO2
* methane
* nitrogen oxides (from vehicles and some bacteria)
* water vapour
* CO2
* methane
* nitrogen oxides (from vehicles and some bacteria)
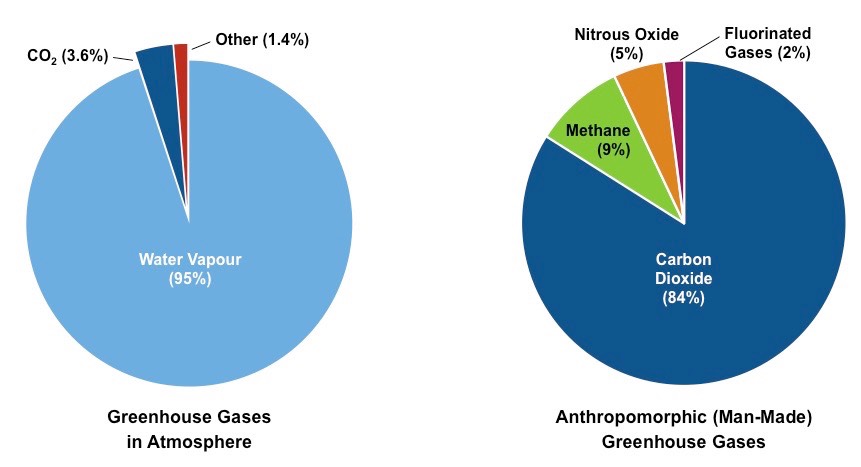
28
New cards
Outline the two factors that determine the impact of the greenhouse gas on warming the atmosphere.
* ability to absorb long-wave radiation - gases that have a greater capacity to absorb long-wave radiation will have a greater warming impact per molecule
* concentration in the atmosphere - determined by the rate of release and ==persistence== within the atmosphere
* concentration in the atmosphere - determined by the rate of release and ==persistence== within the atmosphere
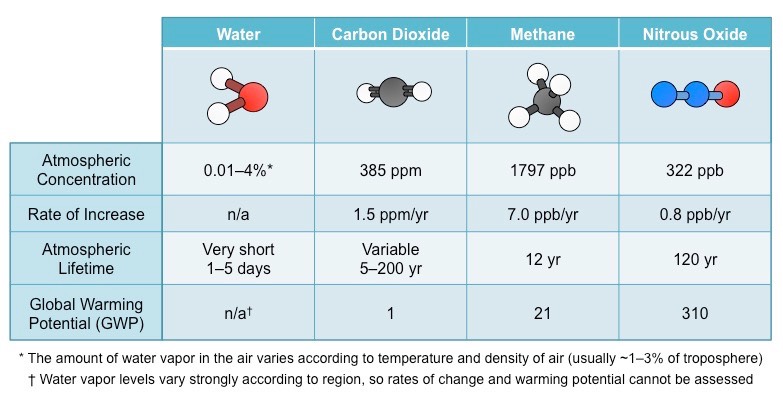
29
New cards
What is the greenhouse effect?
A natural process whereby the atmosphere acquires the ability to trap and retain heat. It ensures that the Earth maintains the moderate temperature needed by organisms to maintain life processes (homeostasis) and that the temperature differences between night and day are not too big and rapid.
* incoming radiation from the sun is a shorter wave radiation (UV and visible light)
* the surface of the Earth absorbs short-wave radiation and re-emits it at a longer wavelength (IR - heat)
* greenhouse gases absorb and re-radiate this longer wave rafiation and hence retain the heat within the atmosphere
* incoming radiation from the sun is a shorter wave radiation (UV and visible light)
* the surface of the Earth absorbs short-wave radiation and re-emits it at a longer wavelength (IR - heat)
* greenhouse gases absorb and re-radiate this longer wave rafiation and hence retain the heat within the atmosphere
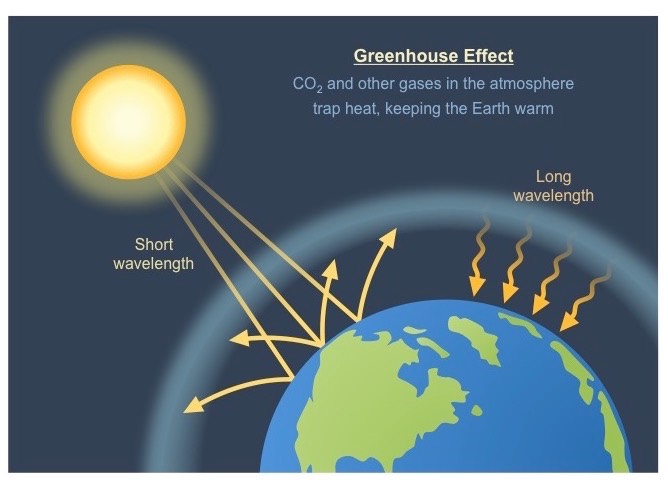
30
New cards
What are the consequences of the enhanced (due to human activity) greenhouse effect?
* more frequent and extreme weather conditions (heat waves, cyclones, tropical storms)
* some areas will become more drought affected and some will become more prone to periods of heavy rainfall
* changes to circulating ocean currents - longer El Niño (warming) and La Niña (cooling) events
* some areas will become more drought affected and some will become more prone to periods of heavy rainfall
* changes to circulating ocean currents - longer El Niño (warming) and La Niña (cooling) events
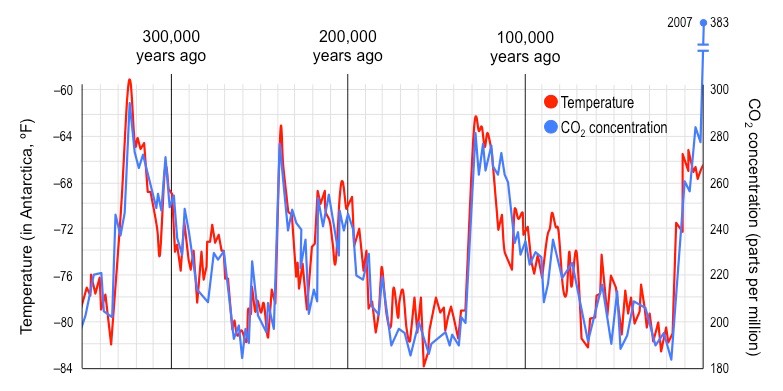
31
New cards
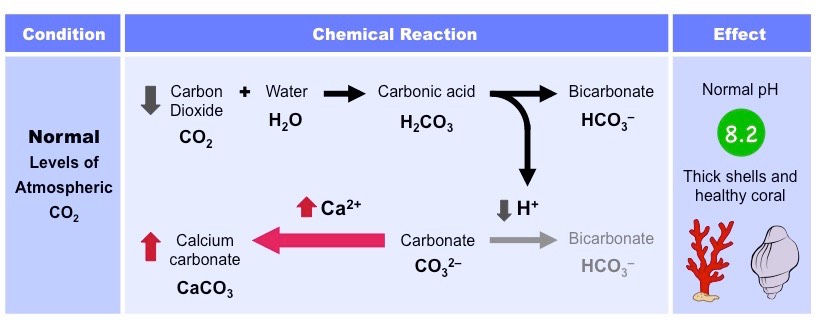
Describe the process of ocean acidification.
* oceans are a major carbon sink and absorb \~33% of all human produced (antrophomorphic) CO2
* CO2 solubility is temperature-dependent (more soluble when cooler), so the higher the temperature the less CO2 will be absorbed
* when ocean absorbs CO2, some of it remains as dissolved gas and some is chemically modified
* CO2 can combine with water to form H2CO3, which dissociates into H+ ions and CO3^2-
* H+ ions lower the ocean pH (acidification) and combine with free carbonate ions (Ca^2+) to form hydrogen carbonate
* with less free carbonate ions in water, marine organism are less able to produce calcium carbonate (via calcification) used to form exoskeletons and shells
* it threatens the vaiblity of coral reefs and molluscs
* since the start of industrial revolution ocean pH has dropped from 8.2 to 8.1 (\~30% increase in acidity), and if currentbconditions continue, it is predicted that oceanic pH could fall to 7.8 by the end of the century
* CO2 solubility is temperature-dependent (more soluble when cooler), so the higher the temperature the less CO2 will be absorbed
* when ocean absorbs CO2, some of it remains as dissolved gas and some is chemically modified
* CO2 can combine with water to form H2CO3, which dissociates into H+ ions and CO3^2-
* H+ ions lower the ocean pH (acidification) and combine with free carbonate ions (Ca^2+) to form hydrogen carbonate
* with less free carbonate ions in water, marine organism are less able to produce calcium carbonate (via calcification) used to form exoskeletons and shells
* it threatens the vaiblity of coral reefs and molluscs
* since the start of industrial revolution ocean pH has dropped from 8.2 to 8.1 (\~30% increase in acidity), and if currentbconditions continue, it is predicted that oceanic pH could fall to 7.8 by the end of the century