acids and bases
1/24
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
define an acid in Arrhenius’ model
substances yielding hydronium ions
define a base in the Arrhenius Model
substances yielding hydroxide ions
define an acid in the Bronsted-Lowry Model
any substance capable of donating hydrogen ion or proton to another substance (proton donors)
define a base in the Bronsted-Lowry Model
any substance capable of accepting a proton or hydrogen from another substance (proton acceptors)
why is water considered amphoteric?
water can act as either an acid or as a base
if an acid is strong, how much does it dissociate in water?
completely
if an acid is weak, how much does it dissociate in water
only dissociate to a very small percentage
what is a weak base?
a base which is only slightly dissociates in aqueous solution
what is a strong base?
a base which is highly dissociated in aqueous solution
What are the five strong bases?
NaOH, KOH, RbOH, Ca(OH)2, Ba(OH)2
what characteristic makes acids strong (easily dissociated)?
bond length - the longer it is, the stronger the acid is
what are the five strong acids?
HCl, HBr, H2SO4, HNO3, and HClO4
what does it mean if an acid is monoprotic?
it has 1 acidic proton (ex: HCl)
what does it mean if an acid is diprotic?
it has 2 acidic protons (Ex: H2SO4
What two things determine how strong an acid is?
in strong acids, the hydrogen is bonded either to a very electronegative element or to an oxygen bonded to a non-metal
in this oxyacids, the strength of the acid increases with the electronegativity of the non-metal (ex: H2SO4 strong, H3PO4 weak) and the number of oxygens present (ex: HNO3 strong, HNO2 weak)
Draw the relationship between [H3O+], [OH-], pH, and pOH (the square of calculations)
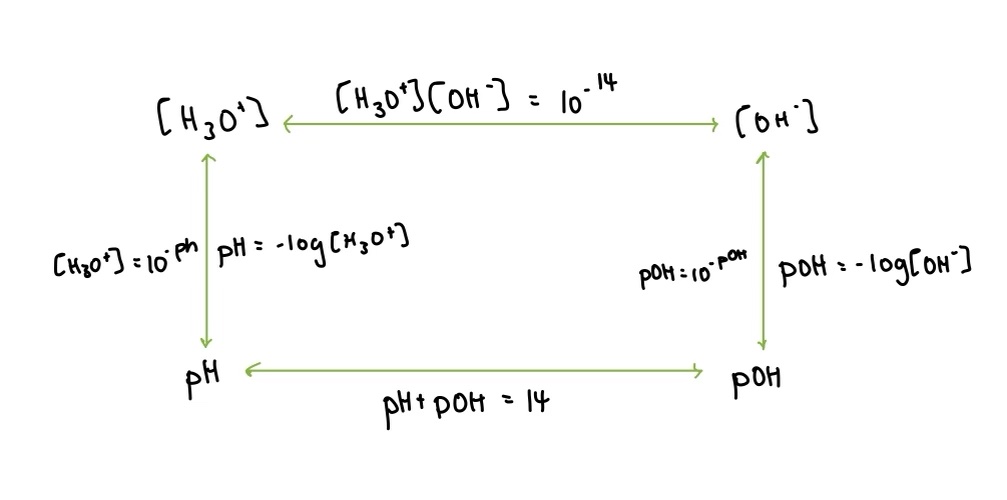
what is the calculation for how water acts as its own acid and conjugate base
2H2O ←→ H3O+ + OH-
What is Kw at 25 degrees
1 × 10-14
how does the pH range change as temperature increases
decreases as temperature increases
what will the Ka value be if the acid is strong?
very high
what will the Ka value be if the acid is weak?
very small
if the pKa is lower, the acid is ____; if the pKa is high, the acid is ____ (strong/weak)
strong, weak
what is the relationship between Kw, Ka, Kb (formula)
Kw=KaKb
what is the relationship between an acid and it’s conjugate base?
the stronger the acid (easier to give away H+), the weaker its conjugate base (less willing to accept H+)
which does equilibrium prefer in acid-base reactions and why? (weaker or stronger?)
prefers the production of the weaker acid and base
the stronger the reacting acid and base, the more complete the reaction