IB biology: topic 2: carbohydrates and lipids
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
what are cabohydrates made up of? (monomers)
long chains of monosaccharide monomers
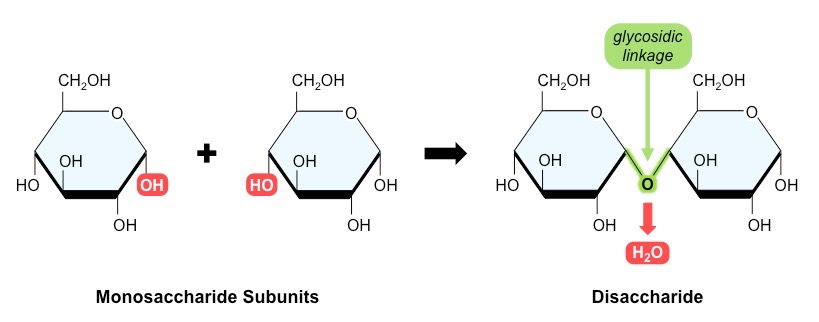
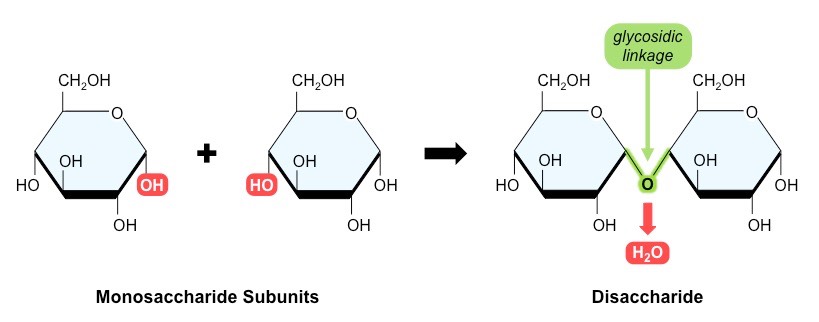
what reaction links monosaccharides? what bonds form as a reult of this?
condensation reactions link monosaccharides, glycosidic bonds form between monosaccharides
what are characteristics of monosaccharides?
sweet-tasting and function as an immediate energy source for cells:
e.g glucose, galactose and fructose
what are characteristics of disaccharides?
small enough to be soluble in water and commonly function as a transport form:
e.g maltose, lactose and sucrose
what are characteristics of polysaccharides?
energy storage or cell structure, and also play role in cell recognition:
e.g cellulose, glycogen and starch
outline cellulose - role / composition / found in
structural polysaccharide.
found in the cell wall of plants.
linear molecule - β-glucose subunits.
1-4 arrangement.
since β-glucose, it is indigestible for most animals.
outline starch - role / composition / found in
energy storage polysaccharide.
found in plants.
composed of α-glucose subunits.
1-4 arrangement.
exists as amylose or amylopectin.
compare amylose and amylopetic as forms of starch
amylose is a linear (helical) molecule.
amylopectin is branched (contains additional 1-6 linkages).
amylose is harder to digest and less soluble, however, as it takes up less space, is the preferred storage form in plants.
outline glycogen - role / composition / found in
energy storage polysaccharide.
formed in the liver in animals.
composed of α-glucose subunits linked together by both 1-4 linkages and 1-6 linkages (branching).
similar to amylopectin in plants, but is more highly branched.
what are fatty acids with no double bond called?
saturated fatty acids:
linear
solid at room temperature
what are fatty acids with a double bond called? what are the two types?
unsaturated fatty acids:
can be cis or trans
typically oil at room temperature
monosaturated vs polyunsaturated
monounsaturated have one double bond,
polyunsaturated have multiple bond bonds.
what are cis fatty acids?
the hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon double bond are on the same side
what are trans fatty acids?
the hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon double bond are on different sides
linear in structure.
solid at room temperature.
do not commonly occur in nature.
produced by hydrogenation.
how are triglycerides formed?
condensation reactions occur between one glycerol and three fatty acids.
the hydroxyl groups of glycerol combine with the carboxyl groups of the fatty acids to form an ester linkage.
this condensation reaction results in the formation of three molecules of water.
what is the function of triglycerides?
function primarily as long-term energy storage molecules.
Triglycerides can be either saturated or unsaturated, depending on the composition of the fatty acid chains
what is the difference in triglyceride storage in plants and animals?
animals tend to store triglycerides as fats (solid), while plants tend to store triglycerides as oils (liquid)
what are the types of triglycerides?
saturated or unsaturated triglycerides
what is the effect of saturated fats and trans unsaturated fats on cholesterol?
raise blood cholesterol levels
what is the effect of cis unsaturated fats on cholesterol?
lower blood cholesterol levels
what are “good fats”?
cis unsaturated fats
what are “bad” fats?
saturated fats and trans unsaturated fats
why are lipoproteins important for fat/cholesterol transport?
fats/cholesterol cannot dissolve in blood and are consequently packaged with proteins, forming lipoproteins, for transport.
outline the role of lipoproteins in cholesterol transport?
Low density lipoproteins (LDL) carry cholesterol from the liver to the rest of the body.
High density lipoproteins (HDL) scavenge excess cholesterol and carry it back to the liver for disposal.
what are “good lipoproteins”?
HDLs - high density lipoproteins - lower cholesterol levels - store cholesterol in liver
what are “bad lipoproteins”?
LDLs - low density lipoproteins - raise cholesterol levels - carry cholesterol from liver around body
how do saturated fats affect lipoprotein levels in body?
saturated fats increase LDL levels within the body, raising blood cholesterol levels.
how do trans unsaturated fats affect lipoprotein levels in body?
trans fats increase LDL levels and decrease HDL levels within the body, significantly raising blood cholesterol levels.
how do cis unsaturated fats affect lipoprotein levels in body?
unsaturated (cis) fats increase HDL levels within the body, lowering blood cholesterol levels.
what is the link between atherosclerosis and cholesterol levels/lipoprotein levels?
high cholesterol levels in the bloodstream lead to the hardening and narrowing of arteries (atherosclerosis).
high LDL levels means LDL form deposits in walls of arteries.
how can atherosclerosis lead to coronary heart disease?
atherosclerosis = high cholesterol levels in the bloodstream lead to the hardening and narrowing of arteries.
accumulation of fat within the arterial walls lead to the development of plaques which restrict blood flow.
if coronary arteries become blocked, coronary heart disease (CHD) will result – this includes heart attacks and strokes.
evidence against coronary heart disease and saturated/trans fats?
incidence of CHD dependent on a myriad of factors besides dietary intake (e.g. exercise, access to health care, etc.)
compare lipids and sugars - STORAGE
lipids are more suitable for long-term energy storage,
sugars more suitable for short-term energy storage.
compare lipids and sugars - OSMOLARITY
lipids have less of an effect on the osmotic pressure of a cell
compare lipids and sugars - DIGESTION
carbohydrates are easier to digest and utilise
compare lipids and sugars - ATP YIELD
lipids store more energy per gram
compare lipids and sugars - SOLUBILITY
carbohydrates are easier to transport in the bloodstream as soluble,
lipids harder to transport in bloodstream.
why are lipids more suitable for long-term storage?
It is not easy to transport - triglycerides are insoluble in water.
It is harder to access - triglycerides cannot be easily digested.
triglycerides store more energy per gram.
why are sugars more suitable for short-term storage?
It is easier to transport - monosaccharides and disaccharides are water soluble.
It is readily accessible - carbohydrates are easier to digest.
carbohydrates store less energy per gram.
how is BMI calculated?
BMI = (mass in kg) / (height in m)²