bmb 460 final exam - paper 3
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
tophat and pptx questions
Last updated 3:43 PM on 4/29/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
1
New cards
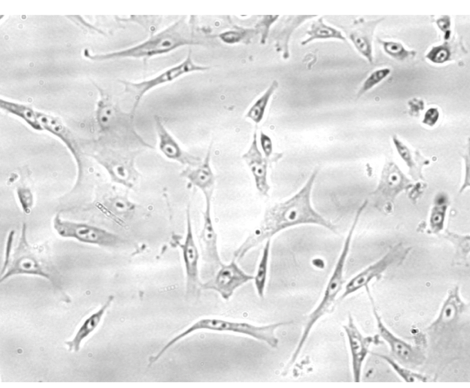
what are mesenchymal cells?
small, spindle-shaped cells with large nuclei, prominent nucleoli, and fine chromatin
2
New cards
what type of cell (multipotent, pluripotent, unipotent, totipotent) are mesenchymal stem cells?
multipotent - differentiate as progenitor cells for all types of ct, such as fibroblasts and osteoblasts
3
New cards
what do mesenchymal cells produce?
extracellular matrix (ECM) that consists of ground substance
4
New cards
what composes the mesenchyme?
mesenchymal cells and ECM
5
New cards
what is mesenchyme?
type of embryonic CT that gives rise to all other CT of the body during development
6
New cards
where do mesenchymal cells originate from?
the mesoderm germ layer
7
New cards
which statement is incorrect about mesenchymal cells?
\
A. mesenchymal cells are small, spindle-shaped cells
B. mesenchymal cells produce ECM
C. mesenchymal cells are pluripotent
D. mesenchymal cells originate from the ectoderm
E. mesenchymal cells are multipotent
F. mesenchymal cells differentiate into CT such as fibroblasts
\
A. mesenchymal cells are small, spindle-shaped cells
B. mesenchymal cells produce ECM
C. mesenchymal cells are pluripotent
D. mesenchymal cells originate from the ectoderm
E. mesenchymal cells are multipotent
F. mesenchymal cells differentiate into CT such as fibroblasts
C. and D.
8
New cards
what is the epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT)?
cell biological process that is required for remodeling of cells and tissues; occurs during embryogenesis, during wound healing, and during the acquisition of malignant traits by carcinoma cells
9
New cards
what cell type starts and ends the EMT?
epithelial to mesenchymal
10
New cards
select all that is true about EMT
\
A. EMT is a biologic process allowing a mesenchymal cell to undergo multiple biochemical changes to assume a polarized epithelial cell status
B. during embryonic development, phenotypic plasticity is afforded by an EMT
C. EMT is signaled by degradation of the basement membrane and the formation of a mesenchymal cell that can migrate away from the epithelial layer where it originated
D. the c-Myc oncogene is a “master regulator” which controls many aspects of EMT
E. cultures of growth-arrested feeder cells have been used inducing EMT
\
A. EMT is a biologic process allowing a mesenchymal cell to undergo multiple biochemical changes to assume a polarized epithelial cell status
B. during embryonic development, phenotypic plasticity is afforded by an EMT
C. EMT is signaled by degradation of the basement membrane and the formation of a mesenchymal cell that can migrate away from the epithelial layer where it originated
D. the c-Myc oncogene is a “master regulator” which controls many aspects of EMT
E. cultures of growth-arrested feeder cells have been used inducing EMT
b. and c.
11
New cards
what is the mesenchymal epithelial transition (MET)?
reverse of EMT; mesenchymal cells convert to epithelial derivatives
12
New cards
what process related to cancer does EMT help with
tumor metastasis
13
New cards
what are neoplastic tissues
self-renewing, stem-like cells within tumors, called CSCs
14
New cards
what is the experimental approach of paper 3?
induce EMT in nontumorigenic, immortalized human mammary epithelial cells (HMLEs) via ectopic expression of transcription factors twist and snail (selected for via puromycin)
15
New cards
what are HMLEs?
not cancerous, but cells that have been changed such that they can divide indefinitely (aka “immortalized”)
16
New cards
what is the point at which a normal cell stops dividing?
called the Hayflick Limit/Phenomenonw
17
New cards
what occurs when a cell undergoes mitosis?
telomeres shorten, and will eventually stop when they reach a certain length
18
New cards
what cells have an exception to the Hayflick limit?
stem cells and cancer cells
19
New cards
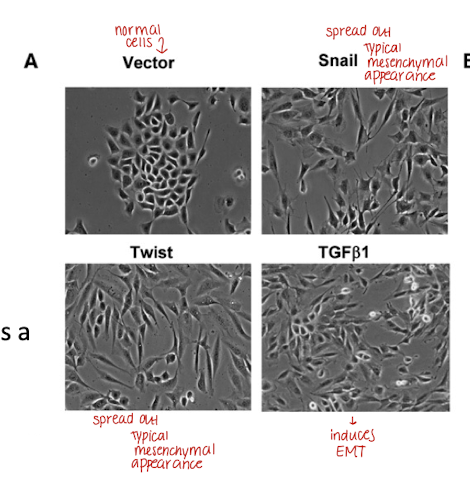
cells that acquired fibroblast-like, mesenchymal appearances look like what?
spread out, spindle shaped
20
New cards
what is an example of an epithelial marker?
E-cadherin
21
New cards
what are examples of mesenchymal markers?
N-cadherin, vimentin, and fibronectin
22
New cards
adding TGF-beta-1 to epithelial cells was a good way to achieve what step?
inducement of EMT
23
New cards
CD44 and CD24 are what?
cell surface markers
24
New cards
what configuration of CD44 and CD24 is associated with human breast CSCs and normal mammary epithelial stem cells?
high CD44/low CD24
25
New cards
mesenchymal-like cells generated by EMT showed what kind of CD configuration?
CD44 high/CD24 low
26
New cards
e-cadherin
epithelial marker
27
New cards
Snail
transcription factor known to induce EMT
28
New cards
vimentin
mesenchymal marker
29
New cards
hTERT
catalytic subunit of the human telomerase (the gene that encodes the catalytic unit)
30
New cards
mammospheres
mammary epithelial stem cell aggregates derived from primary breast tumors (associated with cancer stem cells)
31
New cards
more mammospheres present in the cell is indicative of what?
stem cell character
32
New cards
more mammospheres are formed in cells containing which transcription factors?
snail, twist, and TGF-B-1
33
New cards
undergoing EMT does what to the percentage of mammospheres?
increases presence by >30 fold
34
New cards
how can the authors tell that the cells over expressing snail or twist have undergone EMT?
\
A. cells express more CD44 and less CD24 on average
B. E-cadherin is downregulated
C. Cells acquired fibroblast-like mesenchymal appearances
D. transforming growth factor beta-1 is expressed
\
A. cells express more CD44 and less CD24 on average
B. E-cadherin is downregulated
C. Cells acquired fibroblast-like mesenchymal appearances
D. transforming growth factor beta-1 is expressed
A. B. and C.
35
New cards
some cells naturally express high CD44/low CD24. how did the authors distinguish between them and the EMT cells?
cells that underwent EMT expressed stem cell characteristics K18 and K8
36
New cards
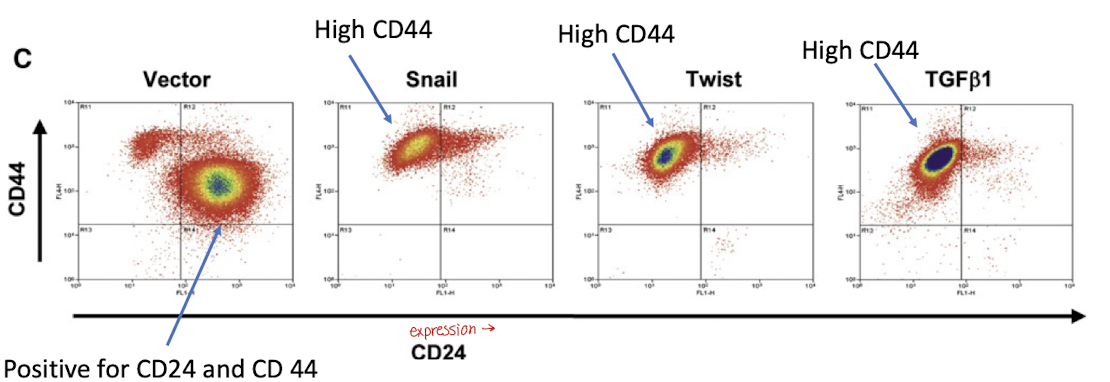
which of the figures labelled in purple shows a CD44 high/CD24 low expression pattern?
B, C, and D
37
New cards
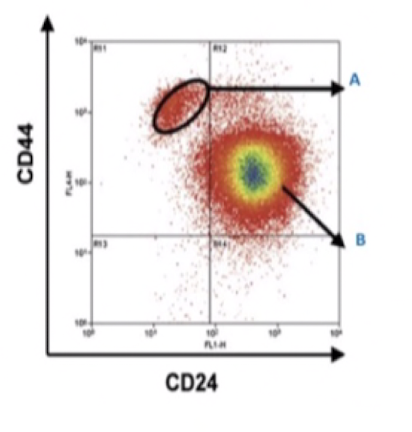
Study the figure and select the correct statements.
\
A. Cell population labelled A have CD44high/CD24low
B. Cell population labelled B CD44high/CD24low
C. Cell population labelled A form mammospheres better than the population labeled B
\
A. Cell population labelled A have CD44high/CD24low
B. Cell population labelled B CD44high/CD24low
C. Cell population labelled A form mammospheres better than the population labeled B
A and C
38
New cards
tamoxifen
drug used to induce EMT; tests if EMT conversion promotes generation of cancer stem cells (it does)