LC CHEMISTRY- TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
REBECCA'S CHEMISTRY- TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS KNOWT
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
substitution reaction
chemical reaction in which an atom or group in a molecule is replaced by another atom or group of atoms
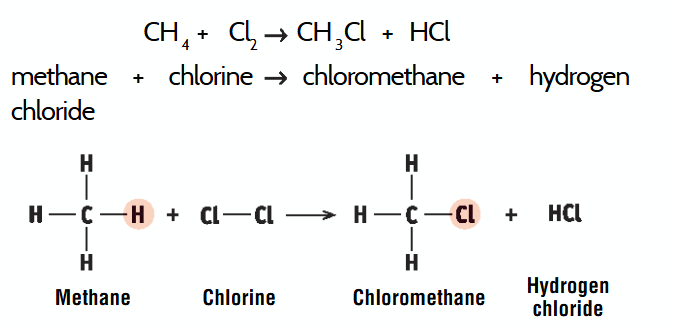
substitution reaction example
mechanism of reaction
step by step description of how a overall reaction occurs
nitrogen and hydrogen toform ammonia
purpose curly arrows
show electron movement

movement of one electron

movement of pair of electrons
initiation
convert the chlorine molecule into two chlorine free radicals

a photochemical reaction
it takes place rapidly if the mixture is exposed to ultraviolet light. The fact that UV light causes the reaction is evidence for the mechanism since UV light possesses enough energy to break the Cl–Cl bond. This step is often called the initiation or starting stage of the reactio
propagtion
one of the Cl radicals attacks the m
termination
When most of the reactants have been used up during Steps 2 and 3, there are only a small number of Cl radicals and methyl radicals left over. These combine to form Cl2, chloromethane and ethane.
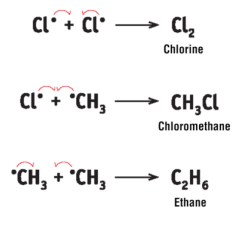
what mechanism example identical to the innerworkings of this reaction
the monochlorination of ethane is identical
evidence 1: reaction takes place when exposed to UV light
example 1: suggests a free-radical mechanism whereby Cl2 is broken down into Cl radicals
evidence 2: for every photon of UV light used, thousands of chloromethane molecules are formed
explaination 2: suggests a chain reaction is involved
evidence 3: addition of an inhibitor, like O2, slows down the reaction
explanation 3: shows a chain reaction is taking place, as O2 combines with free radicals, stopping the chain reaction.
esterfication
when carboxylic acid reacted with alcohol with a small amount of H₂SO₄ as a catalyst, an ester formed. A substitution reaction because H on COOH is relaced by the a aklyl like methyl or ethyl
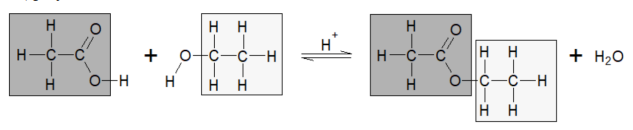
esterfication
acid hydrolysis creates a reversible reaction carboxylic acid and alcohol
base hydrolysis creates a irreversible reaction carboxylate salt and alcohol, saponification how soap is made
hydrolysis
larger molecule is broken down into smaller parts by adding water
saponification
hydrolisis of esters with a base is added like NaOH or KOH it results in formation of the sodium and potassium salt of the carboxylic acid, this is unreversiblke reaction due to teh base
addition reaction
one in which two or more molecules react together to form a single molecule
addition reacton properties
Will always occur on a double/triple bond.
Geometry will change from planar (unsaturated C-C bonds) to tetrahedral (saturated C-C bonds).
Benzene does not undergo addition reactions as its delocalised electrons make it very stable and unreactive.
uses for addn reactions
chloroethane formed by the reaction between ethene and hydrogen chloride is used in dentistry as means of diagnosing a dead tooth. A small amount of the substance is placed on the tooth and because of the low boiling point of the liquid, this creates a localised chilling effect, if tooth alive, the chilling felt by patient
1,2- dichloromethane formed by the reaction between ethene and bromine is used to manufacture chloroethane, used to make polyvinyl chloride (PVC), a widely used plastic
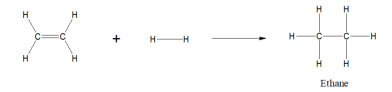
ethene + hydrogen bond =
ethane
ethene + chlorine bond =
1,2-dichloroethane
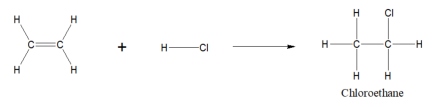
ethene + hydrogen chloride bond=
chloroethane
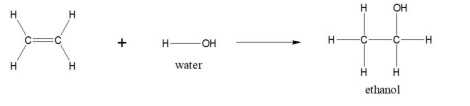
ethene + water
ethanol
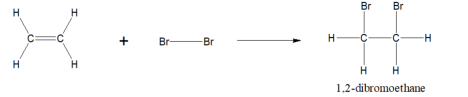
ethene + bromine bond=
1,2- dibromoethane
difference between animal and vegetable fat
animal usually saturated and unsaturated vegetable fats
bromination of ethene is an example of
ionic addition reaction
mechanism
a detailed step-by-step description of how the reaction occurs
name the steps of Bromination of ethene
polarisation
heterolytic fission
carbonium ion formation
ionic attack
Polarisation (bromination of ethene) EXPLAIN AND DRAW
c=c double bond in ethane has a high concentration of negative charge
As the Br₂ approaches the ethene, the electrons are repelled away from the ethene, polarisation the b₂
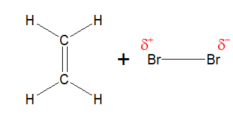
discuss for my own understanding deeper explanation of polarisation
the c=c double bond has high concentration due to the double bond of both sigma and pi bonds, the pi bonds holds more electrons because it’s a sideways overlap so extra electrons, whereas the sigma bond is regular regular head on basic overlap
where as for
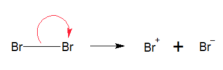
Heterolytic fission (bromation of ethene) EX
the polarisation eventually becomes so great, the molecule splits into Br- and Br+ . we call this heterolytic fission because the Br-took all 2 electrons from the Br-Br bond. (Br- IS BEING GREED ITS HETERO 1 ELEMENT TAKING 2 ELECTRONS)
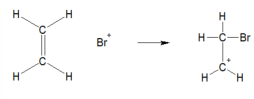
carbonium ion formation (bromination of ethene) EXPLAIN AND DRAW
The Br+ attacks the electron rich C=C double bond. This forms a carbonium ion (positive charge on C)
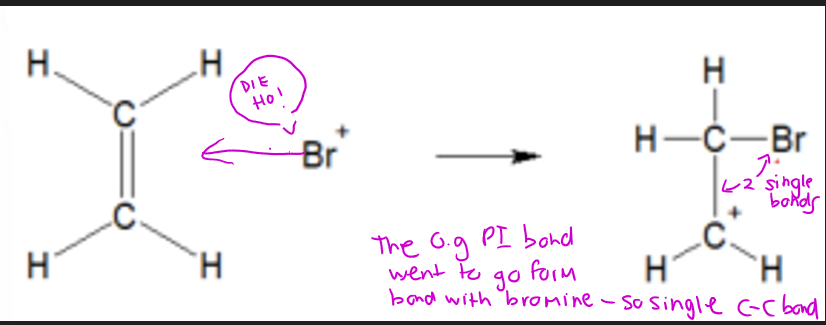
UNDERSTANDING carbonium ion formation deeper
c=c double bond IS BROKEN to form sigma bond with bromine, this leaves only a single sigma bond between the two carbon atoms
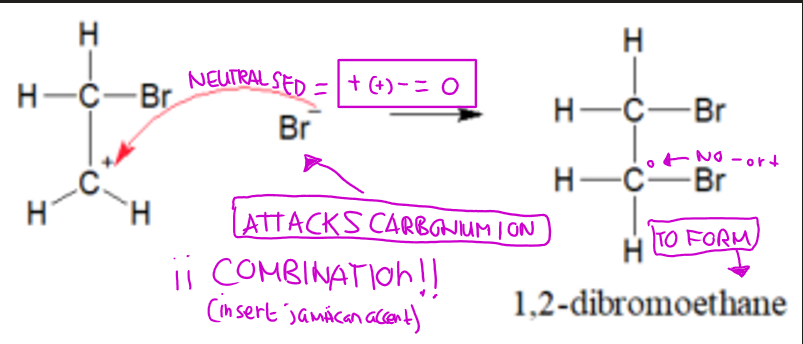
ionic attack (bromination of ethene)
The Br⁺ on attacks the carbonium ion, forming 1,2-dibromoethane
WHAT TO DO TO WRITE TEH ADDITION OF CL₂ OR HCL
SIMPLY REPLACE THE BR₂
Evidence of the bromination of the ionic addition mechanism
If this reaction is carried out in bromine water with some Cl⁻ ions added, we see the normal 1,2-dibromoethane product being formed, but two other products form also; 1-bromo-2-chloroethane and 2-bromoethanol. These form because of the Cl⁻ or the OH⁻ (from water’s self-ionisation) can replace the Br⁺ in step 4.
polymerisation reaction is a type of
addition reaction
polymer definition
long chain molecules made by joining many small molecules (monomers, they are made of many repeating units e.g polyethene (made up of many ethene monomers)
Elimination reaction definition
one in which a small molecule is removed from a larger molecule, leaving a double bond on the larger molecule.
properties of an elimination reaction
geometry changes from tetrahedral to planar as a double bond is formed
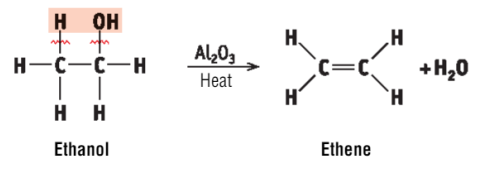
generally involved the removal of a water molecule (H2O) – these are also called dehydration reactions
what is exclusive to dehydration elimination reactions
Al2O3 and heat is used to remove water
what occurs in the production of ethene
water is removed from the ethanol.
Al2O3 and heat is used to remove water from ethanol