Perfect competition, Imperfectly competitive markets and Monopoly
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Difference between market power and monopoly power
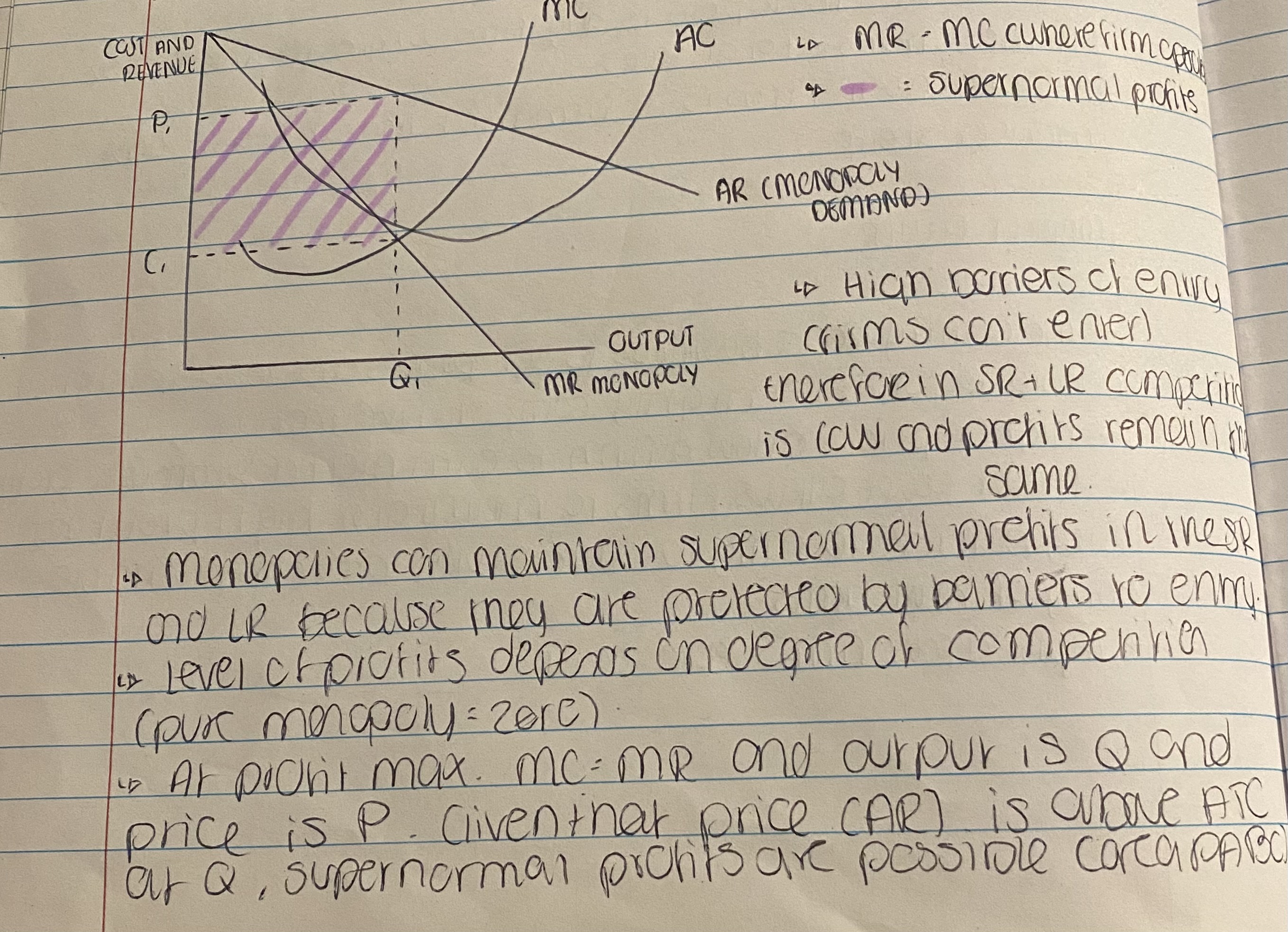
• Monopoly power refers to a situation where a single firm has control over a market for a particular product/service.
• Allows firms to set prices and prod. levels without concern about competition.
• In a monopoly, the firm can effectively act as a ‘price maker’ rather than ‘taker’ (without fear of losing market share).
• Downside is consumers end up paying higher prices and fewer choices (No competition to keep prices in check - market failure).
Short run and Long run Profit Maximisation in a Monopoly
Arguments against monopoly power

Arguments in favour of Monopoly power

What does monopoly power depend on?

What is economic efficiency? Types of efficiency?
• Concerned with how well resources are used to resolve how, what and for whom prod. should take place.
Types of efficiency
• Productive
• Allocative
• Static
• Dynamic
Productive, Allocative and Dynamic Efficiency
• Productive efficiency: Level of output at which AC of prod. are minimised. Exists when producers minimise wastage of resources and operate at lowest point on AC curve. (STATIC)
• Allocative efficiency: Occurs when there is optimal distribution of goods and services. At output level where Price = MC of production. This is because price that consumers are willing to pay is equivalent to marginal utility that they get. (STATIC)
• Dynamic efficiency: Occurs in long run. Concerned with productive efficiency of a firm over a period of time (pace of innovation). Dynamically efficient firm will reduce cost through new prod. processes.
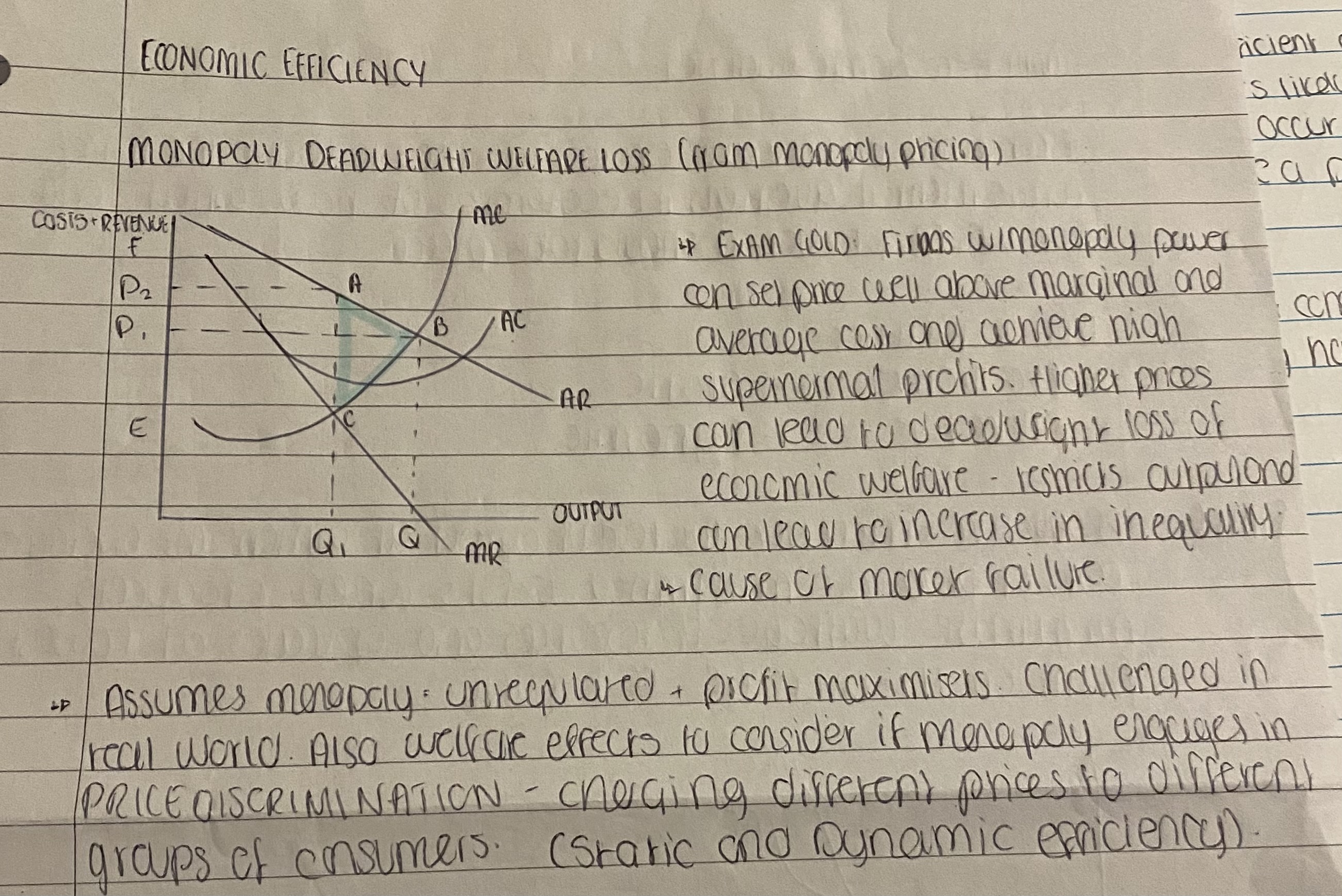
What is Monopoly Deadweight welfare loss (from monopoly pricing)
What is Monopoly power?
• Monopolies have theoretical potential to be able to deliver positive economic outcomes.
• Often lack incentive to do so therefore leads to market failure and resource misallocation.
Inefficiency and Market Failure
• Market failure occurs when markets lead to an inefficient allocation of resources. Where there’s imperfect competition there’s likely to be market failure.
• Allocative and productive inefficiency may occur when firms either over/under produce and attempt to charge a price above marginal cost.
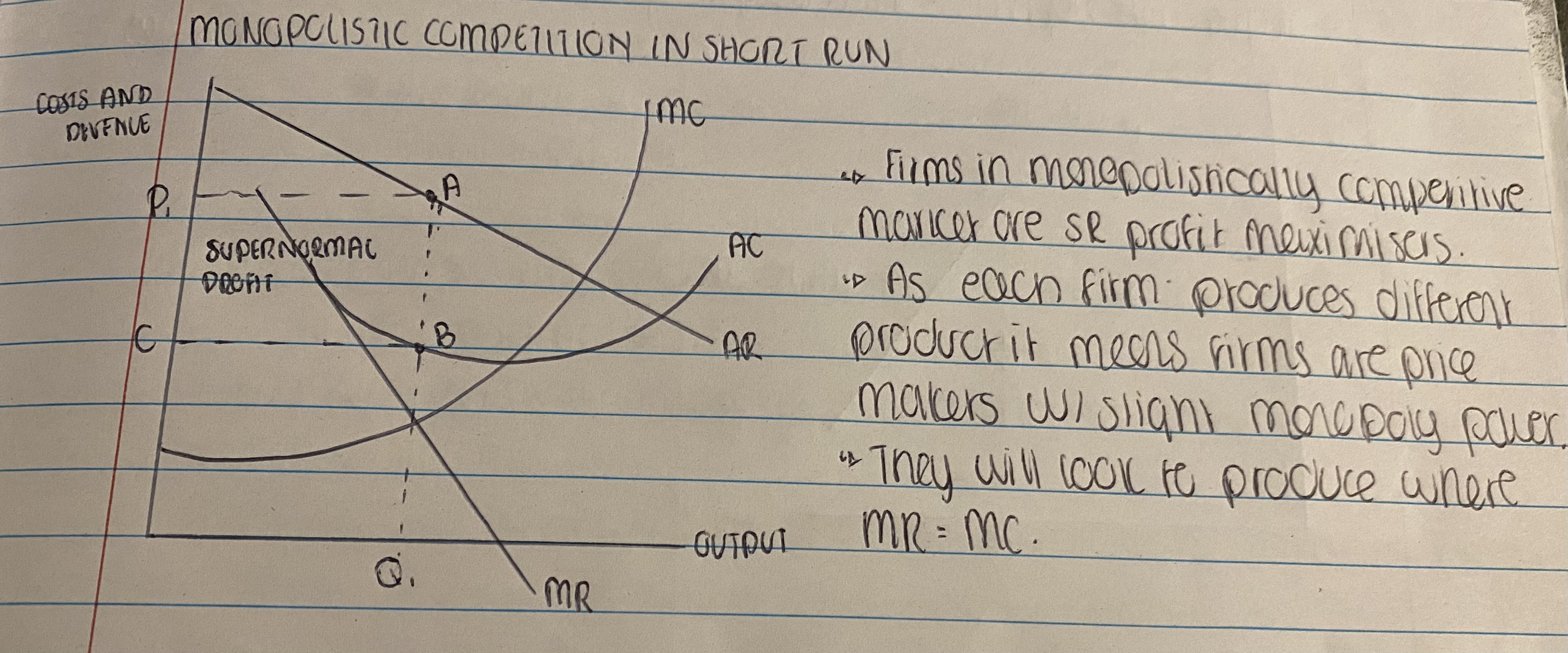
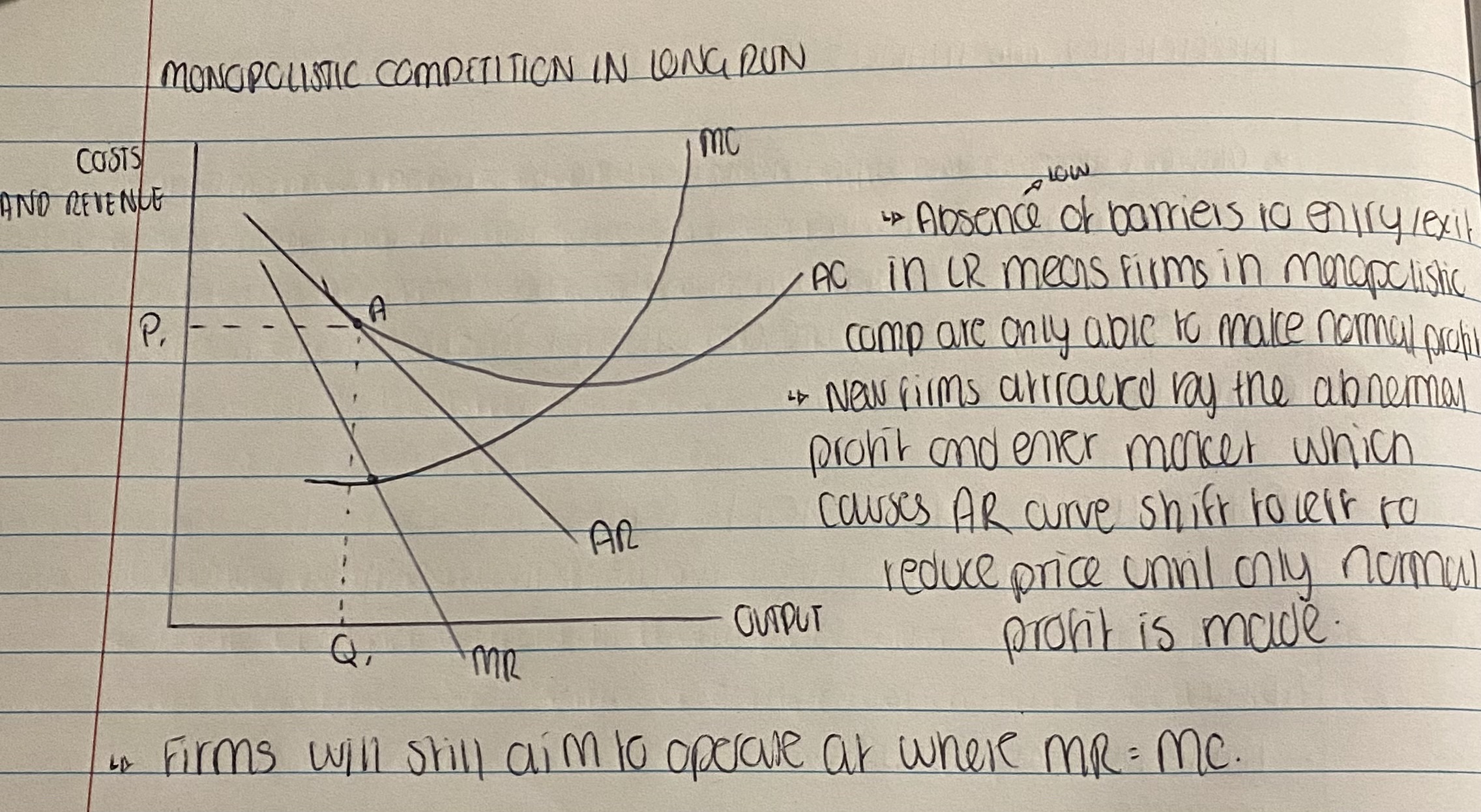
What is Monopolistic Competition?

Monopolistic Competition in the Short Run
Monopolistic Competition in the Long Run
What is Non-Price Competition?
• Apart from price competition firms in imperfectly competitive markets likely to undertake various methods to to compete.
• Persuasive advertising
• Marketing competition (⬆exclusivity)
• Product differentiation (Branding)
• Packaging
• Quality/After sales service
What is an Oligopoly?

What is Market Behaviour like in an Oligopoly?
• Oligopolist firm affects rivals through price and output decisions, but it’s own profit can also be affected by how rivals behave and react to firms’ decisions.
What is a Collusive Oligopoly and Cartels? Collusion vs Market Cooperation?

What is the Kinked Demand Curve?
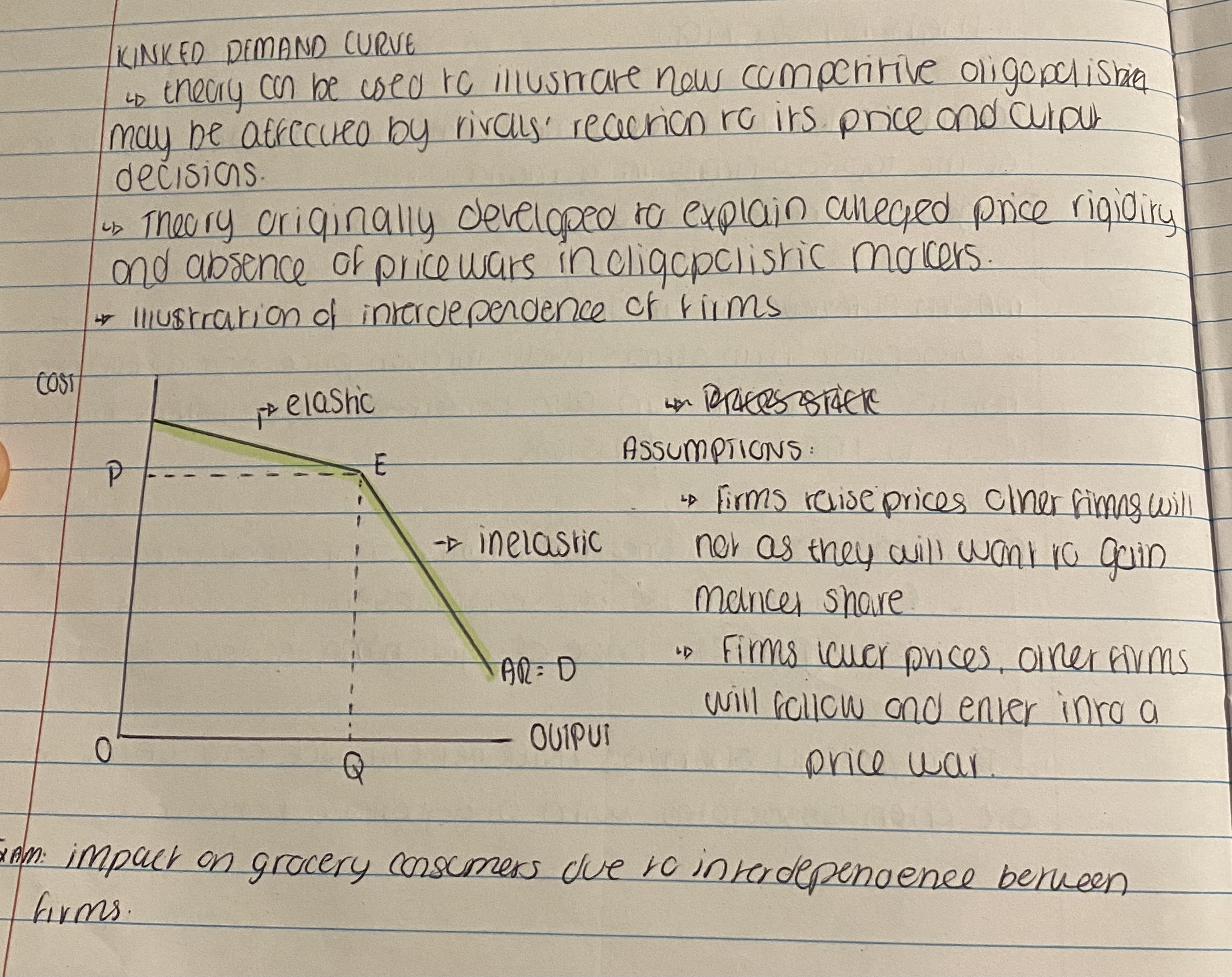
Non price competition for Oligopolists. What are price wars, price leadership and price agreements?

Advantages of Oligopolists

Disadvantages of Oligopolies

What is price discrimination

Conditions needed for price discrimination

How to ensure Profit Maximisation with price discrimination?
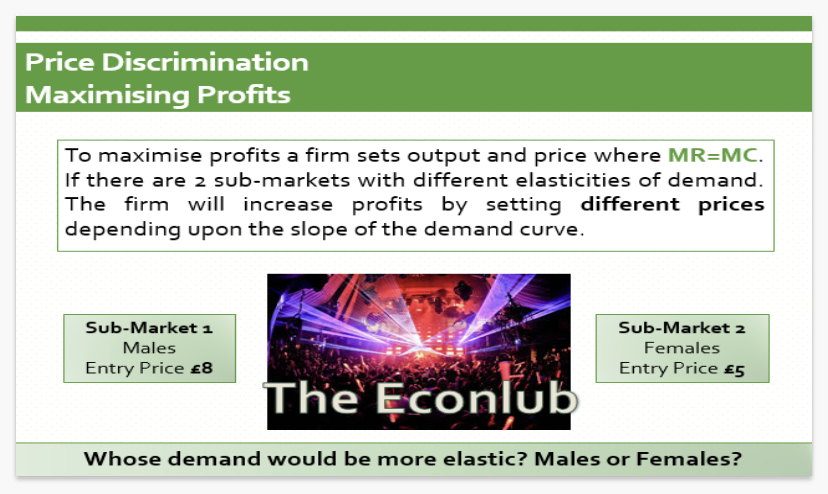
Price Discrimination Curve
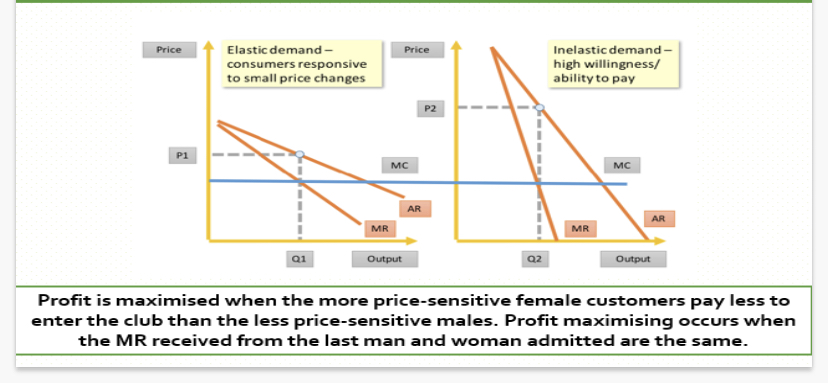
Price Discrimination Advantages and Disadvantages

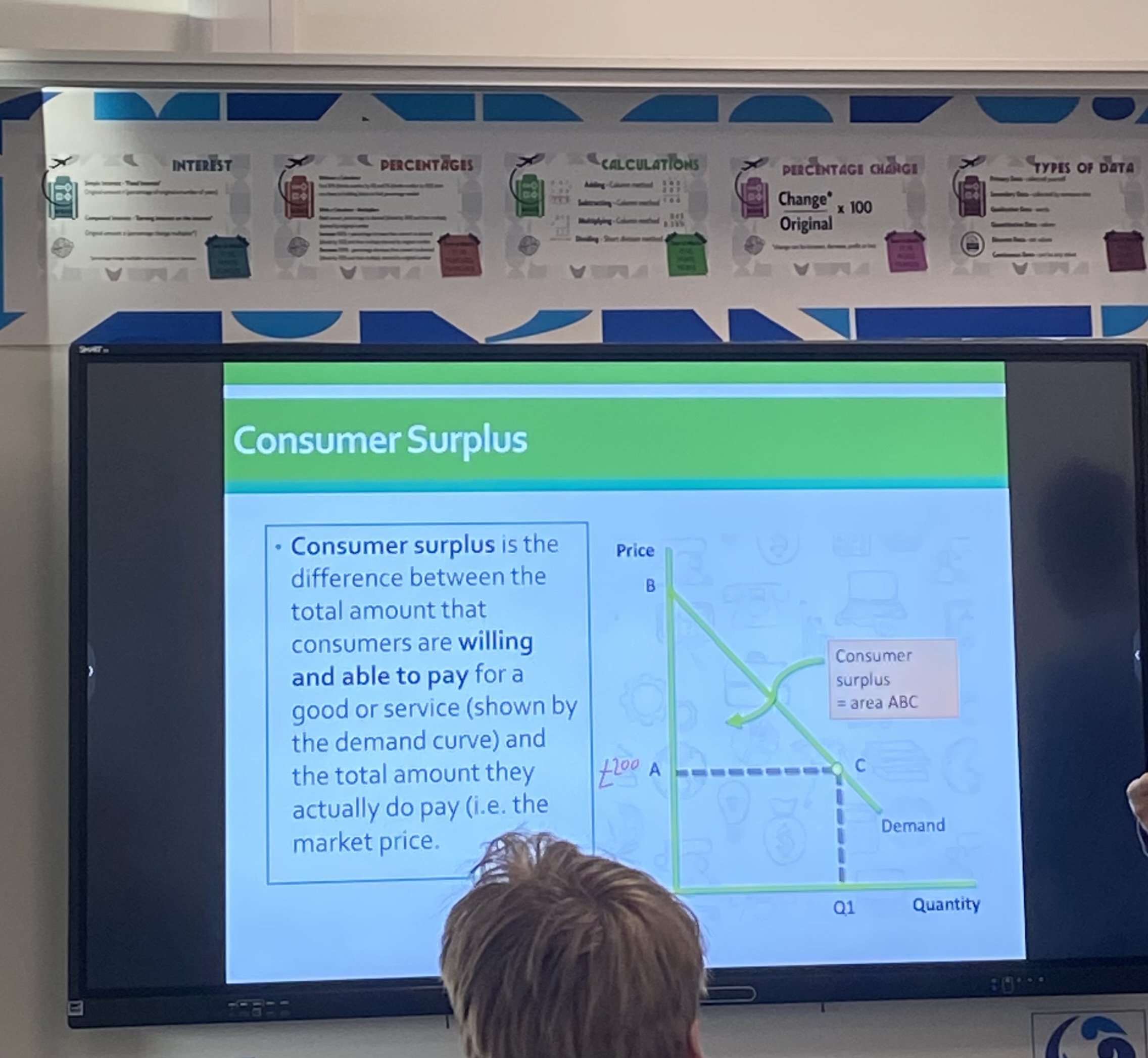
What is consumer surplus?
What is Producer Surplus?
