Lecture #7
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
UP Element
Upstream of the core promoter, stimulating transcription by a factor of 30
Part of promoter because it is recognized by RNA polymerase
Enhancers
Additional cis-elements between -60 and -150 which are bound by transcriptional activators
E.coli sigma factor 70
Sigma factor that contains conserved domains
4 regions of high sequence similarity
Specific areas that recognize the core promoter elements are the -10 and -35 box
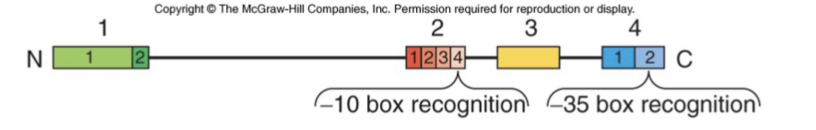
Sequence recognition specification is achieved through interaction between specific aa of sigma factors and the promoter sequence
recognition seals DNA in the polymerase
Temporal (time dependent) control of transcription
At different stages of infection, different genes are turned on
ex: SPO1-infected B. subtitles
Early genes turned on in first 5 minutes of transcription by the host holoenzyme
Sigma factor Gp28: early gene that replaces host sigma 43, changing the specificity of RNA polymerase to transcribe middle genes
Middle genes, gp33 and gp34, encode proteins that bind to each and forma new sigma factor for late genes
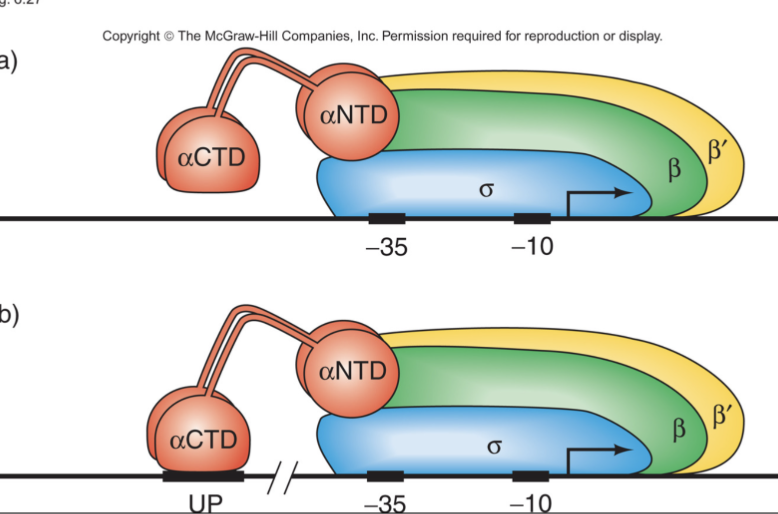
Role of alpha subunit
Recognizes the upstream promoter element
sigma factor recognizes core promoter element
Gel Mobility Shift
Gel electrophoresis can be used to detect DNA and complexes
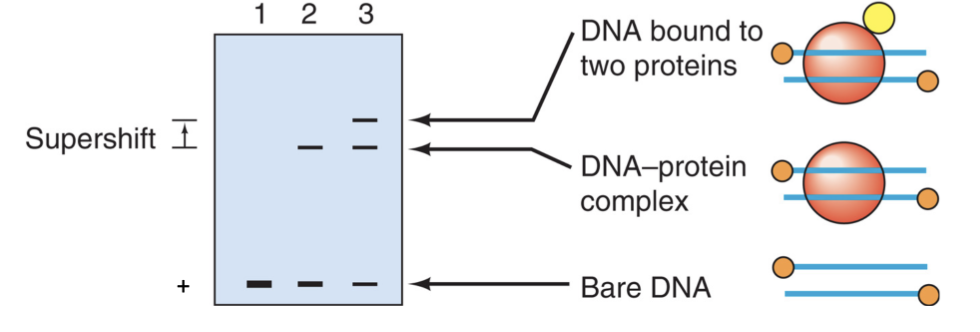
notice the different bands identify parts of complexes
DNase foot printing
Detects DNA-protein interaction using the fact that a protein bound to DNA will often protect that DNA from enzymatic cleavage
Digest DNA-protein complex under mild conditions with DNase 1 (endonuclease)
protein binding prevents the digestion from DNase 1
No bands indicate that DNA is bound to protein; called the footprint
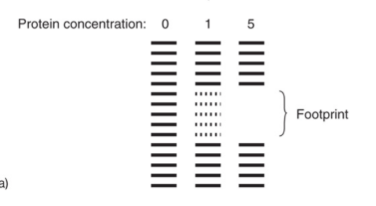
less bands indicate larger protein concentration
Evidence of alpha binding to Up element
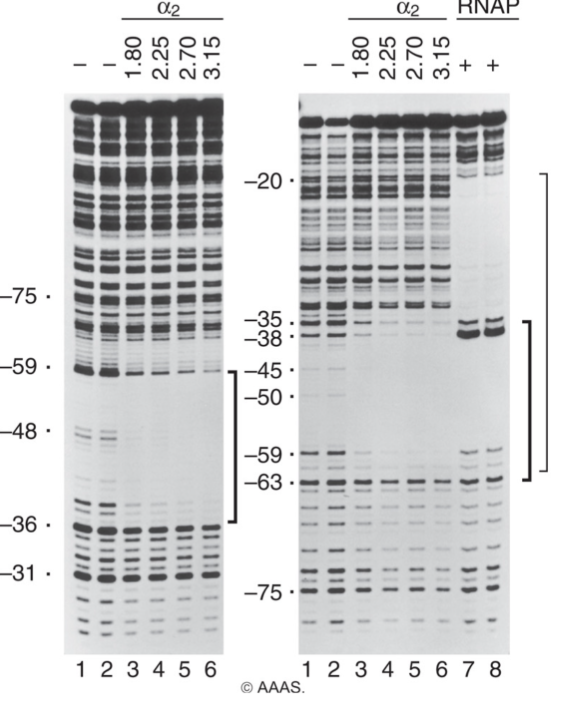
No bands=protein-DNA complex
Alpha subunits show no bands around Up element, giving evidence that it is bound to the UP element
RNA Polymerase shows binding at UP element and at the core promoter
Stages of transcription initiation
Formation of a closed promoter complex
Conversion of closed promoter complex to an open promoter complex
Polymerizing early nucleotides
Promoter clearance: transcript becomes long enough to forma stable hybrid w/ template
Reuse of sigma factor
During initiation, sigma factor can be recycled for additional use with new core polymerase
córę enzyme can release sigma factor which is then free to associate with another core enzyme
Elongation
After initiation:
córę enzyme continues to elongate RNA
Nucleotides are added sequentially
Phosphodiester bonds formation involves B and B’ subunits
Subunits also involved in DNA binding
Rho-independent termination
Depends on:
Inverted repeats followed by T-rich region in the nontemplate strand of the gene
Forms a hairpin structure due to complementary base pairing between inverted repeat sequences
Inverted repeats allows a hairpin to form at a transcript end
String of T’s in contemplate strand results in week base pairs holding the transcript to the template strand
Model of Intrinsic/rho-independent Termination
base pairing of something to the transcript to destabilize RNA/DNA hybrid
Causes hairpin to form
Causes transcription to pause
String of Uc incorporated downstream of hairpin to destabilize hybrid and the RNA falls of the DNA template
Rho-dependent termination
Rho binds to the RNA polymerase in an elongation complex, facilitating the dissociating of the RNA/DNA hybrid, terminating transcription
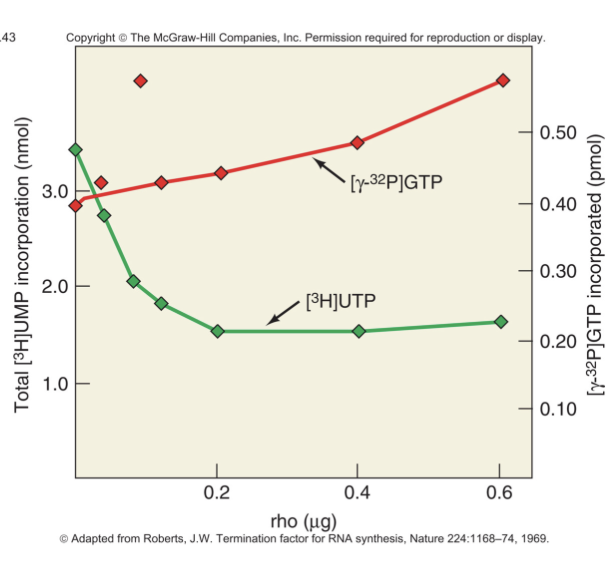
Green line: the presence of rho causes a decrease in total RNA synthesis
consistent w/ action that rho terminates transcription
Mechanism of Rho
Rho follows the polymerase as transcription continues
Catches the polymerase as it pauses at the hairpin
Releases transcript from the DNA polymerase complex by unwinding th RNA-DNA hybrid