Visual pathway
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What cells are in the outer layer of the retina
photoreceptors, bipolar + horizontal dendrites
what cells are in the inner layer of the retina
bodies of horizontal, bipolar, and amacrines cells,
axons of bipolar, amacrines and dendrites of ganglions.
function of rods and cones in retina
generate graded potentials in response to light called photopigements.
rods - black and white vision
cones - colour vision
function of bipolar cells in retina
first neurone in the pathway to the brain, connected to photoreceptors.
what is the role of ganglion cells in the retina
A ganglion cell can receive one or more typically many bipolar inputs
second neurone in the pathway
axons make up optic nerve
detect change in light themselves (effects circadian rhythm)
How do rods detect black and white
These cells generate graded potentials in response to light. The chemical responsible is called a photopigment.
In rods, this is known as rhodopsin.
It consists of two molecules: a large opsin protein long term, and retinal
During light absorption, retinal undergoes synthesis Retinol → Retinal → Retinoic acid
1. Light triggers cis-retinal conformational change
2. Opsin releases retinal, becomes active
3. Active opsin activates transducin's alpha subunit → activates cGMP phosphodiesterase → converts cGMP to GMP
4. Reduced cGMP closes Na+ channels
5. Cell hyperpolarizes, stops glutamate release
What is the purpose of different opsin types (S.M,L)
short medium and long opsins code for different wavelengths of light that animals can see.
How is light converted to chemical then to electrical impulse?
Signal Cascade:
1. Light triggers cis-retinal conformational change
2. Opsin releases retinal, becomes active
3. Active opsin activates transducin's alpha subunit → activates cGMP phosphodiesterase → converts cGMP to GMP
4. Reduced cGMP closes Na+ channels
5. Cell hyperpolarizes, stops glutamate release
Describe the visual (neural) pathway from the retina to the cortex.
Most neurones synapse in the LATERAL GENICULATE NUCLEUS (this is a part of the thalamus).
optic nerve extends caudally from the retina, through the optic foramen in the presphenoid bone into the neurocranium.
It joins the ventral aspect of the diencephalon at the optic chiasm, just rostral to the hypophysis (pituitary gland).
In general, the majority of axons decussate, but the degree of decussation depends on the type of animal. In fishes and birds, all fibres decussate (Fig. 10.10). In mammals, there is partial decussation (ungulates about 80–90%, dogs 75%, cats 65%, primates 50%).
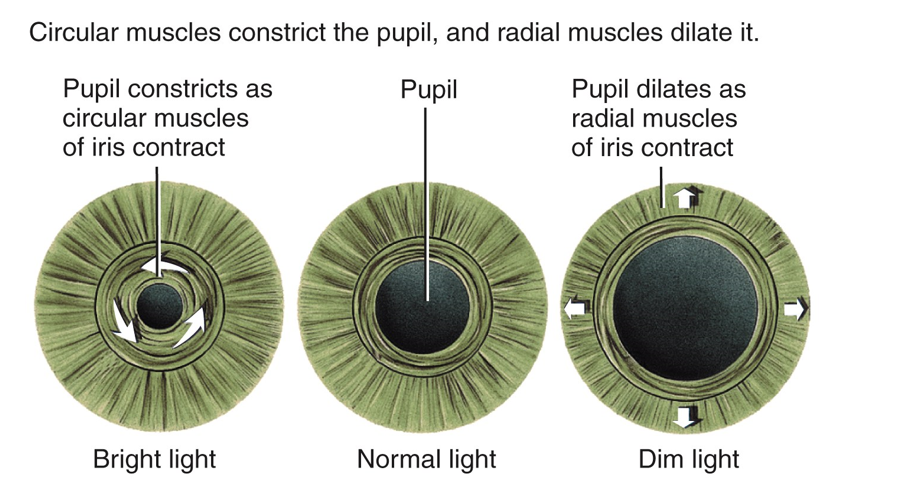
Define the pupillary light reflex, explaining its clinical importance
autonomic reflex that constricts the pupil in response to light adjusting the amount of light that reaches the retina
works as a CN test for the oculomotor nerve
What is amblyopia and what can cause this?
blindness with working eyes
damage to back of the head affecting visual cortex processing areas such as V2, V3, V4.

What animal sees like this?
Deer