Exam 1 - Meristem/Primary Growth
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
TEM - Transmission Electron Microscopy
looks at the internal structure of things
black and white
higher quality that most types
utilizes electrons for imaging
SEM - Scanning electron microscopy
visualizes the exterior of things
utilizes electrons or imaging
black and white
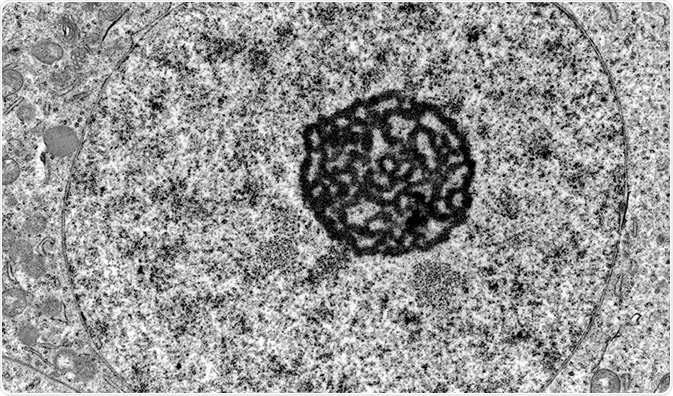
Nucleus
contains chromatin/chromosomes
location of transcription and rna splicing
nucleolus - ribosome subunit assembly
bounded by nuclear envelope containing nuclear pores
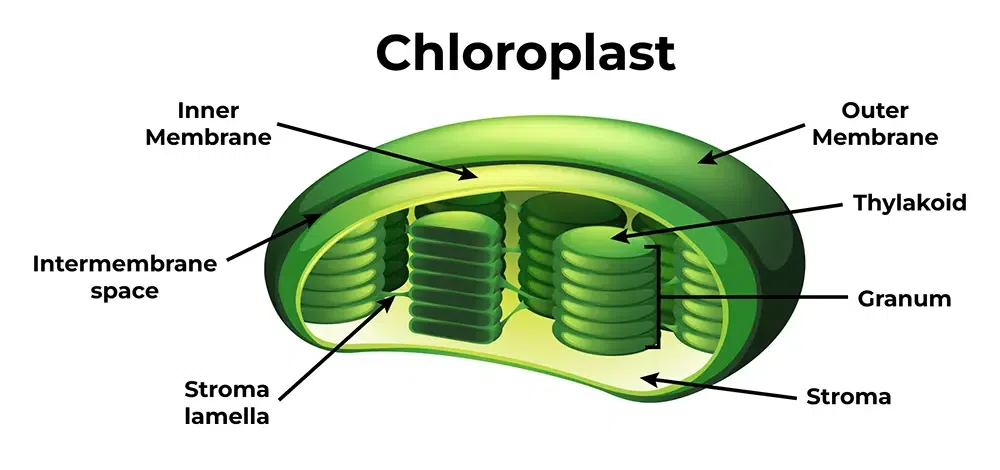
Chloroplast
bound by two membranes (inner and outer)
internal thylakoid membranes and stroma
contain their own genome
biosynthetically very active
contain chlorophyll
site of photosynthesis
Chromoplasts
plastids that contain pigments other than chlorophyll (usualyl carotenoids)
found in flowers, ripening fruit, aging fall leaves, some roots, etc.
no internal membrane structure
Leucoplasts
plastids lacking pigments
no internal membrane structure
Amyloplasts
a type of leucoplast
store starch
Etioplasts
immature plastids
contain rudimentary internal membrane structures called prolamellar bodies
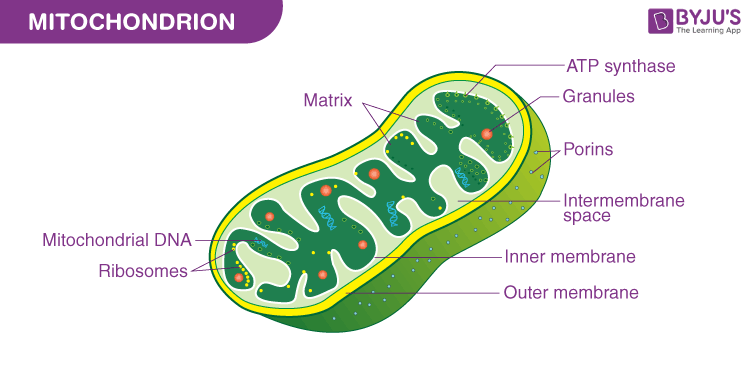
Mitochondira
bound by two membranes
contain their own genome
import majority of proteins from cytoplasm
respiration to produce atp
Peroxisomes
bound by single membrane
fatty acid degradation
photorespiration
auxin metabolism
detoxify h202 (hydrogen peroxide)
Vacuoles
terminal storage compounds
turgor pressure of cell
bound by tonoplast membrane
autophagy of organelles
may contain calcium oxalate crystals
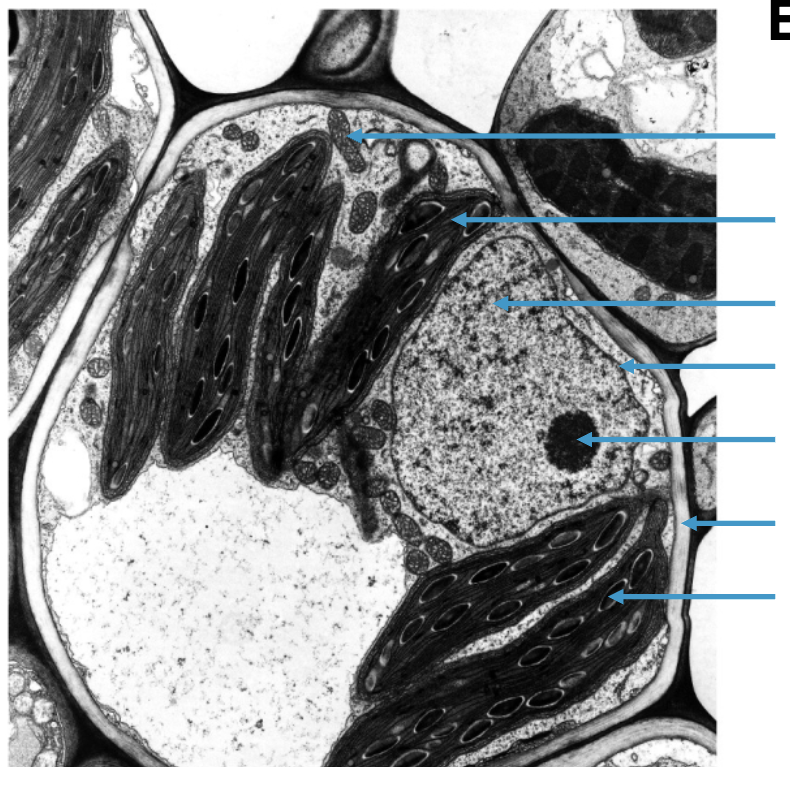
label these structures
(from top to bottom)
mitochondria
chloroplast
nucleus
nuclear envelope
nucleolus
cell wall
starch grain
Endoplasmic reticulum
lipid synthesis
synthesis of membrane bound and secreted proteins
intracellular calcium storage
Golgi apparatus
synthesize cell wall polysaccharides
glycosylate proteins (adds a sugar to proteins)
direct vesicles to intercellular compartments
huge component of the endomembrane system
composed o 5-7 discs of sacs
cis face - faces towards the ER
trans face- faces away from ER/towards cell wall
Plasma membrane
lipid bilayer with embedded proteins
regulate transport of nutrients
protein domains (transmembrane and lipid linked)
Transmembrane domain
single or multi passes through the membrane, protein domain spans the entire membrane at least once
lipid linked
linked to plasma membrane via a lipid
only linked on one side of plasma membrane
Cytoskeleton
microtubules and actin filaments (no intermediate filaments in plants)
Microtubules
polymers of alpha and beta tubulin that come together to form dimers
have dynamic instability, they shrink and grow
heavily aid in cell division
aid in phragmoplast positioning
Actin filaments
tip growth of pollen and root hairs
movement of nucleus and other organelles
vesicle mediated secretion
cytoplasmic streaming
only 1 type of monomer
Cell wall functions
constrains expansion of protoplast
prevents rupture of plasma membrane by water uptake
determines shape and size of cell
defense against pathogens
structural support and rigidity
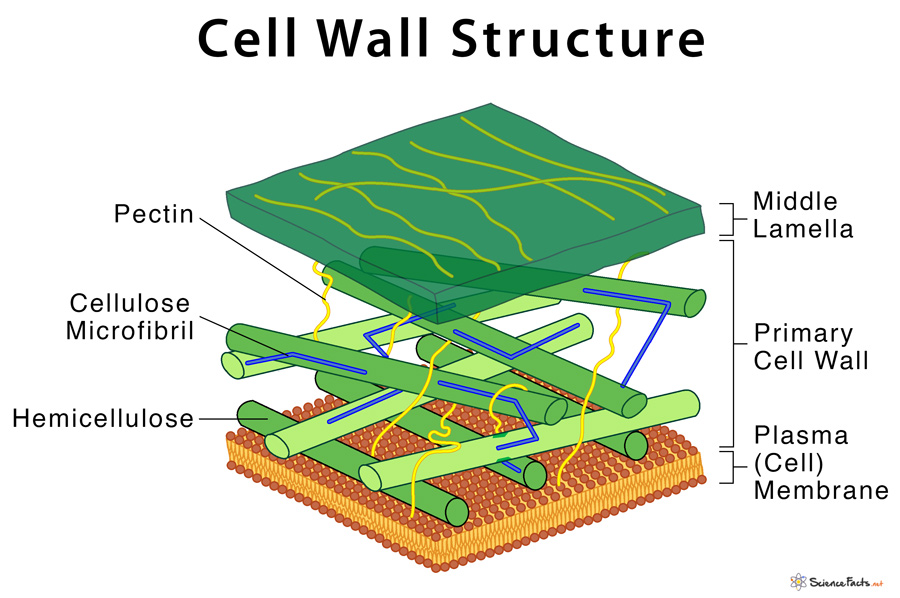
Primary cell wall
cell wall synthesis occurs when cell is formed
can be loosened to allow cell growth
Middle lamella
region between two adjacent primary cell walls
composed of primarily pectins
Cellulose
major component of cell walls
organized in microfibrils
deposition orientation determines cell expansion
Cellulose synthase
takes udp glucose, removes udp and links glucose to microfibrils
connected to microtubules below which aid in movement for deposition
Components of cell wall
cellulose
pectin
hemi cellulose
secondary cell wall
usually 3 layers
array of cellulose is a different orientation in each layer
created during differentiation
Plant cell wall waxes
long carbon and hydrogen chains ontop of the epidermis
prevent water loss
phragmoplast
plant specific
formed during cell division
composed of microtubules, guide the cell wall components to the center to build the cell wall
builds from center outwards (cell wall ← phragmoplast → cell wall)
Plasmodesmata
cytoplasmic connects between adjacent plant cells
plasma membrane lines the pore
desmotubule (modified er) spans the pore
usually occur in clusters
form in pit fields (thin parts of cell wall)
primary and secondary types
lots of things move through them (proteins, rna, etc. viruses can hijack them too)
can open and close
pit fields
thinner parts of the cell wall
the secondary cell wall is usually not built over pits
plasmodesmata are often formed here (easier to bore through less of the cell wall than just a giant chunk of cell wall lol)
primary plasmodesmata
plasmodesmata that form when the cell wall is built
secondary plasmodesmata
plasmodesmata built after cell division
shoot apical meristem
located at the top of stem, protected by leaves
organized in central and peripheral zones
gives rise to the stem, leaves, and reproductive structures (like flowers)
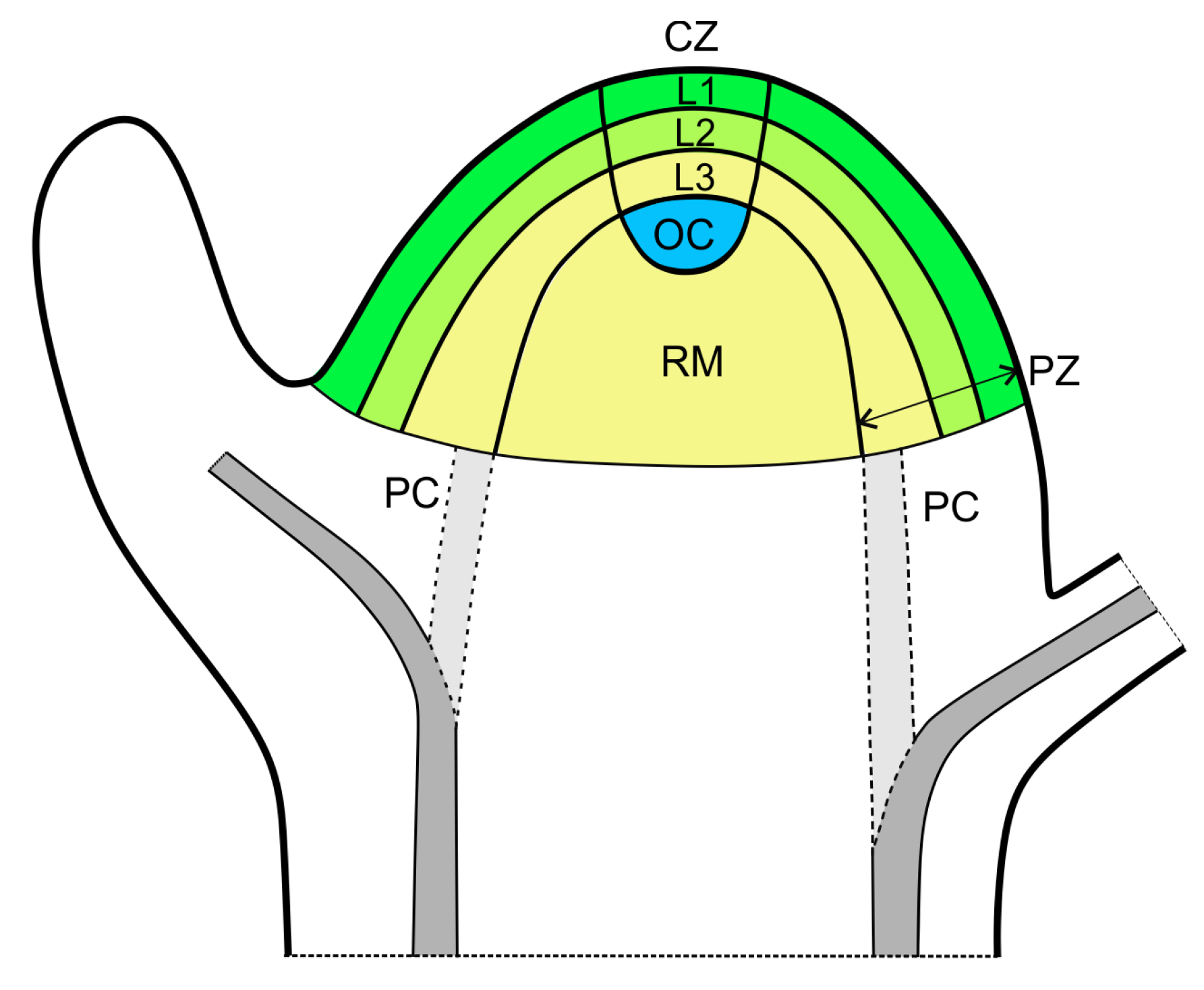
Central zone
slower dividing
function to grow and replace meristem
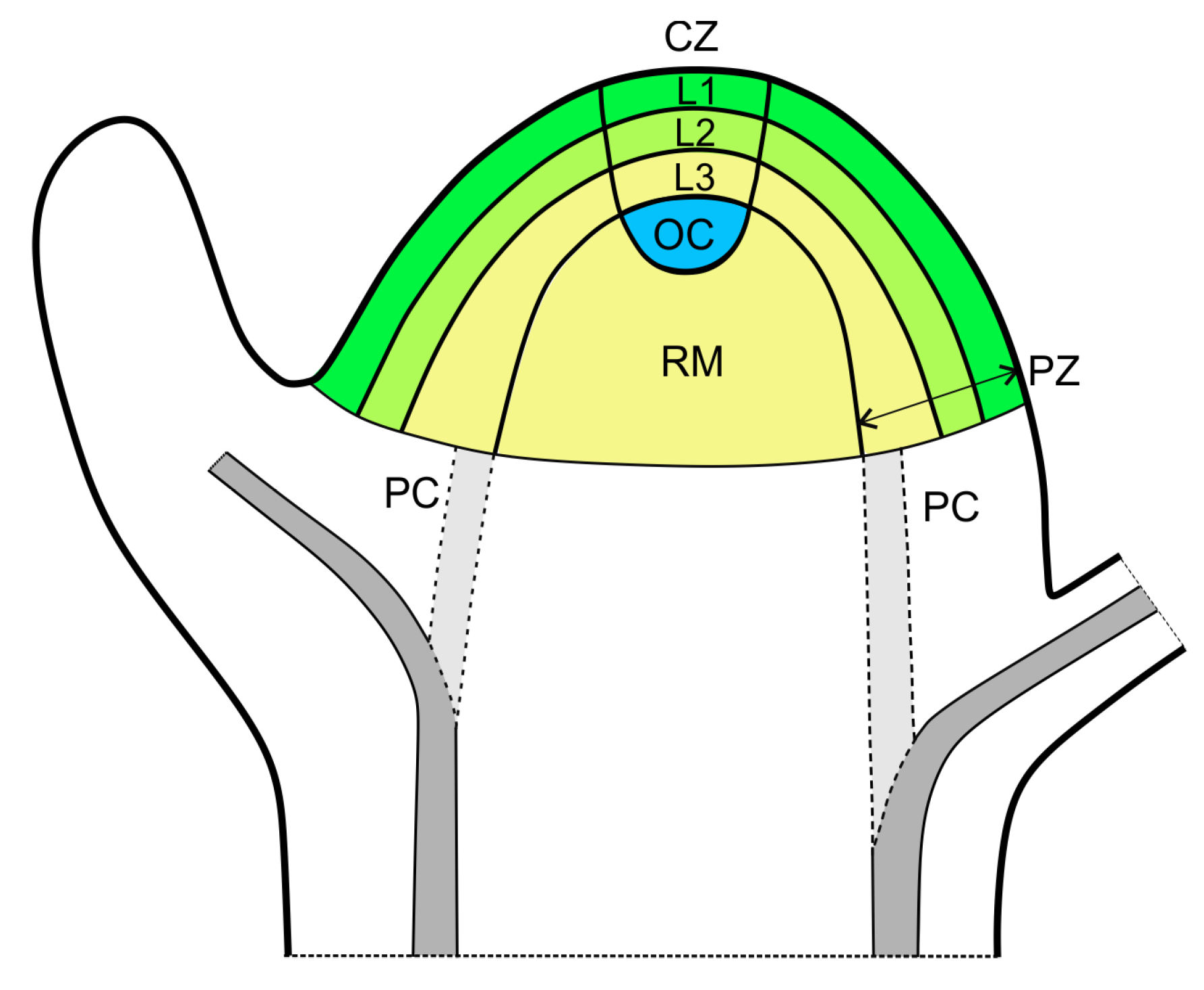
Peripheral zone
faster dividing
cells that are pushed out of the central zone
function to give rise to new organs
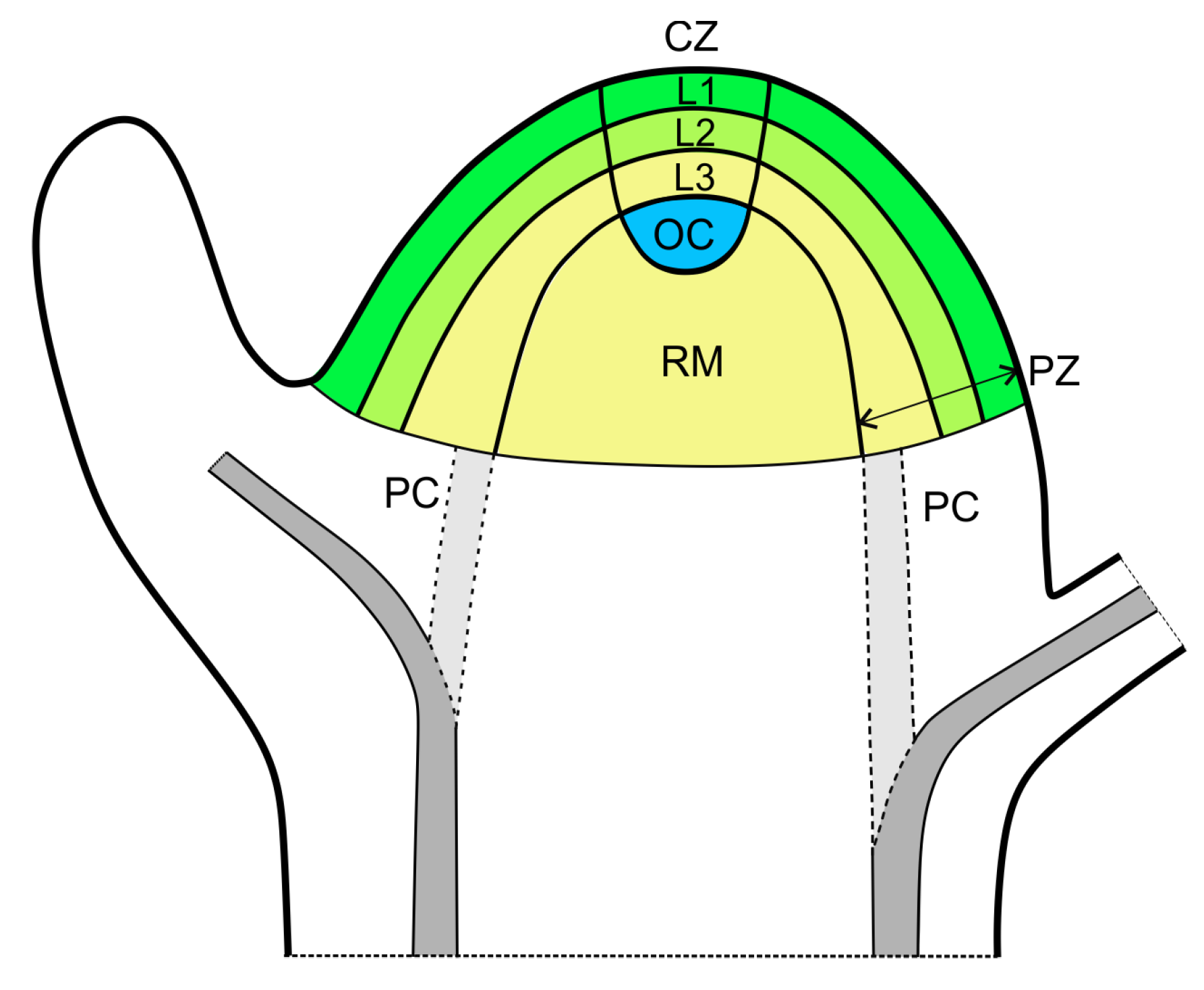
Corpus
consists of an L1, L2, and L3 layer
all function to make organs
L1
outermost layer
referred to as tunica
formed from anticlinal divisions
usually form epidermis
function to make organs
L2
referred to as tunica
next closest layer to L1
function to make organs
formed from periclinal divisions
L3
referred to as corpus
formed from periclinal divisions
not always present
usually form internal plant structures
Anticlinal
L1
daughter cells are in the same plane
daughter cells are pushed to the sides
horizontally
periclinal
L2 and L3, sometimes L1
daughter cells pushed down 1 plane
parallel
vertical
Phytomere
made by SAM
consist of a node, leaf, axillary meristem, and internode
Genes that control shoot apical meristem
knotted 1
clavata
wuschel
shoot meristemless
Clavata 3/1
restricts wusch
without it, meristem becomes very large
Wuschel
increases growth
without it, less growth occurs
usually inhibited by clv1
the two main functions of the meristem
self renewal
organogenesis/differentiation
Epidermis
prevent dehydration
regulate gas exchange
absorb water and materials
excrete toxic molecules
defense against predators
define organ boundaries
specialized epidermis
stomata and trichomes
Stomata
2 guard cells that open and close a pore
interlocking cell walls
subsidiary cells (right next to the guard cells) will swell with water, water will move osmotically to open and close the guard cells/stomata
opening and closing can occur quickly
Grass/monocot stomatas
have asymmetric cell division
the smaller cell (guard mother cell) becomes the guard cell when it divides symmetrically
appear like a road/track under a microscope, oriented very straightly/orderly
Dicot stomatas
not uniform
t least 1 cell separates one stomata from another stomata
asymmetric cell division with the primary meristemoid
Trichomes
grow outwards above the cell surface/leaf
many types
can be glandular
have many functions (ex- additional shade/sun protection, defense against predators, triggering the closing of a mouth on a venus fly trap)
Ground meristem
parenchyma
collenchyma
sclerenchyma
Parenchyma
uniform cell wall thickness (usually thin)
living at maturity
capable of cell division, but usually dont divide
function in photosynthesis, storage, secretion, and wound regeneration
Chlorenchyna
chlorophyll containing parenchyma
Mesophyll ground tissue
both parenchyma
consists of pallisade and spongy mesophyll
Palisade cells
parenchyma
specialized for light capture
rectangular/long cells
Spongy mesophyll
parenchyma
irregular in shape, more blob like
distant gaps from neighboring cells
located in the middle of the leaf (underneath palisade cells)
Parenchyma stem tissue
the pith and cortex are both parenchyma
found in the stem
pith = area inside the ring of vascular tissue
cortex = area outside the ring of vascular tissue
Parenchyma root tissue
the cortex in roots is parenchyma
no pith is present
Collenchyma
uneven cell wall thickness
living at maturity
often found in leaves and supporting stem
non lignified cell walls
function in supportive tissues
tend to form in continuous strands beneath the epidermis of leaves and petioles
brightfield microscopy
light is transmitted from below
Sclerenchyma
thickened, hard secondary cell walls
usually lignified
often dead at maturity
has two types, sclerids and veins
function as strengthening and supporting tissue
Sclerids
smaller
aid in supporting surrounding tissue
smaller clusters of cells
fibrids
larger than sclerids
run in the long axis paralel to the vein
Protoderm
gives rise to epidermis
Procambium
gives rise to vascular tissues
primary xylem and primary phloem
Xylem
conducts transportation of water, dissolved nutrients
lignified and dead at maturity
can have fibers/parenchyma for support
usually located on the top side of the vein
Midrib
a vein that runs down the middle of the leaf that is very rigid
has a large amount of sclerenchyma
Evapotranspiration
the process of water leaving the leaves through the stomata drives the xylem to pull water up the stem of the plant
Tracheary elements
a component of the xylem
tracheids
vessels
lignified, involved in water movement
Tracheids
much smaller than vessels
no perforation in end walls
end wall is not modified, it is capped at the end
Vessels
usually much larger than tracheids
perforation in the end walls
end wall is gone/dissolved, or it has grates/vents
Pits
holes/tubes between xylem cells
Pit membrane
the space where water can cross via pits
Annular rings
present in protoxylem
no complete casing of lignin leaves an empty space when the cells are stretched as the tissue grows rapidly
Protoxylem
first formed xylem
is stretched as the tissue of the plant rapidly grows, leading to annular rings
meta xylem
formed later
has no annular rings
aids in conducting water
has lignin
Vessel element cell apoptosis
primary cell wall swells as perforation plate
localized synthesis of secondary cell walls
dna and tonoplast degenerate
Phloem
principal photosynthate conducting tissue
also conducts amino acids, lipids, hormones, protein, rna, and sometimes viruses
living at maturity
composed of sieve elements and companion cells
Sieve elements
collection of sieve tubes
still living, has reduced cellular contents
companion cells
cells adjacent to sieve elements
support sieve elements by making and providing materials the sieve element cannot make due to its reduced cellular contents
have a smaller vacuole
densely packed
high amount of mitochondria to help support sieve element
why are cucurbits phloem’s studied?
they have two phloem
sieve/sieve plate
at the ends of the sieve element
has small holes similar to a strainer/sieve/net
promotes flow
callose
glucan polymer
regulates pore size of sieves (modified plasmodesmata)
high concentrations = pores close
Sieve Element differentiation
nucleus goes through mitosis, asymmetric cell divison
callose deposited around plasmodesmata to mark sieve pore sites
future sieve tube goes through some of apoptosis, but doesnt fully go through apoptosis and die, many organelles denegerate
pores are developed
callose is degraded
protoplast
the entire cell excluding the cell wall
transitory starch
temporary starch reserves formed during the day during photosynthesis in the thylakoid
broken down at night
prolamellar body
located inside of the etioplast
differentiates to become whatever type of plastid it becomes
co translational
in some scenarios, dna is translated and transcribed at the same time