Cell Function for Bio Quiz
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Includes the Endosymbiant Theory, Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic Cells, Diff Organelles, Cell Types, and Tissues
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What is the first cell on Earth?
Prokaryotic cells
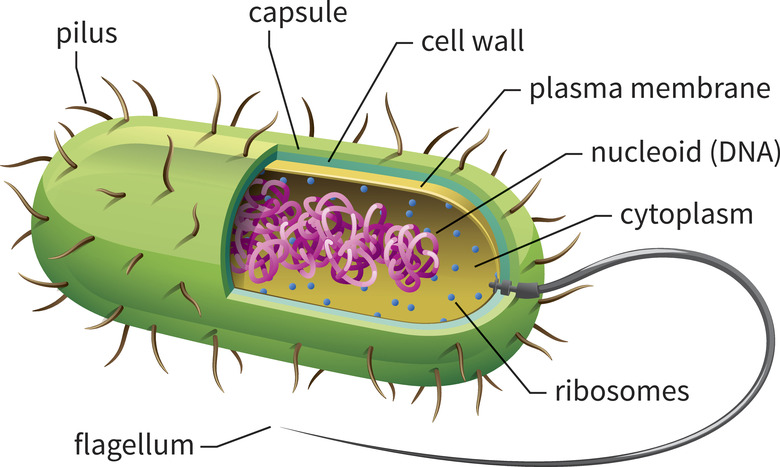
What do old (ancient) Prokaryotic cells have? (First Article)
They have no nuclei, no organelle, they don’t reproduce by mitosis and only have one single DNA strand.
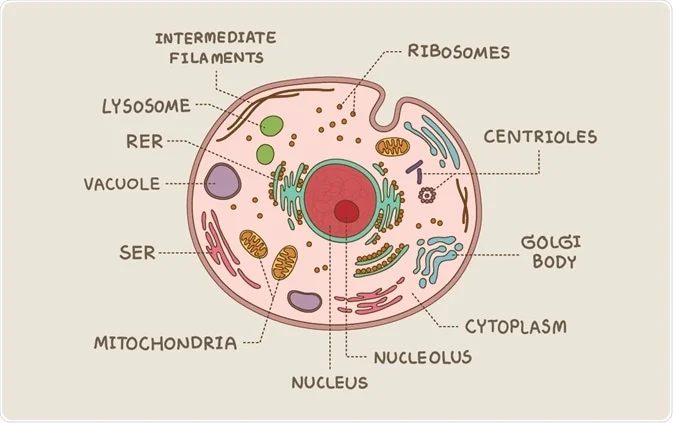
What do Eukaryotic Cells have? (First Article)
They possess nuclei, nuclear membranes, organelles, multiple chromosomes and reproduce by mitosis.
What is the Endosymbiont Theory?
A theory that describes how eukaryotic cells evolved from prokaryotic cells.
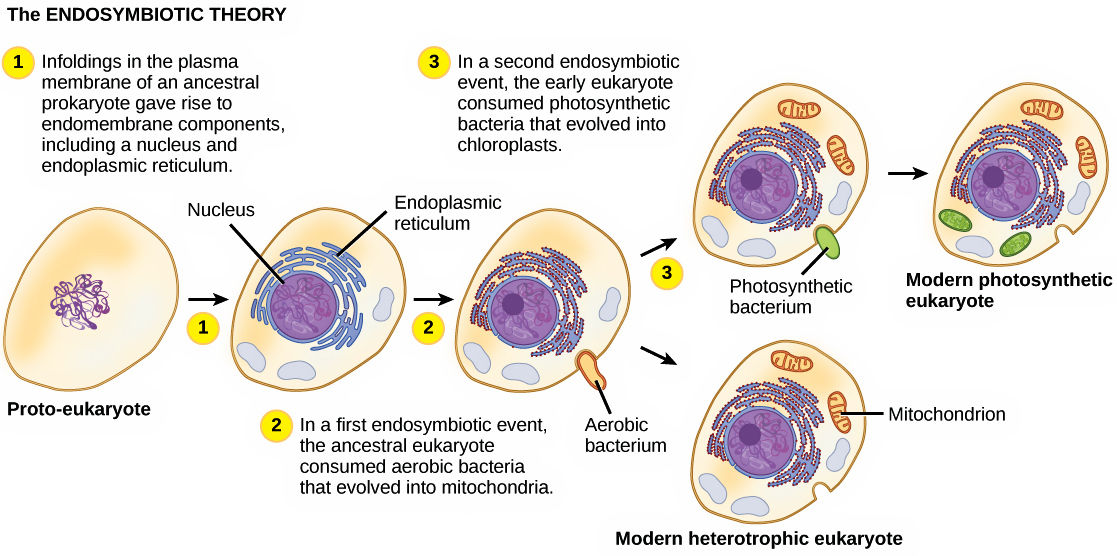
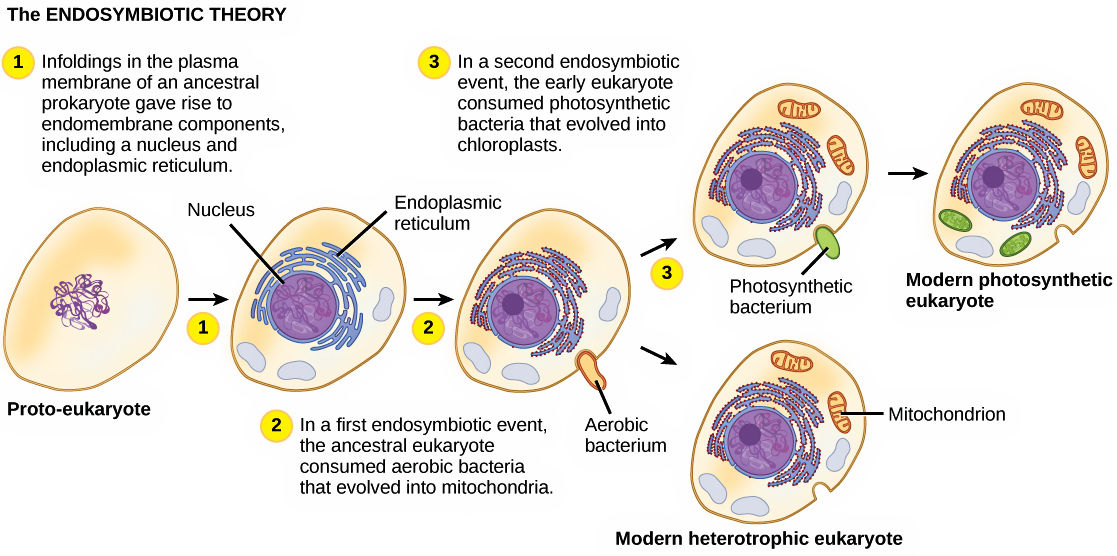
What’s the first step of endosymbiont theory?
First, the aerobic bacteria was taken into the prokaryotic cells by phagocytosis. It’s cell membrane invaginates and the aerobic bacteria becomes symbiotic bacteria inside the prokaryotic cell.
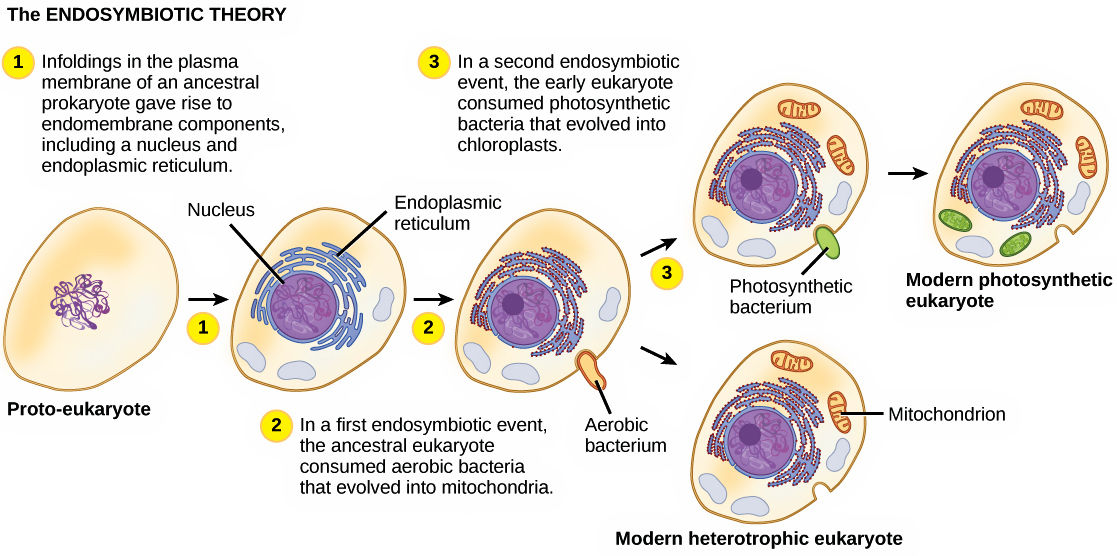
What’s the second step of endosymbiont theory?
The symbiotic bacteria later evolved to be mitochondria and the invaginating cell membrane becomes developing endoplasmic reticulum.
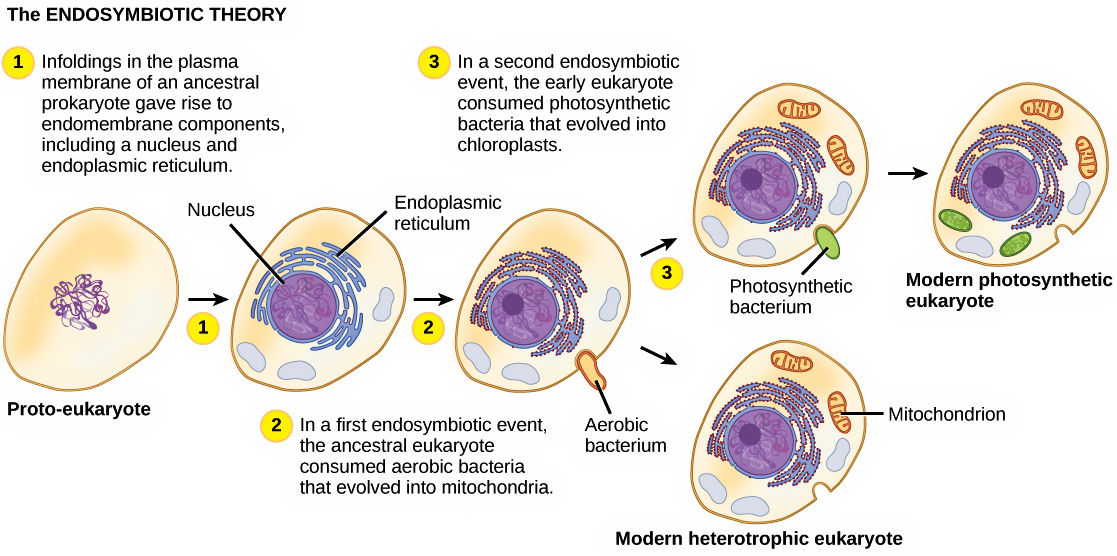
What does the nonphtosynthetic eukaryotic cells have?
They contain a nucleus, nuclear membrane, endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria.
What’s the last step for Endosymbiont Theory (photosynthetic eukaryotic cells)?
Photosynthetic cyanobacteria was engulfed by the eukaryotic cells, thus creating photosynthetic eukaryotic cells that have chloroplasts in them.
What’s the difference between Prokaryotes cells and Eukaryotes cells?
Prokaryotes are cells that lack a nucleus and only have one DNA chromosome. While Eukaryotes are cells that have a nucleus and multiple DNA strands.
What is Chromatin?
Dispersed nuclear material between cell division.
Where are Eukaryotic Cells found?
Animals like Humans, plants, protozoa, fungi, and fungus.
Where are prokaryotic cells found?
Microorganisms like bacteria like rickettsiae and cyanobacteria.
What’s an organelle?
a specialized subunit within a cell that performs a specific function
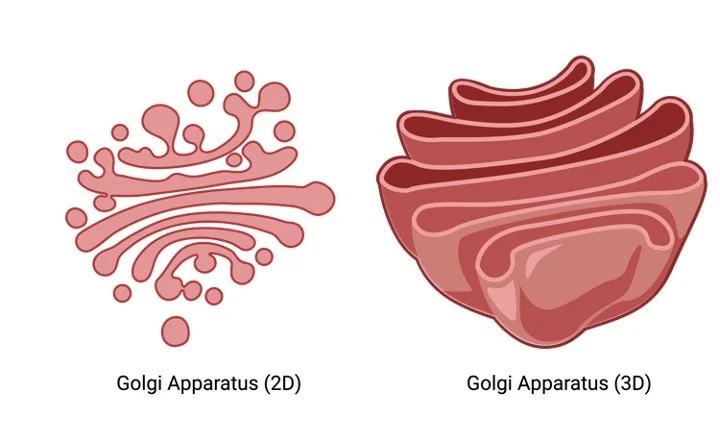
Golgi bodies
Responsible for inspecting and packaging proteins
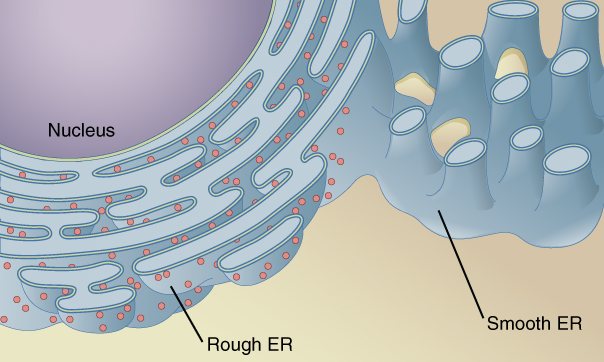
Smooth and Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Smooth ER- contains enzymes that aid in cell function
Rough ER- responsible for transporting proteins
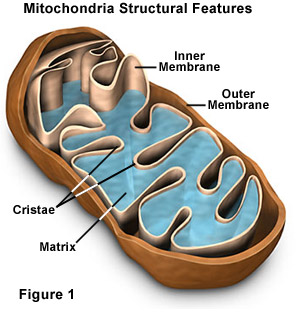
Mitochondria
Responsible for cellular respiration, creates energy in the form of ATP
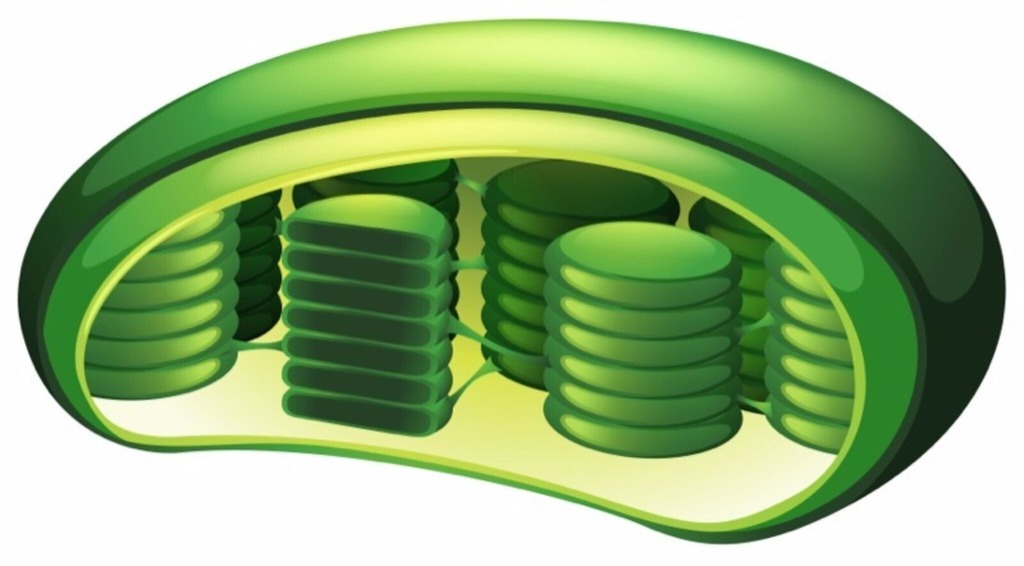
Chloroplasts
Sites of photosynthesis. Only found in plant cells not animal cells.
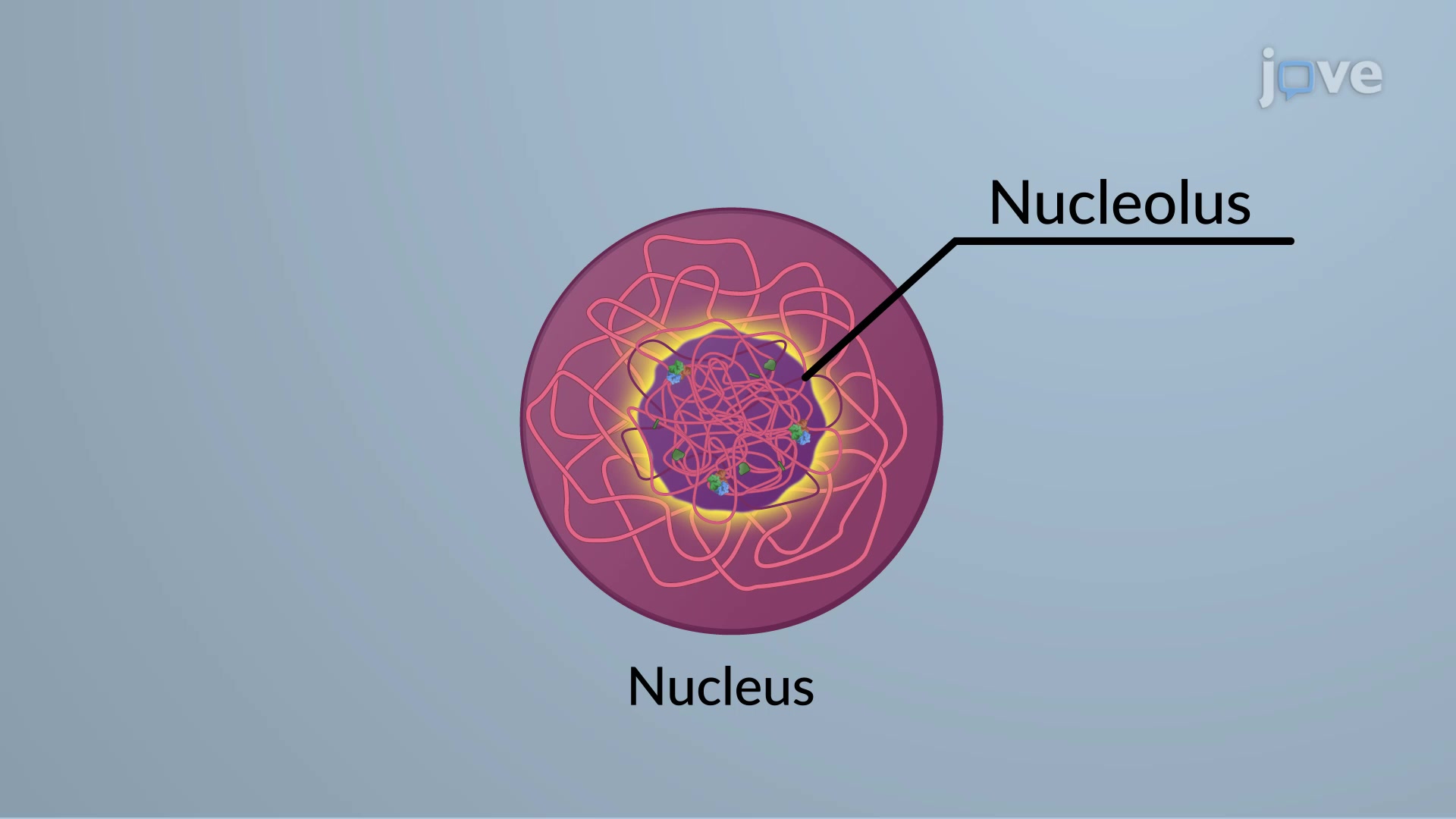
Nucleus and Nucleolus
Nucleus- holds DNA(instructions to make proteins)
Nucleolus- makes ribosomes(in the center of nucleus)
Ribosomes
Responsible for making proteins
Large Vacuole
Responsible for storing water and other materials. (Found in plant cells)
Lyosomes
responsible for cleaning up the cell by getting rid of waste (Only found in animal cells)
Cell Wall
Provides protection and support for the cell. (Found in Plant Cells)
Small Vacuole
Responsible for storing and transporting vesicles to move materials in and out of the cell (Small ones in animal cells)
Cell Membrane
Important for maintaining homeostasis(stable internal environment) by controlling what get’s in and out of the cell (Found in all cells)
Centrioles
Aids in cell division( found in animal cells)
Flagellum and Pilia
Both help with movement
Tissue
cells of the same type, organized in the groups to perform a specific function
What are the four different tissues found in the human body?
Epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, nervous tissue, connective tissue
Epithelial tissue
cells found at the surface of the body and where the body meets with the external environment
What are the three different epithelial cells?
Squamos cells- provide the body with protection from dehydration and makes up the blood vessels and air sacs in the lungs
Columnar Cells- digestive tract, absorbs nutrients from food
Cuboidal cell- make the epithelia of kidney tubules and many glands
Muscle Tissue
made out of muscle cells that move parts of the body like legs. Also lines the hollow structures of the body such as blood vessels.
Nerve Tissue
Made out of Neurons(nerve cells), which receive and transmit impulses to other neurons. Important for activities like processing sensory info, moving muscles, and memory
Connective tissue
supports and binds the other tissues of the body
What are the six types of connective tissue?
Cartilage Tissue, Bone, Tendons, ligaments, fat(adipose), and blood
Cartilage Tissue
Made of chondroblast cells, it provides support, protection, and flexibility in various parts like the ears
Bone
contains osteoblasts cells; provides support and protection for the body and its organs.
Tendons
made by tendon-forming cells; it connects muscle to bone.
Ligaments
made of collegen and elastin fibers; it connects bone to bone
Fat(adipose)
Made out of fat cells, provides insulation for the body and stores fuel for metabolic activity
Blood
Red blood cells- carries oxygen to cells and pick up carbon dixode from cells to release as waste
White blood cells- Protects the body from bacteria and other organisms giving immunity to the body
Platelets- Involves in blood clotting.