mitosis
1/79
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
What is mitosis?
The making of somatic (body) cells
What is an example of when Mitosis occurs?
during growth, tissue repair, and renewal of cells
T or F can mitosis also create new individual via asexual reproduction as in amoebas?
true
What are the phases of Inter phase?
G1, S, and G2
What happens during the G1 phase?
cell growth
What happens during the S phase?
DNA copies
What happens during the G2 phase
organelles are made
How long does Inter phase last for?
22 hours
How long does M phase last for?
2 hours
What does P. M. A. T. stand for?
Pro phase, Meta phase, Ana phase, and Telo phase
What happens during Pro phase?
chromosomes appear, spindle fibers form from the centrioles, and the nuclear membrane breaks down
What happens during Meta phase?
chromosomes line up in the middle and spindle fibers attach to the chormosomes
What happens during Ana phase?
spindle fibers pull sister chromatids to opposite poles
What happens during Telo phase
sister chromatids are at the poles, DNA uncoils, and the nuclear membrane reforms
What is Cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm
What forms in prophase to help with the movement of chromosomes?
spindle fibers
What phase of the cell cycle do centromeres divide and the chromosome move toward their respective poles?
Ana phase
What phase does chromatin condense to from chromosomes?
Pro phase
What is the name of the structure that connects the two sister chromatids?
the centromere
What forms across the center of a plant cell near the end of cell division?
cell plate
Which phase of mitosis is the last phase the chromatids are together?
metaphase
What is a daughter cell?
a cell that is produced as a result of cell division
What is a Diploid?
two copies
What is a Haploid?
one copy
How many chromosomes are in a human?
46
What is the G0 phase?
the resting phase
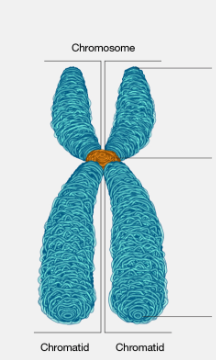
What is the orange part called?
the centromere
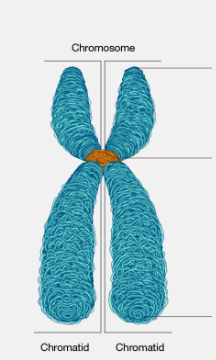
What is top and bottom part called?
telomere
What do regulator proteins do?
regulate the timing of the cell cycle
What are the two types of regulator proteins?
internal and external
What is the most common example of an internal regulator protein and what internal regulator proteins do
cyclins and responds to events inside of the cell
What is the most common example of an external regulator protein and what external regulator proteins do
growth factors and respond to events outside of the cell
Whats oncology?
the study of cancer
What’s an oncologist
doctor that treats cancer paients
How many stages does cancer have
4
The higher stage number in cancer the more it has what?
spread
Whats a biopsy?
a sample of tissue taken to test
Whats remission?
no signs or symptoms of cancer
What are the two results activation of p53 can have?
1- halts cell cycle until repair is completed or 2- launches cell into apoptosis
What does apoptosis mean?
cell death
What are the four ways to treat cancer?
surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, and immunotherapy
What are the two most common drugs used on cancer?
taxol and vinblastine
What does taxol do?
freezes spindle fibers
What does vinblastine do?
prevents spindle fibers from forming
What is Cancer?
cells that have an uncontrolled growth rate
What is a tumor?
mass of cells due to uncontrolled division
What are the two types of cancer tumors?
benigh and malignant
Which type of cancer tumor is usually harmless?
benigh
Which type of cancer tumor is disorganized?
malignant
What is Angiogenesis?
formation of blood vessels
What does metastasize mean?
break away
What is a carcinogen?
a cancer causing agent
What is contact inhibition?
growth returns to normal once in contact with each other
What cells does Meiosis produce?
gametes (sex) cells
What is the female sex cell?
the egg
What is the female sex organ?
ovaries
What do fallopian tubes do?
connect the ovaries to the uterus
How long into pregnancy is a zygote?
1 week
How long into pregnancy is a blastocyst?
2 weeks
How long into pregnancy is a embryo?
3 to 8 weeks
How long into pregnancy is a fetus?
9 weeks and on
What is puberty?
the beginning of production of sex cells
What are primary oocytes?
the supply of eggs at birth
What are secondary oocytes?
mature eggs that can be fertilized
How many average primary oocytes are females born with?
1 million
How many average secondary oocytes are females born with?
400-500
What is gametogenesis?
formation of gametes
What part of cell division does not happen twice in females during meiosis
Interphase
How many sperm are made per day for ages UNDER 50 after puberty?
290 million
How many sperm are made per day for ages OVER 50?
130 million
Whats spermatogenesis?
formation of sperm
Whats the male sex cells?
sperm
Whats the male sex organ?
testies
Whats the epididymis?
where sperm is stored
What are the vas deferens?
a long tube that connects the epididymis to the urethra
Which scientist discovered sperm?
leeuwenhoek
What does sperm prefer to use over glucose?
fructose
Whats a name for virgin birth?
parthenogenesis
What is oogenesis?
formation of eggs
What is the name, age and roommates name of the snake that gave virgin birth?
Thelma, 11 years old, Louise