Edexcel A Level Biology, topic 1: Lifestyle, Health and Risk
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
Which factors effect an organism's need for a transport system? (3)
Size, surface area to volume ratio, level of activity
How do the circulatory systems of very small organisms work? And why?
Substances move around the organism by diffusion, all distances are short so diffusion is usually fast enough to meet needs
What is a mass transport system?
All particles in a liquid move in one direction around the body due to difference in pressure
How does an open circulatory system work? (3)
A simple heart pumps blood into cavities surrounding the animal's organs, substances diffuse from blood to cells, when heart muscles relax blood is drawn back into the heart through small valved openings
How does a closed circulatory system work? (3)
Blood is inclosed within tubes, heart pumping generates high pressure, forces blood around the body quickly
How does a single circulatory system work? (eg fish) (3)
Heart pumps deoxygenated blood to gills, carbon dioxide diffuses out and oxygen diffuses in, blood travels around rest of body before returning to the heart
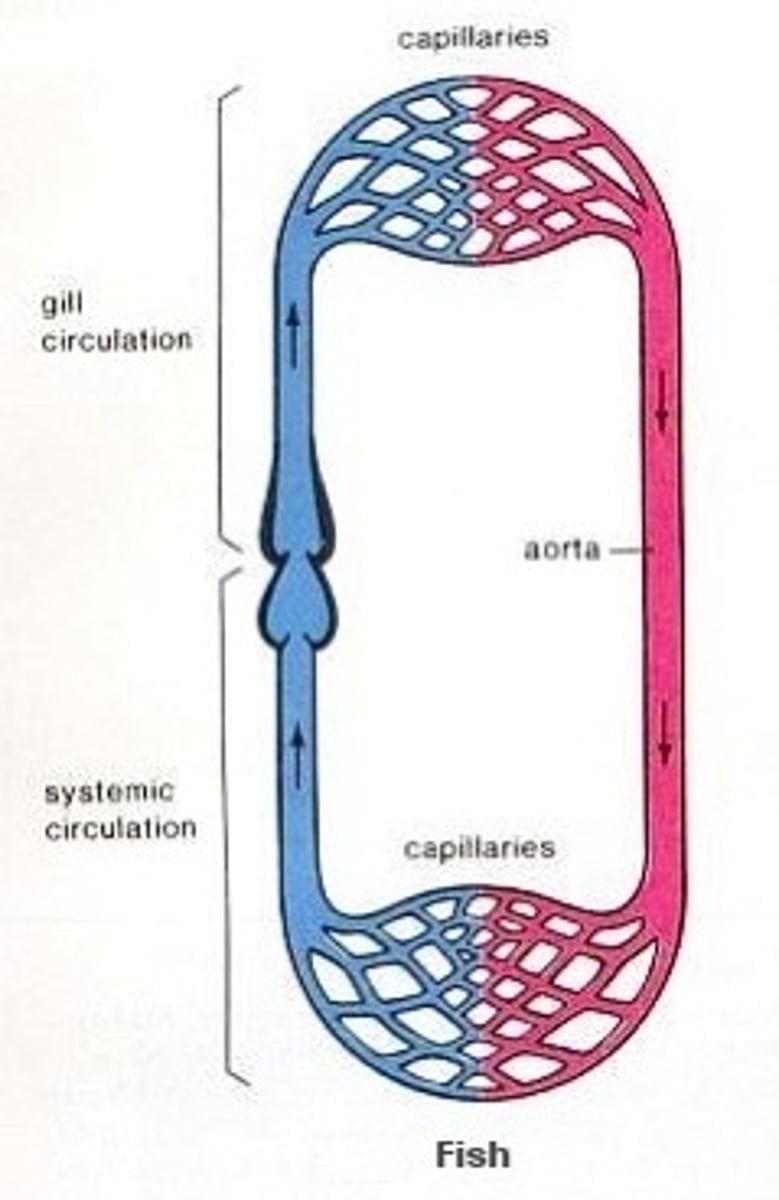
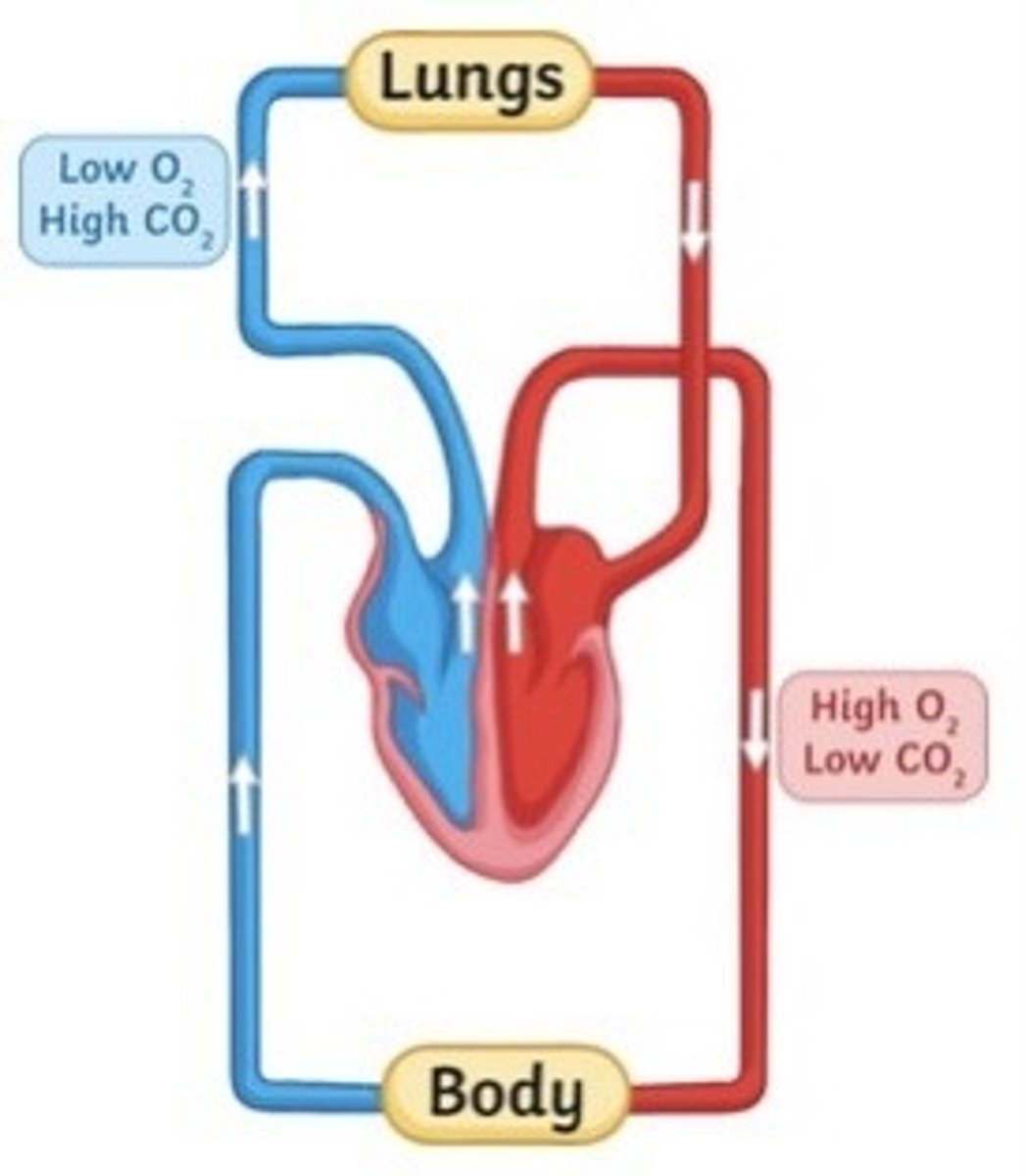
How does a double circulatory system work? (2)
Right ventricle of heart pumps blood to lungs where it is oxygenated, blood returns to heart where left ventricle pumps it to the rest of the body
How are arteries adapted for their function? (3)
Narrow lumen to maintain high bp
Thick walls of muscle and elastic tissue so walls can expand and recoil after each beat
Thin outer layer of mainly collagen fibres to strengthen
How are veins adapted to their function? (3)
Wide lumen and thin walls because low bp
Low levels of collagen, smooth muscle cells and elastic fibres because no recoil and less strength needed
Semilunar valves to prevent blood from flowing backwards
How are capillaries adapted to their function?
Endothelium only one cell thick to allow for rapid diffusion
Vessels are only one cell wide to increase speed of flow
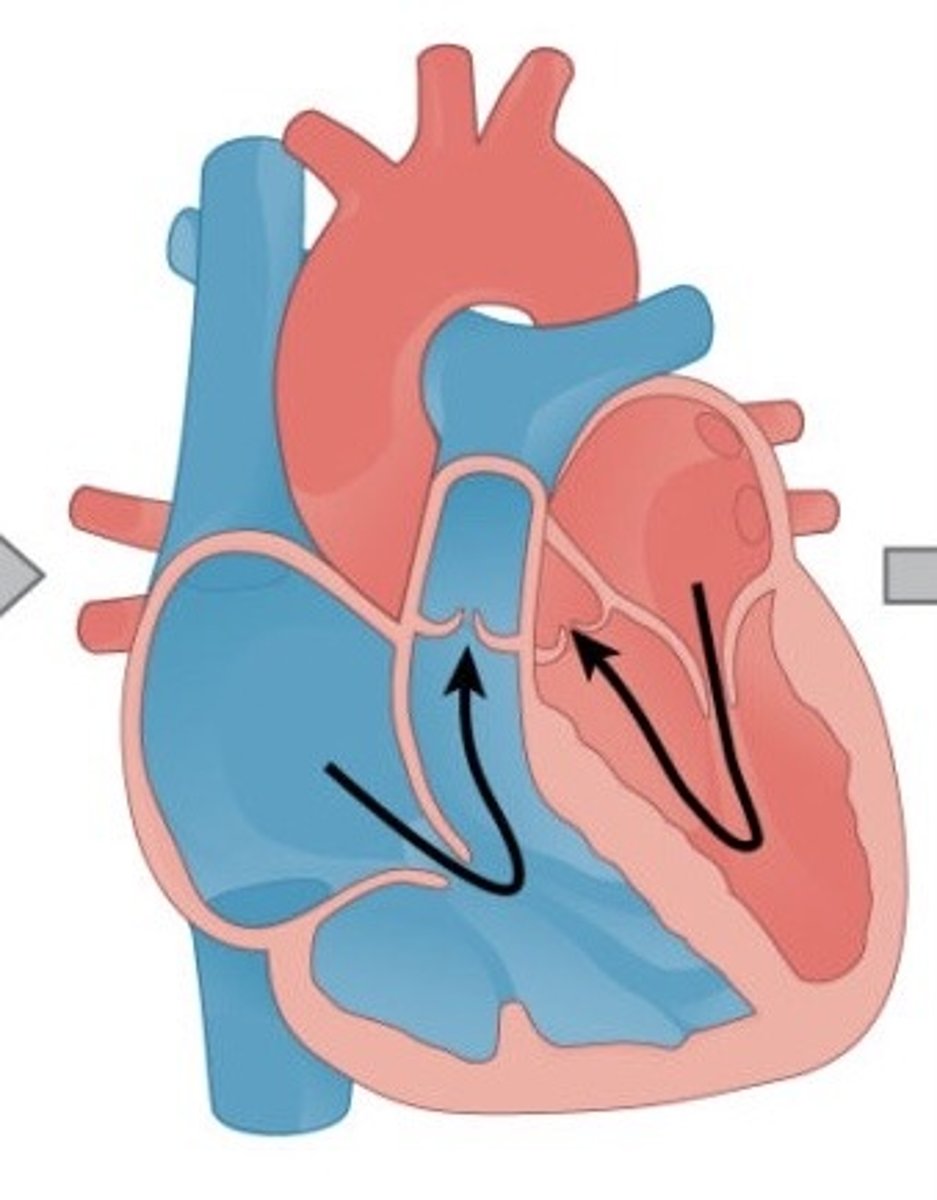
Describe atrial systole (3)
Low pressure blood flows into r and l atria from pulmonary veins and vena cava
Atrioventricular valves open due to high bp in atria
Blood flows into ventricles as atria walls contract
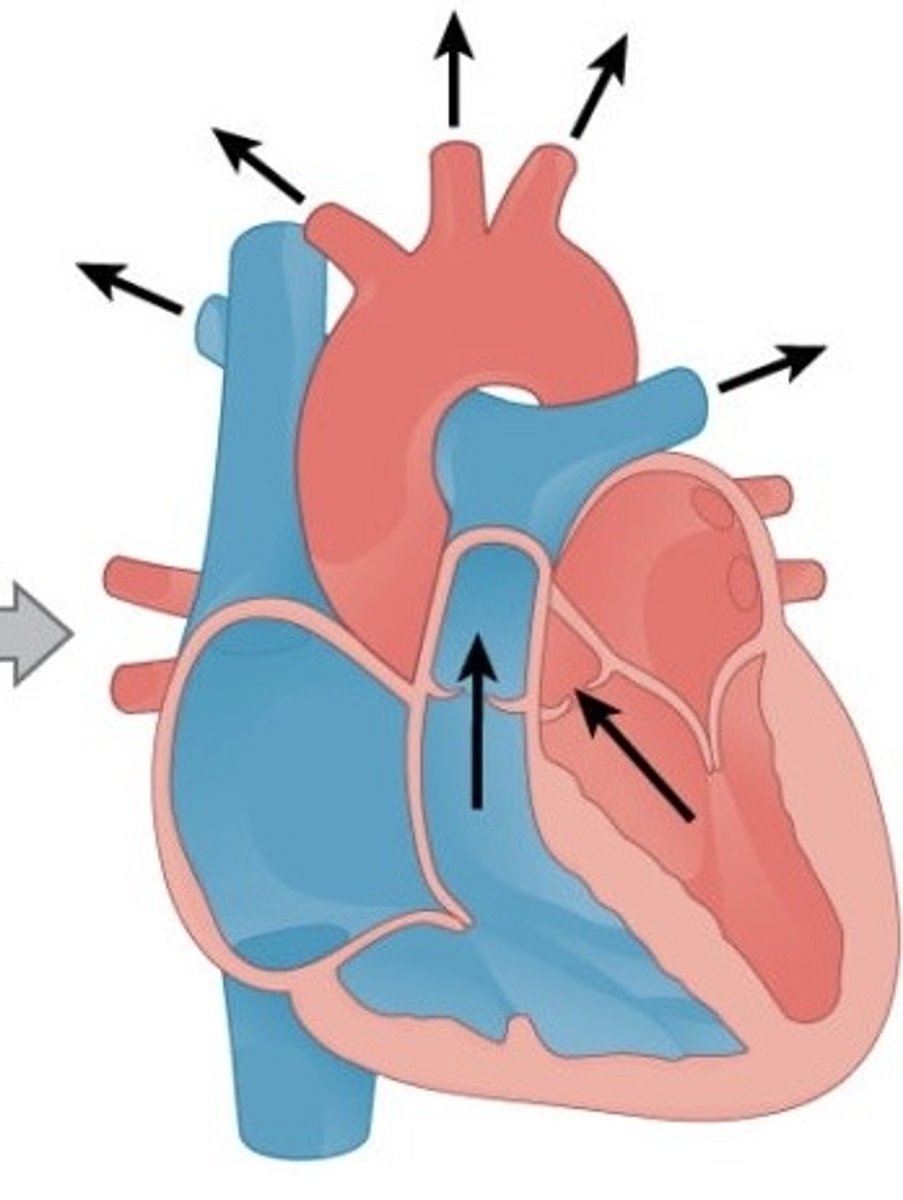
Describe ventricular systole (4)
Ventricle walls contract
Semilunar valves are forced open
Blood is forced into pulmonary arteries and aorta
Atrioventricular valves close dues to high bp in ventricle
Describe cardiac diastole (4)
Elastic recoil as atria and ventricles relax causing low bp in heart
High bp in pulmonary arteries and aorta close semilunar valves
Coronary arteries fill
Low bp in atria draws blood into heart from veins
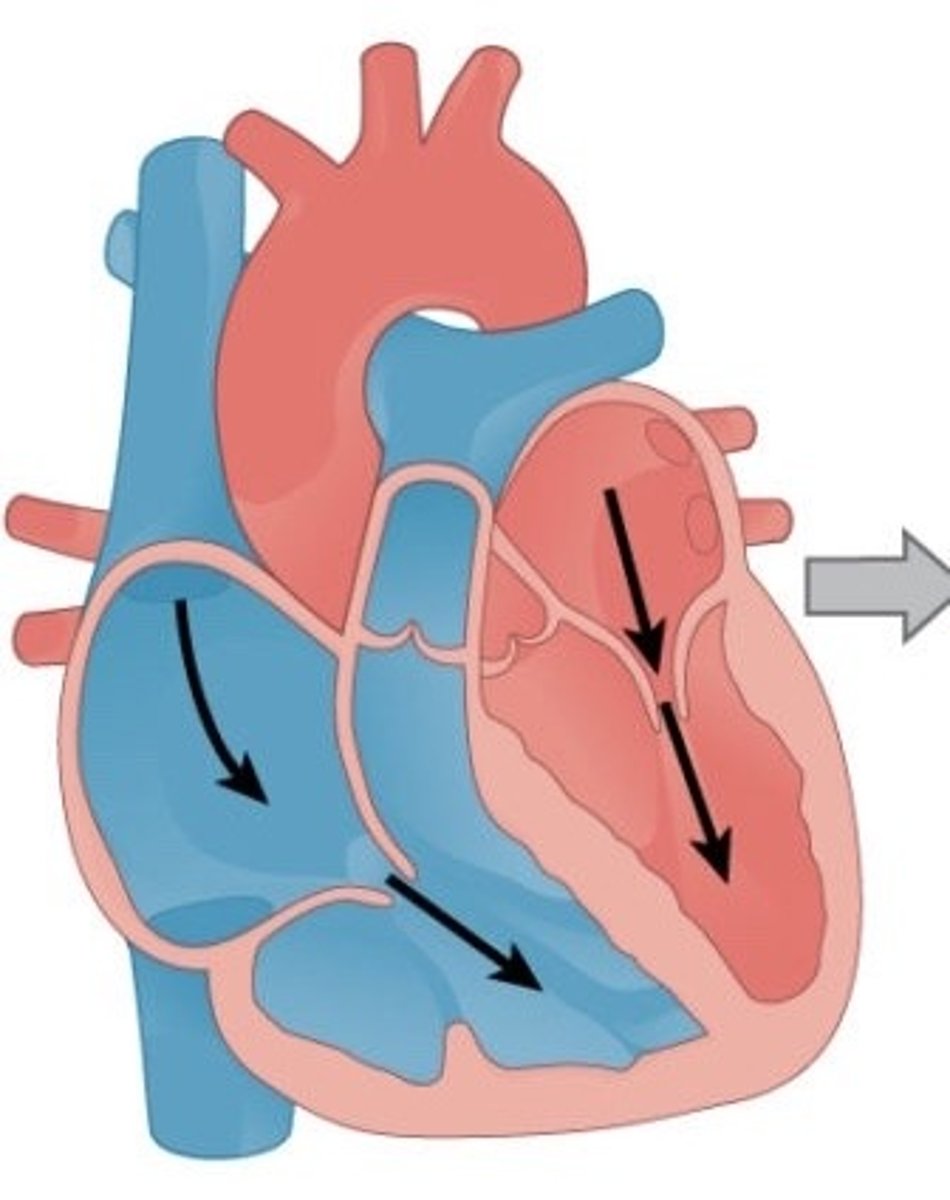
What is the name of the valve between the right atrium and right ventricle?
Right AV valve (tricuspid)

What is the name of the valve between the left atrium and left ventricle?
Left AV valve (bicuspid)
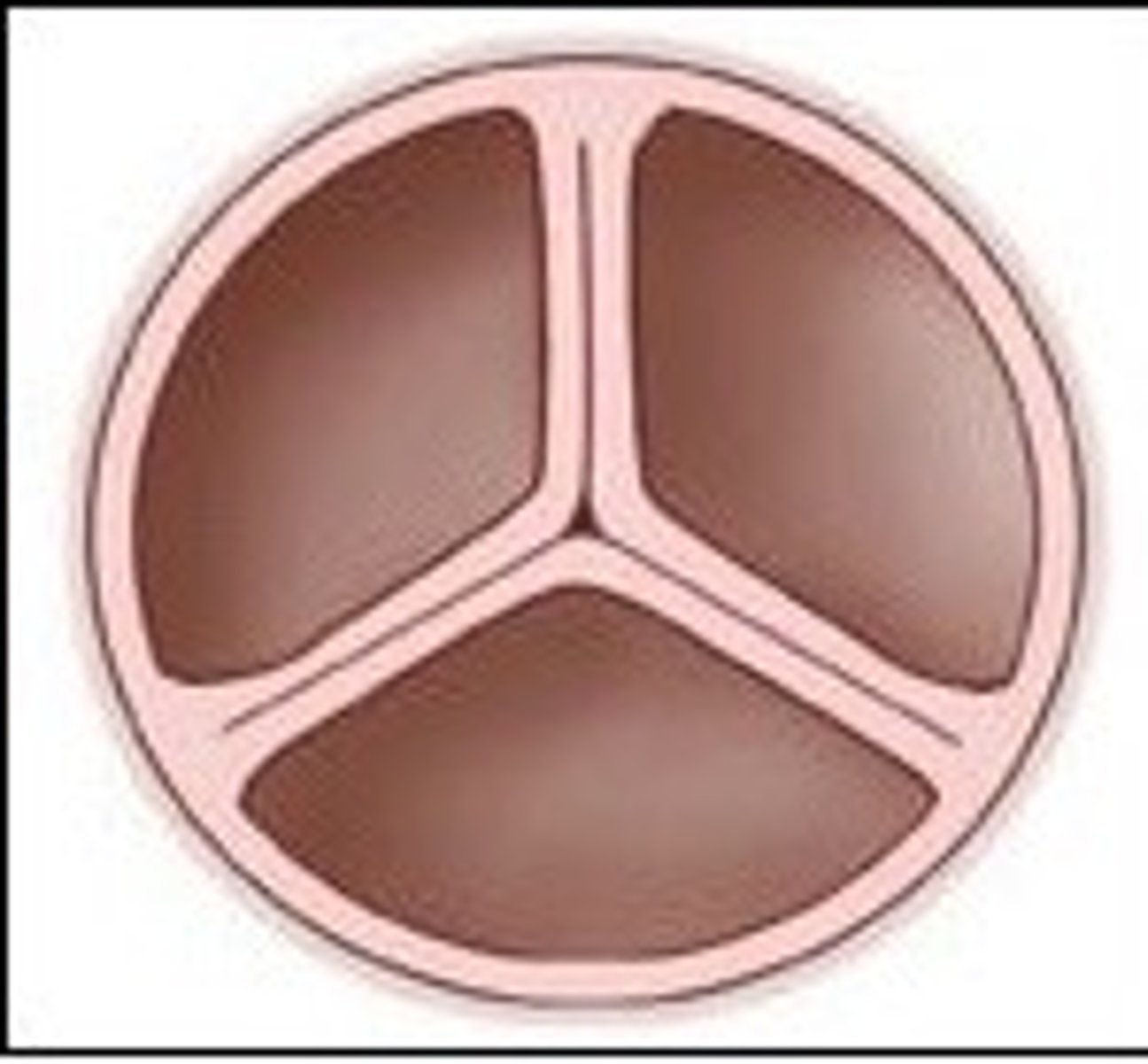
What are the names of the valves at the entrance to the pulmonary arteries and aorta?
Semilunar valves
Describe the pathway of blood through the heart (13)
Superior and inferior vena cava
right atrium
right AV valve
right ventricle
Semilunar valve
pulmonary arteries
lungs
pulmonary veins
left atrium
left AV valve
left ventricle
semilunar valve
aorta
How is the heart's structure adapted for its function? (1)
Myocardium is much thicker on left side of heart because is needed to pump blood to entire body rather than just lungs
What are some of the main risk factors of atherosclerosis? (5)
Age
Smoking
Obesity
Excessive alcohol
Family history of CVD
Describe the steps leading to atherosclerosis (8)
Endothelium is damaged (often due to high bp)
Inflammatory response: large white blood cells from blood enter the wall
Causes accumulation of calcium salts, fibrous tissues and cholesterol
Fatty deposit builds up
Hard plaque forms on inner wall of artery as a result of calcium salts and fibrous tissues
Causes artery to harden (atherosclerosis)
Atheroma causes lumen to narrow, which increases bp
Positive feedback loop forms
Why can atheromas only form in arteries?
The bp is not high enough in veins or capillaries
How can atherosclerosis be treated? (3)
Medicine to reduce bp or cholesterol
Surgery to widen or bypass affected artery
Lifestyle changes
What can atherosclerosis lead to? (4)
Myocardial infarction
Stroke
Tissue death
Burst artery
What is an atheroma?
Build up of fatty deposits (mainly LDL) within the endothelium of an artery
Describe the blood-clotting process (8)
Platelets come into contact with damaged vessel wall
They become sticky to form a platelet plug
Platelets reacting with collagen in walls releases thromboplastin (triggering clotting cascade)
Thromboplastin with calcium and vitamin K from blood catalyses conversion of prothrombin into thrombin
Thrombin catalyses conversion of soluble fibrinogen into insoluble fibrin
Fibrin acts as a glue to trap more platelets and blood cells
Temporary platelet plug turns into blood clot
Once damage is repaired clot can dissolve back into blood
How can unwanted blood clotting be prevented? (6)
Prevent or treat atherosclerosis
Diet
Exercise
Not smoking
Bp medicine
Artery bypass
What are some of the main risk factors for CVD? (6)
Genetics
Diet
Age
High bp
Smoking
Inactivity
How does smoking increase risk of CVD? (4)
Carbon monoxide in smoke binds to haemoglobin (decrease oxygen supply to cells). Results in increase heart rate
Nicotine in smoke triggers production of adrenaline, increases heart rate and vasoconstriction so increased bp
Chemicals in smoke damage endothelium
Reduces HDL levels in blood
How does inactivity increase risk of CVD? (4)
Sufficient exercise:
Decreases bp
Helps maintain healthy weight
Increases HDL levels without effecting LDL
Deceases risk of type 2 diabetes
How do genetics affect risk of CVD? (1)
Apolipoprotein gene cluster is associated with CVD, some alleles increase risk some decrease
What are are apolipoproteins? (4)
Protein component of lipoproteins
Produces in liver and intestines
Stabilise structure of lipoproteins
Recognise receptor involved in lipoprotein uptake on plasma membrane of cells
What is apolipoprotein A (APOA)? (3)
Major protein in HDL
Helps move cholesterol from blood to liver for excretion
Mutations cause decreased HDL levels and increase risk of CVD
What is apolipoprotein B (APOB)? (3)
Major protein in LDL
Transfers cholesterol from blood to cells
Mutations cause increase in LDL levels so increase risk of CVD
What is Apolipoprotein E (APOE)? (3)
Major protein in HDL and VLDL
APOE gene has three alleles: E2, E3, E4
Having E4 slows removal of cholesterol from blood so increases risk of CVD
How does high bp increase risk of CVD? (1)
Can cause damage to the endothelium, resulting in atherosclerosis and therefore blockage of arteries
What is cholesterol and how is it transported around the body? (3)
Short lipid molecule
Insoluble
Must be combined with proteins to form soluble lipoproteins to be transported
What is LDL cholesterol and how does it effect the body? (3)
Low-density lipoprotein
Triglyceride of saturated fat, cholesterol and protein
Increases cholesterol deposition in blood so increases risk of atheromas
What is HDL cholesterol and how does it effect the body? (3)
High-density lipoprotein
Triglyceride of unsaturated fat, cholesterol and protein
Transports cholesterol from body tissues to the liver where it can be broken down and excreted
What is "good cholesterol"?
HDL cholesterol
What are the "bad cholesterols"?
LDL and VLDL cholesterol
How does diet effect risk of CVD? (3)
High LDL cholesterol diets will increase risk of developing atherosclerosis
High antioxidants diets will reduce the effect of radicals and reduce risk of CHD
High salt diets cause kidneys to retain water, increasing bp
What are radicals?
Oxidising agent that pulls hydrogen atoms from another molecule
What are the effects of free radicals? (2)
Cause damage to DNA, proteins and lipids
Damaged linked to development of CHD and cancer
What is the name of drugs used to reduce bp?
Antihypertentives
What are the four main types of anti hypertensives?
ACE inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, diuretics, statins
How do ACE inhibitors work? (1)
Decrease synthesis of angiotensin ii (hormone inducing vasoconstriction)
What are some of the side effects of ACE inhibitors? (2)
Arrhythmia and kidney disease
How do calcium channel blockers work? (1)
Prevent muscle contraction and therefore vasoconstriction
What are the side effects of calcium channel blockers? (1)
May worsen effects of heart failure
How do diuretics work? (1)
Decrease water uptake in the kidneys so lower bp
How do statins work? (1)
Inhibits enzyme involved in LDL production in liver
What are the side effects of statins? (1)
Can lead to some cancers
What is the name of the group of drugs used to prevent blood clots? (2)
Anticoagulants or platelet inhibitors
What are the two most commonly used platelet inhibitors?
Aspirin and clopidogrel
How does aspirin work?
Reduces the sickness of platelets and likely hood of clot formation
What is the major risk of combining aspirin and clopidogrel?
Bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract
What is one of the most commonly used anticoagulant?
Warfarin
How does warfarin work? (2)
Interferes with the production of vitamin K, reducing synthesis of clotting factors
What will happen if energy intake is greater than energy requirement?
Weight gain
What will happen if energy intake is less than energy requirement?
Weight loss
What will happen if energy intake is the same as energy requirement?
No change in weight
What determines somebody's basal metabolic rate (BMR)? (3)
Mass, height, age
What are the two methods of determining whether somebody is obese?
BMI and waist to hip ratio
What is the formula for BMI?
Body mass (kg) / height² (m²)
What are the two types of studies used to determine the impact of risk factors?
Cohort and case-control studies
How do cohort studies work? (2)
Large group who don't have condition
Compare risk factors and observe who go on to develop condition
How do case-control studies work? (3)
Group that have condition compared to group that don't
Info collected about past risk factors to see if there's a pattern
Important control group is representative of case group (age, sex)
What are the features of a good study? (5)
Clear aim or hypothesis
Sample representative of relevant population
Valid results
Large sample size
Control variable
People will often overestimate a risk when it is... (6)
Involuntary
Not natural
Unfamiliar
Dreaded
Unfair
Very small
What is coronary heart disease?
blockage of coronary arteries, limiting blood flow to the myocardium
What is oedema?
Build up of fluid in tissues causing swelling
What causes oedema? (5)
High bp at arterial end of capillary forces fluid and small molecules from plasma though gaps between cells in capillary walls into the intercellular space
This fluid is called tissue fluid or interstitial fluid
Blood cells and plasma proteins in capillary stop fluid from returning to blood through gaps in capillary wall
Fluid drains into network of lymph capillaries and then into the vena cave
If bp is too high fluid builds up causing swelling
Who tends to have higher BMRs? (4)
Males
Heavier people
Younger people
More active people
How does a bp monitor (sphygmomanometer) work? (4)
When cuff is inflated blood flow through artery in upper arm is stopped
Pressure above the cuff starts to build up
When cuff starts to deflate and blood can flow though artery again, pressure is measured (systolic)
A second reading is taken when no sound can be heard with a stethoscope below the cuff (diastolic)
What is systolic pressure?
Maximum bp when heart contracts
What is diastolic pressure?
Bp when heart is relaxed
What is considered a healthy range for systolic bp?
100- 140 mmHg
What is considered a healthy rage for diastolic bp?
60- 90 mmHg
How do you calculate heart rate from a cardiac cycle chart?
Divide 60 by the amount of time one cardiac cycle takes
What is stroke volume?
volume of blood pumped out by one ventricle with each beat
What is cardiac output? (2)
Volume of blood ejected by the heart in one minute:
cardiac output = heart rate x stroke volumne
What is the difference between a calorie and a Calorie? (3)
1000 calories = 1 Calorie
calorie = 1 calorie
Calorie = 1 kilocalorie
1 calorie = ____ joules
4.18