Global Economics
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
international trade benefits
lower prices
grater choice
increased competition
a source of foreign exchange
advantage types
Absolute advantage
can produce more goods/services than other countries
due to: resources, technology, workforce
Comparative advantage
can produce the same amount of output at a lower opportunity cost
limits:
ignores transport costs
overlooks externalities
overspecialization: vulnerability to shocks-dependency
Tariffs and quotas, effects on different sectors
tax imposed on goods and services-a way to support domestic firms
effect on:
Consumers: prices go up-less consumer choice
Producers: face less competition-sell more-better off
Market: less total trade-efficiency and welfare fall
Governments: short term benefit, other countries might complain, start a trade war
Quotas:
limits how much of a good/service can be imported
same effects except governments do not generate tax revenue
administrative barriers
measures that restrict trade, but can protect national interests
ex. licensing requirements, complex documents
Free trade vs protectionism
For trade protection
national security
protect domestic jobs
prevent unfair competition
preserve cultural identity
For free trade
lower price for consumers, more choice
greater efficiency: focus on comparative advantage
international cooperation
economic integration types
-countries cooperating to reduce trade barriers
preferential trade agreement
deal between countries giving them special access for trading
bilateral=2 countries, multilateral=2+
Trading blocs
groups of countries joining together to reduce trade barriers
no tariffs, free trade areas (FTA)
Monetary union
group of countries sharing a common currency ex. EU union
single central bank
exchange rate types
-shows how much one currency is worth compared to another
Floating exchange rate: value of currency changes based on supply and demand in the forex market
appreciates: value increases compared to other countries
depreciates: value decreases compared to other countries
factors:
foreign demand: foreign D🔼=D🔼-USD will appreciate
domestic demand: domestic D🔼=S🔼-USD will depreciate
Fixed: currency kept at set value by buying, selling currencies
Devaluation: deliberately lowering the value
exports are cheaper and more competitive-reduces trade barriers
Revaluation: increasing the value of a currency
to control inflation, reduce trade surplus
reflects strong economic performance
Managed: central bank intervenes to influence the exchange rate-no specific target, but range
Overvalued currencies: value above equilibrium in the long run
imported goods are cheaper than what they should be-exports become expensive
Undervalued currencies: below equilibrium in the long run
imported goods more expensive than should be-exports become cheaper
balance of payments credit vs debit
-a record of the value of all transactions between a country and the rest of the world
+Credit item: payments received from foreign consumers, firms
-Debit: payments given to foreign consumers, firms
what BOP consists of
Current account
trade goods
trade in service
income
current transfers (transfer of money with no goods/services)
Capital account
non-financial, asset transfers
(natural resources, intangible assets)
Financial account
direct investment (property, land)
portfolio investment (bonds, stocks, shares, bonds)
reserve assets (government reserves)
account surplus, account deficit and how to fix it
surplus: credit>debit
deficit: credit<debit
how to fix deficit:
reducing imports-boost exports
supply side policies
improve a country’s competitiveness
marshall lerner condition
states a currency depreciation will improve the trade balance only if PED exports+PED imports>1
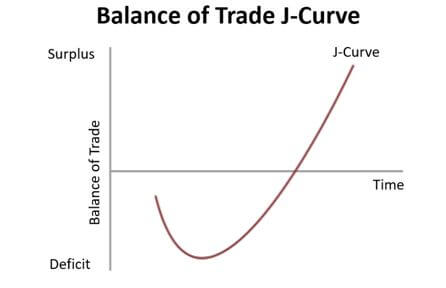
the J curve effect
when a country devaluates its currency balance gets worse before it gets better
why:
short run: more money going out than coming in-country spends more than it earns = trade deficit gets worse
long run: Other countries start buying more exports because they’re cheaper,
exports go up-the country earns more and spends less = trade balance improves