IBDP geo option G - characteristics of urban places, hierarchy of settlement, PVLI
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
site
the actual ground where the settlement is built
land use/function
main activities taking place at a function
wet point site
sites close to a supply of water
Urbanization
An increase in the proportion of people living in towns and cities
Urban Growth
The increase in the size of a particular settlement or an increase in the number of people living in urban centres.
Urban Sprawl
The unplanned and uncontrolled physical expansion of an urban area into the surrounding countryside. It is closely linked to the processes of suburbanization.
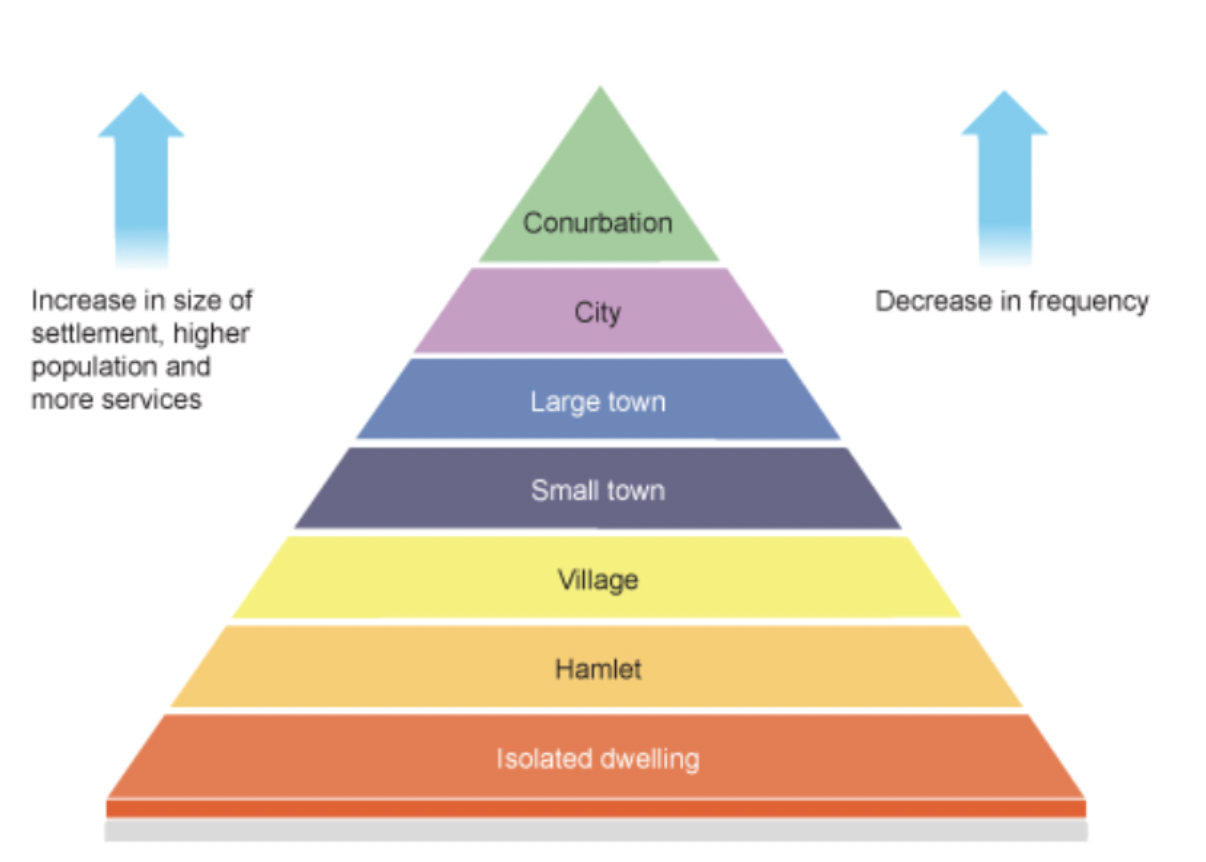
hierarchy of settlement
the arrangement of a settlement in terms of its importance or significance, based on the area and population of the settlement
the range and number of services/functions within each settlement, the relative sphere of influence in each settlement
sphere of influence
distance people are willing to travel in order to get to a certain place, based on threshold population and range
threshold population
minimum number of people needed to support a settlement, or a service
range
maximum distance people are willing to travel to obtain a particular service
high order goods
comparison goods that are not purchased often, and has a higher threshold population
low order goods
convenience goods that are used regularly and prices are not needed to be compared, has a smaller threshold population and located in smaller settlements
bid-rent theory
theory shows how the price and demand for land changes as the distance from the Central Business District (CBD) increases
assumptions made by the bid-rent theory
the highest bidder gets the land and is expected to obtain maximum profit from the land
population density hollow
caused by the bidding process of land in the central business district, in the PLVI, residential land is usually outbid retailing and office space in the CBD
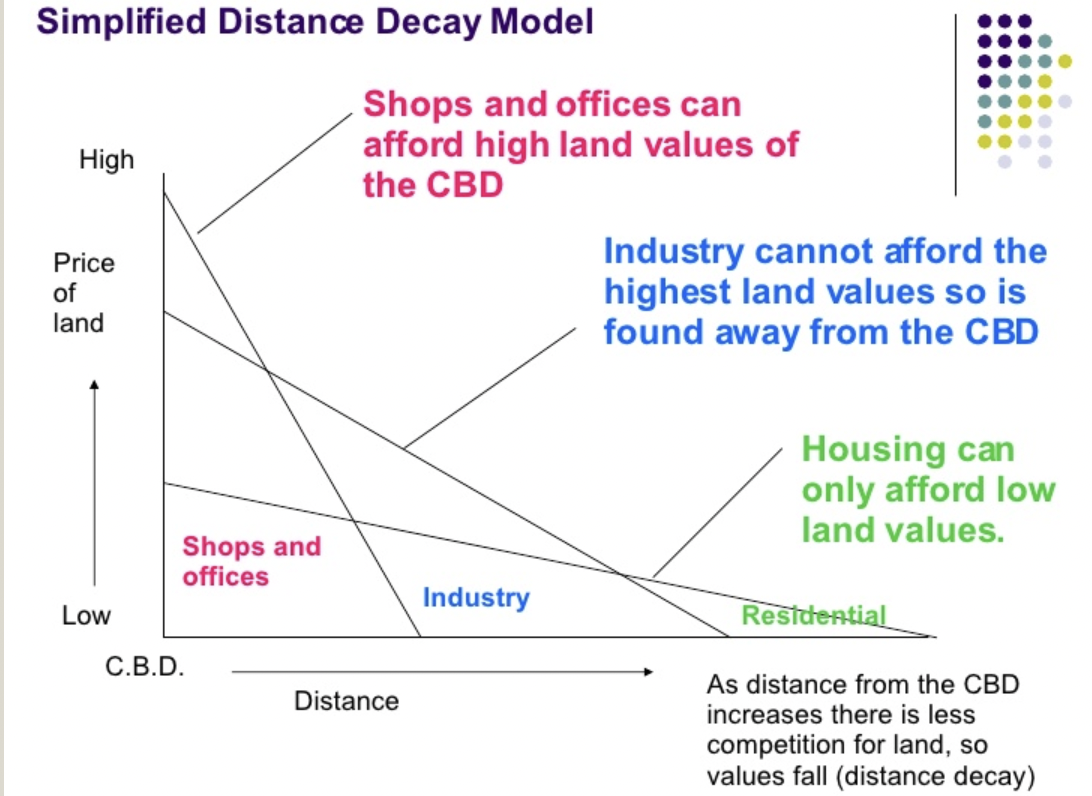
describe and draw the distance decay model
the model explains why population density is high near the city centre and why wealth people live near the city boundary and commute to the city, shops and offices can afford high land values of the CBD, industry cannot afford the highest land values so it is found away from the CBD, housing can only afford low land values
peak landmarks value intersection (PVLI)
a location within a city or an urban area where land values are at their highest point, result of various factors such as high demand for certain types of land use, proximity to amenities and services, transportation infrastructure and overall desirability of the location
nodality
the degree of connectedness a location has in relation to transport
urban morphology
refers to the communications shape and appearance of urban land uses
patterns of land reflect land values
businesses within the CBD have greater levels of accessibility and therefore attract more businesses and make more money, land value falls rapidly when moved away from the CBD