Biology; Macromolecules
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
What are the four Macromolecules?
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids
The Monomer of Carbohydrates
Monosaccharides (Galactose, Glucose or Fructose)
The Monomer of Proteins
Amino Acids
The Monomer of Nucleic Acids
Nucleotides
The Monomer of Lipids
Glycerol and Fatty Acid Chains (2-3)
The Function of Carbohydrates
Short-term or immediate Energy Source
The Function of Lipids
Long-term Energy Source
The Function of Nucleic Acids
Store and Transmit your Genetic Information
The Function of Proteins
1. Controls the Rates of Reactions
2. Fights Diseases
3. Forms Cell Structures
4. Regulates Cell Processes
5. Transports stuff In/Out of the Cell
Examples of Carbohydrates
Monosaccharides - Glucose, Fructose
Disaccharides
Polysaccharides
monosaccharides
glucose, fructose
disaccharides examples
sucrose (glucose + fructose)
maltose (glucose + glucose)
lactose (galactose + glucose)
examples of polysaccharides
glycogen, starch, and cellulose
Examples of Lipids
Fats, Oils, Waxes, Lipid Steroids (cholesterol), triglycerides, phospholipids
Examples of Proteins
Enzymes, Hormones, Antibodies, Hemoglobin, Collagen, keratin
Examples of Nucleic Acids
DNA and RNA
organic
a molecule that contains carbon hydrogen bonds
Four groups of organic molecules
Carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, lipids
1.A. What are the major elements of life?
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur, and nitrogen.
1.B. What properties of carbon explain carbon's ability to different large and complex structures?
Carbon can bond to itself, has 4 valence electrons, causing strong covalent bonds to occur between carbon and another element.
2.A. Name four groups of organic compounds found in living things.
Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.
2.B. Describe at least one function of each group of organic compound.
Carbohydrates: main source of energy for plants and animals; proteins: regulation of cellular transportation of materials, cellular processes, formation of structures, and anti-bodies; lipids: storage of energy; storage or transmission of genetic information.
2.C. Why are proteins considered polymers but lipids not?
Proteins have long chains of monomers, but lipids do NOT made up of components that make up a chain.
3.A. What atoms constitute the compound above?
Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms.
3.B. What class of macromolecule does the compound belong to?
Carbohydrates
dehydration synthesis
forms polymers and a water molecule
hydrolysis
Divides a polymer into monomers through the addition of water
Where do macromolecules get energy?
macromolecules get energy from bonds
polymer
result of many monomers linking together (protein or peptide and amino acids or polypeptide)
What makes up proteins?
polymers made of amino acids (50-500 chains long)
amino acid is also known as a...?
peptide or protein
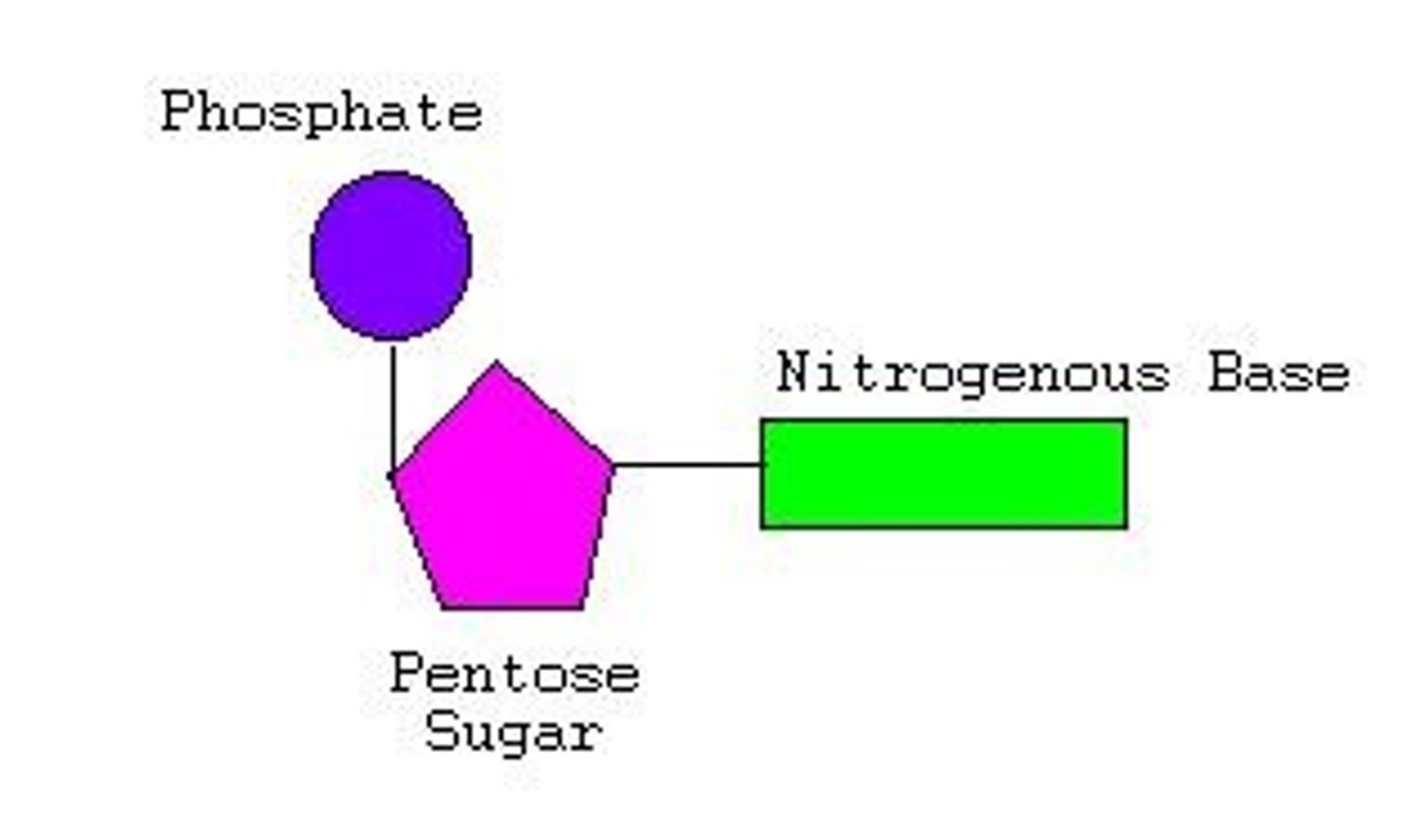
What are nucleic acids made up of?
hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, phosphorus
monomer
single molecule; small chemical unit that makes up a polymer
2 monosaccharides
disaccharide
Key ideas
-All macromolecules are formed through dehydration synthesis
-all covalent bonds
-water breaks bonds and gives off energy through hydrolysis
hydrolysis
Requires water and releases energy
Taking molecules apart
Which is the only macromolecule that isn't a polymer
lipid
What does "acid" indicate?
hydrogen ion is present
Elements present in carbohydrates
Carbon
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Elements present in proteins
Carbon
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Nitrogen
Elements present in lipids
Carbon
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Elements present in nucleic acids
Carbon
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Nitrogen
Phosphorus
Other name for Carbohydrate
saccharides
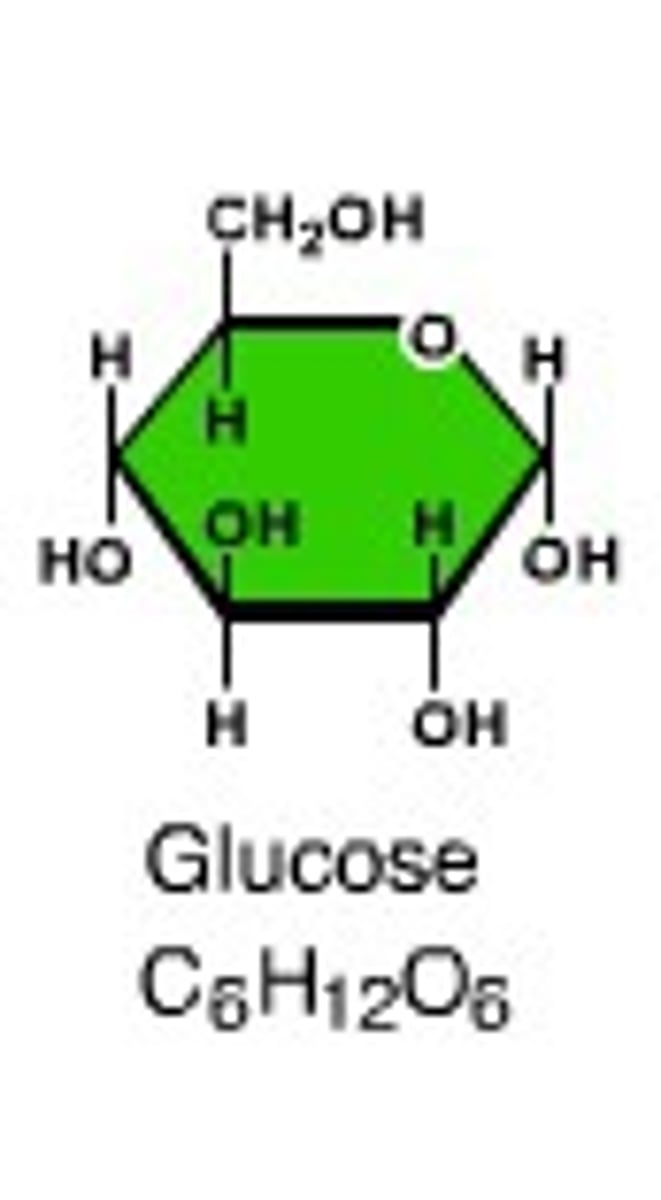
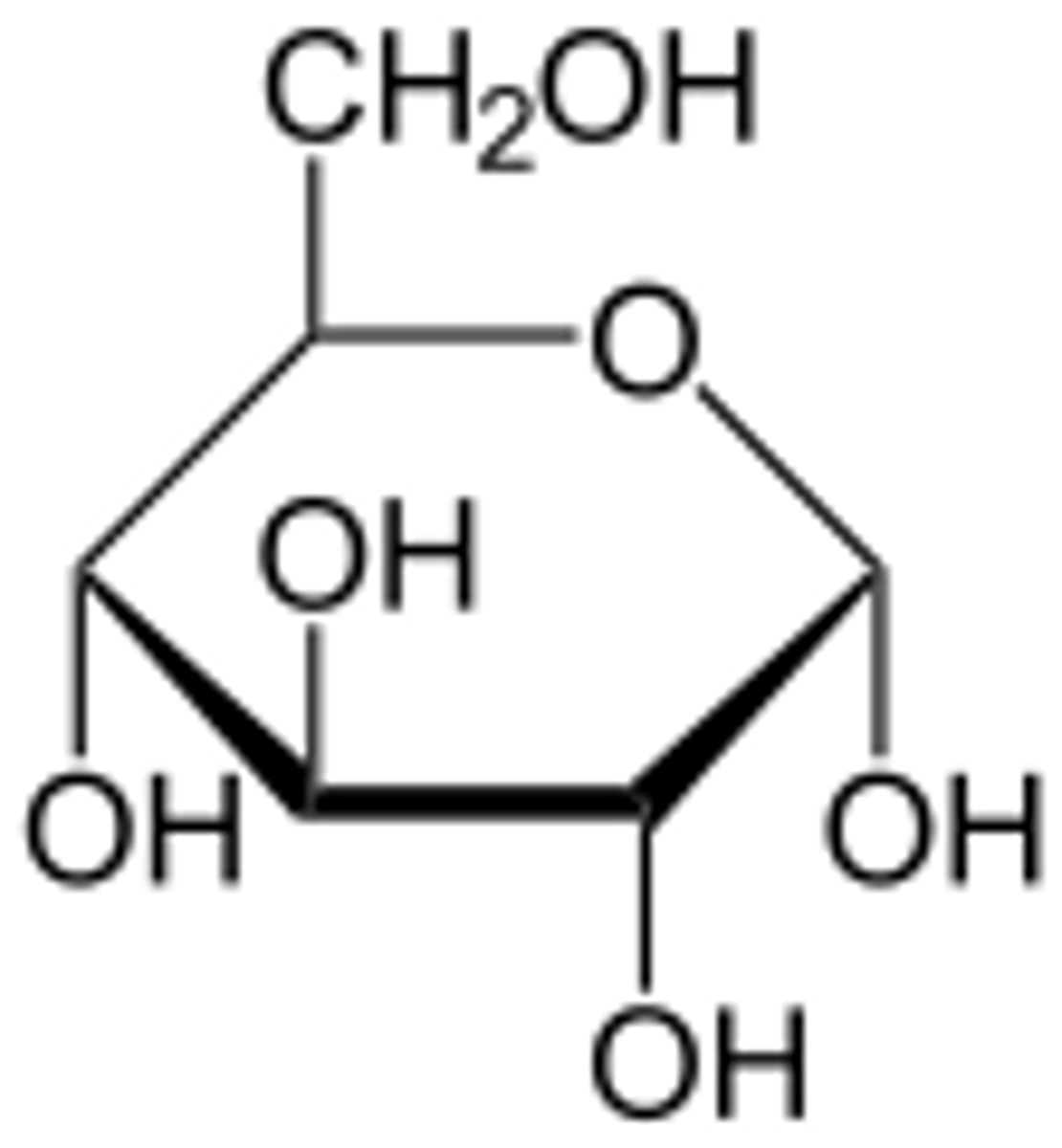
monosaccharide diagram of glucose
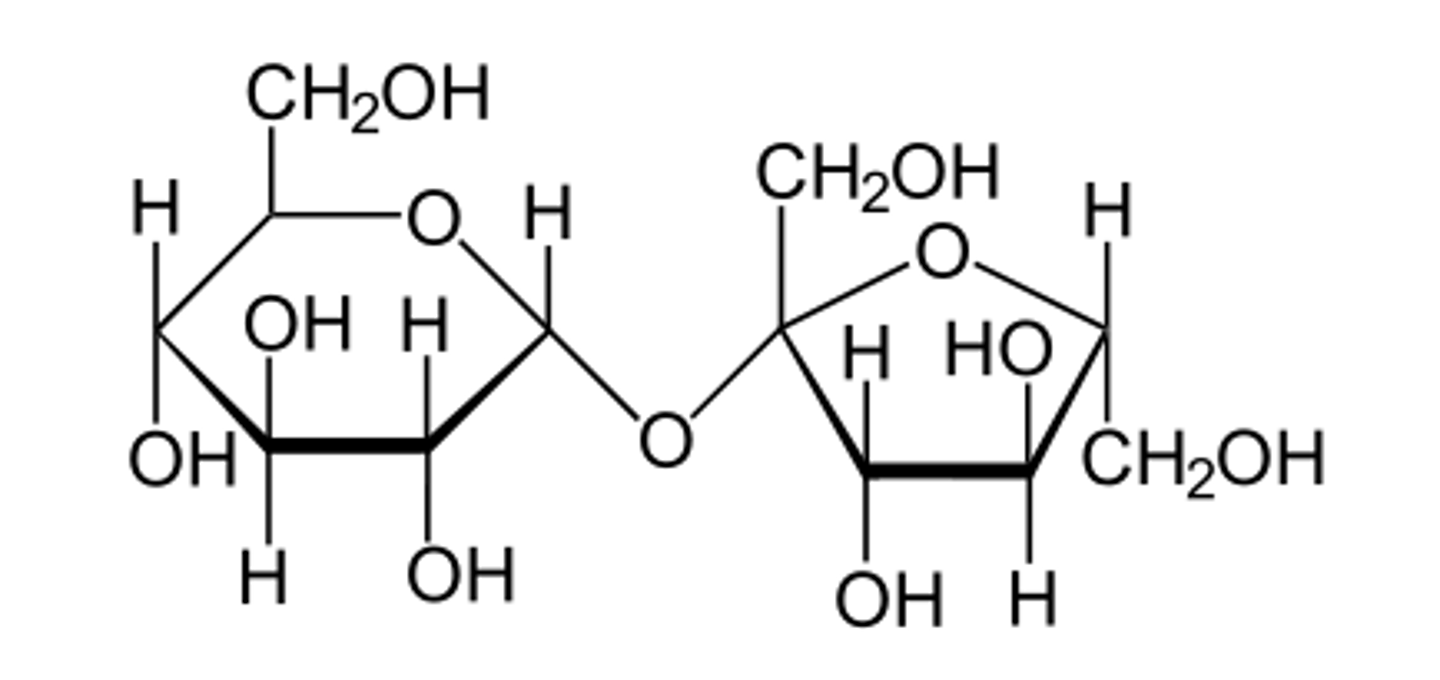
disaccharide diagram of sucrose
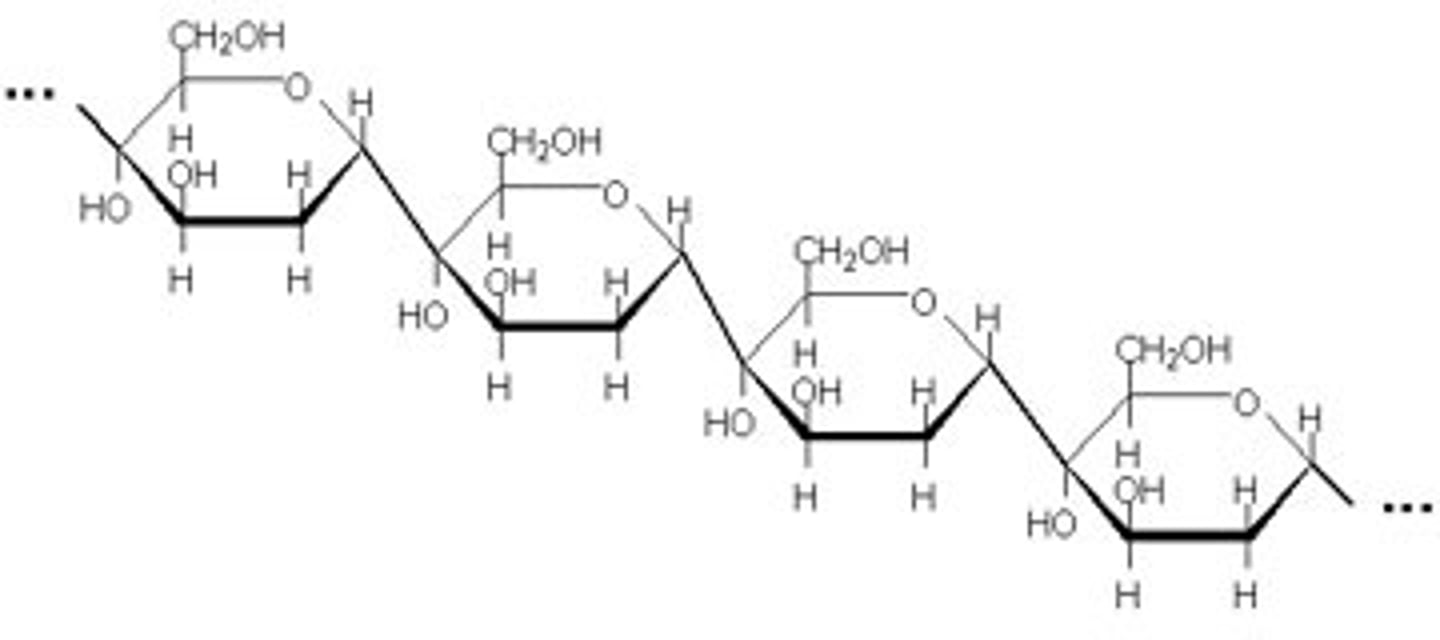
polysaccharide diagram of amylose
amino acid structure
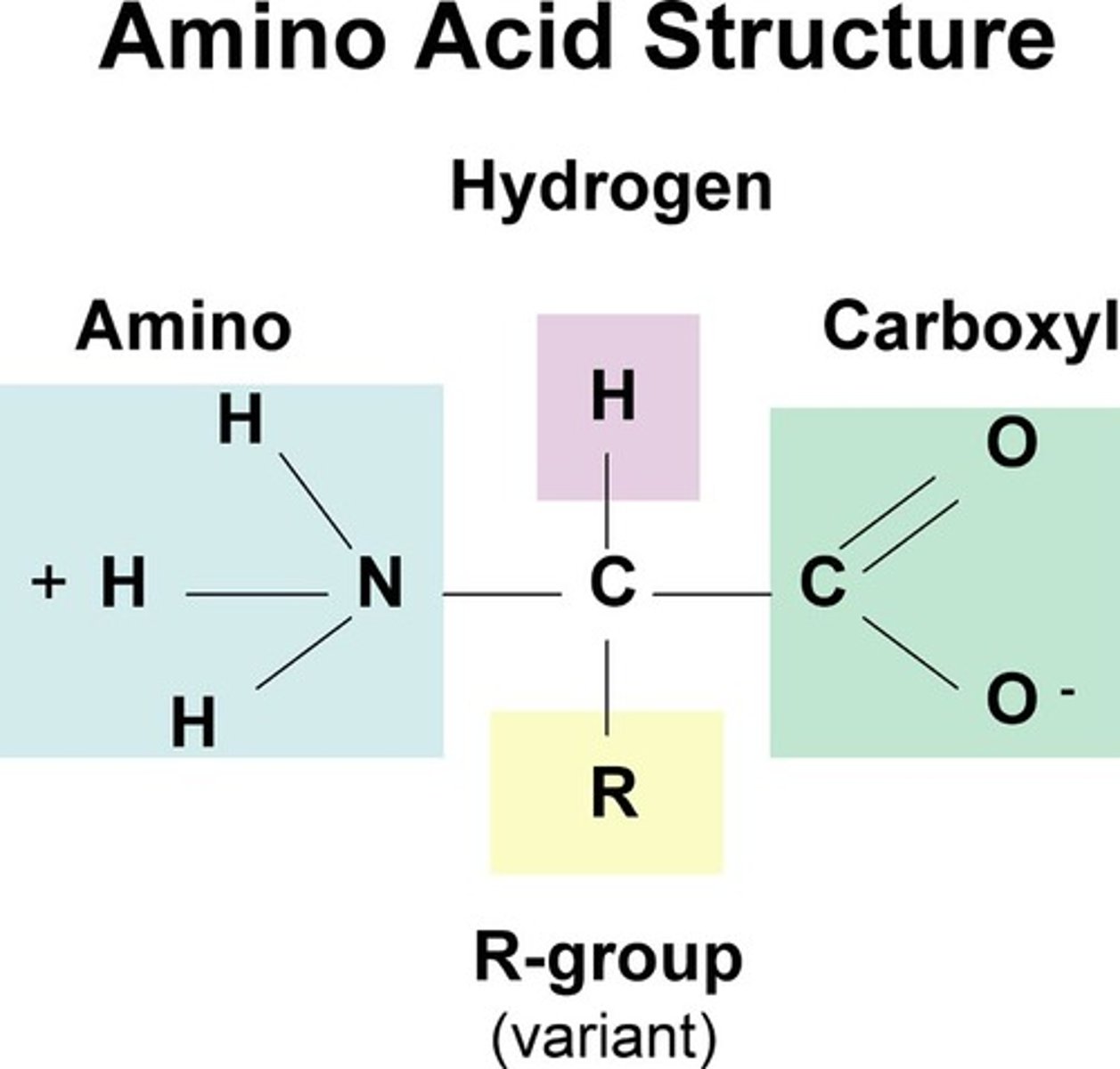
diagram of saturated
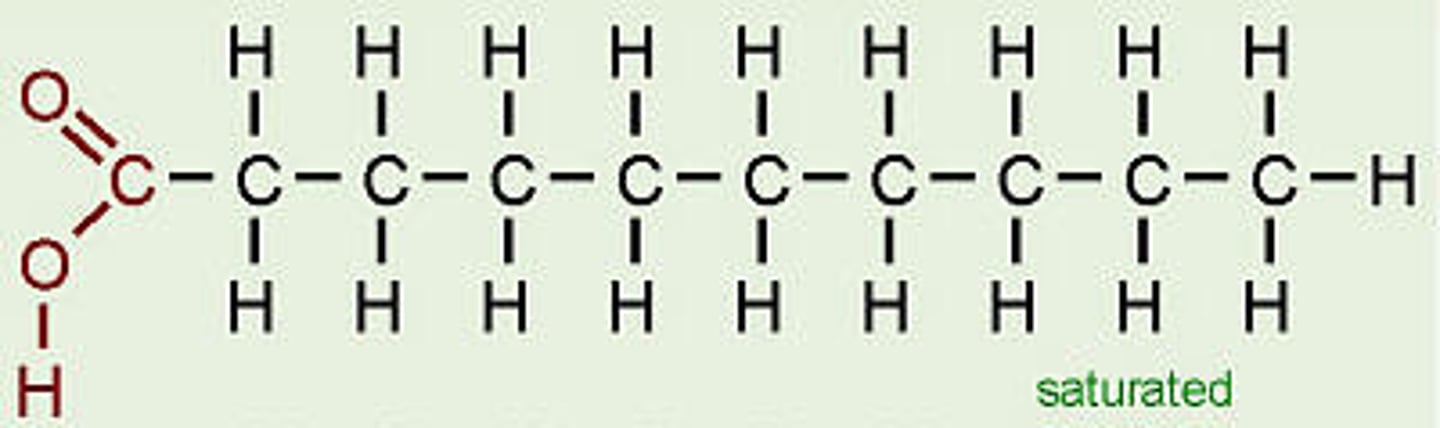
diagram of unsaturated
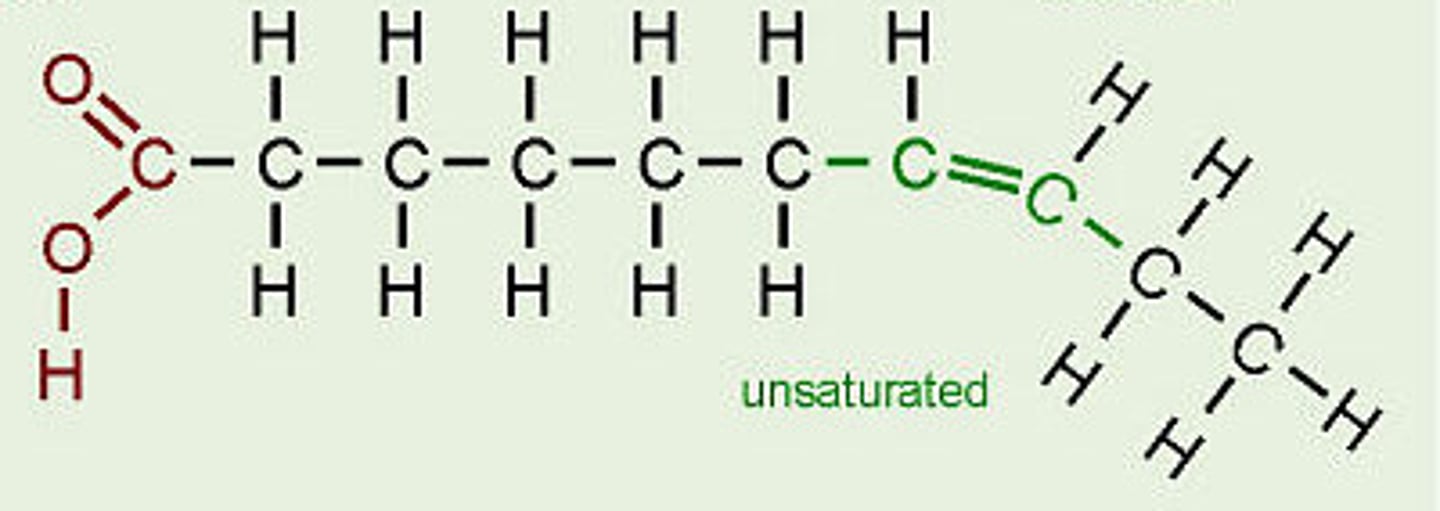
diagram of nucleotide
Dipeptides
two amino acids joined together by a peptide bond
Nitrogen bases in DNA
Adenine
Guanine
Thymine
Cytosine
polymer and amino acid relationship
Polymer is a protein aka peptide
Lots of amino acids linked together
Triglycerides
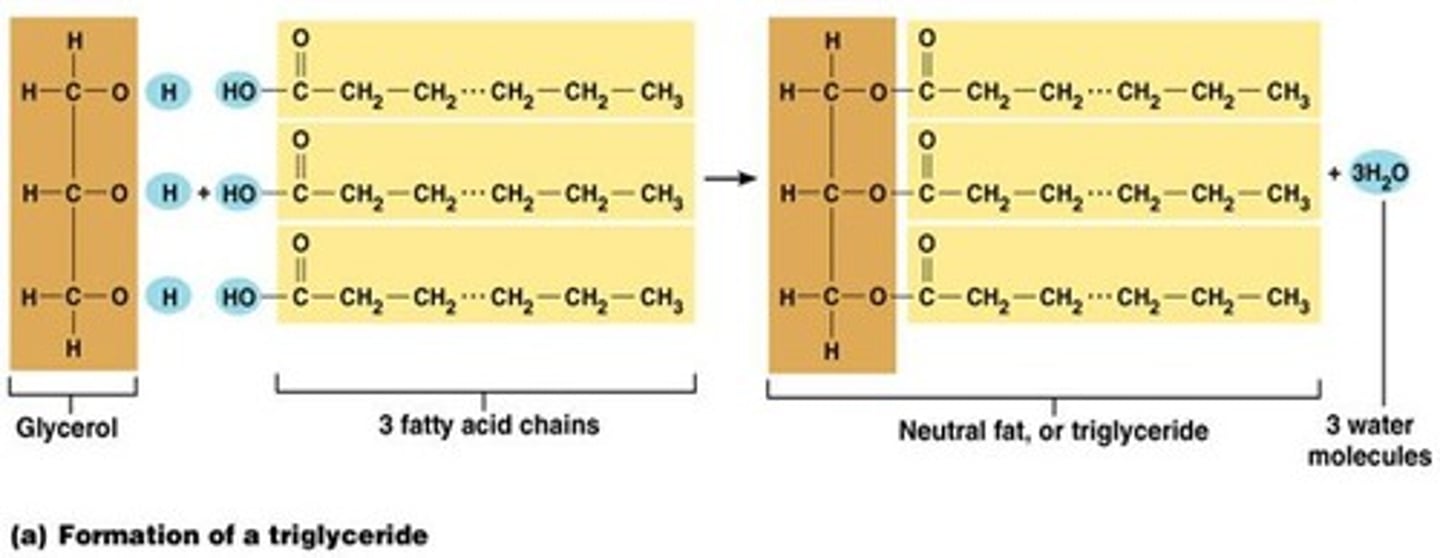
carbohydrate structure
Saturated
Fatty acid consists of single bonds
Unsaturated
Fatty acid contains double bonds
Which macromolecule speeds up chemical reactions?
Protein (enzyme)