LEC 8.2: Preventing Nosocomial Infections (or HAIs)
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Hand Hygiene, Hand Hygiene Using Alcohol-Based Rub, Supporting Defenses of a Susceptible Host, Disinfecting & Sterilizing,
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Hand Hygiene
Considered one of the most effective infection prevention measures
Before eating
After using the bedpan or toilet
After the hands have come in contact with any body substances
Before & after giving care of any kind
When do hands need to be cleansed?
15-20
For routine client care, vigorous hand washing under a stream of water for ___ seconds using a granular soup, soap-filled sheets or liquid soap
Beginning of the nurses’ shift
When the hands are visibly soiled
After using the toilet
According to WHO in 2009, when should Hand Hygiene should be done?
Antimicrobial Soaps
Usually provided in high-risk areas
Utilized in the following situations, as recommended by the CDC:
When there are known multiple resistant bacteria
Before invasive procedures
In special care units, such as nurseries and ICUs
Before caring for severely immunocompromised clients
When there are known multiple resistant bacteria
Before invasive procedures
In special care units, such as nurseries and ICUs
Before caring for severely immunocompromised clients
According to the CDC, when should antimicrobial soaps be used?
40-60 seconds
How long should hand washing in total take?
Hand Hygiene Using Alcohol-Based Hand Rub
Used before and after each direct client contact
Not sufficient in the following situations:
Hands have visible dirt or matter
C. difficile may be present
Hands have visible dirt or matter
C difficile may be present
What are the situations where Hand Hygiene Using Alcohol-Based Hand Rub may not be sufficient?
They kill bacteria more effectively and more quickly than hand washing with soap and water (Except for some microorganisms that are resistant to alcohol).
They are less damaging to skin than soap and water, resulting in less dryness & irritation
They require less time than hand washing with soap & water
Bottles/dispensers can be placed at the point of care so they are more accessible
Why does the CDC promote the use of alcohol-based hand rubs?
Handwashing Before Performing Sterile Skills
Hands must be held higher than the elbows
Susceptibility
Degree to which an individual can be affected
Hygiene
Nutrition
Fluid
Sleep
Immunizations
5 Measures that can Reduce a Person’s Susceptibility
Antiseptics
Disinfectants
Sterilization
What interrupt the etiologic agent and reservoir?
Antiseptics
Interrupt the etiologic agent and reservoir
Agents that inhibit the growth of the microorganisms
Disinfectants
Interrupt the etiologic agent and reservoir
Agents that destroy pathogens other than spores
Sterilization
Interrupt the etiologic agent and reservoir
Under surgical asepsis
Removes all microorganisms
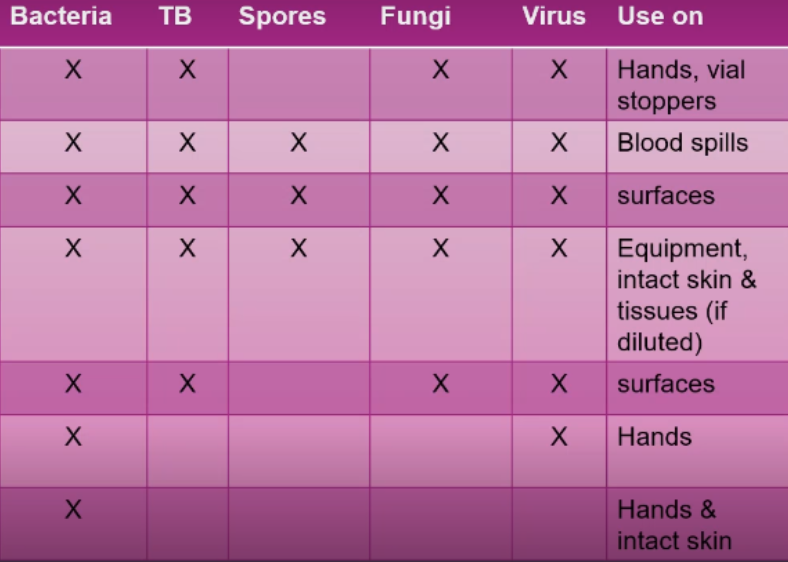
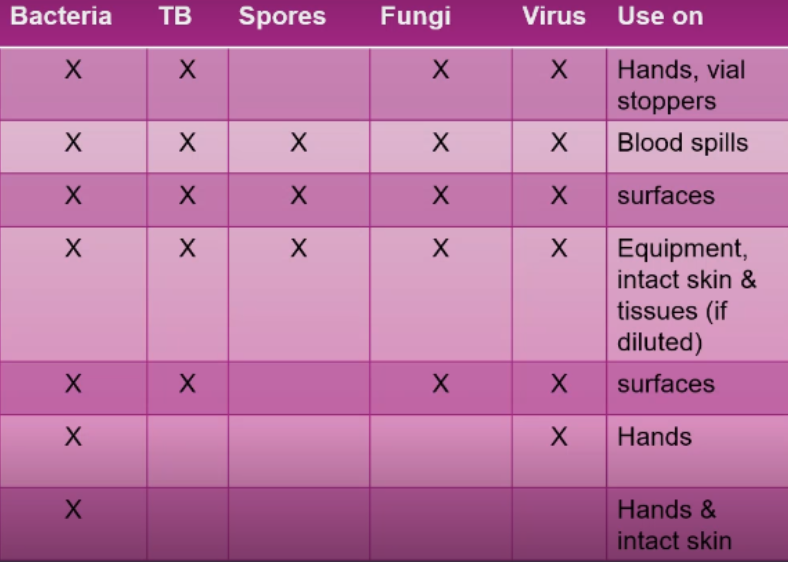
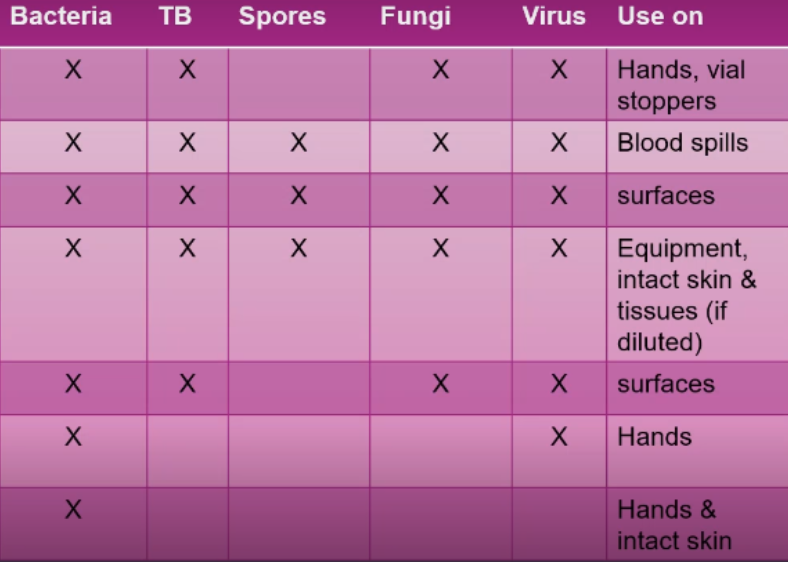
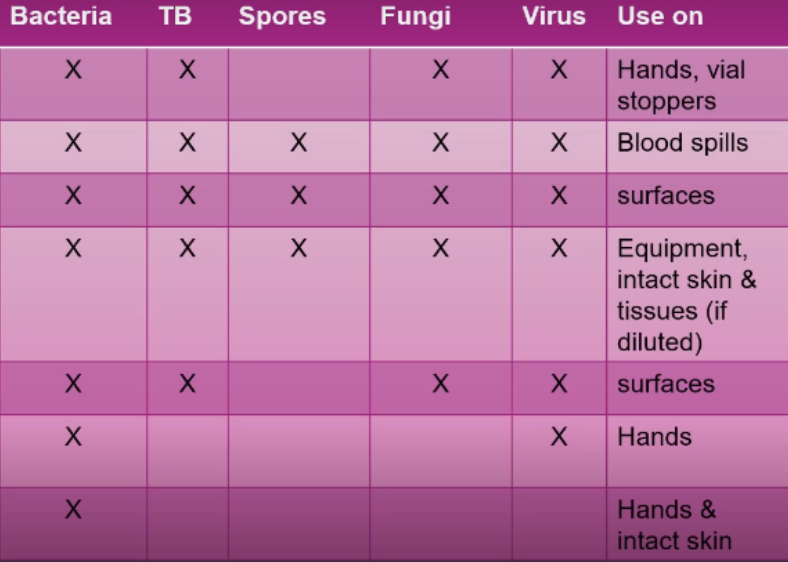
Antiseptics and disinfectants have similar chemical components and have bactericidal or bacteriostatic properties. However, disinfectant is a more concentrated solution.
How are antiseptics and disinfectants similar and different?
Bactericidal
Property of antiseptics and disinfectants
Kills or destroys the bacteria
Bacteriostatic
Property of antiseptics and disinfectants
Prevents the growth and reproduction of the bacteria but the bacteria is still present in that particular area
Alcohol
One of the commonly used antiseptics and disinfectants
(1)
Chlorine
One of the commonly used antiseptics and disinfectants
(2)
H2O2
One of the commonly used antiseptics and disinfectants
(3)
Iodophors
One of the commonly used antiseptics and disinfectants
(4)
Phenol
One of the commonly used antiseptics and disinfectants
(5)
Chlorhexidine Gluconate
One of the commonly used antiseptics and disinfectants
(6)
Triclosan
One of the commonly used antiseptics and disinfectants
(7)
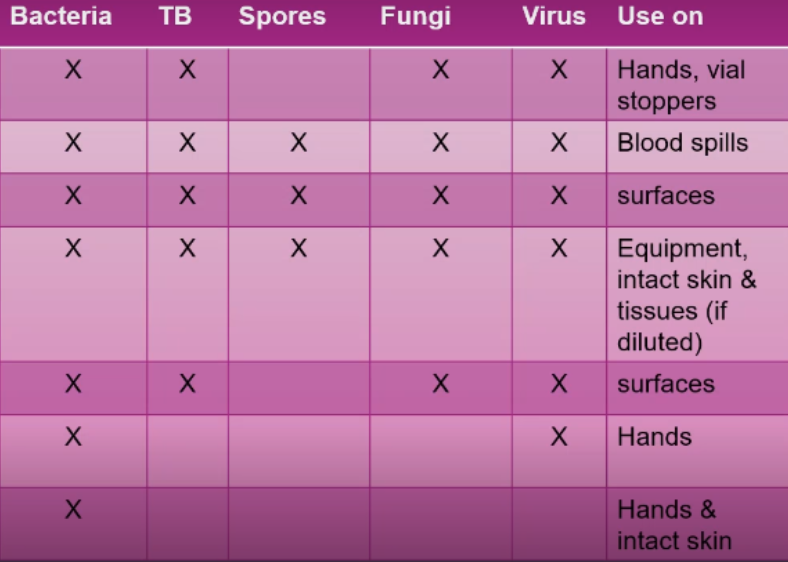
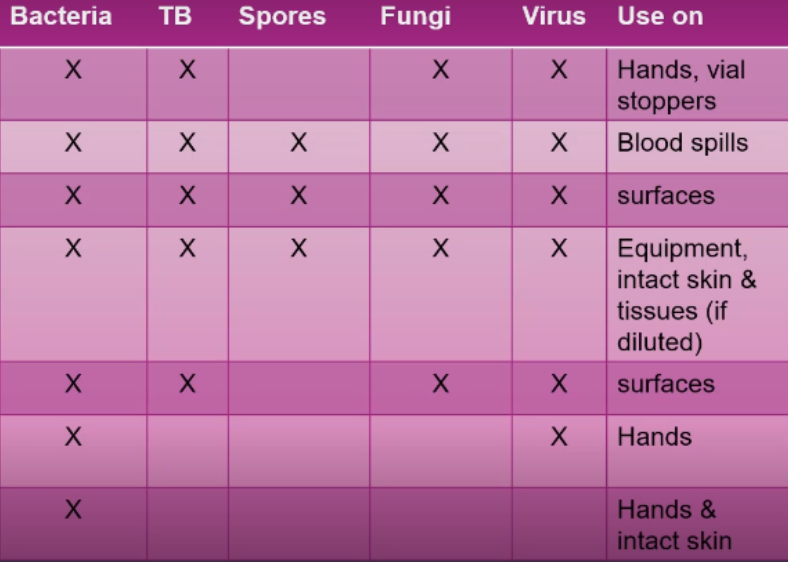
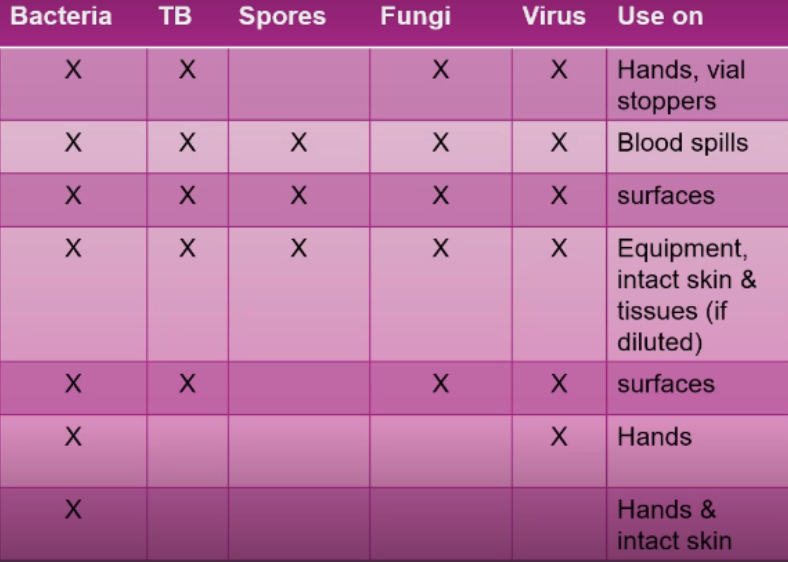
Type and number of infectious organisms
Recommended concentration of the disinfectant and duration of contact
Presence of soap
Presence of organic materials
Surface areas to be treated
When disinfecting articles, what 5 things must the nurse consider?
Type and number of infectious organisms
One of the things the nurse must consider when disinfecting articles
Virulence, type, and spread, the probability of causing infection is very high.
Recommended concentration of the disinfectant and duration of contact
One of the things the nurse must consider when disinfecting articles
For example, alcohol, needs to be used for 15 seconds to be considered effective.
Presence of soap
One of the things the nurse must consider when disinfecting articles
There are certain ingredients in the soap that makes germicidal effects of certain disinfectant becomes inactivated when exposed to it.
Presence of organic materials
One of the things the nurse must consider when disinfecting articles
Blood, puss, feces may have an effect on the effectiveness of certain disinfectants. For example, fecal matter may deactivate chlorine.
Surface areas to be treated
One of the things the nurse must consider when disinfecting articles
For example, some disinfectants can’t be used on metal or a porous mat.
Sterilization
Process that destroys all microorganisms, including spores and viruses
Moist Heat
Gas
Boiling
Radiation
4 Commonly Used Sterilization Methods
Moist Heat
One of the commonly used sterilization methods
Steam under pressure is used because it attains temperatures higher than the boiling point
Autoclave machine
Gas
One of the commonly used sterilization methods
Ethylene oxide
Destroys microorganisms, including spores, by interfering with metabolic processes
Has good penetration and effectiveness to heat-sensitive items
Disadvantages: Carcinogenic & Teratogenic
Ethylene Oxide
What is the gas used for gas sterilization?
Carcinogenic
Teratogenic
2 Disadvantages of Gas Sterilization
Boiling
One of the commonly used sterilization methods
Minimum of 15 minutes (1st minute should be counted when the bubbling FIRST starts)
Radiation
One of the commonly used sterilization methods
Uses ionizing and non-ionizing radiation
Uses UV rays
Ionizing Radiation
Type of radiation used for sterilization
Non-Ionizing Radiation
Type of radiation used for disinfection