Exam 1 review POLS 207
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
1
New cards
When did Texas become a state?
1845
2
New cards
When was the TEXAS constitution ratified?
1876
3
New cards
What is policy conservatism?
A state's tendency to limit the welfare benefits, deregulate business, keep taxes low, and generally place less reliance on government and more reliance on individuals and the marketplace to achieve social goals
4
New cards
What is policy liberalism?
A state's tendency to expand welfare benefits, regulate business, adopt progressive state income taxes, and generally use government to achieve social change
5
New cards
Where do STATE governments derive their revenue?
STATE government revenue comes from income, sales, and other taxes; charges and fees; and transfers from the federal government. Taxes accounted for about half of STATE general revenue in 2017.
6
New cards
Where do LOCAL governments derive their revenue?
LOCAL government revenue comes from property, sales, and other taxes; charges and fees; and transfers from federal and state governments. Taxes accounted for 42 percent of LOCAL general revenue in 2017.
7
New cards
What is Federalism?
National and regional (state) governments share powers, "independent equals"
8
New cards
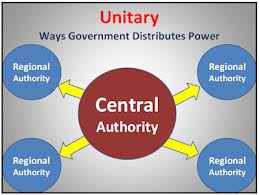
What is a unitary government (Unitary Systems)?
System where legal authority is exclusively held by the central (national) government
9
New cards
What is a confederation?
A voluntary association of independent sovereign states
10
New cards
Why are states called "laboratories of democracy?"
They can more easily implement new policies than the national government. (Policy innovation), States are small representations of the whole country
11
New cards
What is nullification?
The process of a state's rejecting (nullifying) a federal law and making it invalid within its borders
12
New cards
What are enumerated or delegated powers?
Powers SPECIFICALLY mentioned in the Constitution as belonging to the national government.
(Among the most important of these is the national supremacy clause)
(Among the most important of these is the national supremacy clause)

13
New cards
What are implied powers?
Broad, but undefined, powers given to the federal government by the Constitution.
(Such as the necessary and proper clause)
(Such as the necessary and proper clause)

14
New cards
What does the 10th amendment state?
The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the States, are reserved to the States respectively, or to the people.
(Known as the "reserved powers")
(Known as the "reserved powers")

15
New cards
What was the result of Marbury v. Madison? (1803)?
Established the principle of judicial review in the United States, meaning that American courts have the power to strike down laws, statutes, and some government actions that they find to violate the Constitution of the United States.
(Declared the judiciary act of 1789 unconstitutional)
(Declared the judiciary act of 1789 unconstitutional)

16
New cards
What was the result of McCulloch v. Maryland (1819)?
Defined the scope of the U.S. Congress's legislative power and how it relates to the powers of American state legislatures.
(established that the federal government has a BROAD set of powers over the states)
(established that the federal government has a BROAD set of powers over the states)
17
New cards
What was the result of Brown v. Board of Education?
Ruled unanimously that racial segregation of children in public schools was unconstitutional.
18
New cards
What was the result of Gibbons v. Ogden?
The court reinforced the federal government's authority to regulate trade between the states.
(Reinforced the commerce clause)
(Reinforced the commerce clause)
19
New cards
What does the 14th amendment state?
Prohibits any state from depriving individuals of the rights and privileges of citizenship, and requires states to provide due process and equal protection guarantees to all citizens

20
New cards
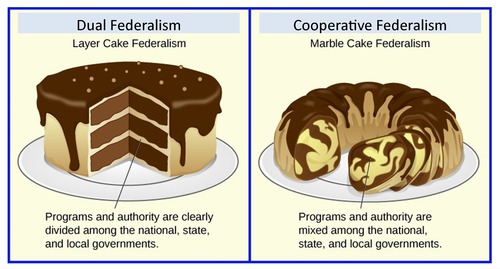
What is dual federalism?
LAYER CAKE!
A system of government in which both the states and the national government remain supreme within their own spheres, each responsible for some policies.
A system of government in which both the states and the national government remain supreme within their own spheres, each responsible for some policies.
21
New cards
What is cooperative federalism?
MARBLE CAKE!
A system of government in which powers and policy assignments are shared between states and the national government.
A system of government in which powers and policy assignments are shared between states and the national government.

22
New cards
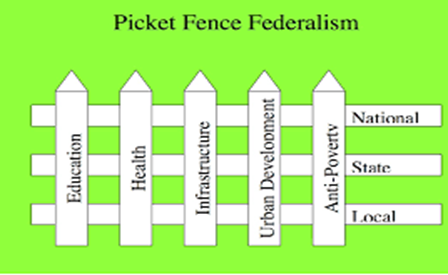
What is Centralized Federalism?
PICKET FENCE
The notion that the federal government should take the leading role in setting national policy, with state and local governments helping implement the policy
The notion that the federal government should take the leading role in setting national policy, with state and local governments helping implement the policy
23
New cards
What are federal grants-in-aid?
Cash appropriations given by the federal government to the states.
24
New cards
Why are federal grants-in-aid important?
They give the state funding to help the population and help the government function, fund social programs, and avoid budget deficits
25
New cards
What are categorical grants?
grants from the federal government to state and local governments given for narrowly defined purposes
26
New cards
What are project grants?
grant programs in which state and local governments submit proposals to federal agencies and for which funding is provided on a competitive basis
27
New cards
What are formula grants?
grants-in-aid in which a formula is used to determine the amount of federal funds a state or local government will receive
28
New cards
What are block grants?
Federal grants given more or less automatically to states or communities to support broad programs in areas such as community development and social services
29
New cards
What are revenue sharing grants?
Federal grants-in-aid given with few constraints, leaving states and localities almost complete discretion over how to spend the money
30
New cards
What are mandates?
Orders the state or local governments to comply with federal laws, may or may not provide funding
31
New cards
What are unfunded mandates?
a statute or regulation that requires a state or local government to perform certain actions, with NO MONEY PROVIDED for fulfilling the requirements
32
New cards
What is preemption?
The process of the federal government's over-riding areas regulated by state law.
(National government is supreme)
(National government is supreme)
33
New cards
What is a bill of rights?
Specific guarantees of personal freedoms and rights, clear limitations on the government's power in judicial and other proceedings, and explicit declarations that all powers not specifically granted by the Constitution are reserved for the states or the people.
(The first 10 amendments of our constitution)
(The first 10 amendments of our constitution)
34
New cards
What is constitutionalism?
A government of laws, not people, operating on the principle that governmental power must be limited, that government officials should be restrained in their exercise of power over individuals.
35
New cards
Why are state constitutions long?
State constitutions are easier to amend. Because of this, state constitutions are amended and added on to fairly often.
Whereas the federal constitution creates a framework for government, state constitutions often get into policy details.
Whereas the federal constitution creates a framework for government, state constitutions often get into policy details.
36
New cards
How do most states amend their constitution?
Legislative proposal
37
New cards
What are special districts?
Local governmental units created for a SINGLE PURPOSE, such as water distribution
There are two types of special districts in Texas
1. School district
2. Non-school special district:
Common examples include municipal utility districts, economic development corporations, hospital districts
There are two types of special districts in Texas
1. School district
2. Non-school special district:
Common examples include municipal utility districts, economic development corporations, hospital districts
38
New cards
What are at-large elections?
Elections in which city or county voters vote for council or commission members from any part of the jurisdiction
39
New cards
What are single member districts?
Electoral districts represented by a single officeholder.
40
New cards
What are nonpartisan elections?
elections in which the candidates' names appear on a ballot without indication of their party affiliation.
41
New cards
What is the incumbent advantage?
Incumbents council members are elected at very high rates in nonpartisan elections
42
New cards
What are combination election systems?
Some officials are elected at large; others from single-member districts
43
New cards
What are the different political cultures?
Moralistic
Individualistic
Traditionalistic
Individualistic
Traditionalistic
44
New cards
Moralistic political culture
Role of gov:
Promote public interest & policy innovation
Attitude of representatives:
Politicians can cause change, serving is an honor
Role of citizens:
active participation in voting & public office
Party competition:
High
Spending on services:
High
Political culture:
Strong
Most common in:
Northeast, Northwest
Promote public interest & policy innovation
Attitude of representatives:
Politicians can cause change, serving is an honor
Role of citizens:
active participation in voting & public office
Party competition:
High
Spending on services:
High
Political culture:
Strong
Most common in:
Northeast, Northwest
45
New cards
Individualistic political culture
Role of gov:
utilitarian, a service provider
Attitude of representatives:
Businesslike politics is a career, very high levels of corruption
Role of citizens:
citizens should leave the politics to the professionals
Party competition:
moderate
Spending on services:
moderate
Political culture:
fragmented
Most common in:
midwest, midatlantic
utilitarian, a service provider
Attitude of representatives:
Businesslike politics is a career, very high levels of corruption
Role of citizens:
citizens should leave the politics to the professionals
Party competition:
moderate
Spending on services:
moderate
Political culture:
fragmented
Most common in:
midwest, midatlantic
46
New cards
Traditionalistic political culture
Role of gov:
preserve the status quo
Attitude of representatives:
politics is the province of the ruling elite
Role of citizens:
ordinary citizens are not expected to be involved
Party competition:
low
Spending on services:
low
Political culture:
strong
Most common in:
south, rural areas
preserve the status quo
Attitude of representatives:
politics is the province of the ruling elite
Role of citizens:
ordinary citizens are not expected to be involved
Party competition:
low
Spending on services:
low
Political culture:
strong
Most common in:
south, rural areas
47
New cards
What is the political culture of Texas?
Traditionalistic :(
48
New cards
What is the philosophy behind the current Texas constitution?
easy to amend, but VERY difficult to overhaul/scrap and start over
Legislature proposes amendments
A majority of state voters must approve:
Majority of those who vote; turnout usually low
Thus a low number of actual votes needed
Legislature proposes amendments
A majority of state voters must approve:
Majority of those who vote; turnout usually low
Thus a low number of actual votes needed
49
New cards
What is history of the Texas constitution?
Constitution of Coahuila y Tejas, 1827
Republic of Texas, 1836
Texas State Constitution of 1845
Confederate Constitution of 1861
Constitution of 1866
Reconstruction Constitution of 1869
Republic of Texas, 1836
Texas State Constitution of 1845
Confederate Constitution of 1861
Constitution of 1866
Reconstruction Constitution of 1869
50
New cards
What was the political climate of the Constitutional Convention of 1875?
Convention was needed due to Governor Davis corruption and power imbalance allowed in 1869 Constitution
Was the result of the determination of the Democrats of Texas to eliminate the radical Constitution of 1869
The time before the constitutional convention was marked by a number of Democratic measures designed to undo many Republican acts previously passed. The centralized school system was weakened. State salaries and expenditures were cut, and the governor was stripped of his powers to appoint some state officers and declare martial law.
Four goals in this constitution:
1.Strong popular control of government (voters)
2.Powers were to be limited
3.Restrain spending
4.Promote agriculture interests
Was the result of the determination of the Democrats of Texas to eliminate the radical Constitution of 1869
The time before the constitutional convention was marked by a number of Democratic measures designed to undo many Republican acts previously passed. The centralized school system was weakened. State salaries and expenditures were cut, and the governor was stripped of his powers to appoint some state officers and declare martial law.
Four goals in this constitution:
1.Strong popular control of government (voters)
2.Powers were to be limited
3.Restrain spending
4.Promote agriculture interests
51
New cards
What are the differences between the Bill of Rights in the Texas and U.S Constitutions?
Texas Bill of Rights is longer and more detailed.
Texas Bill of Rights is subordinate to the US
Texas Bill of Rights is subordinate to the US
52
New cards
What were the conditions of the annexation agreement for Texas to join the United States in 1845?
Texas could retain control over their public lands, thus giving the ability to extinguish its debt.
Provided that Texas could be divided into several states as needed to deal with future "balance" between slave states and free states
No slavery would be allowed north of the old Missouri Compromise line.
Provided that Texas could be divided into several states as needed to deal with future "balance" between slave states and free states
No slavery would be allowed north of the old Missouri Compromise line.
53
New cards
What is the process to amend the Texas Constitution?
Legislative Proposal:
the most common method; an amendment is passed by the legislature and put to the voters in a referendum
Popular Initiative:
citizens can bypass the legislature for a direct vote if they obtain a requisite number of petition signatures
Constitutional Convention:
has lost favor as a method
Constitutional Revision Commissions:
rarely used but effective when attempted
the most common method; an amendment is passed by the legislature and put to the voters in a referendum
Popular Initiative:
citizens can bypass the legislature for a direct vote if they obtain a requisite number of petition signatures
Constitutional Convention:
has lost favor as a method
Constitutional Revision Commissions:
rarely used but effective when attempted
54
New cards
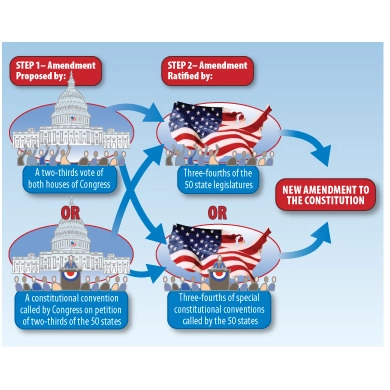
What is the process to amend the U.S Constitution?
1. Amendment is Proposed, requires 2/3 majority of votes from house members and senators to pass
2. Amendment is Ratified, requires 3/4 majority of states' legislatures
OR
1. State legislatures request a special convention, requires 2/3 majority to pass
2. Amendment is ratified, requires 3/4 majority vote to be ratified
2. Amendment is Ratified, requires 3/4 majority of states' legislatures
OR
1. State legislatures request a special convention, requires 2/3 majority to pass
2. Amendment is ratified, requires 3/4 majority vote to be ratified
55
New cards
How has federalism evolved over time?
Initially States were more powerful, overtime national government has grown stronger
56
New cards
Commission (City government)
Gives legislative and executive power to a small body, usually of five members
57
New cards
Council-manager (City government)
Elected council or commission appoints manager
58
New cards
Elected mayor (hybrid mayor-manager form of government)
About two-thirds of council-manager communities elect a mayor
59
New cards
Mayor-council (City government)
May be "strong" or "weak"
60
New cards
What does the 16th amendment state?
Enables the federal government to levy a national income tax, which has helped further national policies and programs
61
New cards
What does the 17th amendment state?
Provides for direct election of U.S. senators, rather than election by each state's legislature.