5. BUILDING SELF-KNOWLEDGE + CULTURE AND THE SELF
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Sally sees herself as a generous person.
According to research on the looking-glass self,
which of the following is most likely true about
how Sally's self-perception was formed?
A. Sally's best friend views Sally as a generous person
B. Sally believes that others see her as a generous person
C. Sally views herself as generous because she has observed herself behaving in a generous way many tiems
D. Sally's family members are all generous people
B. Sally believes that others see her as a generous person
What change would be made that should result in a correspond in change to our self concept according to social comparison?
change in the point of comparison results in a change in our self-concept
What change would be made that should result in a correspond in change to our self concept according to social role?
gains and losses of social roles trigger changes to the self-concept
what can a lot of social change with less positive feeling bring?
low Self concept clarity => self-concept confusion
What change would be made that should result in a correspond in change to our self concept according to looking-glass?
purposely initiating change to their self-concept if they believe they are perceived by others undesirably
what is the most important part of self
desired reputation
What change would be made that should result in a correspond in change to our self concept according to person close to
self-concept will change when we become closer to new people
Where is the Individualistic cultures common in?
Western countries
Where is the Collectivistic cultures common in?
East Asian countries
What does the Individualistic cultures prioritize?
individual via self-interest and self-expression
What does the Collectivistic cultures prioritize?
group harmony via suspension of self-interest
What is the driver of behaviour for Individualistic cultures?
internal states (own thoughts, feelings, desires)
What is the driver of behaviour for Collectivistic cultures?
external factors (duties, norms, others' expectations)
How does Individualistic cultures shape self-concept?
by fostering an independent self-concept
How does Collectivistic cultures shape self-concept?
by fostering an interpendent self-concept
What does fostering an independent self-concept mean?
distinguishing self from others by focusing on what makes one unique from others by focusing on personal identity
What does fostering an interdependent self-concept mean?
fitting self with others by focusing on aspects of identity that make one similar to close others and collective by focusing on the self in relation to tohers
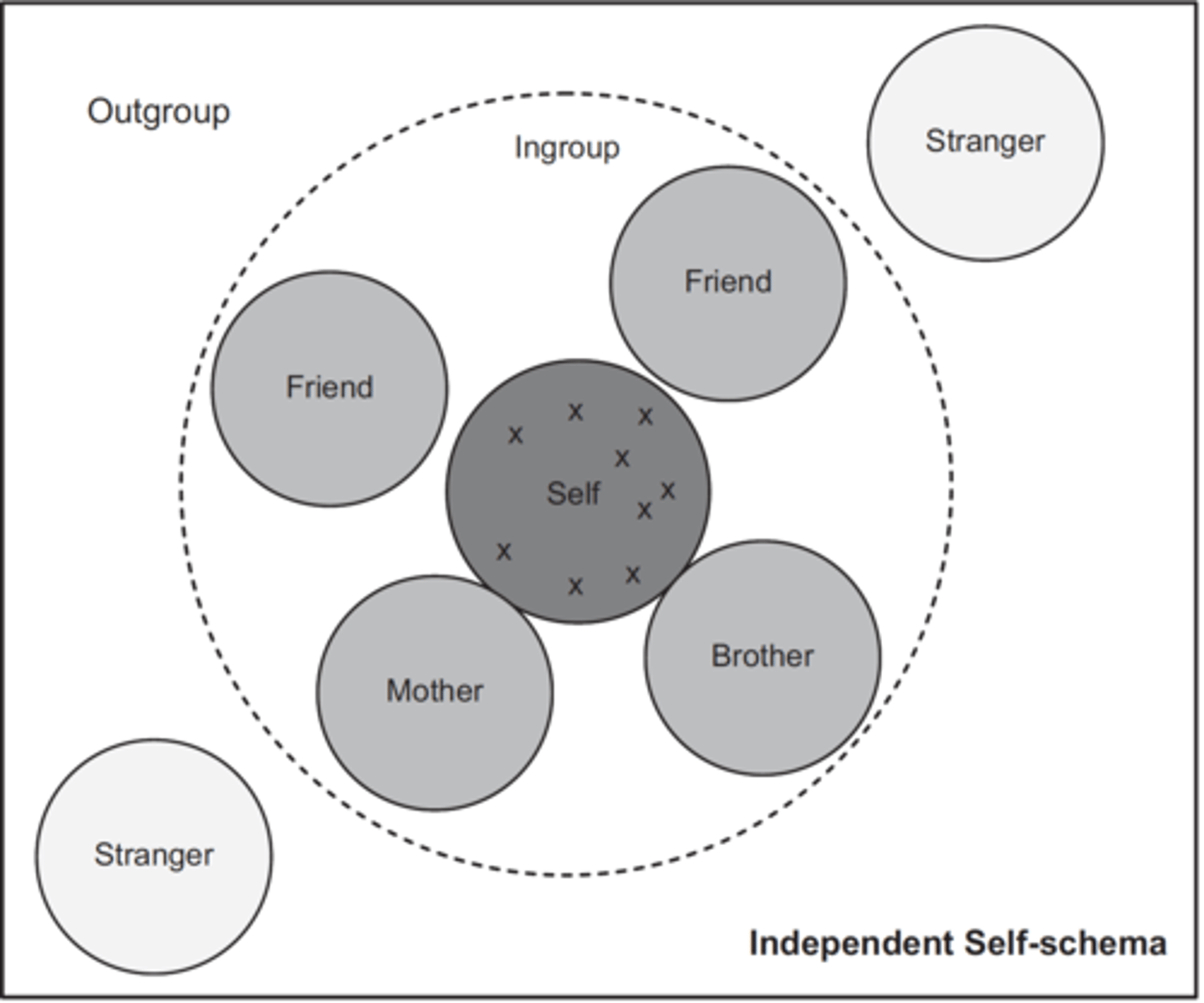
How is independent self-schema depicted
seperate from others (distinct) & ingroup outgroup is fluid
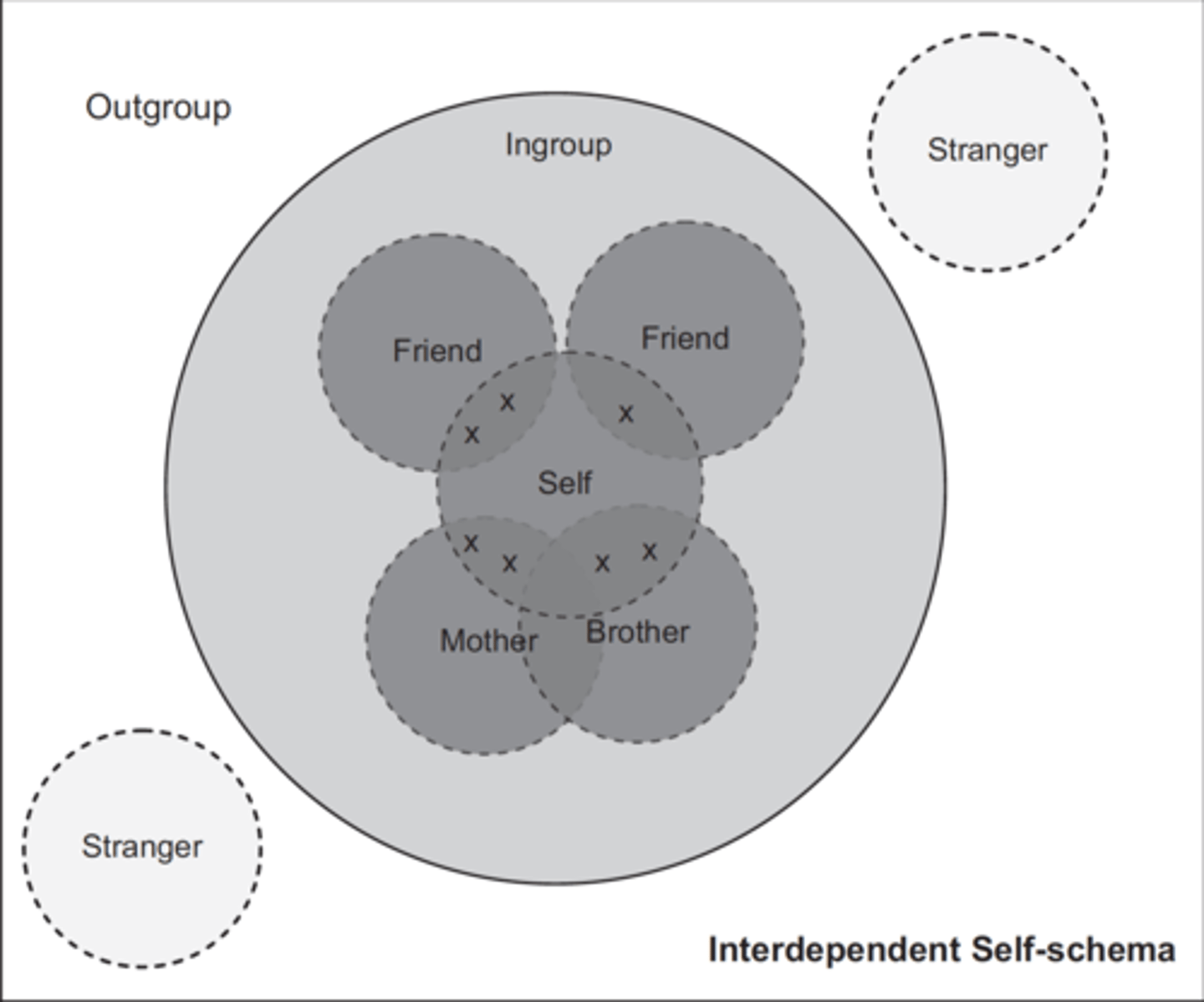
How is interdependent self-schema depicted
boundaries between self and others are shared & in group and outgroup is clear
How do culture get transmitted
through social interactions
How does Individualistic cultures influence parenting
Mothers teach infants early on to spend time on their own, babies are expected to start sleeping alone wout parents starting 3months
What does Individualistic cultures encourage in children?
They encourage emotional self-expression(ex. to smile and make positive vocalizations
How does Collectivistic cultures influence parenting
Mothers teach infants early on that obedience and respect are important, co-sleeping for the first couple of years of life
What kind of conversations with children are seen in Collectivistic cultures?
Conversations with children are directive and instructional and obedience is praised
Where did the the two cultures (individualistic and collectivistic) originate from?
Subsistence theory
Subsistence Theory
the way people in a culture historically made a living influences culture
According to Subsistence theory, what did farming cultures (interdependent) turn in?
collective culture
According to Subsistence theory, what did herding and fishing rming cultures (independent) turn into?
individualistic culture
What are the cultural differences in cognition seen in collectivistic cultures?
Holistic thinking, focusing on the whole and the relationship between parts, reasoning relives on experiences and detecting patterns
What are the cultural differences in cognition seen in individualistic cultures?
analytic thinking, focusing on individual components of a situation/object, with reasoning relying on categorization and logic
When asked "which two go together, cow - chicken or grass" what do individualistic cultures answer?
Chicken and cow due to categorization
When asked "which two go together, cow - chicken or grass" what do collectivistic cultures answer?
grass and cow due to relationship
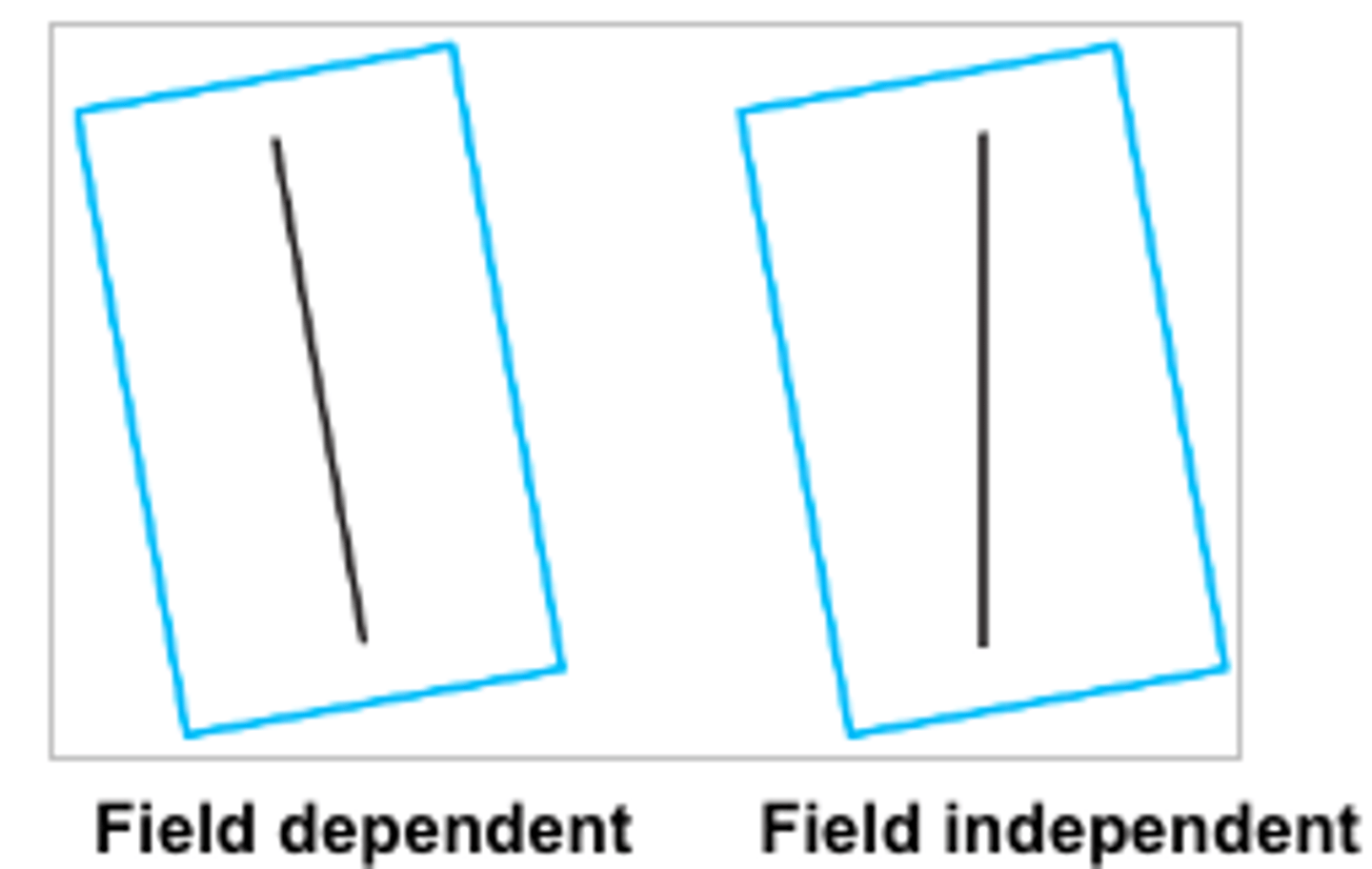
During the rod and frame test, what do individualistic cultures answer?
field independent
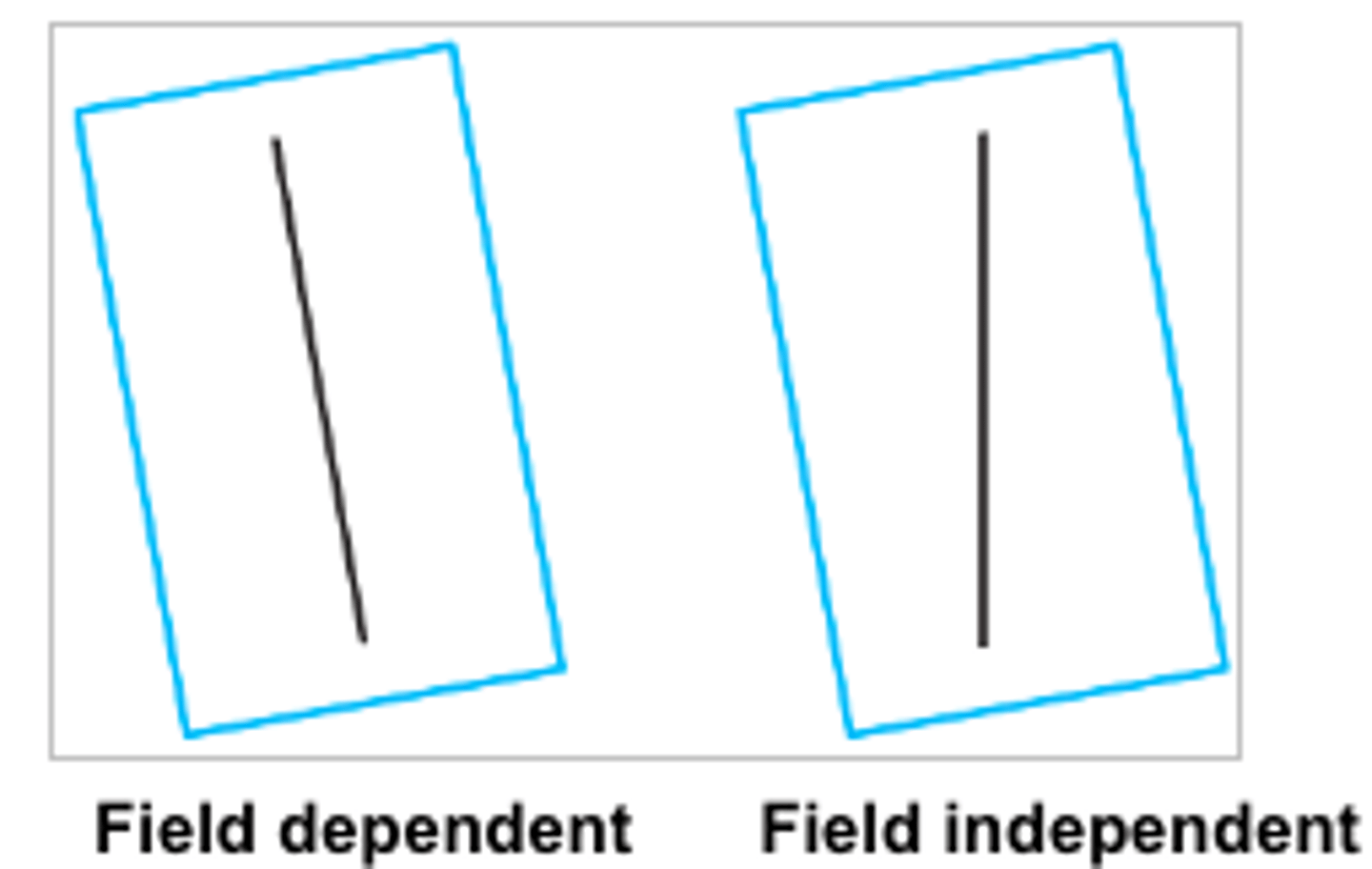
During the rod and frame test, what do collectivistic cultures answer?
field dependent, more affected by context
cultural differences in causal attribution study (how the two culturs attribute responsibility differently)
US: blames individual>organization
Japan: blame organization>individual
What are the cultural differences in emotion seen in individualistic cultures?
more emotionally expressive
What are the cultural differences in emotion seen in collectivistic cultures?
more emotionally restrained
Cultural differences in value of expressing emotions study
greater emotional suppression related to poorer psychological functioning only for european americans but not for hong kong chinese
Knowing that Yuna is from a collectivistic culture, how is she most likely to describe herself?
A. I am creative and independent
B. I am ambitious and strive to stand out in my community
C. I am a supportive sister and a loyal friend
D. I'm an avid reader and love volunteering
C. I am a supportive sister and a loyal friend
Latin America being considered collectivistic, how are they different from east asian emotionally
They achieve interdependence by being emotionally expressive
emotional expression in Latin Culture study result between americans, colombians and japanese
like japan, they are expressing more socially engaging emotions(vs disengaging) than the US. but like US, they are more emotional expressive
Arab culture being considered collectivistic, how are they different from east asian emotionally
They promote interdependence through self-assertion
Assertive Interdependence in Arab study result between european american, japanese, arab
like japan, shows holistic cognition
like Americans, shows self-assertion
Germany being considered independent culture, how are they different from USA emotional experience wise
USA(vs. Germans) reported greater desire to avoid negative emotions