Muscles and Motor Locomotion
Muscle Movement
- Muscles do work by contracting
- Skeletal muscles come in antagonistic pairs
- Flexor vs. extensor
- Contracting = shortening
- Move skeletal parts
- Tendons
- Connect bone to muscle
- Ligaments
- Connect bone to bone
Structure of Striated Skeletal Muscle
- Muscle fiber
- Muscle cell
- Divided into sections = sarcomeres
- Sarcomere
- Functional unit of muscle contraction
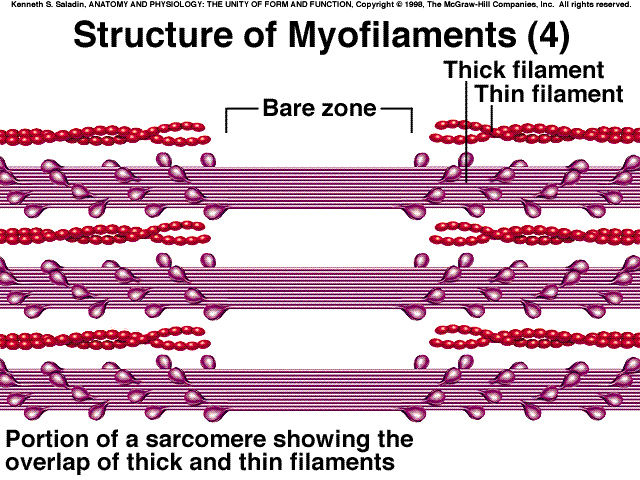
- Alternating bands of thin (actin) and thick (myosin) protein filaments
Actin
- Complex of fibers
- Brain of actin molecules and tropomyosin fibers
- Tropomyosin fibers secured with troponin molecules
Myosin
- Single protein
- Myosin molecule
- Long protein with globular head
Thick and thin filaments
- Myosin tails aligned together and heads pointed away from center of sarcomere
Interaction of Thick and Thin Filaments
- Cross bridges
- Connections formed between myosin heads and actin
- Cause muscle to shorten
Muscle Cell Organelles
- Sarcoplasm
- Muscle cell cytoplasm
- Contains many mitochondria
- Sarcoplasmic reticulum
- Organelle similar to ER
- Network of tubes
- Stores Ca2+
- Ca2+ released from sarcoplasmic reticulum through channels
- Ca2+ restored to sarcoplasmic reticulum by Ca2+ pumps
- Pump Ca2+ from cytosol
- Pumps use ATP
Muscle at Rest
- Interacting proteins
- At rest, troponin molecules hold tropomyosin fibers, so that they cover the myosin-binding sites on actin
- Troponin has Ca2+ binding sites
Motor Neurons
- Motor neuron triggers muscle contraction
- Release acetylcholine (Ach) neurotransmitter
Nerve Trigger of Muscle Action
- Nerve signal travels down T-tubule
- Stimulates sarcoplasmic reticulum of muscle cell to releases stored Ca2+
- Flooding muscle fibers with Ca2+
Ca2+ Triggers Muscle Action
- At rest, tropomyosin blocks myosin-binding sites on actin
- Secured by troponin
- Ca2+ binds to troponin
- Shape change accuses movement of troponin
- Releasing tropomyosin
- Exposes myosin-binding sites on actin
How Ca2+ Controls Muscle
- Sliding filament mode
- Exposed actin binds to myosin
- Fibers slide past each other
- Ratchet system
- Shorten muscle cell
- Muscle contraction
- Muscle doesn’t relax until Ca2+ is pumped back into sarcoplasmic reticulum
- Requires ATP
How It All Works
- Action potential causes Ca2+ release from sarcoplasmic reticulum
- Ca2+ binds to troponin
- Troponin moves tropomyosin, uncovering myosin binding site on actin
- Myosin bonds actin
- Uses ATP to ratchet each time
- Releases and bonds to next actin
- Myosin pulls actin chain along
- Sarcomere shortens
- Z discs move closer together
- Whole fiber shortens
- Contraction
- Ca2+ pumps restore Ca2+ to sarcoplasmic reticulum
Fast Twitch and Slow Twitch Muscles
- Slow twitch muscle fibers
- Contract slowly, but keep going for a long time
- More mitochondria for aerobic respiration
- Less sarcoplasmic reticulum
- Ca2+ remain in cytosol longer
- Long distance runner
- “Dark” meat = more blood vessels
- Fast twitch muscle fibers
- Contract quickly, but get tired rapidly
- Store more glycogen for anaerobic respiration
- Sprinter
- “White” meat
Muscle Limits
- Muscle fatigue
- Lack of sugar
- Lack of ATP to restore Ca2+ gradient
- Low O2
- Lactic acid drops pH which interferes with protein function
- Synaptic fatigue
- Loss of acetylcholine
- Muscle cramps
- Build up of lactic acid
- ATP depletion
- Ion imbalance
- Massaging or stretching increases circulation
Diseases of Muscle Tissue
- ALS
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Lou Gehrig’s disease
- Motor neurons degenerate
- Myasthenia gravis
- Autoimmune
- Antibodies to acetylcholine receptors
Botox
- Bacteria Clostridium botulinum toxin
- Blocks release of acetylcholine
- Botulism can be fatal
Rigor Mortis
- No life, no breathing
- No breathing, no O2
- No O2, no aerobic respiration
- No aerobic respiration, no ATP
- No ATP, no Ca2+ pumps
- Ca2+ stays in muscle cytoplasm
- Muscle fibers continually contract
- Eventually, tissues breakdown and relax
- Measure of time of death