Soil Mechanics Exam 2
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Sieve Analysis Definition
Determines particle size and distribution by separation of grains on graded series of wire screens.
Hydrometer Analysis
Principles of sedimentation to measure size distribution of silt and clay
What are the four states in the Atterburg Limits?
Solid, Semi-solid, plastic, liquid
What are the three limits between the states and where are they?
Between Liquid and Plastic is Liquid Limit, Between plastic and Semi-solid is plastic limit, between semi-solid and solid is shrink limit.
Description of Plastic Limit test
Water content at which soil begins to crumble when rolled in a thread 1/8 inch diameter
For the Liquid Limit Test (w% vs # of blows) when does LL occur?
At # of blows equals 25
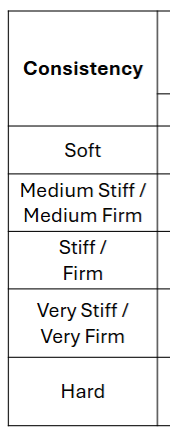
Practice the Consistency and Feel or Touch table
Here are answers
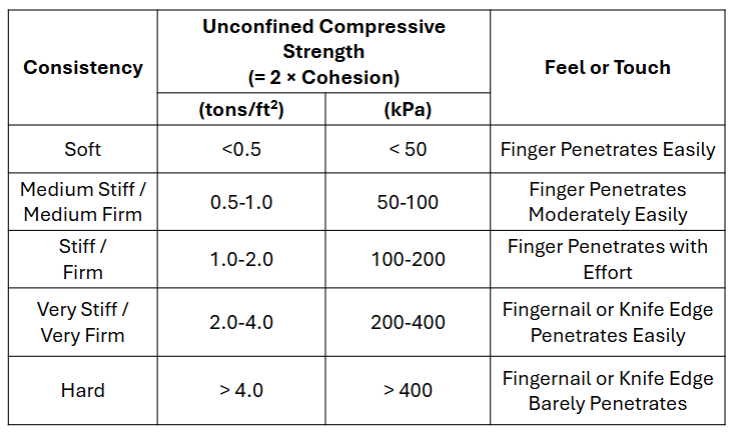

Practice Shape and Age Table
Here are answers.
Give the LL, PL, and SL for the following soil types
Answers
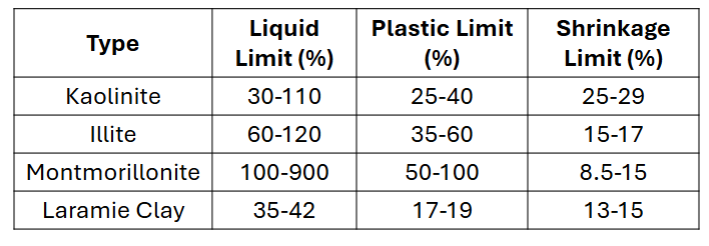
In the USCS, what are the two descriptions given?
Soil Type and Soil Modifier
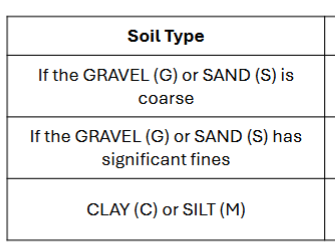
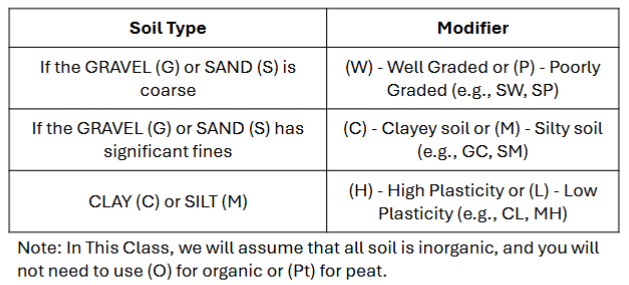
Given soil types, give possible modifiers.
Should be able to give soil types if given modifiers.
What are the actual sieve openings (mm) for Sieve #’s 4, 10, 40, and 200
4.75 mm, 2.00 mm, 0.425 mm, 0.075 mm
What does the AASHTO classification system classify soils on?
It is based of the suitability of soils as subgrade materials for road constructions.
Until what classification is GI = 0? When else is GI = 0?
A-2-5, and when soils are non-plastic, the LL cannot be found, and when the GI is calculated as a negative.
What portion of the GI equation is used for soils class A-2-6 and A-2-7?
The PI portion, the portion right of the “+” sign
What does it mean when the soil has a high GI value?
The higher the GI value, the lower the quality of the soil as a subgrade material
How can you tell is a soil will be A-7-5 or A-5-6?
If PI <= (LL-30) it is an A-7-5, else it is A-7-6
In what fashion should you run through the AASHTO classification test?
Left-to-Right
Definition of Total Stress?
The external stresses developed by the solids and, if present, water in the soil.
How to calculate effective stress?
Effective stress = Total Stress - Water Pressure
What is the phreatic surface?
The start of the ground water table, it is considered a new layer
Why can’t we multiply Ko and Vertical stress to find horizontal stress?
Water has no shear strength and cannot provide shear reduction while it does add to the total stress.
If a soil is dry/damp/moist what is the water pressure considered?
Zero
Definition of Liquefaction?
High pore water pressure reduces effective stress
How does higher pore water pressure reduce effective stress?
Since Total stress does not change and water pressure increases, effective stress needs to decrease to satisfy the unchanging total Stress
What is the process of findint the stresses in a soil system?
Vertical total stress, water pressure, vertical effective stress, horizontal effective stress, horizontal total stress
In a stress profile, what would cause a horizontal shift in horizontal stresses?
A new soil layer leading to a new Ko shifting horizontal stress values
What are the two factors that can effect vertical effective stress?
Changes in water pressure and changes in total stress
What is an example of an added load to soils?
Building a wall
Was is an example of removing a load on a soil?
Excavation
What are the four loading conditions?
Uniform surface pressure, point load on surface, distributed strip pressure, and distributed finite surface pressure (circle, square, and rectangle)
For uniform surface pressure, what is the change in total vertical stress equal to?
The load applied (q)
What are the assumptions in Boussinesq’s Equation?
Homogenous, isotropic, linear, elastic, and semi-infinite mass (bounded on one side)
What loads are considered finite?
Point load, circle load, and rectangular load
What loads are considered infinite loads?
Line load and strip loads
What are the following variables? Z, B, x, and R
Z is the depth to the POI, the x is the horizontal distance to the POI, B is the base length of the load, and R is the radius of a circular load, and B = 2R (diameter)