Unit 2B Intelligence
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
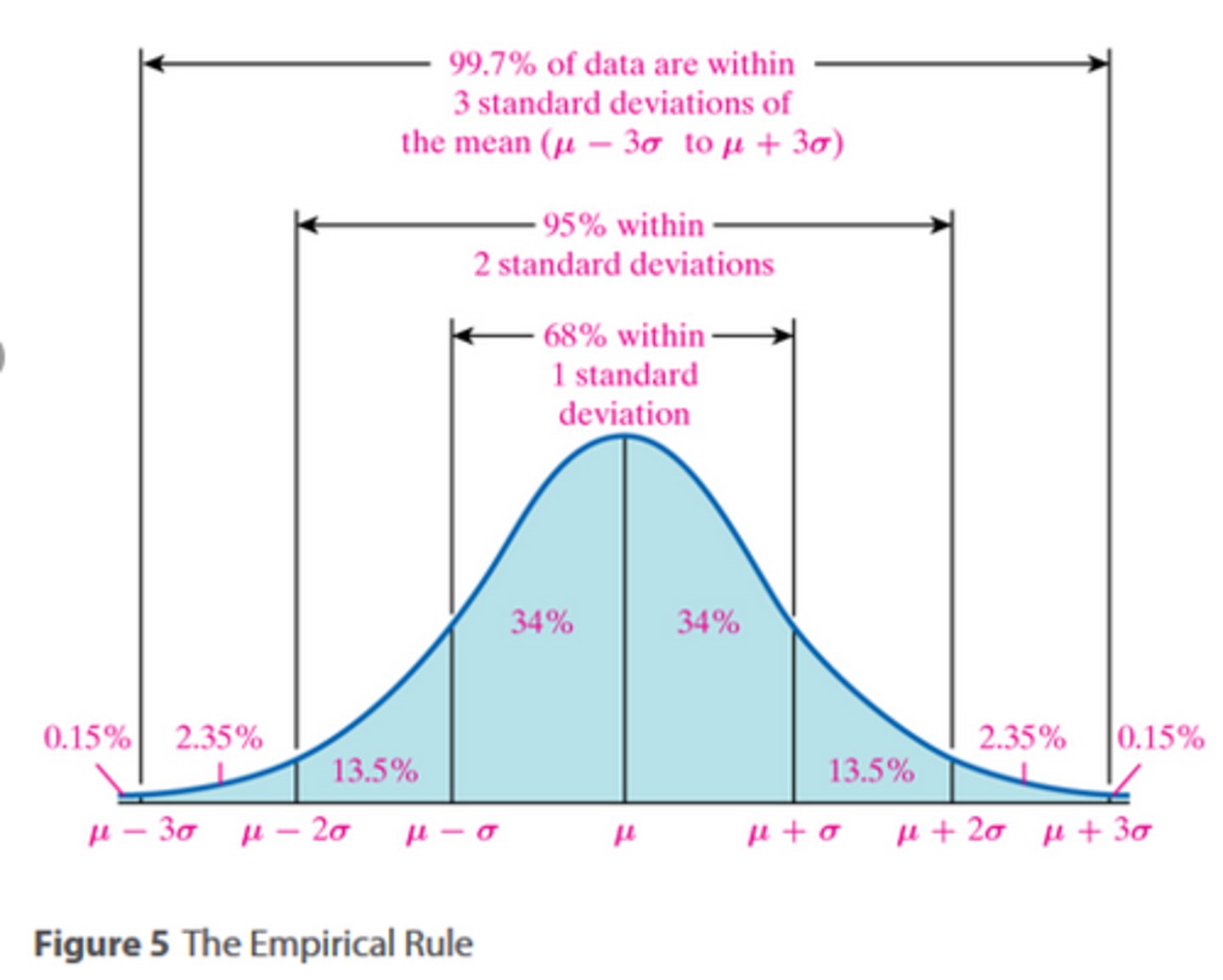
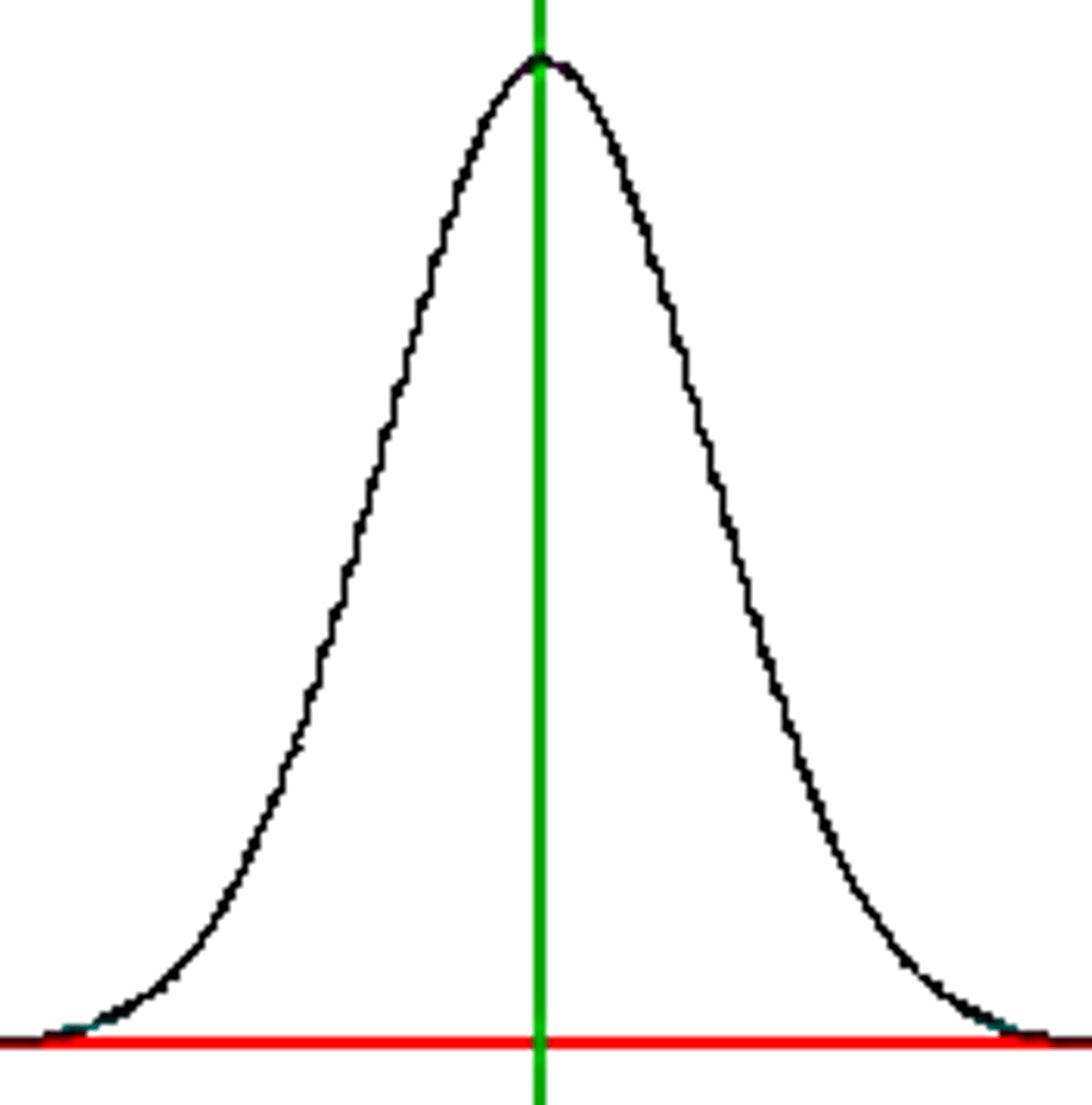
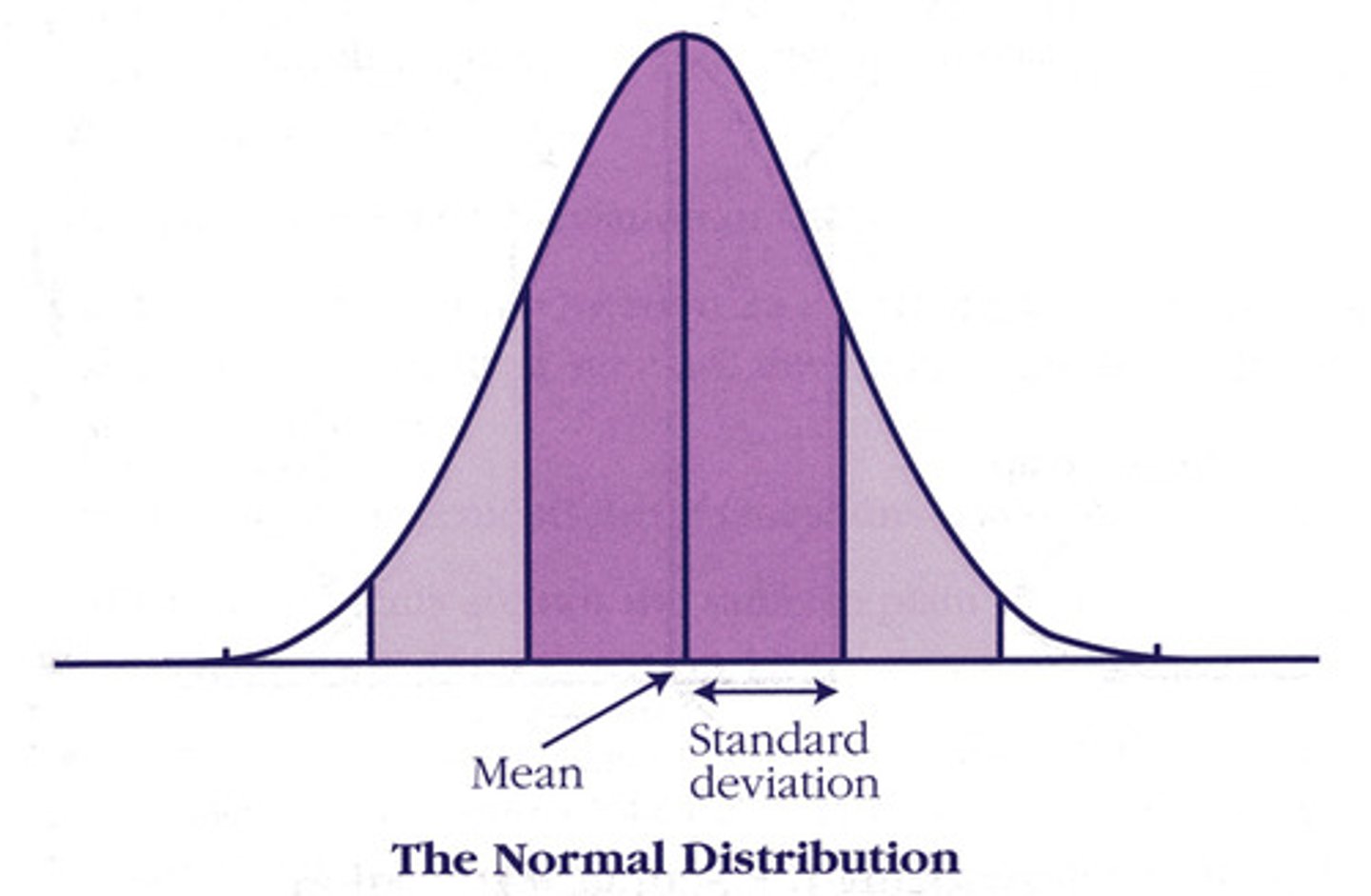
+1/-1 standard deviation
68% of scores on standard bell curve
+2/-2 standard deviations
95% of scores on standard bell curve
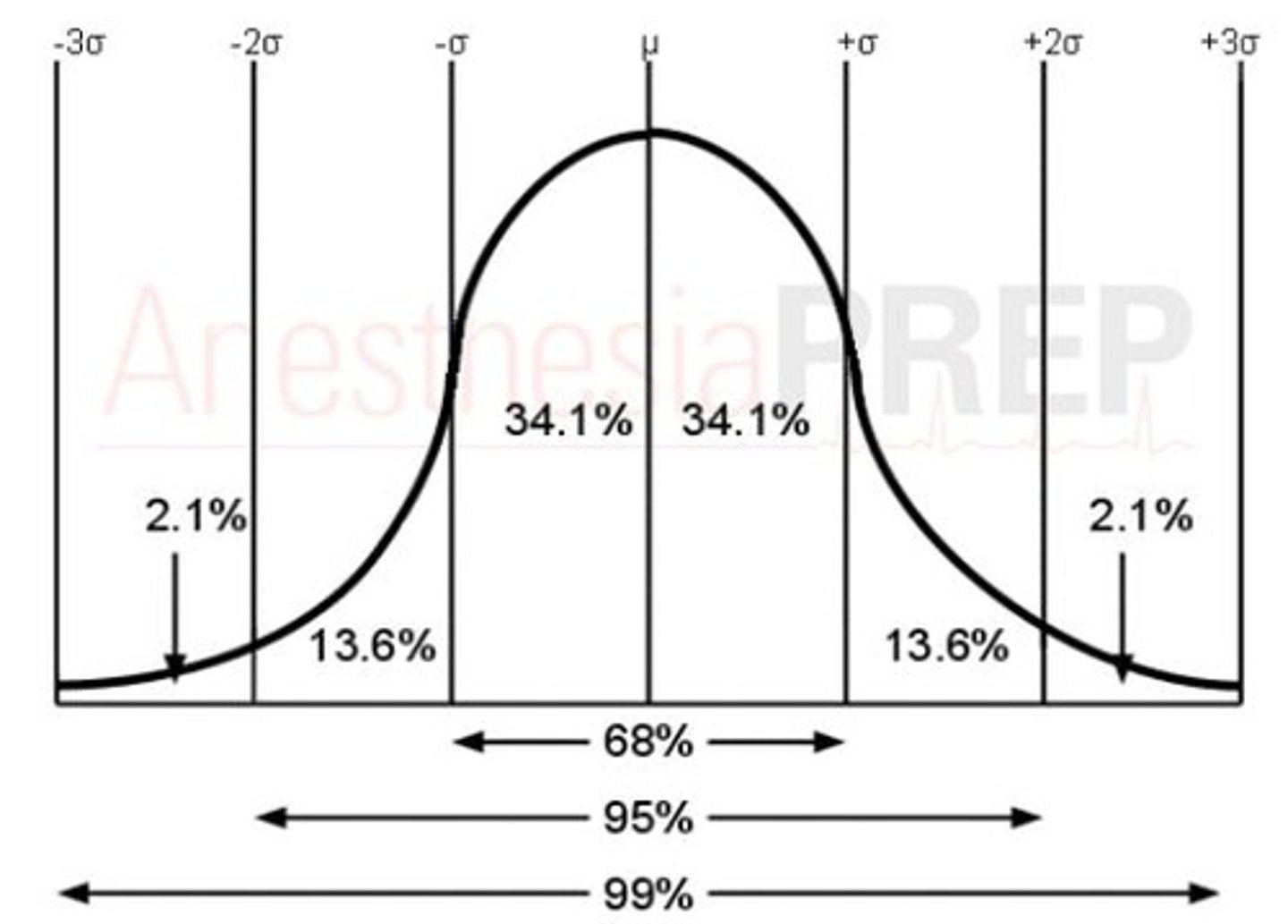
+3/-3 standard deviations
99% of scores on standard bell curve
Achievement Test
Measures PAST ACQUIRED knowledge

Adopted Children
Larger intellectual correlation to their biological parents than adopted parents

Alfred Binet
Developed questions that would predict children's future progress in the Paris school system (was looking to identify students that needed help). Additionally, developed the concept of mental age

Aptitude Test
PREDICTS FUTURE performance

Aptitude tests ARE biased
in the sense that they are sensitive to performance differences caused by cultural differences
Aptitude tests ARE NOT biased
in the sense that they accurately predict performance of one group over the other

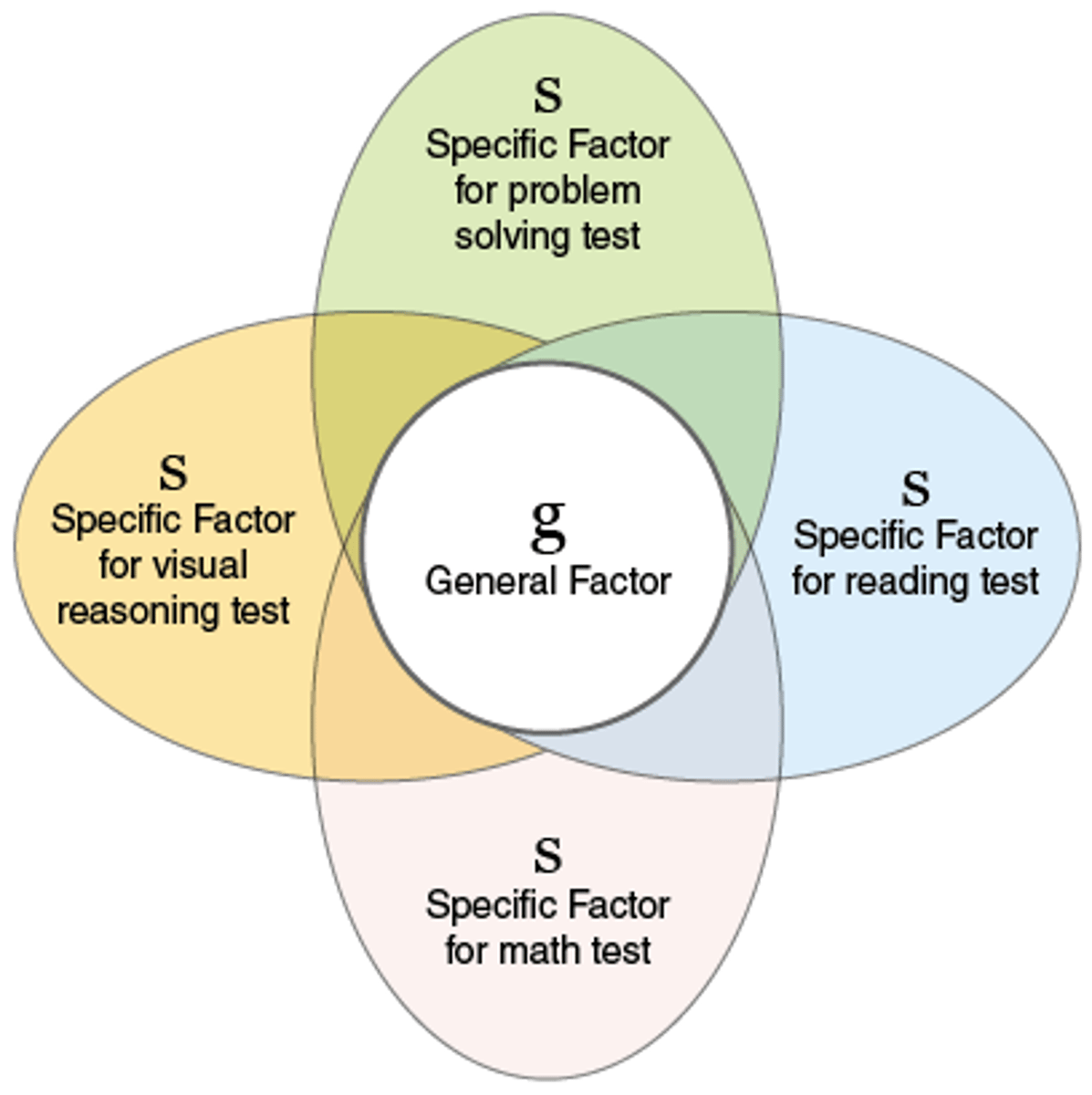
Charles Spearman
"g-factor." Intelligence is an "overall" quality, a generalized ability

Content Validity
Refers to the extent a test measures a particular behavior or trait. (i.e., Driving exam should NOT contain psychology questions)
Creativity
Ability to invent new solutions to problems or to create original/ingenious materials.

Crystallized Intelligence (Gc)
Accumulated knowledge, skills, strategies that have been learned through experience; tends to increase throughout life

David Wechsler
Developed most modern and used test, WAIS & WISC.

Eugenics
the science of improving a human population by controlled breeding to increase the occurrence of desirable heritable characteristics

Factor-Analysis
A statistical procedure that identifies clusters of related items on a test.
Fluid Intelligence (Gf)
Information-processing capabilities, reasoning and memory; tend to decline with age.

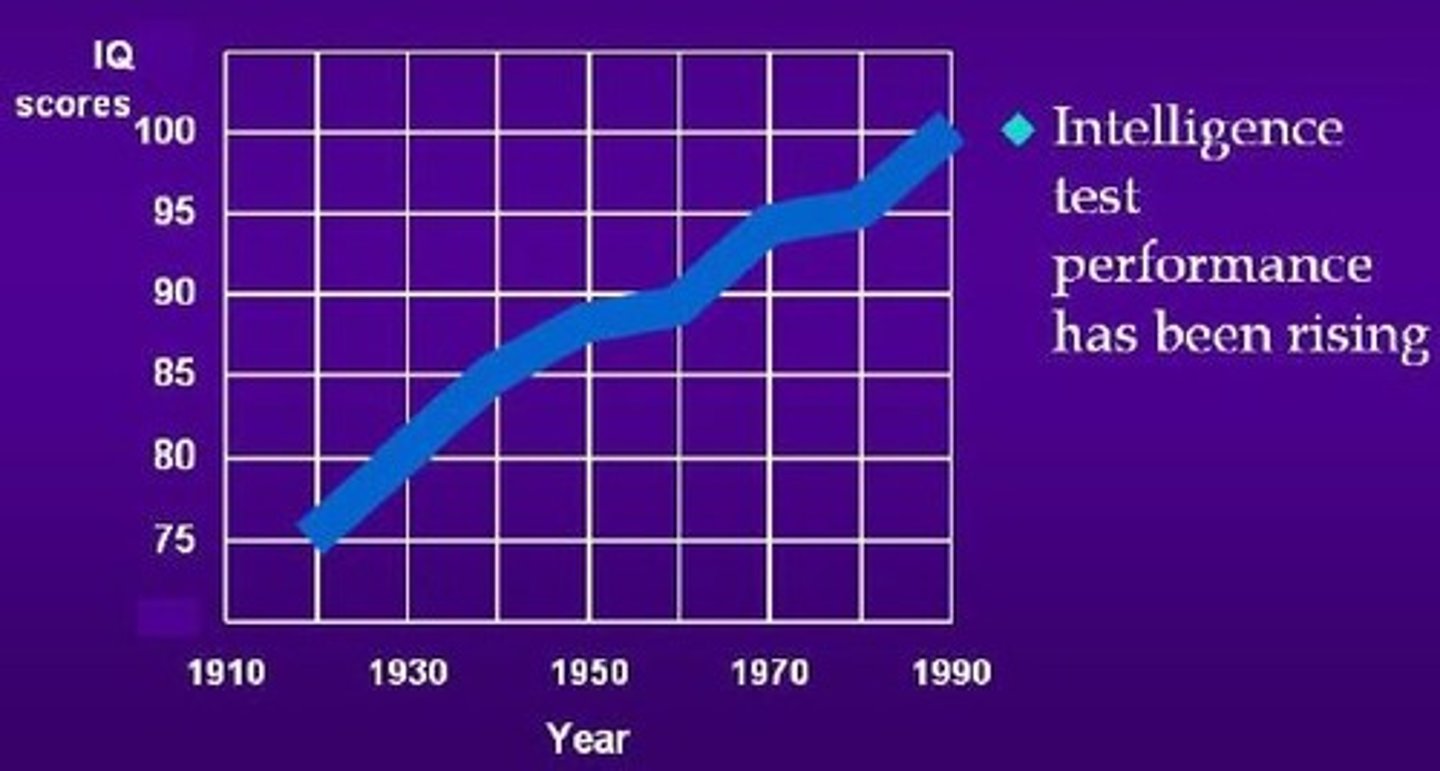
Flynn Effect
Substantial increase in average scores on intelligence tests all over the world. Increase could be due to improved childhood health, nutrition, and educational opportunities.
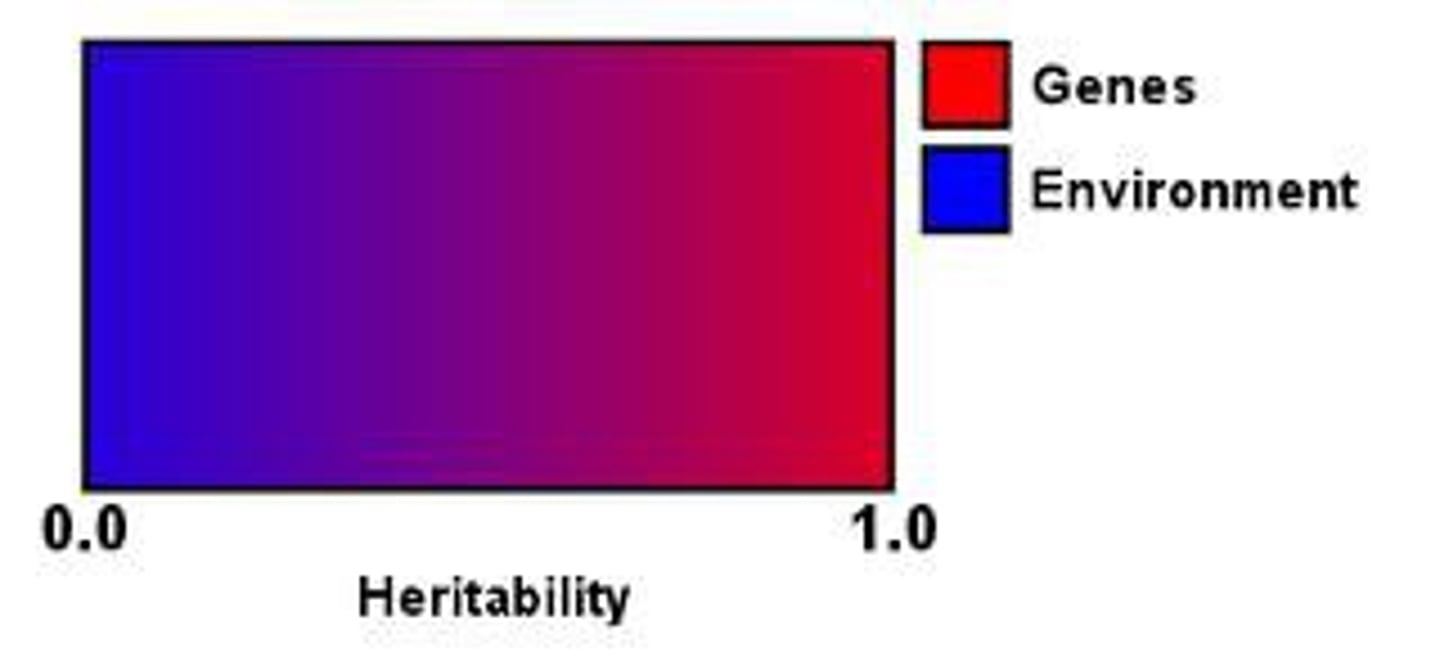
Heritability
The proportion of variation among individuals that we can attribute to genes.
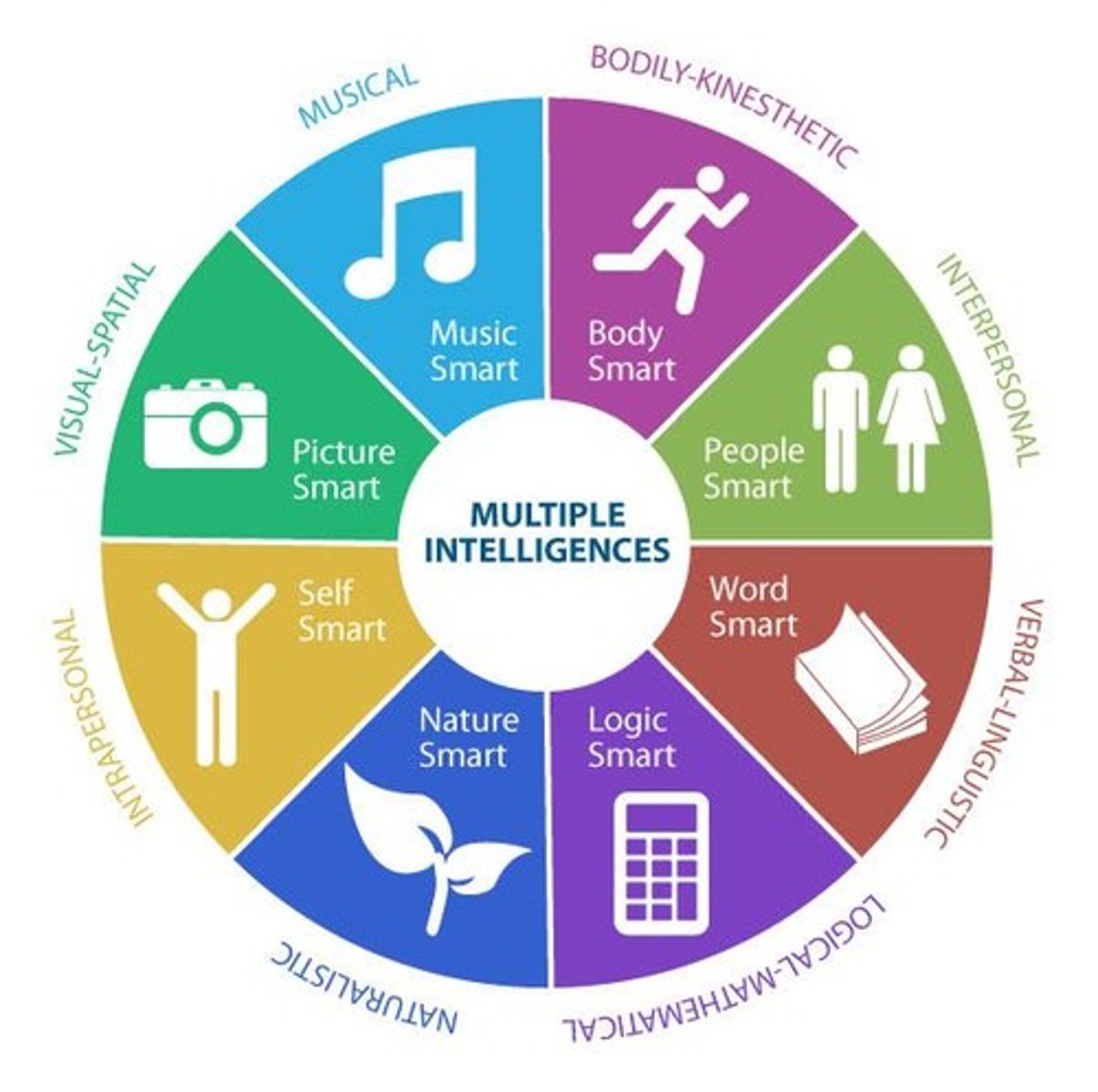
Howard Gardner
Proposed Multiple Intelligence Theory. Someone can be musically smart, but not academically. (Lazy llama makes big, silly ice-cream in nature)

L.L. Thurstone
Critic of Spearman, believed the there are 7 Primary Mental Abilities. Intelligence is not one thing; you cannot be good at everything.

Lewis Terman
Stanford University Professor who adapted Binet's test for American schoolchildren, test was named after his school and the person who preceded him (Stanford-Binet Test).

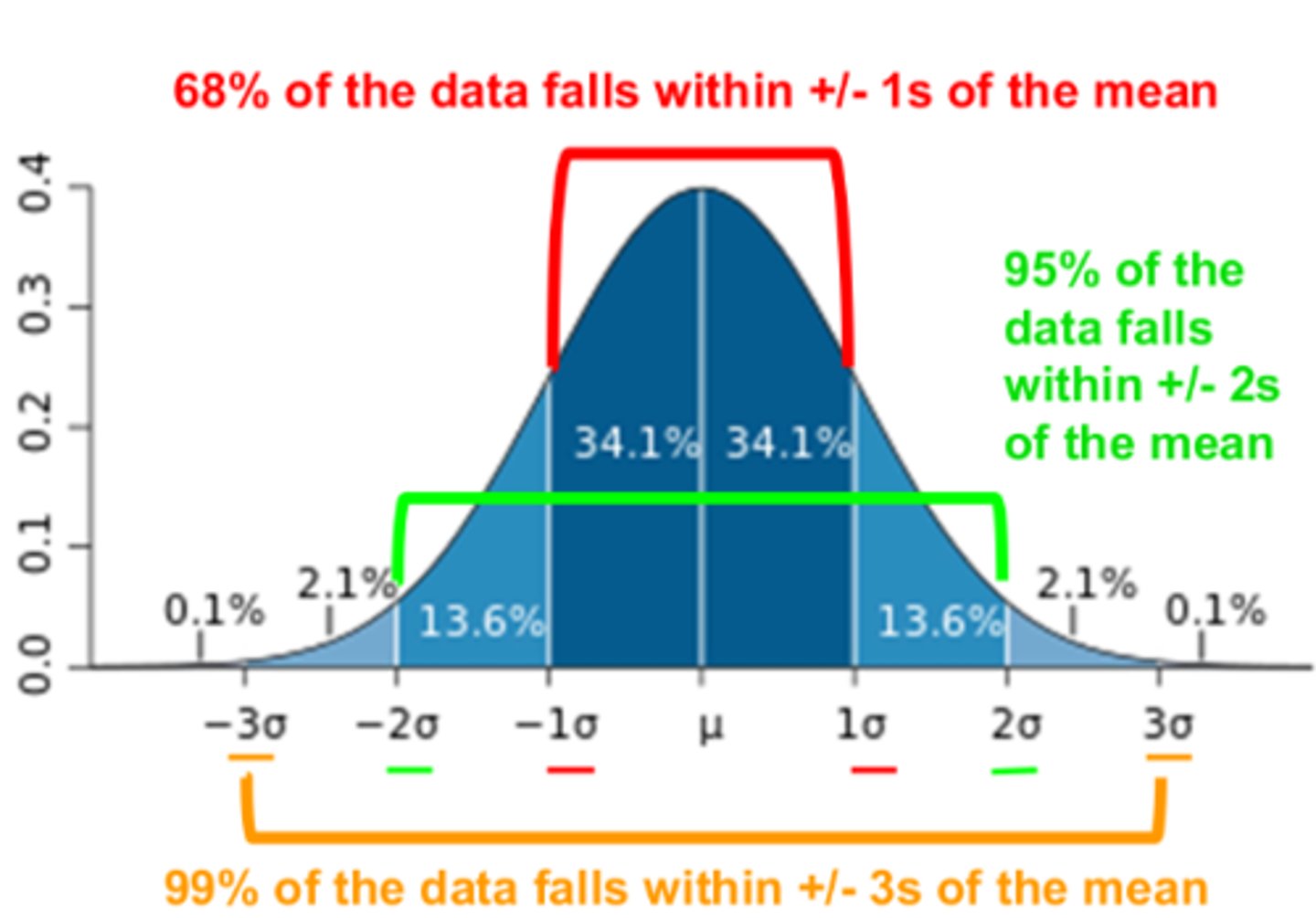
Normal Curve
Standardized tests establish a normal distribution of scores on a tested population in a bell-shaped pattern.
Predictive Validity
Refers to the function of a test in predicting a particular behavior or trait. (i.e., Driving exam predicts good driving habits.) Does the test accurately predicts what it claims to measure?
Principles of Test Construction
Standardization, Reliability, Validity
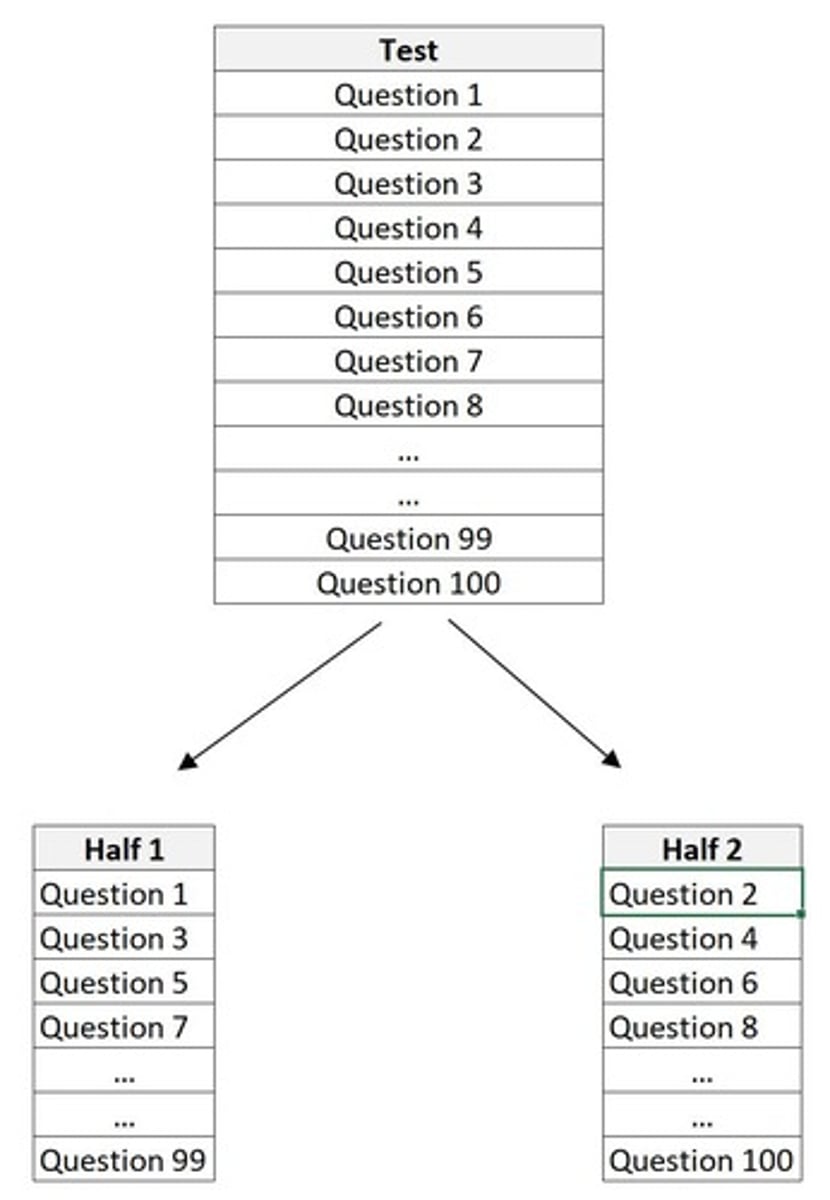
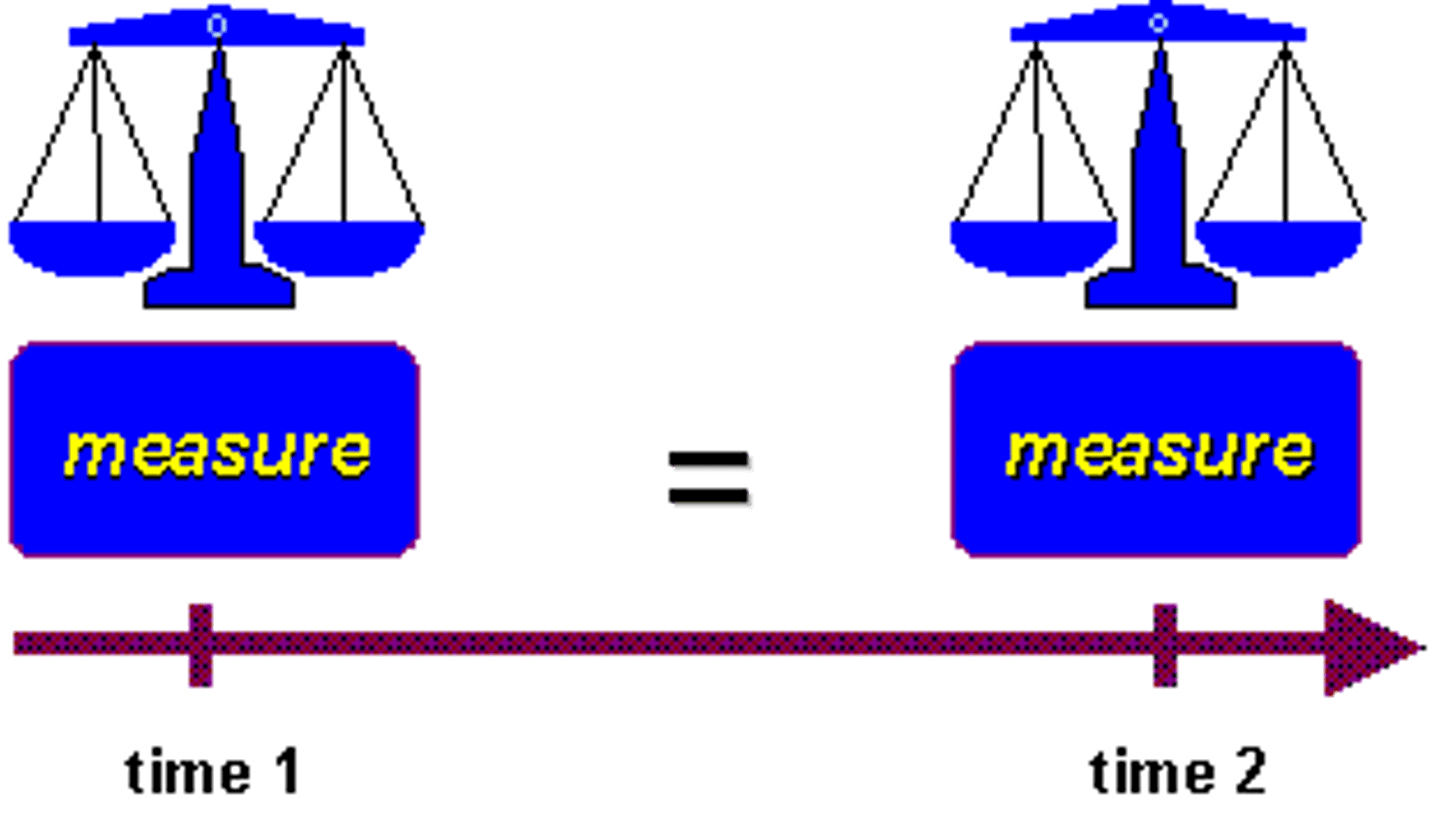
Reliability
Consistency of scores. Types: Test-retest between group/scorer and split-half.

Robert Sternberg
Triarchic Component of Intelligence. Student could be stronger in one category than others. Intelligence in three categories. Creative, Analytical, Practical.

Savant Syndrome
a condition in which a person otherwise limited in mental abilities has an exceptional specific skill, such as computation or drawing. Supports Gardner's Multiple Intelligence Theory, disproves Spearman's General Intelligence Theory

Split-Half Reliability
A measure of reliability in which a test is split into two parts and an individual's scores on both halves are compared.
Standard Deviation
How various percentages of scores FALL AWAY from the average (mean).
Standardization
defining meaningful scores by comparison with the performance of a pretested group
Stanford-Binet Test
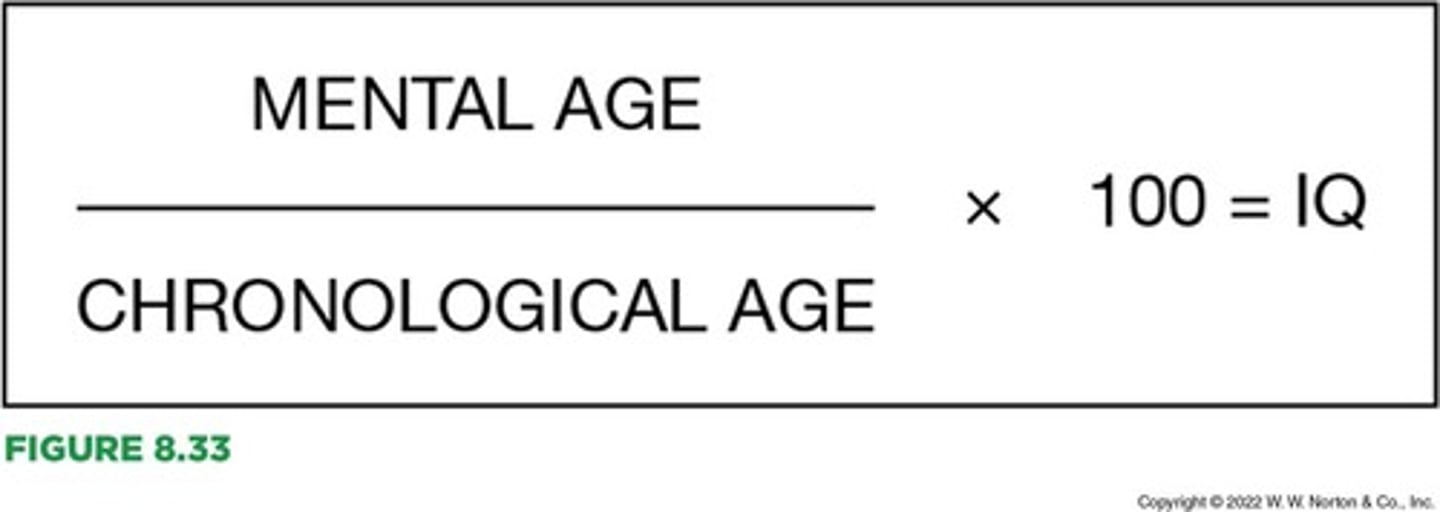
Originally developed by Lewis Terman. Converted mental age to IQ using Stern's formula. (MA/CA X 100= IQ) 70= feeble-minded. Above 150= genius.
Stereotype Threat
a self-confirming concern that one will be evaluated based on a negative stereotype

Test-Retest Reliability
a method for determining the reliability of a test by comparing a test taker's scores on the same test taken on separate occasions
Validity
Whether the test truly measures what it claims to measure.
Carol Dweck
Stated that believing intelligence being biologically set and unchanging can lead to a "fixed mindset." However, believing intelligence is changeable, a "growth mindset" results in a focus on learning and growing.

Francis Galton
Measured "natural ability" and encouraged those of high ability to mate with one another. Supported eugenics. Darwin's cousin.

Cohort
A group of individuals of the same age.

IQ (intelligence quotient)
quantitative measure, typically with a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 15, used to indicate a child's intelligence relative to that of other children of the same age
Mental Age
the age-level at which a person function mentally or intellectually
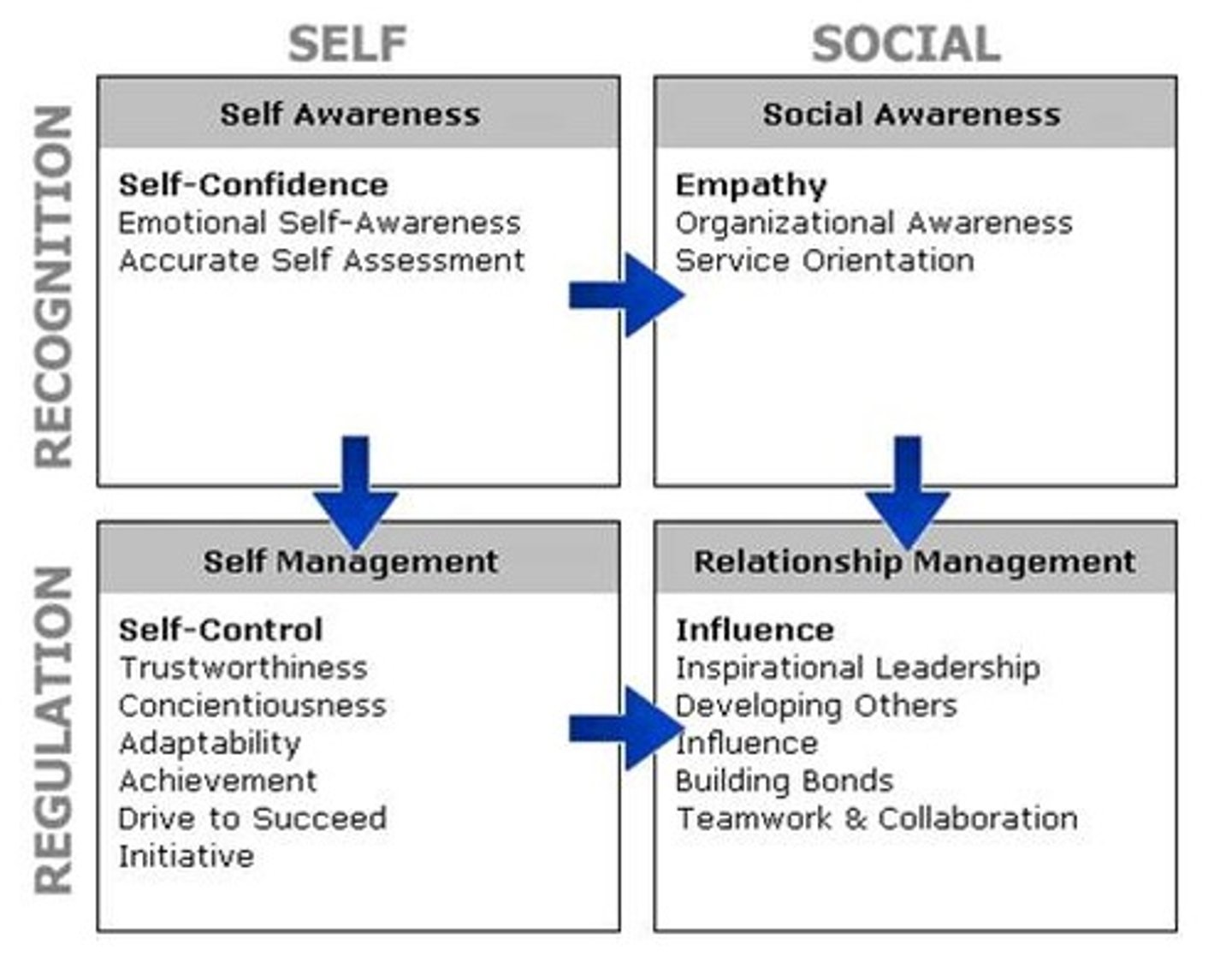
Emotional Intelligence
the ability to perceive, understand, manage, and use emotions. (PUMU) Gardner's interpersonal & intrapersonal intelligence.
Grit
in psychology, grit is passion and perseverance in the pursuit of long-term goals.

Intelligence
mental quality consisting of the ability to learn from experience, solve problems, and use knowledge to adapt to new situations.

General Intelligence (g)
(g) a general intelligence factor that, according to Spearman and others, underlies specific mental abilities and is therefore measured by every task on an intelligence test.
Gardner's multiple intelligences
Linguistic intelligence ("word smart"), Logical-mathematical intelligence ("number/reasoning smart"), Spatial intelligence ("picture smart"), Bodily-Kinesthetic intelligence ("body smart"), Musical intelligence ("music smart"), Interpersonal intelligence ("people smart"), Intrapersonal intelligence ("self smart")