AP Bio Ch 4
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
direct contact
communications through cell junctions, passing freely through adjacent cells (gap junctions, plasmodesmata)
local regulators
secreting cells releasing chemical messages (ligands/local regulators) that travel a short distance through extracellular fluid and cause a response in a target cell
paracrine signaling
secretory cells release local regulators (ie growth factors) via exocytosis to an adjacent cell
synaptic signaling
neurons secreting neurotransmitters that diffuse across the synaptic cleft (aka the space between the nerve cell and target cell)
long distance signaling
hormones, endocrine signaling through circulatory system
cell signaling steps
reception (ligand binds to receptor), transduction (signal is converted), response (cell process is altered)
reception
detection and receiving of ligand by target cell
one area of receptor interacts with ligand and one area transmits a signal to another protein, highly specific bonding
plasma membrane receptors
most common receptor in signal pathways, binds to polar large water soluble ligands (ex: peptide hormones, GPCRs)
intracellular receptors
found in the cytoplasm or nucleus of target cell, binds to hydrophobic ligands passed through plasma membrane (ex: steroid and thyroid hormones)
transduction
conversion of an extracellular signal to an intracellular signal that will bring about a cellular response, requires changes in the signal transduction pathway
phosphorylation
adding phosphate via ATP or enzyme protein kinase to relay signal inside cell (part of transduction)
dephosphorylation
removing phosphate by enzyme protein phosphatase, shuts off pathways (part of transduction)
second messengers
small, nonprotein molecules and ions inside the cell that help relay the message and amplify the response during transduction
response
final molecule in signaling pathway converts the signal to a response that will alter a cellular process (ex: proteins or enzymes)
G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs)
largest category of cell surface receptors, important for animals’ sensory systems, binds to a G protein that can bind to GTP (molecule similar to ATP), inactive until ligand binds to it
ligand binding changes cytoplasmic side’s shape
activates/binds to enzyme, amplifying signals
ion channels
receptors in plasma membrane that open or close for diffusion of specific ions to start off cellular response events
negative feedback loop
reduces the effect of the stimulus (ex: heat —> skin receptors —> sweat glands —> sweat), stops when problem is solved
positive feedback loop
increases the effect of a stimulus (ex: blood clotting, fruit ripening), stops when problem is solved
centromere
region on each sister chromatid where they are most closely attached
kinetochore
proteins attached to the centromere that link each sister chromatid to the mitotic spindle
chromatin
formed by strings of nucleosomes. in a non-condensed form when not dividing, but condenses into a chromosome after DNA replication
homologous chromosomes
one chromosome from each parent that are the same length, have the same centromere position, and carry genes controlling the same characteristics
somatic cells
diploid (2n): 2 sets of chromosomes, one set from each parent, divides by mitosis, humans have 46 total (23 from each parent)
gametes
reproductive cells, haploid (n): one set of chromosomes, divides by meiosis, humans have 23
interphase
longest portion of cell cycle
G1 (first gap) phase
cell grows, carries out normal function
S (synthesis) phase
DNA replication, chromosome duplication occurs
G2 (second gap) phase
final growth and preparation for mitosis
mitosis
division of nucleus, results in 2 identical diploid daughter cells
cytokinesis
cytoplasm divides
prophase
chromatin condenses, nucleoli disappear, duplicated chromosomes appear as sister chromatids, mitotic spindle forms, centromeres move away from each other
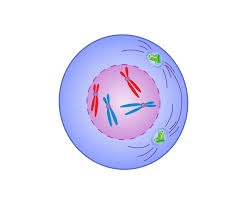
prometaphase
nuclear envelope fragments, microtubules enter nuclear area and some attach to kinetochores
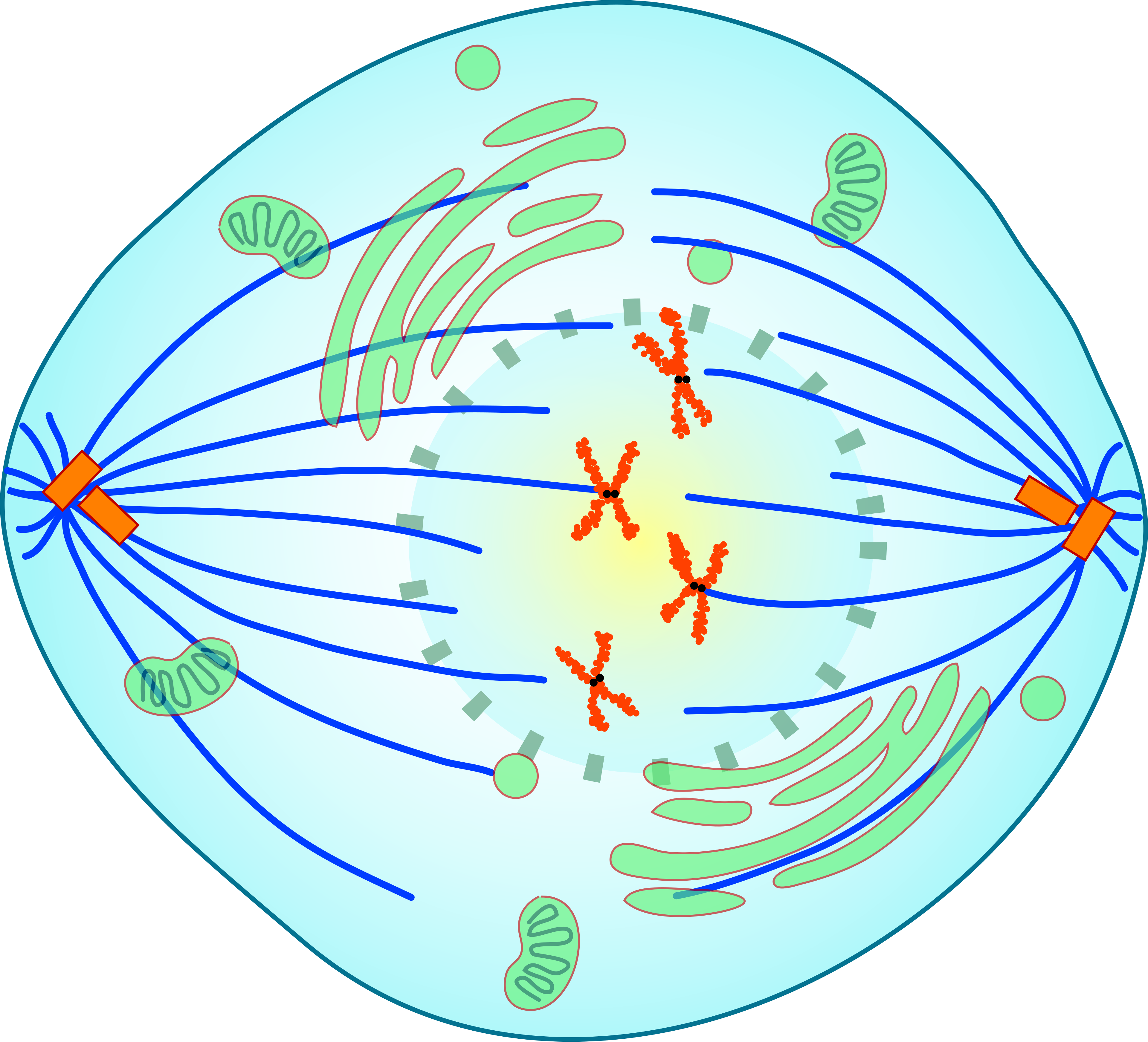
metaphase
centrosomes are at opposite poles, chromosomes line up at metaphase plate, microtubules are attached to each kinetochore
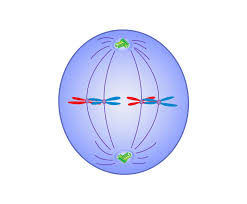
anaphase
sister chromatids separate and move to opposite ends of the cell due to microtubule shortening, cell elongates
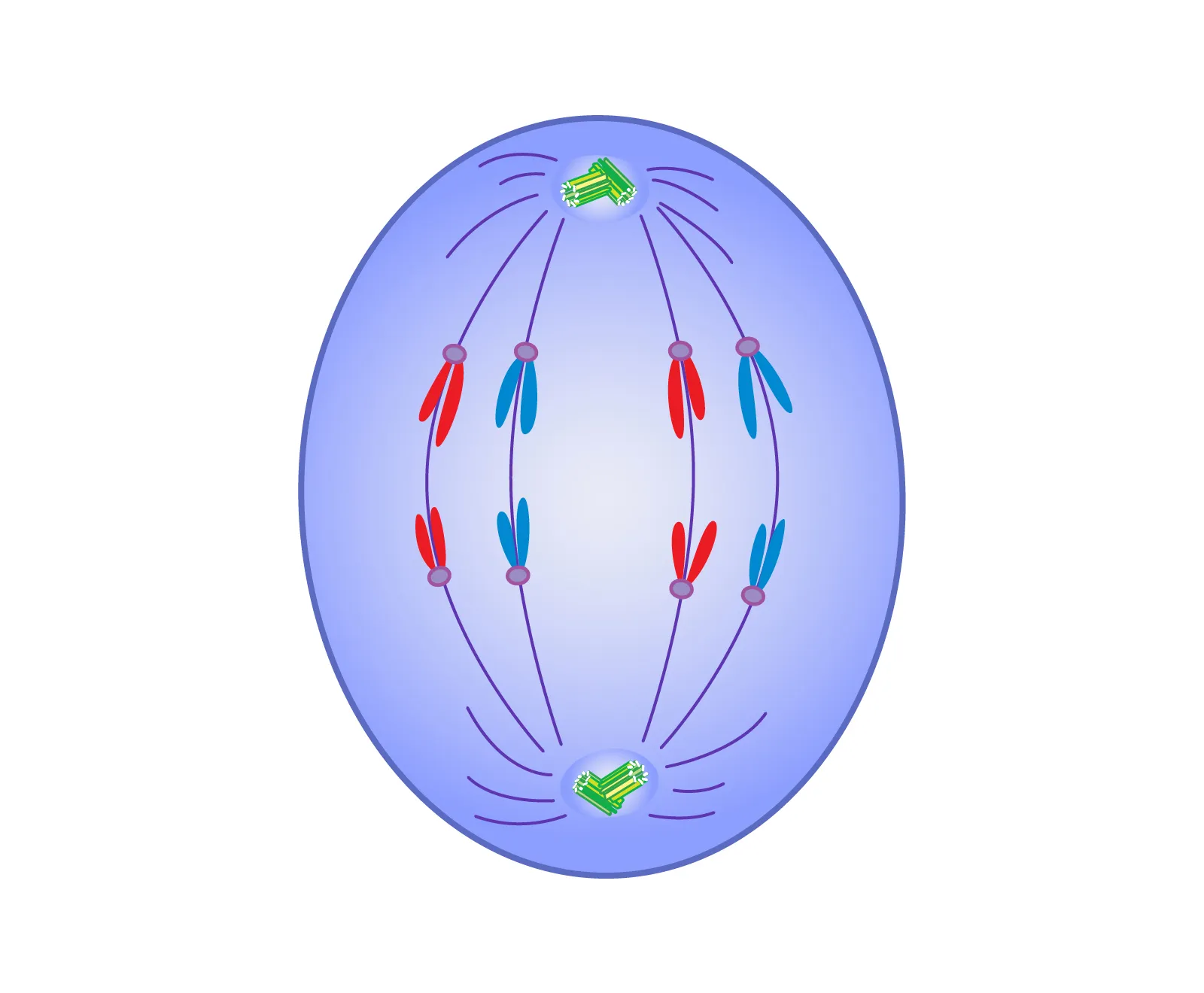
telophase
2 daughter nuclei form, nucleoli reappear, chromosomes decondense
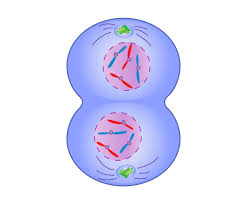
cytokinesis
cleavage furrow appears due to a contractile ring of actin filament in animals, and vesicles produced by the Golgi travel to the middle of the cell and form a cell plate in plants
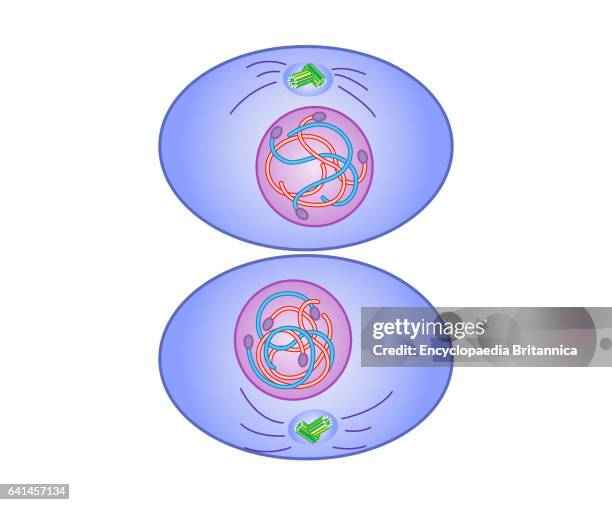
G1 checkpoint
most important, checks for cell size, growth factors, and DNA damage, gives go/stop signal
G2 checkpoint
checks for completion of DNA replication and DNA damage
apoptosis
programmed cell death
M (spindle) checkpoint
checks for microtubule attachment to chromosomes at the kinetochores at metaphase
cyclins
regulatory proteins that control the cell cycle by binding to and activating cyclin-dependent kinases
cyclin-dependent kinases
enzymes that are only active when its specific cyclin is present, constant concentration throughout cell cycle
growth factors
hormones released by cells that stimulate cell growth, initiates signal transduction pathway
contact (or density) inhibition
cell surface receptors recognize contact with other cells, initiates signal transduction pathway that stops the cell cycle in G1 phase
anchorage dependence
cells rely on attachment to other cells or the extracellular matrix to divide
cancer cells
don’t follow checkpoints, divide infinitely, evade apoptosis and continue dividing with cell errors