IB Biology Topic 5: Evolution / Biodiversity
5.0(2)Studied by 26 people
Card Sorting
1/104
Earn XP
Last updated 5:51 PM on 4/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
1
New cards
Evolutionary theory by Charles Darwin
All species are descended from ancestral species
Mechanism that drives changes in species is natural selection
Mechanism that drives changes in species is natural selection
2
New cards
Common ancestry
Sharing a common ancestor (jack rabbit and snowshoe hare)
3
New cards
Natural selection drives evolution due to:
Struggle for existence: tendency of species to overproduce results in direct competition between members of species
Natural variation: differences among members of same species
Role of environment: selects individuals with traits best-suited for environment
Natural variation: differences among members of same species
Role of environment: selects individuals with traits best-suited for environment
4
New cards
Darwin vs Lamarck
Darwin says heritable traits drive evolution, Lamarck says acquired traits drive evolution (traits inherited throughout lifetime rather than genetically)
5
New cards
Evidence (3) for evolutionary theory
1. fossil record
2. geographic distribution
3. comparative anatomy
6
New cards
Fossil record
Fossils are chronological; however deep they are in the Earth is a rough estimate of how long they've been there.
7
New cards
2 forms of geographic distribution
Closely related but different: Descendants of single ancestral species pass on adaptations best suited to that habitat
Distantly related but similar: descendants of different species living in similar habitats share similar adaptations
Distantly related but similar: descendants of different species living in similar habitats share similar adaptations
8
New cards
Structures (3) in comparative anatomy
Homologous structures: similar structures in species with common ancestor
Vestigial structures: important to ancestral species but no clear function in modern descendants (wisdom teeth, appendix)
Analogous structures: anatomically different structures with same function (insects, birds, bats all have wings)
Vestigial structures: important to ancestral species but no clear function in modern descendants (wisdom teeth, appendix)
Analogous structures: anatomically different structures with same function (insects, birds, bats all have wings)
9
New cards
Microevolution
\- Changing of allele frequencies within a population
10
New cards
Hardy-Weinberg Principle
\- Allele and genotype frequencies will remain constant from gen to gen in the absence of other evolutionary influences
o No environmental differences, no reason to change so stays constant
o No environmental differences, no reason to change so stays constant
11
New cards
Conditions of Hardy-Weinberg
\- Large population
\- Random mating (no sexual selection)
\- No mutations
\- No migration between populations
\- All genotypes reproduce with equal success to be passed on (no selection)
Reality: Populations don’t follow these rules so microevolution occurs
\- Random mating (no sexual selection)
\- No mutations
\- No migration between populations
\- All genotypes reproduce with equal success to be passed on (no selection)
Reality: Populations don’t follow these rules so microevolution occurs
12
New cards
Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
\- Monohybrid cross (Aa x Aa) create 1:2:1 genotype frequency
o 25% homozygous dominant, 50% heterozygous, 25% homozygous recessive
o 25% homozygous dominant, 50% heterozygous, 25% homozygous recessive
13
New cards
Sexual selection
\- Form of natural selection where certain traits are favoured
14
New cards
Artificial selection
\- Human controlled, selects desired traits to breed
\- Drives microevolution quicker while reducing genetic variation
\- Unfavourable traits also passed on with favourable due to multiple alleles on chromosomes
\- Drives microevolution quicker while reducing genetic variation
\- Unfavourable traits also passed on with favourable due to multiple alleles on chromosomes
15
New cards
Gene flow
genes exchanged between populations, occurs when individuals migrate
16
New cards
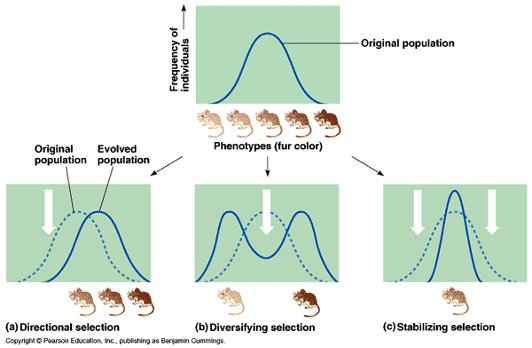
Natural selection
\- Selective pressures within environment affecting frequencies of traits
o Directional selection: favours one end of phenotypes
o Diversifying/disruptive selection: favours extreme ends of phenotypes
o Stabilizing selection: favours middle phenotypes
o Directional selection: favours one end of phenotypes
o Diversifying/disruptive selection: favours extreme ends of phenotypes
o Stabilizing selection: favours middle phenotypes
17
New cards
Genetic drift
\- Bottleneck effect: reduces size of gene size immensely due to natural disaster
o Reduces genetic variation, some alleles present more frequently
\- Founder effect
o Colonization of habitat impacts gene pool, increases founder genes
o Reduces genetic variation, some alleles present more frequently
\- Founder effect
o Colonization of habitat impacts gene pool, increases founder genes
18
New cards
Macroevolution
Biological change on large scale
* speciation/extinction
* speciation/extinction
19
New cards
Speciation requirements
Offspring is viable and fertile
20
New cards
Reproductive isolation
\- Formation of new species where members of parent species are unable to continue reproducing due to physical or behavioural barrier
\- Over time, members of the new species will not mate with parent species (behavioural barrier)
\- Change in geology separate different populations (canyons, colonization)
\- Over time, members of the new species will not mate with parent species (behavioural barrier)
\- Change in geology separate different populations (canyons, colonization)
21
New cards
Barriers for reproduction (6)
\- Hybrid infertility – offspring viable not fertile (mule)
\- Hybrid inviability – nonviable offspring
\- Mechanical isolation – physical incapable (brodyboena snails have different shell spirals)
\- Behavioural isolation – different courtship (birds)
\- Temporal – different breeding season
\- Habitat isolation - Same geographic location, species live in different habitats (bottom vs top of lake)
\- Hybrid inviability – nonviable offspring
\- Mechanical isolation – physical incapable (brodyboena snails have different shell spirals)
\- Behavioural isolation – different courtship (birds)
\- Temporal – different breeding season
\- Habitat isolation - Same geographic location, species live in different habitats (bottom vs top of lake)
22
New cards
Divergent vs convergent evolution
Divergent – different species evolve from common ancestor due to habitat differences (snowshoe hair vs jackrabbit)
Convergent – distantly-related species living in similar habitats develop similar adaptations (analogous structures like wings)
Convergent – distantly-related species living in similar habitats develop similar adaptations (analogous structures like wings)
23
New cards
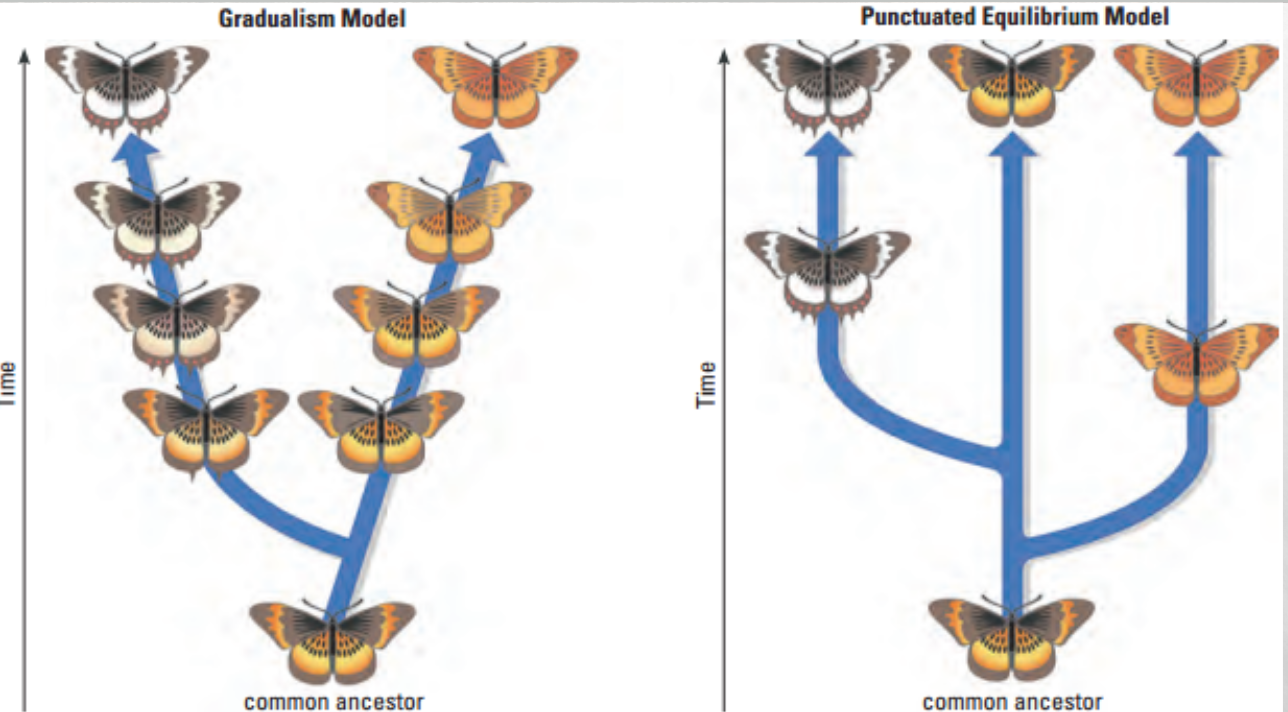
Gradualism vs punctuated equilibrium
Gradualism: small, constant, changes slowly over time
Punctuated: Periods of small change with times of huge change in 1-2 traits, is due to mutations in genes of few individuals
* results in rapid change within next few generations
Punctuated: Periods of small change with times of huge change in 1-2 traits, is due to mutations in genes of few individuals
* results in rapid change within next few generations
24
New cards
Levels of classification (7)
Kingdom (ex. Fungi, Animals, Plants)
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
**K**ing **P**hillip **C**ame **O**ver **F**or **G**reat **S**paghetti
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
**K**ing **P**hillip **C**ame **O**ver **F**or **G**reat **S**paghetti
25
New cards
Kingdoms (6)
o Archaea – extreme high/low conditions
o Eubacteria – salmonella, e. coli
o Protista – single celled, aquatic
o Fungi – yeast, mushrooms
o Plantae – plants
o Animals
o Eubacteria – salmonella, e. coli
o Protista – single celled, aquatic
o Fungi – yeast, mushrooms
o Plantae – plants
o Animals
26
New cards
Virus
\- Small, nonliving material that can infect all types of organisms
o Coat of proteins surrounding genetic information
o Cannot survive outside of a host
o Coat of proteins surrounding genetic information
o Cannot survive outside of a host
27
New cards
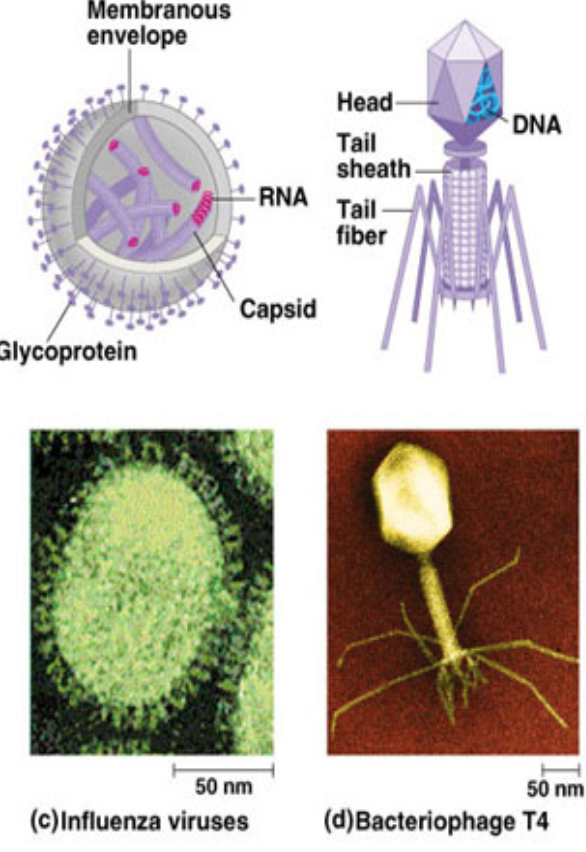
Virus structure
\- Genetic material (DNA/RNA)
\- Protective protein coat - capsid
\- Protective protein coat - capsid
28
New cards
Types of viruses (3)
DNA/RNA (Single stranded + capsid)
Bacteriophage - infects bacteria (can be either)
Some bacteria can have glycoproteins, possess different shapes
Bacteriophage - infects bacteria (can be either)
Some bacteria can have glycoproteins, possess different shapes
29
New cards
Lytic cycle
1\. Attachment: attaches to host cell
2\. Entry: virus/DNA enters cell
3\. Replication: uses host cell to create parts of virus (genetic material, spike proteins)
4\. Assembly: various components of virus are assembled into virus
5\. Release: host cell bursts (lysis)
cycle takes 25-45 mins, can create 100+ viruses per cycle
2\. Entry: virus/DNA enters cell
3\. Replication: uses host cell to create parts of virus (genetic material, spike proteins)
4\. Assembly: various components of virus are assembled into virus
5\. Release: host cell bursts (lysis)
cycle takes 25-45 mins, can create 100+ viruses per cycle
30
New cards
Lysogenic cycle
Virus naturally reproduces alongside cell, acts as parasite
31
New cards
Treatment of viruses
\- Can be pre-emptively treated with vaccines made from dead/weakened virus particles
o Results in immune system to make attack cells (**lymphocytes**) to destroy the specific virus from vaccine
o Results in immune system to make attack cells (**lymphocytes**) to destroy the specific virus from vaccine
32
New cards
mRNA vaccine
\- mRNA sequence derived from spike protein
o encapsulated into lipid coating
\- cells begin to produce copies of spike proteins
o triggers body to produce lymphocytes against protein
o encapsulated into lipid coating
\- cells begin to produce copies of spike proteins
o triggers body to produce lymphocytes against protein
33
New cards
Viral Vector vaccine
\- uses harmless virus (adenovirus) to contain spike proteins
\- can be stored in regular fridge conditions
\- can be stored in regular fridge conditions
34
New cards
Host range of virus infection
Viruses are host specific
\- Wide range: rabies can get rodents, dogs, humans
\- Narrow range: human flu only occurs in upper respiratory tract
\- Wide range: rabies can get rodents, dogs, humans
\- Narrow range: human flu only occurs in upper respiratory tract
35
New cards
Zoonosis
when virus passed from animal to human (mad cow)
36
New cards
Gene therapy using viruses
Hypothetical solution for sickle cell anemia
\- Harmful genetic material in virus removed and replaced with functioning human gene, placed into capsid
o Virus can then infect human cells to insert the correct gene into human DNA
Limitations: virus does not control where DNA is inserted, may cause unwanted mutations
\- Harmful genetic material in virus removed and replaced with functioning human gene, placed into capsid
o Virus can then infect human cells to insert the correct gene into human DNA
Limitations: virus does not control where DNA is inserted, may cause unwanted mutations
37
New cards
Dichotomous key
\- Series of yes/no questions about organism characteristics to aid in classification
38
New cards
Archaebacteria
prokaryote bacteria found in extremely harsh environments (salty, hot, anaerobic)
39
New cards
Eubacteria
typical prokaryote bacteria (true bacteria) - salmonella, e.coli
40
New cards
Bacterial structure (3/3)
Shapes:
* coccus - spherical
* bacillus - rod shaped
* spirillum - spiral
Grouping
o Diplo – paired
o Staphylo – clustered
o Strepto – long chains
* coccus - spherical
* bacillus - rod shaped
* spirillum - spiral
Grouping
o Diplo – paired
o Staphylo – clustered
o Strepto – long chains
41
New cards
Bacterial cell wall structure
o Gram positive – lots of peptidoglycan (glycoprotein), thick cell wall
o Gram negative – less peptidoglycan, thin
o Gram negative – less peptidoglycan, thin
42
New cards
Bacterial Reproduction (4)
o Asexual – **binary fission**
o Sexual – known as **conjunction**, transfers chromosome to another cell then binary fission
o Gene transfer – pilus acts as bridge, exchanges plasmid containing DNA
o Spore formation – allows bacterial to survive in harsh conditions
* Forms spore coat, contains DNA → goes dormant **(endospore)**
o Sexual – known as **conjunction**, transfers chromosome to another cell then binary fission
o Gene transfer – pilus acts as bridge, exchanges plasmid containing DNA
o Spore formation – allows bacterial to survive in harsh conditions
* Forms spore coat, contains DNA → goes dormant **(endospore)**
43
New cards
Bacterial energy production (4)
o Photo**autotroph** – photosynthesizes
o Photo**heterotrophs** – use light to create ATP, consumes organic matter for carbon (NO CO2)
o Chemoautotrophs, use CO2, no light, use inorganic matter (NH3 / H2S) for energy via chemosynthesis
o Chemoheterotrophs: consume organic molecules for energy and carbon; most bacteria are chemoheterotrophs, e.g. decomposers and parasites
o Photo**heterotrophs** – use light to create ATP, consumes organic matter for carbon (NO CO2)
o Chemoautotrophs, use CO2, no light, use inorganic matter (NH3 / H2S) for energy via chemosynthesis
o Chemoheterotrophs: consume organic molecules for energy and carbon; most bacteria are chemoheterotrophs, e.g. decomposers and parasites
44
New cards
Bacterial oxygen usage (3)
o Obligate aerobes – requires oxygen
o Obligate anaerobe – cannot tolerate oxygen, use anaerobic processes (glycolysis) to obtain ATP
o Facultative anaerobe – use oxygen when possible, use fermentation when anaerobic conditions
o Obligate anaerobe – cannot tolerate oxygen, use anaerobic processes (glycolysis) to obtain ATP
o Facultative anaerobe – use oxygen when possible, use fermentation when anaerobic conditions
45
New cards
Gram stain test for cell wall structure
1\. Stain bacteria with crystal violet dye
2\. Treat with alcohol or acetone
3\. Stain again with red or pink dye
a. Gram positive bacteria: will retain violet dye as peptidoglycan absorbs crystal violet dye well
b. Gram negative bacteria: violet dye is washed out in Step 2, then absorbs pink dye in step 3, therefore has less peptidoglycan due to less absorption properties
2\. Treat with alcohol or acetone
3\. Stain again with red or pink dye
a. Gram positive bacteria: will retain violet dye as peptidoglycan absorbs crystal violet dye well
b. Gram negative bacteria: violet dye is washed out in Step 2, then absorbs pink dye in step 3, therefore has less peptidoglycan due to less absorption properties
46
New cards
Protista
Mostly single celled eukaryotes, not bacteria but bacteria-like
difference between bacteria and protists is prokaryote vs eukaryote
* animal like (protozoa, ciliate, zooflagellate)
* algae like (Euglenophyta, Chrystophyta)
* fungi like (slime mould)
difference between bacteria and protists is prokaryote vs eukaryote
* animal like (protozoa, ciliate, zooflagellate)
* algae like (Euglenophyta, Chrystophyta)
* fungi like (slime mould)
47
New cards
Protozoa - animal-like
* Single-celled, motile heterotrophs classified by how they move: via **cilia**, **flagella**, or **pseudopodia** (false feet)
* Digest food in vacuoles formed by a process known as phagocytosis (“cell-eating”)
* Entamoeba hystolitica – intestinal parasite in humans causing dehydration, causes amebic dysentery
* Digest food in vacuoles formed by a process known as phagocytosis (“cell-eating”)
* Entamoeba hystolitica – intestinal parasite in humans causing dehydration, causes amebic dysentery
48
New cards
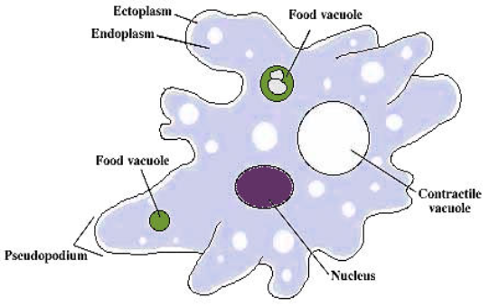
Protozoa structure
\- Cytoplasmic extensions of false feet, produce ameboid movement
\- Food vacuoles
\- Contractile vacuole helps with water regulation, contraction movements
\- Food vacuoles
\- Contractile vacuole helps with water regulation, contraction movements
49
New cards
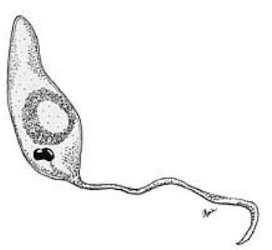
Zooflagellate
\- Phylum Mastigophora
\- Use one or more flagella for movement
\- free-living or parasitic
* *Trypanosoma:* requires two hosts, uses insect as host (not affected), infects mammal causing Chagas disease and sleeping sickness
\- Use one or more flagella for movement
\- free-living or parasitic
* *Trypanosoma:* requires two hosts, uses insect as host (not affected), infects mammal causing Chagas disease and sleeping sickness
50
New cards
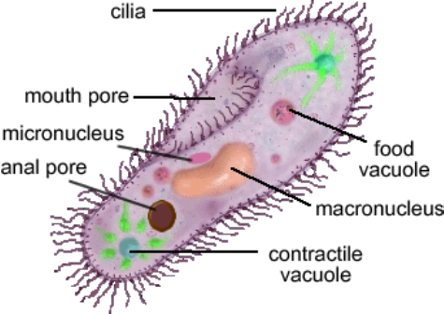
Ciliate
\- Phylum ciliophoran
\- Uses multiple cilia covering cell membrane to move, travels along in spiral path rotating along sine wave
o ex. Paramecium species
\- Micro and macro nucleus
\- Mouth/anal pore, specified pores for digestive functions
\- Perform conjugation (sexual reproduction)
\- Uses multiple cilia covering cell membrane to move, travels along in spiral path rotating along sine wave
o ex. Paramecium species
\- Micro and macro nucleus
\- Mouth/anal pore, specified pores for digestive functions
\- Perform conjugation (sexual reproduction)
51
New cards
Paramecium conjunction
Paramecium join at mouth pore and exchange DNA from micronucleus, then conduct mitosis
52
New cards
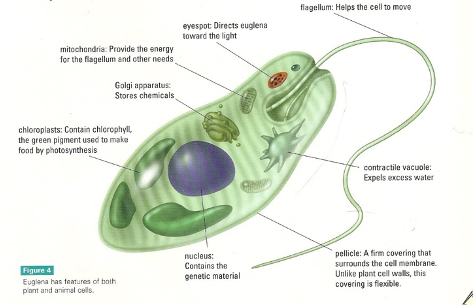
Euglenophyta
* Autotrophic via photosynthesis
* Flagella, motile protists
* Use photosynthesis as main, can become heterotrophic in low light
* Can move towards light source using eyespot
* Have both mitochondria and chloroplast
* Pellicle – flexible film covering cell membrane
* Flagella, motile protists
* Use photosynthesis as main, can become heterotrophic in low light
* Can move towards light source using eyespot
* Have both mitochondria and chloroplast
* Pellicle – flexible film covering cell membrane
53
New cards
Chrystophyta “Diatoms”
o Found in freshwater, sea, land
o Some have a shell made of silicon dioxide
o Food is stored as oils
o Certain diatoms can be indicator species, also useful in fossil dating
\
o Some have a shell made of silicon dioxide
o Food is stored as oils
o Certain diatoms can be indicator species, also useful in fossil dating
\
54
New cards
Slime moulds - fungi like
* Spend some of their life cycle as single cells, can aggregate to form colonies
* phylum myxomycota
* phylum myxomycota
55
New cards
Fungi
\- Eukaryotic heterotrophs, lack chloroplasts
o Multinucleate – multiple nuclei
\- Cell walls made of chitin, polymers of glucose derivative, contains nitrogen
\- Except yeast, most are multicellular with long thread-like cells called hyphae, Grow in masses called mycelia (single mycelium)
\- Growth of hyphae only occurs at tip, allows for colonization of organic matter
\- Consumes food via absorption (saprotrophs)
o Multinucleate – multiple nuclei
\- Cell walls made of chitin, polymers of glucose derivative, contains nitrogen
\- Except yeast, most are multicellular with long thread-like cells called hyphae, Grow in masses called mycelia (single mycelium)
\- Growth of hyphae only occurs at tip, allows for colonization of organic matter
\- Consumes food via absorption (saprotrophs)
56
New cards
Fungi reproduction
o Asexual reproduction favourable during harsh conditions and need for quicker population
o Sexual requires greater investment of energy, more time, creates greater genetic diversity
o Sexual requires greater investment of energy, more time, creates greater genetic diversity
57
New cards
Phylum Zygomycota (yoke fungi)
\- Fewer than 1000 species
o Bread molds, parasites of plants and animals - Multinucleate hyphae
\- Reproduce asexually using spores produced by structure called sporangia
- Sexually reproduced by forming zygospore, fusing mating hyphae together
o Bread molds, parasites of plants and animals - Multinucleate hyphae
\- Reproduce asexually using spores produced by structure called sporangia
- Sexually reproduced by forming zygospore, fusing mating hyphae together

58
New cards
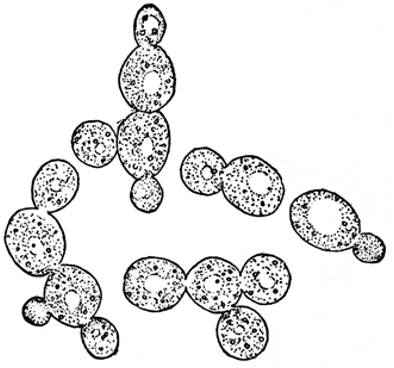
Phylum Ascomycota (sac fungi)
\- 30k species
o Yeast, multicellular fungi
\- Asexual reproduction by budding, sexual by forming ascus (sac), fuse
\- Commercial importance for baking, brewing (ferments alcohol), gene research
o Uses yeast
\- Decomposers and parasites
\- Can cause diseases
* *Ophiostoma ulmi* causes Dutch Elm tree disease
* *Claviceps purpurea* causes wild ergot, affects crops, natural source of LSD
o Yeast, multicellular fungi
\- Asexual reproduction by budding, sexual by forming ascus (sac), fuse
\- Commercial importance for baking, brewing (ferments alcohol), gene research
o Uses yeast
\- Decomposers and parasites
\- Can cause diseases
* *Ophiostoma ulmi* causes Dutch Elm tree disease
* *Claviceps purpurea* causes wild ergot, affects crops, natural source of LSD
59
New cards
Phylum Basidiomycota (mushrooms)
\- Mushrooms
o The cap/stem is called fruiting body where spores are produced
\- Body has short lifetime, vegetative mycelium lives in soil, survives for years
\- Some produce poisons/hallucinogens
o *Amanita phalloides* is death cap mushroom
o The cap/stem is called fruiting body where spores are produced
\- Body has short lifetime, vegetative mycelium lives in soil, survives for years
\- Some produce poisons/hallucinogens
o *Amanita phalloides* is death cap mushroom
60
New cards
Phylum Deuteromycota (imperfect fungi)
\- Incapable of sexual reproduction
o Blue-green mold
\- Classified by asexual spore
\- *Trichophyton* causes ringworm and athlete’s foot
o Blue-green mold
\- Classified by asexual spore
\- *Trichophyton* causes ringworm and athlete’s foot
61
New cards
Symbiont
\- Fungi that live symbiotically with other organisms
\- Lichens – symbiosis between fungus and photosynthetic algae or bacterium
\- Mycorrhizae – zygomycete or basidiomycete that lives in symbiosis with roots of plants
o Plants receive nutrients from fungus, fungus receives carbs from plants
\- Lichens – symbiosis between fungus and photosynthetic algae or bacterium
\- Mycorrhizae – zygomycete or basidiomycete that lives in symbiosis with roots of plants
o Plants receive nutrients from fungus, fungus receives carbs from plants
62
New cards
Plantae
\- Eukaryotic autotrophs via photosynthesis with cellulose cell walls
\- Many hermaphroditic (produce both gametes)
\- Many hermaphroditic (produce both gametes)
63
New cards
Phylum Brytophyta
* mosses, liverwort
\- Non-vascular (no veins, leaves, stems, roots)
\- Small, grow close to ground in moist areas, high SA/V ratio
\- Sensitive to air pollution
\- Life cycle includes alternation of generations (alternate between **gametophyte** production \[haploid\] and **sporophyte** generation \[diploid, do not reproduce\])
\- Peat mosses genus *Sphagnum* becomes acidic when release hydrogen ions into environment, inhibits growth of other organisms
o Very absorbent, holds 20x its dry mass in water
\- Non-vascular (no veins, leaves, stems, roots)
\- Small, grow close to ground in moist areas, high SA/V ratio
\- Sensitive to air pollution
\- Life cycle includes alternation of generations (alternate between **gametophyte** production \[haploid\] and **sporophyte** generation \[diploid, do not reproduce\])
\- Peat mosses genus *Sphagnum* becomes acidic when release hydrogen ions into environment, inhibits growth of other organisms
o Very absorbent, holds 20x its dry mass in water
64
New cards
Phylum Tracheophyte
\- Vascular (have veins to transport water, nutrients, gases through plants)
\- Larger due to transport system (leaves, stems, roots)
\- Reproduction involves alternation of generations (seedless vs seed-bearing)
\- Larger due to transport system (leaves, stems, roots)
\- Reproduction involves alternation of generations (seedless vs seed-bearing)

65
New cards
Class Filicineae
* ferns
* belong to Phylum Tracheophyte
\- Stems grown in soil, vessels called xylem (water) and phloem (food) for transport
\- Have true roots with conducting tissues
\- Asexual reproduction by spores produced in sporangia
* belong to Phylum Tracheophyte
\- Stems grown in soil, vessels called xylem (water) and phloem (food) for transport
\- Have true roots with conducting tissues
\- Asexual reproduction by spores produced in sporangia
66
New cards
Class Coniferae
* woody plants, belong to Phylum Tracheophyte
\- Non-flowering seed plants – gymnosperms
* gymnosperms are any vascular plant that reproduces by means of an **exposed seed**, or ovule
\- Cone-bearing and/or evergreen
o Yew is not cone-bearing, larch is not evergreen
\- Most are soft wood, yellow pine is hard wood
\- Leaves may be needle-like (pine) or scale-like (Cedar)
\- Non-flowering seed plants – gymnosperms
* gymnosperms are any vascular plant that reproduces by means of an **exposed seed**, or ovule
\- Cone-bearing and/or evergreen
o Yew is not cone-bearing, larch is not evergreen
\- Most are soft wood, yellow pine is hard wood
\- Leaves may be needle-like (pine) or scale-like (Cedar)

67
New cards
Class Angiospermae
* main flora of the earth
* flowering plants; have concealed seeds within mature ovaries
* can be classified into 2 evolution lines: monocots, dicots
* flowering plants; have concealed seeds within mature ovaries
* can be classified into 2 evolution lines: monocots, dicots

68
New cards
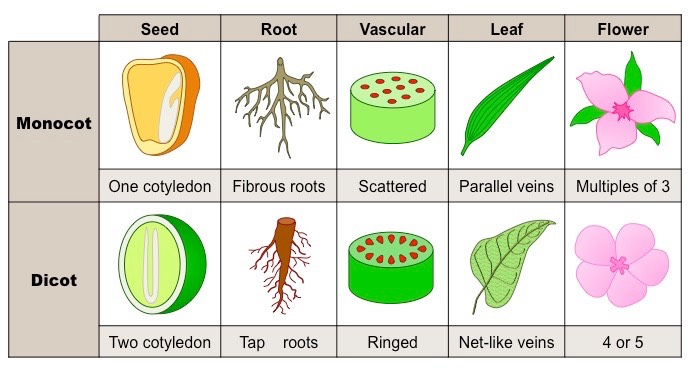
Monocot vs dicot structure
Monocots
\- One-seed leaf (cotyledon – amount of seed leaves)
\- Parallel leaf venation (ex corn)
\- Scattered vascular bundles
\- Fibrous root system
\- Floral parts (petals) in multiples of 3
o Trillium flower
Dicots
\- Two-seed leaves (2 cotyledons)
\- Vascular bundles arranged in rings
\- Taproot system (carrot)
\- Floral parts (petals) in multiples of 4
o daisy
\- One-seed leaf (cotyledon – amount of seed leaves)
\- Parallel leaf venation (ex corn)
\- Scattered vascular bundles
\- Fibrous root system
\- Floral parts (petals) in multiples of 3
o Trillium flower
Dicots
\- Two-seed leaves (2 cotyledons)
\- Vascular bundles arranged in rings
\- Taproot system (carrot)
\- Floral parts (petals) in multiples of 4
o daisy
69
New cards
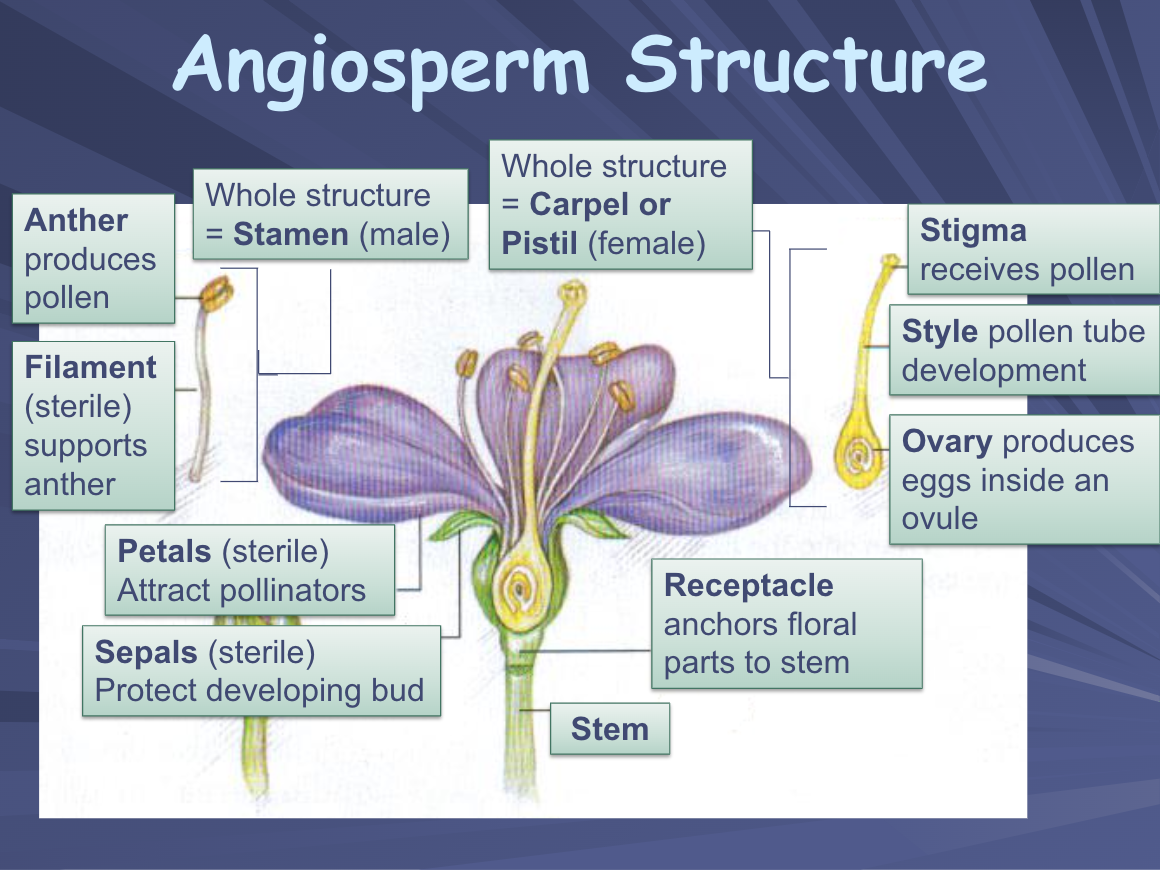
Angiospermae structure
General structure:
* Petals - attract pollinators
* Sepals - protect developing bud
* Receptacle - connects flower to stem
* Stem - connects vascular system to roots
Reproductive organs:
Stamen (male):
* anther - produces pollen
* filament - supports anther, allows for extension so wind/pollinators can spread pollen
Carpel/Pistil (female)
* stigma - receives pollen
* style - pollen tube development
* ovary - produces eggs inside **ovule**
* Petals - attract pollinators
* Sepals - protect developing bud
* Receptacle - connects flower to stem
* Stem - connects vascular system to roots
Reproductive organs:
Stamen (male):
* anther - produces pollen
* filament - supports anther, allows for extension so wind/pollinators can spread pollen
Carpel/Pistil (female)
* stigma - receives pollen
* style - pollen tube development
* ovary - produces eggs inside **ovule**
70
New cards
Phylum Ponifera
* aquatic sponges
* multicellular
\- no organs or body systems
\- cellular digestion (heterotrophic)
o eats small plankton
o obtain food by filter feeding (catches food via current)
\- asymmetrical bodies
\- Sessile – do not move
\- Skeleton composed of spongin (soft) and spicules (hard)
* multicellular
\- no organs or body systems
\- cellular digestion (heterotrophic)
o eats small plankton
o obtain food by filter feeding (catches food via current)
\- asymmetrical bodies
\- Sessile – do not move
\- Skeleton composed of spongin (soft) and spicules (hard)
71
New cards
Ponifera reproduction (2)
o Sexual – sperm and eggs
o Asexual – regeneration
* Prone to breakage, can regenerate to a certain degree
o Asexual – regeneration
* Prone to breakage, can regenerate to a certain degree
72
New cards
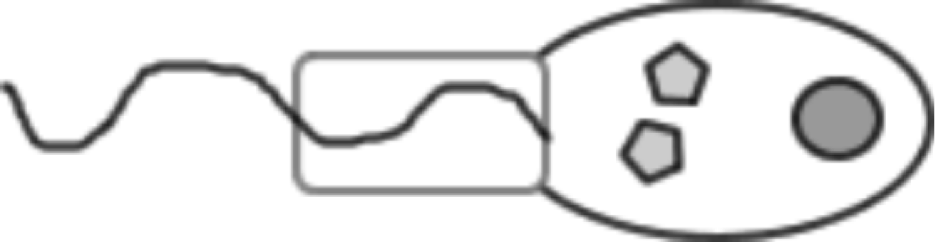
Ponifera specialized cells (2)
\- Amoebocytes – specialized cells within sponge responsible for intake of nutrients and waste management
\- Choanocytes – collar cells
o Layer of cells with flagella, keeps water current going through sponge
o Food vacuoles digest plankton and other organisms
\- Choanocytes – collar cells
o Layer of cells with flagella, keeps water current going through sponge
o Food vacuoles digest plankton and other organisms
73
New cards
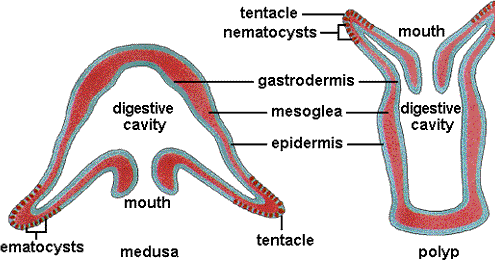
Phylum Cnidaria
* jellyfish, hydra, sea anemone, coral
\- Have cnidocytes - stinging cells found on tentacles
o Jellyfish have no stinging on their cups (head), only tentacles
\- Physiology
o Tentacles
o Cnidocytes
o Nematocysts (prickly barbs)
o Gastrovascular cavity (digestion), abdominal with vessel like network
\- Most have radial symmetry
\- Body forms
o Polyp (vase shaped)
o Medusa (cup shaped)
\- Big jellyfish with tentacles, Portuguese man of war
\- Hydra – freshwater cnidarian, polyp
o Participates in asexual reproduction, cloning
\- Coral reefs are skeletons of cnidaria
\- Have cnidocytes - stinging cells found on tentacles
o Jellyfish have no stinging on their cups (head), only tentacles
\- Physiology
o Tentacles
o Cnidocytes
o Nematocysts (prickly barbs)
o Gastrovascular cavity (digestion), abdominal with vessel like network
\- Most have radial symmetry
\- Body forms
o Polyp (vase shaped)
o Medusa (cup shaped)
\- Big jellyfish with tentacles, Portuguese man of war
\- Hydra – freshwater cnidarian, polyp
o Participates in asexual reproduction, cloning
\- Coral reefs are skeletons of cnidaria
74
New cards
Phylum Platyhelminthes
Flatworms
1. **3 germ layers**
**o Endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm**
2. **Bilayer symmetry**
3. **Cephalization – has a head**
**- Acoelomates – have no fluid filled body cavity**
\- Ingestion
o Free-living – carnivores or scavenger, have digestive cavity (mouth pharynx)
o Parasites – feed on blood/tissue of a host, no digestive system, absorbs nutrients directly from host
\
\- Reproduction
o Sexual – hermaphroditic
o Asexual – fission, split in two and regenerate
\
\- Some are harmless – planaria
\- Cause disease
o Tapeworms from uncooked meats
Flukes from unsanitary water – schistosamo mansoni
1. **3 germ layers**
**o Endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm**
2. **Bilayer symmetry**
3. **Cephalization – has a head**
**- Acoelomates – have no fluid filled body cavity**
\- Ingestion
o Free-living – carnivores or scavenger, have digestive cavity (mouth pharynx)
o Parasites – feed on blood/tissue of a host, no digestive system, absorbs nutrients directly from host
\
\- Reproduction
o Sexual – hermaphroditic
o Asexual – fission, split in two and regenerate
\
\- Some are harmless – planaria
\- Cause disease
o Tapeworms from uncooked meats
Flukes from unsanitary water – schistosamo mansoni
75
New cards
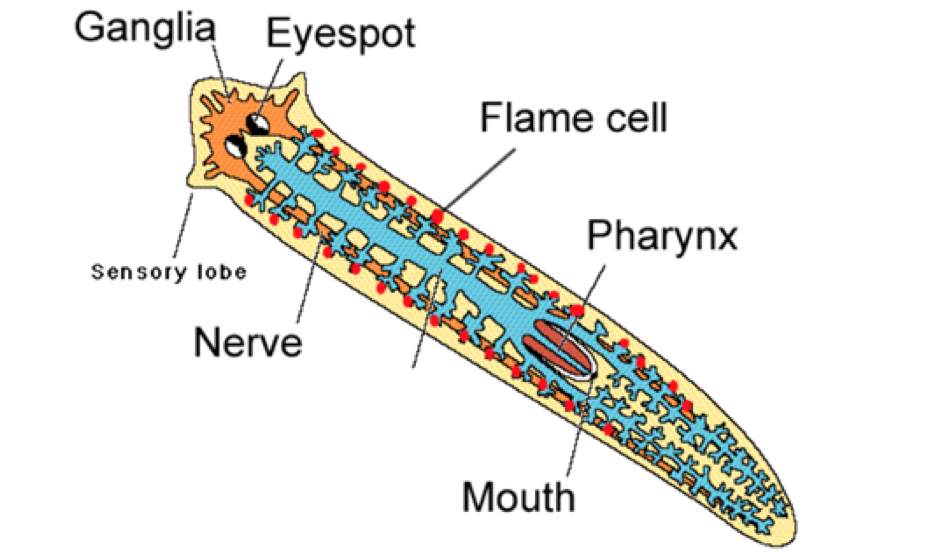
Platyhelminthes physiology
\- Thin bodies allow for diffusion for exchange of nutrients
\- Flame cells - remove excess water
\- Ganglia – nerve cells control functions in place of a brain
\- Eyespot – group of cells detect light
\- Movement
o Cilia glide through water
o Muscle like cells help them twist/turn
\- Flame cells - remove excess water
\- Ganglia – nerve cells control functions in place of a brain
\- Eyespot – group of cells detect light
\- Movement
o Cilia glide through water
o Muscle like cells help them twist/turn
76
New cards
Phylum nematoda
Roundworms
1. **Unsegmented worms**
2. **Pseudocoelom – fake coelom**
3. **body cavity containing organs**
\- Free-living or parasitic
\- Reproduce separately, not hermaphroditic
\- Diseases
o Trichinosis in muscles from uncooked food (*trichinella*)
o *Filaria* causes elephantiasis
o *Ascaris* from feces infects eyes, bowel
o Soil hookworms burrow into skin
1. **Unsegmented worms**
2. **Pseudocoelom – fake coelom**
3. **body cavity containing organs**
\- Free-living or parasitic
\- Reproduce separately, not hermaphroditic
\- Diseases
o Trichinosis in muscles from uncooked food (*trichinella*)
o *Filaria* causes elephantiasis
o *Ascaris* from feces infects eyes, bowel
o Soil hookworms burrow into skin
77
New cards
Phylum annelida
Segmented worms (annelida)
* Classes: Earthworms (Oligochaeta), marine worms (polychaeta), leeches (hirudinea)
\- With coelom
\- “Little rings,” body segments separated by septa (internal walls)
\- Septa have bristles called setae
\- Closed circulatory system and advanced nervous system
\- mostly sexual reproduction, some hermaphroditic
o some ability to regenerate
* Classes: Earthworms (Oligochaeta), marine worms (polychaeta), leeches (hirudinea)
\- With coelom
\- “Little rings,” body segments separated by septa (internal walls)
\- Septa have bristles called setae
\- Closed circulatory system and advanced nervous system
\- mostly sexual reproduction, some hermaphroditic
o some ability to regenerate
78
New cards
Class oligochaeta
Earthworms
\- streamlined bodies with few setae
\- live in soil or freshwater
\- castings – worm feces enrich soil
\- streamlined bodies with few setae
\- live in soil or freshwater
\- castings – worm feces enrich soil
79
New cards
Class polychaeta
Marine worms
\- sandworms, lood worms
\- paired paddlelike appendages with setae (looks like centipede feet)
\- sandworms, lood worms
\- paired paddlelike appendages with setae (looks like centipede feet)
80
New cards
Class hirudinea
Leeches
\- external parasites with suckers
\- medicinal uses for breaking blood clots
o no longer used
\- external parasites with suckers
\- medicinal uses for breaking blood clots
o no longer used
81
New cards
Phylum Mollusca
* clams, snails, slugs, squid, octopi, and others
* Mollusca = “soft”
Soft bodied with internal/external shell
Body plan:
o Foot: takes on many forms
o Mantle: covers the body
o Shell: present in most
o Visceral mass: internal organs
* Mollusca = “soft”
Soft bodied with internal/external shell
Body plan:
o Foot: takes on many forms
o Mantle: covers the body
o Shell: present in most
o Visceral mass: internal organs
82
New cards
Mollusca classification (3)
* Gastropods (no shell or single shelled)
* Move by a muscular foot
* Some are poisonous with bright colours
* ex. snails, slugs, limpets and nudibranchs (sea slug)
* Bivalves → things with two shells
* ex. Clams, scallops, mussels
* Cephalopods → Soft-bodied with head is attached to a foot which is divided into tentacles with sucking disks
* ex. octopi, squids, cuttlefish, nautilus
* Have small internal shells or no shell at all
* Nautilus – only shelled cephalopod
* Squid have a modified shell called a pen
* Have well developed eyes; most complex of all molluscs
* Move by a muscular foot
* Some are poisonous with bright colours
* ex. snails, slugs, limpets and nudibranchs (sea slug)
* Bivalves → things with two shells
* ex. Clams, scallops, mussels
* Cephalopods → Soft-bodied with head is attached to a foot which is divided into tentacles with sucking disks
* ex. octopi, squids, cuttlefish, nautilus
* Have small internal shells or no shell at all
* Nautilus – only shelled cephalopod
* Squid have a modified shell called a pen
* Have well developed eyes; most complex of all molluscs
83
New cards
Phylum Echinodermata
Starfish, brittle stars, sand dollars, sea urchins, & sea cucumbers
\- Marine, unsegmented coelomates; “spiny-skinned” animals
\- Endoskeleton known as a test is made of calcium plates called ossicles w/spines
\- Metamorphosis: bilateral, free-swimming larva → sessile or sedentary adult
\- Adults have pentaradial (5 part) symmetry with 5 arms
\- Breathe through skin gills; no circulatory, respiratory, or excretory systems
\- Arms capable of regeneration; asexual reproduction
Physiology
\- Ventral (lower) surface = oral surface where mouth is located
\- Dorsal (upper) surface = aboral surface where anus is located
\- Marine, unsegmented coelomates; “spiny-skinned” animals
\- Endoskeleton known as a test is made of calcium plates called ossicles w/spines
\- Metamorphosis: bilateral, free-swimming larva → sessile or sedentary adult
\- Adults have pentaradial (5 part) symmetry with 5 arms
\- Breathe through skin gills; no circulatory, respiratory, or excretory systems
\- Arms capable of regeneration; asexual reproduction
Physiology
\- Ventral (lower) surface = oral surface where mouth is located
\- Dorsal (upper) surface = aboral surface where anus is located
84
New cards
Phylum Arthropoda
Spiders, insects, crustaceans
\- Jointed appendages on a segmented body
\- **Exoskeleton:** skeleton on outside
\- **Mandibles:** chewing mouthparts
\- Metamorphosis: egg → larva → adult
3 subphylum: Chelicerata (spiders, scorpions, ticks), crustacea (shrimp, lobster, crab), Uniramia (centipede, millipede, bees)
\- Jointed appendages on a segmented body
\- **Exoskeleton:** skeleton on outside
\- **Mandibles:** chewing mouthparts
\- Metamorphosis: egg → larva → adult
3 subphylum: Chelicerata (spiders, scorpions, ticks), crustacea (shrimp, lobster, crab), Uniramia (centipede, millipede, bees)
85
New cards
Subphylum chelicerata
spiders, ticks and scorpions
* 2 body segments: cephalothorax (head & chest), abdomen
* 8 legs; no antenna
* 2 body segments: cephalothorax (head & chest), abdomen
* 8 legs; no antenna
86
New cards
Subphylum crustacea
shrimp, lobsters, crabs, crayfish
* 4 pairs of legs; 2 claws called chelipeds
* 2 pairs of antennae
* 4 pairs of legs; 2 claws called chelipeds
* 2 pairs of antennae
87
New cards
Subphylum uniramia
\- Centipedes
o Predators, poisonous
o 1 pair of legs per segment
\- Millipedes
o Herbivores
o 2 pairs of legs per segment
\- Other insects (bees)
o 3 pairs of legs
o 1 pair of antennae
o 3 body segments (head, thorax, abdomen)
o Predators, poisonous
o 1 pair of legs per segment
\- Millipedes
o Herbivores
o 2 pairs of legs per segment
\- Other insects (bees)
o 3 pairs of legs
o 1 pair of antennae
o 3 body segments (head, thorax, abdomen)
88
New cards
Phylum Chordata
Mostly vertebrates; mammals, birds, fish, reptiles, amphibians
\- General characteristics
o Notochord: firm, flexible rod of tissue located on the dorsal side of the body which is a part of the endoskeleton (spine in humans)
o Dorsal nerve cord: hollow tube to the notochord connected to brain (spinal chord)
* Pharyngeal pouches: small pouches of the anterior digestive tract
* Gills in aquatic chordates
* Jaws connected to inner ear, tonsils in terrestrial
o Post-anal tail: consists of muscle tissue behind the posterior opening of the digestive tract, tail extends beyond anus
All chordates will have all aspects at some point during lifetime
\- General characteristics
o Notochord: firm, flexible rod of tissue located on the dorsal side of the body which is a part of the endoskeleton (spine in humans)
o Dorsal nerve cord: hollow tube to the notochord connected to brain (spinal chord)
* Pharyngeal pouches: small pouches of the anterior digestive tract
* Gills in aquatic chordates
* Jaws connected to inner ear, tonsils in terrestrial
o Post-anal tail: consists of muscle tissue behind the posterior opening of the digestive tract, tail extends beyond anus
All chordates will have all aspects at some point during lifetime
89
New cards
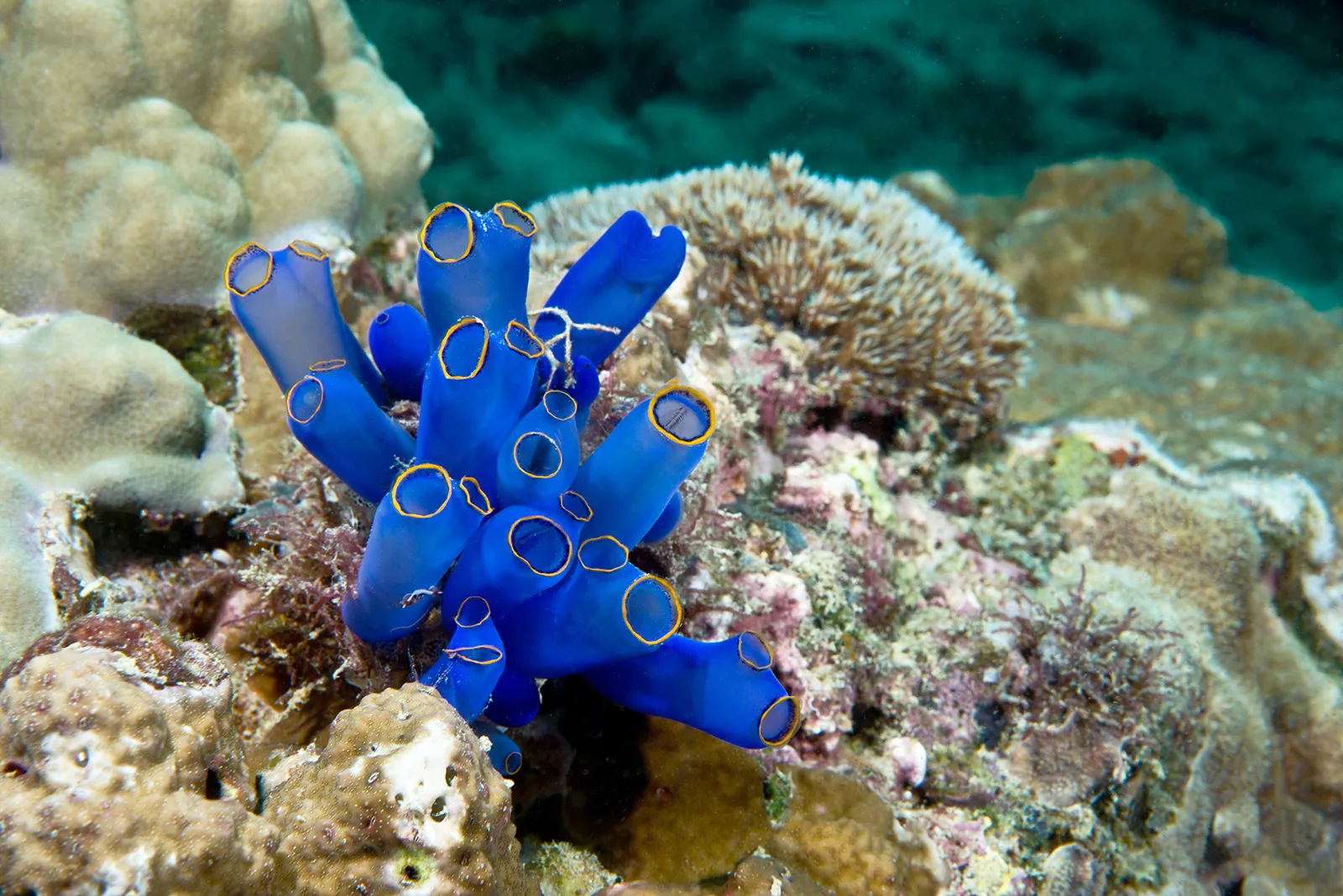
Subphylum Urochordata
Non-vertebrate chordates (sea squires, tunicates)
* bodies covered by a tough covering, or **tunic**
* shoot out a stream of water when touched
* sessile, barrel-shaped, sea bottom filter feeders
* Adults DO NOT have a notochord, dorsal nerve cord, or post-anal tail
* bodies covered by a tough covering, or **tunic**
* shoot out a stream of water when touched
* sessile, barrel-shaped, sea bottom filter feeders
* Adults DO NOT have a notochord, dorsal nerve cord, or post-anal tail

90
New cards
Subphylum Vertebrata
* Skeletons consist of bone and/or cartilage
* Brain is protected by a cranium
* Well developed 2-4 chambered heart with a closed circulatory system
* Brain is protected by a cranium
* Well developed 2-4 chambered heart with a closed circulatory system

91
New cards
Chordate reproduction
\- All sexual reproduction
\- **Spawning** – fish lay eggs, fertilized externally
o Some fish can do live birth
\- **Oviparous**: lays eggs
* chickens, frogs
\- **Ovoviviparous**: eggs stay in mom
* sharks, rays, snakes
\- **Viviparous**: babies get nourishment from mom.
* Ex. Humans, cats, some fish
\- **Spawning** – fish lay eggs, fertilized externally
o Some fish can do live birth
\- **Oviparous**: lays eggs
* chickens, frogs
\- **Ovoviviparous**: eggs stay in mom
* sharks, rays, snakes
\- **Viviparous**: babies get nourishment from mom.
* Ex. Humans, cats, some fish
92
New cards
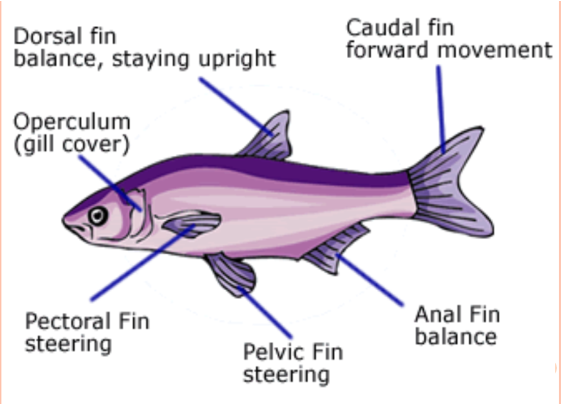
Fish
* must have gills, fins, scales
* Devionian Period - Age of Fish
* 2 chambered heart - blood is oxygenated from gills
* some fish have lungs - lungfish
Physiology
* fins help with movement
* gills
* operculum - gill covers
* swim bladder - maintains buoyancy
* Devionian Period - Age of Fish
* 2 chambered heart - blood is oxygenated from gills
* some fish have lungs - lungfish
Physiology
* fins help with movement
* gills
* operculum - gill covers
* swim bladder - maintains buoyancy
93
New cards
Homeostasis
mechanism in fish that maintains water balance
* salt water loses water
* freshwater gains water
* salmon can do both
* salt water loses water
* freshwater gains water
* salmon can do both
94
New cards
Fish nervous system
o Cerebrum – thinking, voluntary activities
o Cerebellum - coordination and balance
o Medulla oblongata – functions of internal organs
o Lateral line system – sensing vibration
o Cerebellum - coordination and balance
o Medulla oblongata – functions of internal organs
o Lateral line system – sensing vibration
95
New cards
Amphibians
frogs, axolotl
\- “double life” → lives in water then land
\- Moist skin
\- Metamorphosis from fish
* Bones become stronger
* Have lungs to breathe air
* Walk on land
\- Feeding
o Larva are herbivores with gills
o Adult frogs – carnivores with lungs
o Some have gills for whole life – mudpuppy
\- Respiration
o Double loop, 3 chambers, partially divides ventricle
\- Reproduction
o Lay eggs, fertilization external - **spawning**
\- “double life” → lives in water then land
\- Moist skin
\- Metamorphosis from fish
* Bones become stronger
* Have lungs to breathe air
* Walk on land
\- Feeding
o Larva are herbivores with gills
o Adult frogs – carnivores with lungs
o Some have gills for whole life – mudpuppy
\- Respiration
o Double loop, 3 chambers, partially divides ventricle
\- Reproduction
o Lay eggs, fertilization external - **spawning**
96
New cards
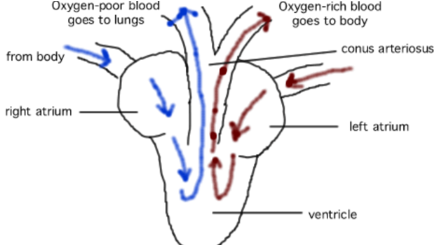
Reptiles
Orders: Crocodilia (crocodile, alligator), Testudines (turtles and tortoises), Sphenodonta (tuatara), Squamata (lizards, snakes) → largest group
\- Strong, bony skeletons with clawed feet
\- Ectothermic – cold-blooded
\- Dry, scaly skin
\- **Oviparous** - lay amniote eggs
\- Respiration with lungs
\- 3 chambered, Ventricle divided heart (crocodilia have 4)
\- Strong, bony skeletons with clawed feet
\- Ectothermic – cold-blooded
\- Dry, scaly skin
\- **Oviparous** - lay amniote eggs
\- Respiration with lungs
\- 3 chambered, Ventricle divided heart (crocodilia have 4)
97
New cards
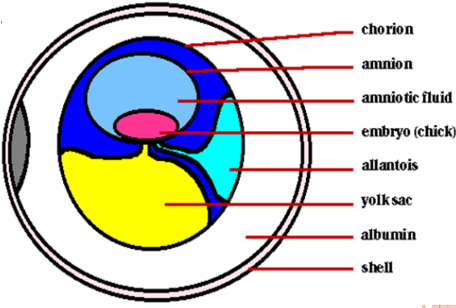
Amniote egg
\- Amnion: watery environment
\- Yolk: food for embryo
\- Allantois: stores waste
\- Chorion: membrane, gas exchange
\- Albumen: egg white, cushion
\- Yolk: food for embryo
\- Allantois: stores waste
\- Chorion: membrane, gas exchange
\- Albumen: egg white, cushion
98
New cards
Class Aves
\- Forelimbs modified into wings
\- Feathers
\- Hollow, lightweight bones
\- Endothermic (warm-blooded)
\- Efficient respiration
\- Heart with a completely divided ventricle (4 chambers)
\- Scaly feet (birds are related to reptiles)
\- Furculum (wishbone)
\- Feathers
\- Hollow, lightweight bones
\- Endothermic (warm-blooded)
\- Efficient respiration
\- Heart with a completely divided ventricle (4 chambers)
\- Scaly feet (birds are related to reptiles)
\- Furculum (wishbone)
99
New cards
Bird feathers anatomy
o Down feathers – provide insulation
o Contour feathers – cover head and body, provide colouration
o Flight feathers – on wings/tail, provide lift
o All feathers covered in oil to waterproof, secreted from **preen gland**
→ Preening can repair broken links on the vanes
o Contour feathers – cover head and body, provide colouration
o Flight feathers – on wings/tail, provide lift
o All feathers covered in oil to waterproof, secreted from **preen gland**
→ Preening can repair broken links on the vanes
100
New cards
Bird adaptations for flying
\- Aerodynamic feathers
\- Efficient digestive, respiratory, circulatory systems
\- Strong chest muscles
\- Lightweight bones
\- Beak/feet shape related to food
o Hooked beaks tear meat
o Long sharp beaks for spearing fish
\- Efficient digestive, respiratory, circulatory systems
\- Strong chest muscles
\- Lightweight bones
\- Beak/feet shape related to food
o Hooked beaks tear meat
o Long sharp beaks for spearing fish