Bio Test 2
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
For Bio Test 2 SLSS
Last updated 9:47 PM on 5/16/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
1
New cards
What are tissues?
Tissues are **groups of specialized cells that function together** to perform specialized tasks.
2
New cards
What are the 4 types of tissue?
\-Epithelial
\-Muscle
\-Nervous
\-Connective
\-Muscle
\-Nervous
\-Connective
3
New cards
What is the function of epithelial tissue?
To form a protective barrier: covers the outer surface of the body lines body cavities such as the digestive or respiratory system
* **Protection**
* Skin tissue protects underlying tissue from mechanical injury, harmful chemicals, invading bacteria and from excessive water loss
* **Secretion**
* Glands secrete enzymes, hormones & lubricating fluids
* **Absorption**
* Cells in the small intestine absorb nutrients from digested food
\
* **Protection**
* Skin tissue protects underlying tissue from mechanical injury, harmful chemicals, invading bacteria and from excessive water loss
* **Secretion**
* Glands secrete enzymes, hormones & lubricating fluids
* **Absorption**
* Cells in the small intestine absorb nutrients from digested food
\
4
New cards
What are the 3 types of muscle tissue?
**Skeletal**
* Voluntary
* Striated
* Contract to pull on bones to create movement
**Smooth**
* Involuntary
* Smooth
* Contract to facilitate movement of liquids and solids throughout the body
**Cardiac**
* Involuntary
* Smooth
* Muscles of the heart contract to move blood throughout the circulatory system
* Voluntary
* Striated
* Contract to pull on bones to create movement
**Smooth**
* Involuntary
* Smooth
* Contract to facilitate movement of liquids and solids throughout the body
**Cardiac**
* Involuntary
* Smooth
* Muscles of the heart contract to move blood throughout the circulatory system
5
New cards
What is nervous tissue?
\-Nerve tissue can create impulses & transmit them throughout the body
\-Nerve cells receive information from inside & outside the body
\
\-Nerve cells receive information from inside & outside the body
\
6
New cards
What is connective tissue and explain all the types
**The main function is to join other tissues together.**
* **Tendons & ligaments**: connect muscles to bones
* **Bones**: provide structural support
* **Cartilage**: cushioning between bones
* **Blood:**
* **Red Blood Cells: transport O2 and CO2**
* **White Blood Cells: fight off infection**
* **Platelets: form blood clots for wound healing**
* **Adipose (fat): provides cushioning and insulation**
* **Collagen**: gives strength & support to bones, muscles, skin
* **Tendons & ligaments**: connect muscles to bones
* **Bones**: provide structural support
* **Cartilage**: cushioning between bones
* **Blood:**
* **Red Blood Cells: transport O2 and CO2**
* **White Blood Cells: fight off infection**
* **Platelets: form blood clots for wound healing**
* **Adipose (fat): provides cushioning and insulation**
* **Collagen**: gives strength & support to bones, muscles, skin
7
New cards
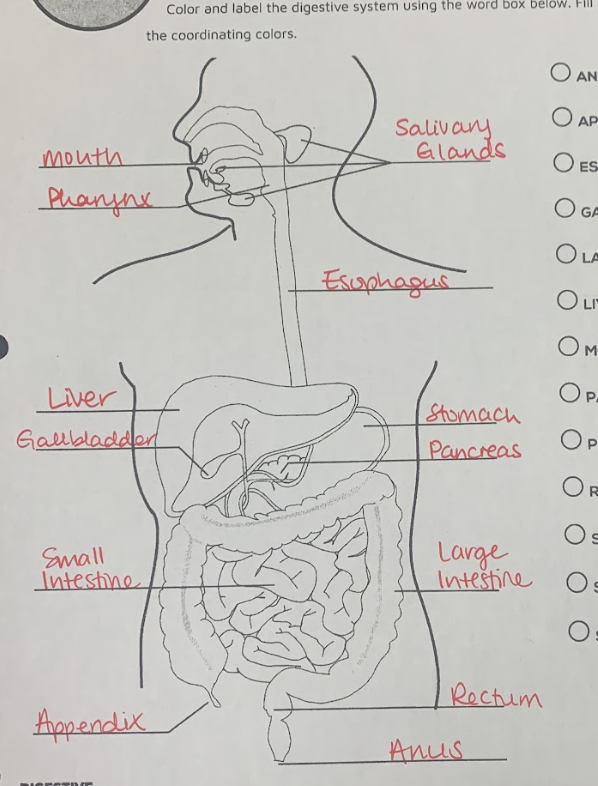
What are the components of the alimentary canal?
* Mouth
* Pharynx
* Esophagus
* Stomach
* Small Intestine
* Duodenum
* Jejunum
* Ileum
* Large Intestine/Colon
* Cecum
* Ascending Colon
* Transverse Colon
* Descending Colon
* Sigmoid Colon
* Rectum
* Anus
* Pharynx
* Esophagus
* Stomach
* Small Intestine
* Duodenum
* Jejunum
* Ileum
* Large Intestine/Colon
* Cecum
* Ascending Colon
* Transverse Colon
* Descending Colon
* Sigmoid Colon
* Rectum
* Anus
8
New cards
What are the accessory organs?
* Salivary glands
* Liver
* Gallbladder
* Pancreas
* Liver
* Gallbladder
* Pancreas
9
New cards
What is the pharynx?
The pharynx, or throat, connects the mouth to the esophagus and trachea.
10
New cards
What is the esophagus and how does it push food?
The esophagus is a tube of smooth muscle that connects the pharynx to the stomach. The esophagus is able to push food along because of peristaltic muscle contractions.
11
New cards
What is the stomach and how does an ulcer occur?
The stomach further digests food by using enzymes and acid. An ulcer occurs when the stomach acid gets through to the actual muscle.
12
New cards
What is the small intestine & its role?
The small intestine uses enzymes from the pancreas and bile produced in the liver to further break down nutrients. The role of the small intestine is to absorb nutrients.
13
New cards
What is the large intestine & its role?
Food that cannot be further digested moves from the small intestine to the colon (large intestine).
The colon absorbs water and vitamins into the bloodstream.
The colon absorbs water and vitamins into the bloodstream.
14
New cards
What is the liver?
The liver produces bile, which is a greenish-brownish fluid that aids in digesting fats (emulsification)
15
New cards
What is the gallbladder?
The bile is stored in the gallbladder. The bile travels through ducts from the gallbladder to the small intestine.
16
New cards
What is the pancreas?
The pancreas is an accessory organ that makes enzymes that goes into the small intestine and it creates insulin, which is a hormone used to regulate blood sugar levels.
17
New cards
How does heartburn happen?
Heartburn is a burning sensation in the chest that is caused by the regurgitation of acid from the stomach into the esophagus.
18
New cards
What are goblet cells?
Goblet cells are specialized epithelial cells found in the respiratory and digestive systems. They produce and secrete mucus.
\
Goblet cells are primarily found in the respiratory tract, including the lining of the trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles. They are also present in the digestive system, particularly in the epithelial lining of the intestines
\
Goblet cells are primarily found in the respiratory tract, including the lining of the trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles. They are also present in the digestive system, particularly in the epithelial lining of the intestines
19
New cards
What are ciliated cells?
Ciliated cells are epithelial cells that possess hair-like structures called cilia on their surface. They are found in the respiratory tract, including the trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles, where their coordinated movement helps propel mucus and trapped particles out of the airways.
20
New cards
What are red blood cells?
* Disc-shaped cells
* Contain hemoglobin, a protein that binds to
oxygen and carbon dioxide
* O2 enters cells via **diffusion**
* Made in the bone marrow
* Contain hemoglobin, a protein that binds to
oxygen and carbon dioxide
* O2 enters cells via **diffusion**
* Made in the bone marrow
21
New cards
What are white blood cells?
* Fight infection in the blood
* Also produced in the bone marrow
* Also produced in the bone marrow
22
New cards
What are platelets?
* Help blood clot to seal injuries and prevent blood loss
* Result from fragmentation of large cells in the bone marrow
* Result from fragmentation of large cells in the bone marrow
23
New cards
What is plasma?
* It’s a protein-rich liquid that carries the blood cells and other dissolved components
* Maintains fluid balance in the body
* Maintains fluid balance in the body
24
New cards
What are chief cells?
Chief cells are specialized cells found in the stomach lining, specifically in the gastric glands of the stomach. They are responsible for secreting pepsinogen, an inactive enzyme that is later activated to pepsin, aiding in the digestion of proteins.
25
New cards
What are parietal cells?
Parietal cells are specialized cells located in the stomach lining, particularly in the gastric glands. They secrete hydrochloric acid (HCl) and intrinsic factor.
26
New cards
What is mechanical digestion and what are the forms of it?
Mechanical digestion is the physical breakdown of food (chewing food is an example)
\
* The actual chewing and crushing of food is known as **mastication**
* Another form of mechanical digestion is the smooth muscle contractions, called **peristalsis**, that occur as the food is passed along the digestive tract
\
* The actual chewing and crushing of food is known as **mastication**
* Another form of mechanical digestion is the smooth muscle contractions, called **peristalsis**, that occur as the food is passed along the digestive tract
27
New cards
What is chemical digestion?
Chemical digestion is the chemical breakdown of food into simpler nutrients that can be absorbed. This is done with the aid of enzymes
28
New cards
What is segmentation?
Segmentation is when digested food is moved back and forth in short segments.
29
New cards
What is the chemical formula for cellular respiration?
C6H12O6 + O2 → CO2 + H20 + ATP energy
30
New cards
What are the circulatory system’s functions
**1. Transport**
* O2
* Nutrients
* CO2
* Waste
* Hormones
**2. Regulation**
* Homeostasis (steady state)
**3. Protection/ Immune Response**
* O2
* Nutrients
* CO2
* Waste
* Hormones
**2. Regulation**
* Homeostasis (steady state)
**3. Protection/ Immune Response**
31
New cards
What are the components of the circulatory system?
* **Blood**
* **Blood Vessels**
* Arteries, Veins, Capillaries
* **Heart**
* **Blood Vessels**
* Arteries, Veins, Capillaries
* **Heart**
32
New cards
What is the approximate composition of blood?
55% plasma, 45% RBCs,
33
New cards
What are arteries and what are the smaller ones called?
* Arteries carry blood **away** from the heart
* **Arterioles** are small arteries that
regulate blood pressure
* Their walls have **3 layers:**
* Thin inner epithelium
* Thick elastic smooth muscle layer
* Outer connective tissue
Need to be thick to withstand the **high pressure** of the blood pumping through them
* **Arterioles** are small arteries that
regulate blood pressure
* Their walls have **3 layers:**
* Thin inner epithelium
* Thick elastic smooth muscle layer
* Outer connective tissue
Need to be thick to withstand the **high pressure** of the blood pumping through them
34
New cards
What are veins and what are the smaller ones called?
* Veins carry blood **toward** the heart
* Venules are small veins
* Venule and vein walls have **3 layers**
* Thin inner epithelium
* Thinner, inelastic smooth muscle layer
* Outer connective tissue
* Veins are thinner than arteries, they have **less pressure**
* Veins that carry blood against gravity have **valves** to keep blood flowing toward the heart
* Venules are small veins
* Venule and vein walls have **3 layers**
* Thin inner epithelium
* Thinner, inelastic smooth muscle layer
* Outer connective tissue
* Veins are thinner than arteries, they have **less pressure**
* Veins that carry blood against gravity have **valves** to keep blood flowing toward the heart
35
New cards
What are capillaries?
* Tiny blood vessels between arterioles and venules
\
* Made of one layer of epithelial tissue
* one cell thick
* Allow for diffusion of oxygen and nutrients into cell and carbon dioxide out of the cell
\
\
* Made of one layer of epithelial tissue
* one cell thick
* Allow for diffusion of oxygen and nutrients into cell and carbon dioxide out of the cell
\
36
New cards
What is the difference between an open and closed circulatory system?
Open circulatory systems which are commonly found in invertebrates have free flowing blood because unlike closed systems, they do not have vessels to contain them.
37
New cards
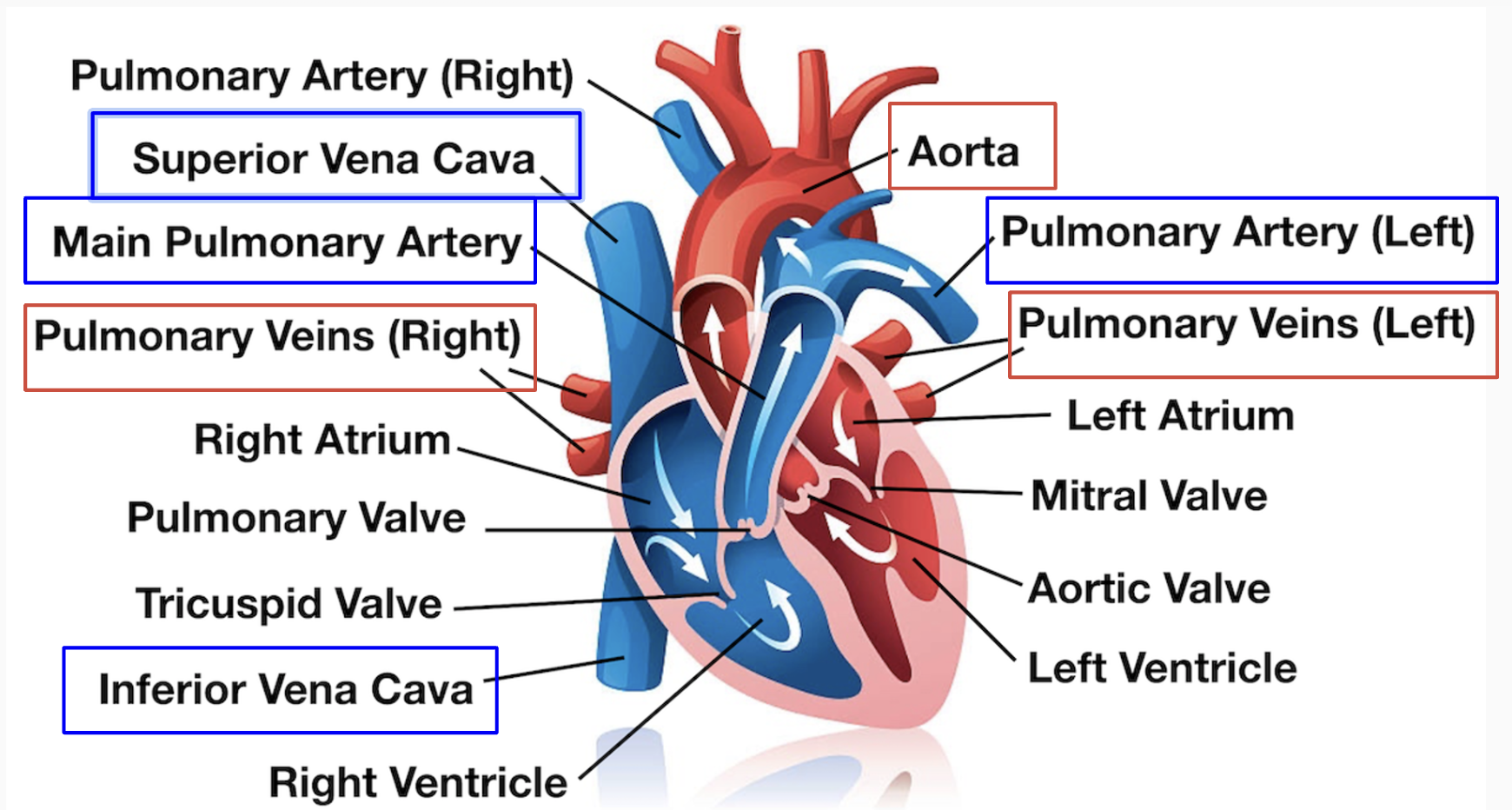
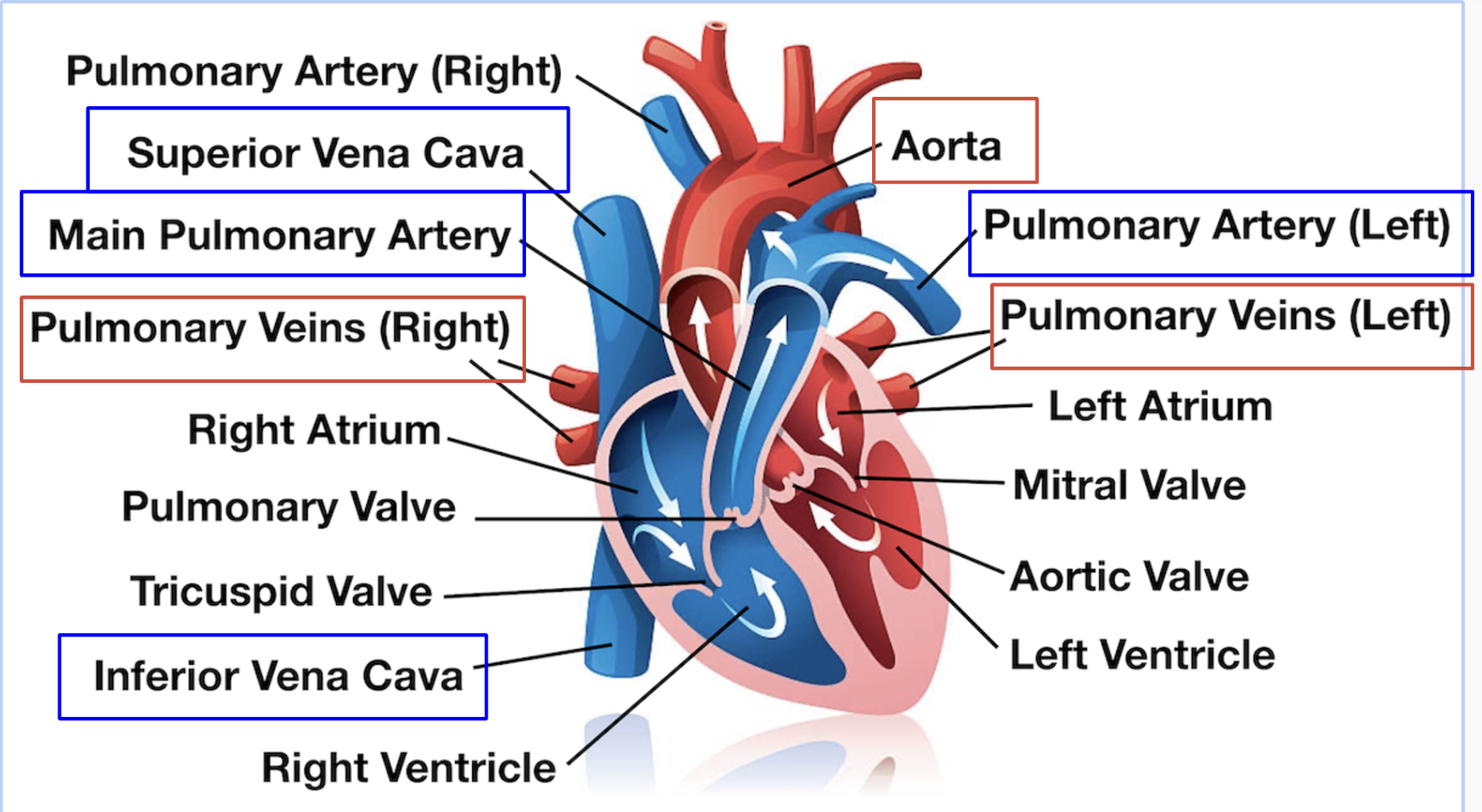
What are the four chambers of the heart?
* **Right Atrium** receives oxygen-poor blood from the body
* **Right Ventricle** pumps oxygen-poor blood into the lungs
* **Left Atrium** receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs
* **Left Ventricle** pumps oxygen-rich blood into the rest of the body
* Note that heart has 4 valves
* **Right Ventricle** pumps oxygen-poor blood into the lungs
* **Left Atrium** receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs
* **Left Ventricle** pumps oxygen-rich blood into the rest of the body
* Note that heart has 4 valves
38
New cards
What is the blood’s pathway?
\
* **Deoxygenated blood** in the heart is pumped to the lungs through **arteries** to “pick up” oxygen
* **Gas exchange** occurs in the **lungs** through capillaries
* CO2 diffuses from blood into lungs
* O2 diffuses from lungs into blood
* **Oxygenated blood** returns to heart through **veins**
* **Oxygenated blood** is pumped from the heart to the body through **arteries**
* **Deoxygenated blood** in the heart is pumped to the lungs through **arteries** to “pick up” oxygen
* **Gas exchange** occurs in the **lungs** through capillaries
* CO2 diffuses from blood into lungs
* O2 diffuses from lungs into blood
* **Oxygenated blood** returns to heart through **veins**
* **Oxygenated blood** is pumped from the heart to the body through **arteries**
39
New cards
What are the largest veins and arteries called
* Vena cava
* Has inferior and superior to carry blood from upper and lower body
* Aorta
* Has inferior and superior to carry blood from upper and lower body
* Aorta
40
New cards
What are pulmonary arteries and veins?
* The pulmonary veins are responsible for carrying oxygenated blood from the lungs back to the heart
* The pulmonary arteries, on the other hand, are responsible for carrying deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs, where it undergoes oxygenation
* The pulmonary arteries, on the other hand, are responsible for carrying deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs, where it undergoes oxygenation
41
New cards
What is the respiratory system’s main function?
Gas exchange
42
New cards
What are the parts of the respiratory system
Note that the larynx is also called the voice box and the trachea is often called the windpipe
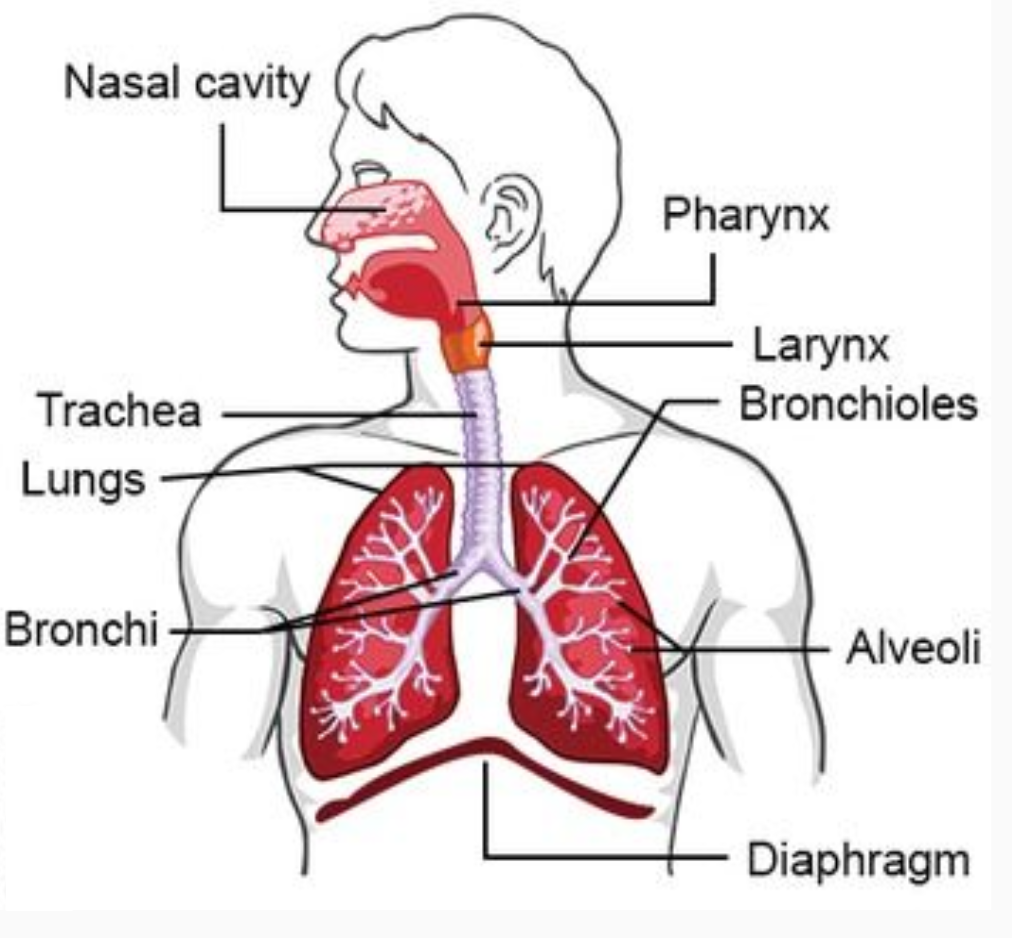
43
New cards
What protects the respiratory tract when eating?
* The **uvula** is a small muscle that covers the nasal cavity when swallowing food
* The **epiglottis** is a flap that covers the opening of the trachea when swallowing, prevents choking while eating
\
* The **epiglottis** is a flap that covers the opening of the trachea when swallowing, prevents choking while eating
\
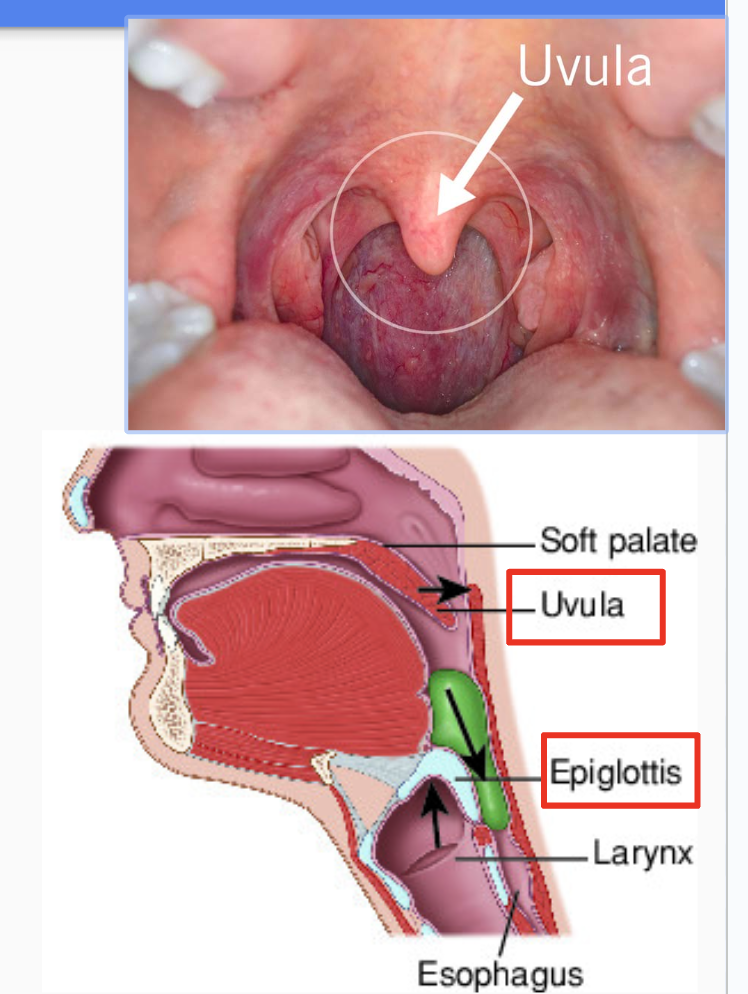
44
New cards
How many lobes does each side of the lung have?
3 on the right and 2 on the left
45
New cards
What are alveoli?
* Tiny **air sacs** at the end of the bronchioles
* Look like bunches of grapes
* Site of **gas exchange**
* Covered in **capillaries**
* Maximized surface area to increase diffusion
* Very thin (few cells)
* Shortens diffusion distance
**Surfactant** (mix of lipids and proteins) covers the alveoli to prevent them from collapsing during exhalation
* Look like bunches of grapes
* Site of **gas exchange**
* Covered in **capillaries**
* Maximized surface area to increase diffusion
* Very thin (few cells)
* Shortens diffusion distance
**Surfactant** (mix of lipids and proteins) covers the alveoli to prevent them from collapsing during exhalation
46
New cards
What is the diaphragm?
The **diaphragm** is a skeletal muscle that separates the abdominal and thoracic cavity (chest)
* Dome-shaped
* Responsible for inhalation and exhalation
* Dome-shaped
* Responsible for inhalation and exhalation
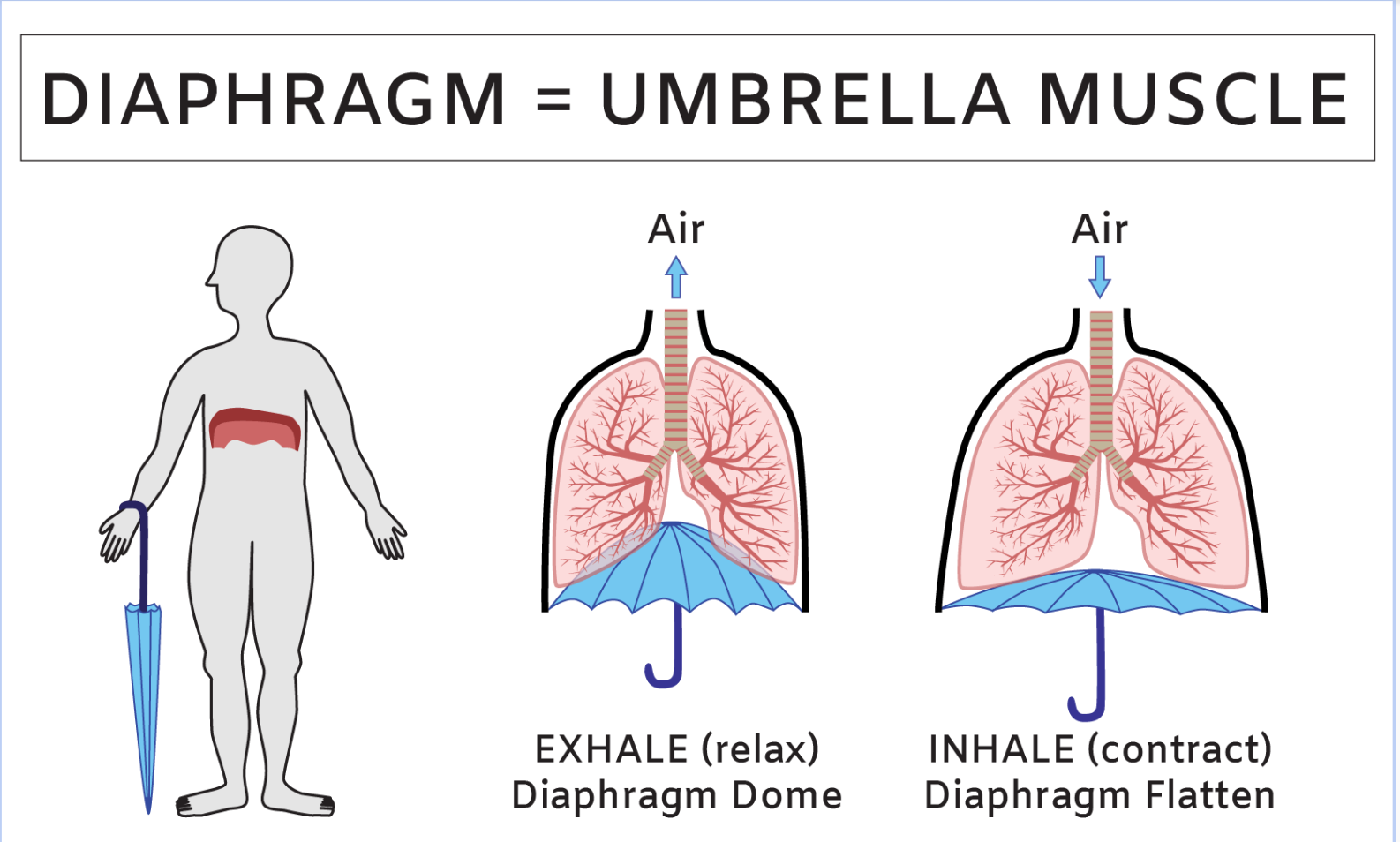
47
New cards
What happens when you inhale?
\
* **Diaphragm** **contracts** and **moves** **down**
* Rib muscles **contract** and **move out**
* Air pressure in chest cavity **decreases**
* Causes your chest cavity to **fill with air** as you breathe in
* **Diaphragm** **contracts** and **moves** **down**
* Rib muscles **contract** and **move out**
* Air pressure in chest cavity **decreases**
* Causes your chest cavity to **fill with air** as you breathe in
48
New cards
What happens when you exhale?
\
* **Diaphragm** **relaxes** and **moves up**
* Rib muscles **relax** and **move in**
* Air pressure in chest cavity **increases**
* Causes air to be **pushed out** during exhalation
* **Diaphragm** **relaxes** and **moves up**
* Rib muscles **relax** and **move in**
* Air pressure in chest cavity **increases**
* Causes air to be **pushed out** during exhalation