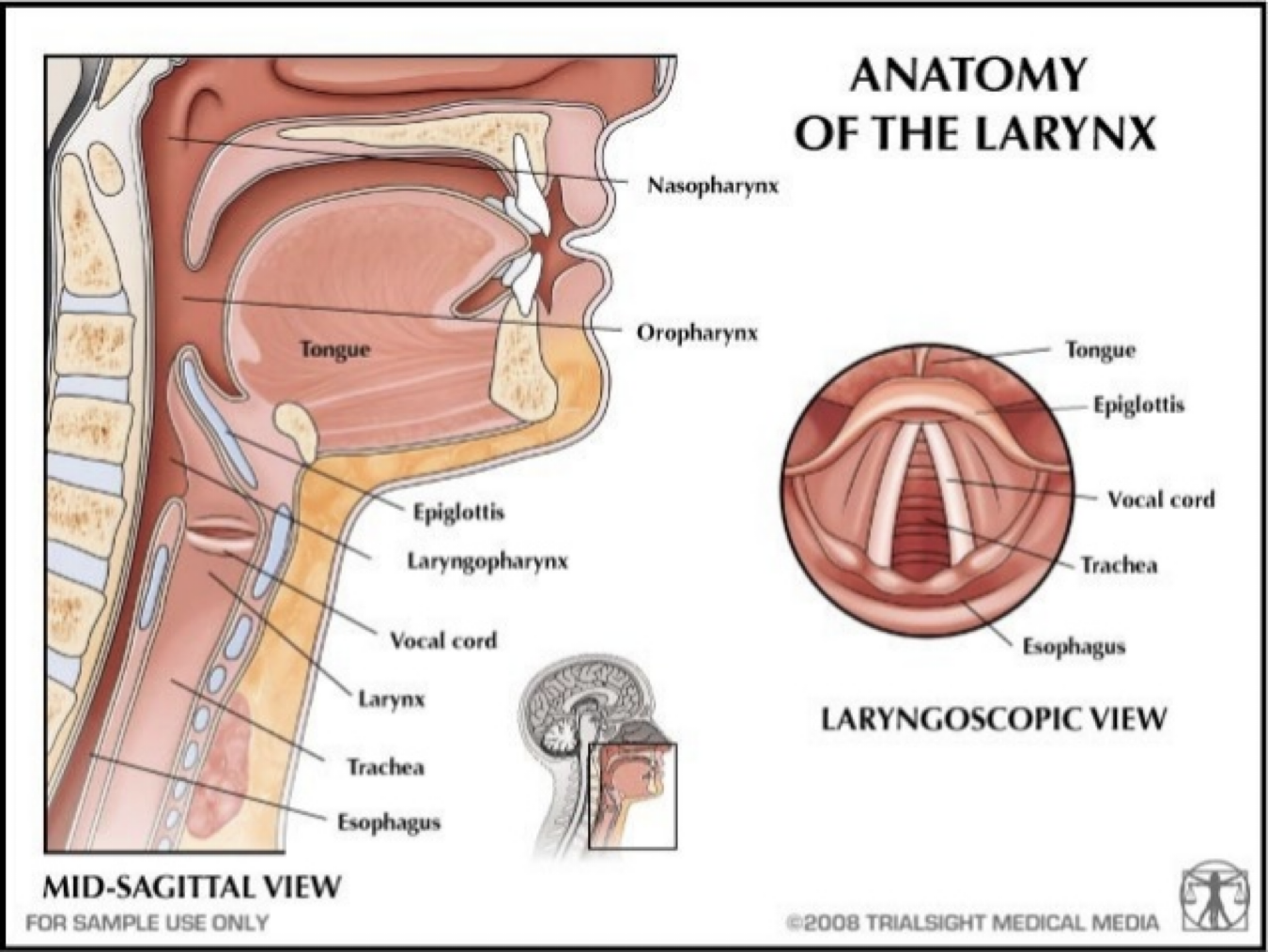
Chapter 6: Voice Disorders
Basic Vocabulary
Words
- Edema - Swelling
- Velum - Soft Pallet
- Aphonia - Loss of Voice
- Atrophy - Reduction in Tissue
- Hyperfunction - Increased Muscle Activity
- Hypofunction - Reduced Muscle Activity
Prefixes
- A - total loss
- Dys - abnormal
- Hyper - over/excessive
- Hypo - under/inadequate
- Ad - to/toward
- Ab - away from
Voice quality can be described:
Harsh - excessive muscle tension
Breathy - partial whisper
Hoarse - voice that is both harsh and breathy, irregular vocal fold vibrations
Speech Language Pathology - vocal folds in action
Vocal Fold Abnormalities that Affect Voice
a variety of structural changes in the vocal folds can affect the voice
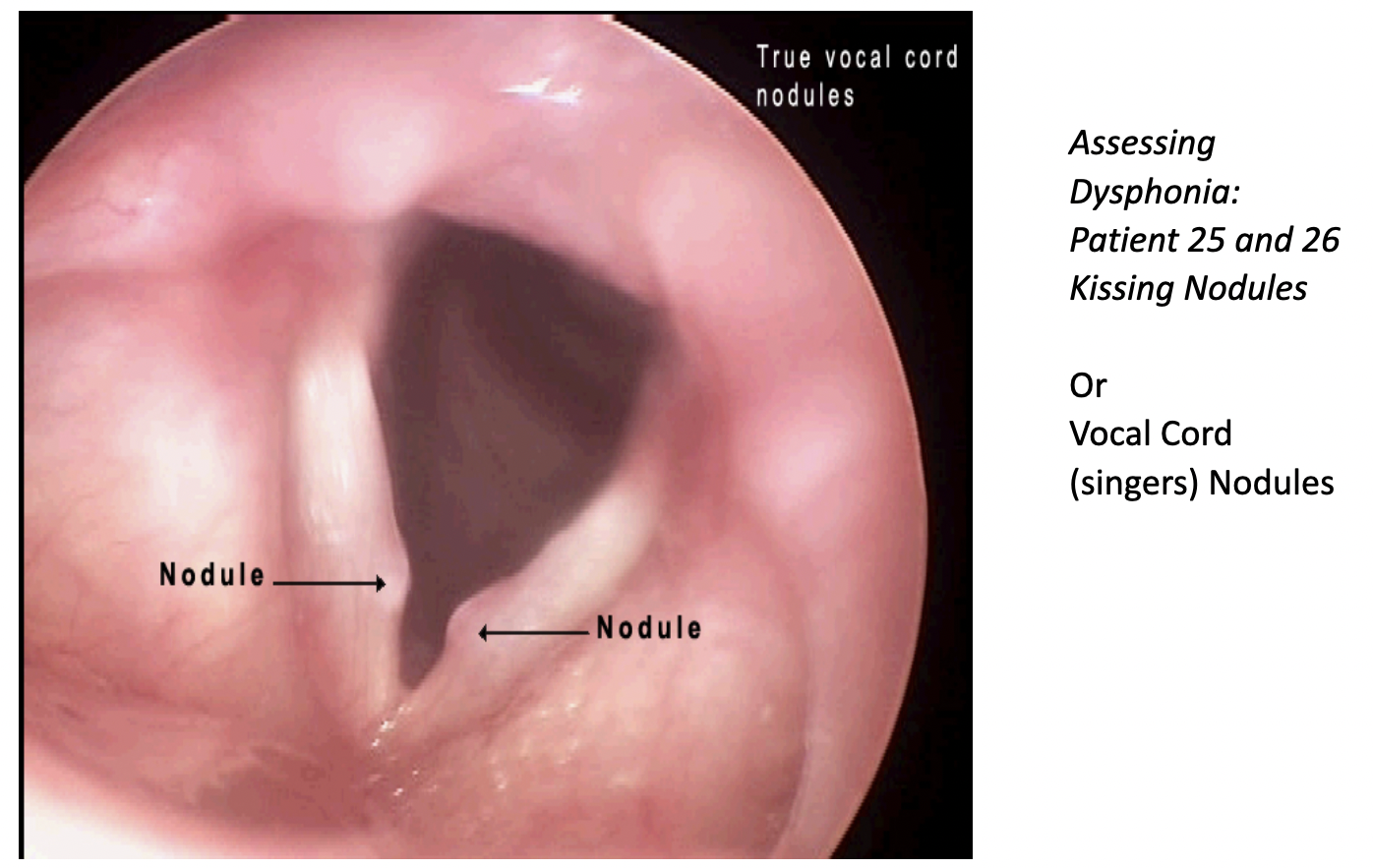
Nodules - calluses that develop on the vocal folds
- Most common form of vocal fold abnormality
- Male children 5-10 years old and adult females
- Extroverted, “talkers”
- Hoarse voice quality
- Nodules form in pairs at the point of maximum contact along the length of the vocal fold where the amplitude of vibration is greatest
- Patient alters phonatory behavior to eliminate vocal abuse, the nodules will almost always be eliminated
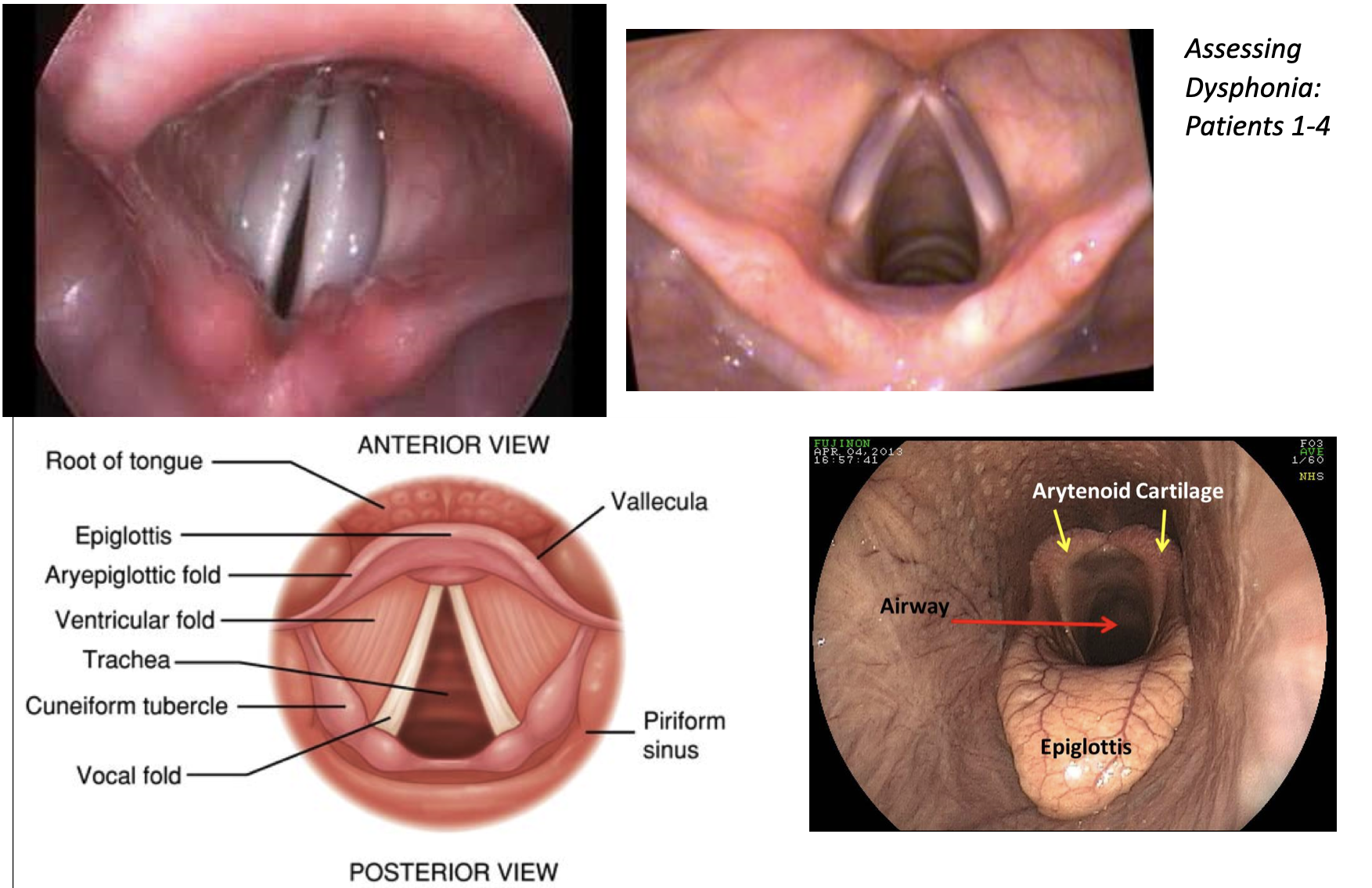
Vocal Misuses and Abuses of the Larynx
- Talking in a noisy environment
- Yelling, screaming, or cheering
- Frequent coughing or clearing of the throat
- Giving speeches or lectures
- Using caffeine products
- Spending time in smoky environments
Treatment Techniques
- Yawn-Sigh
- Vocal folds are abducted during a yawn and they are not fully adducted during a sigh
- Helps patient feel/hear/produce a less tense sounds
- Extend breathy phonation into vowels, open syllables, words, phrases, and sentences
Polyps
Polyps - Blisters
Polyps are relatively common
Shapes:
- Pedunculated - small balloons connected to the vocal fold by a narrow foot
- Sessile [ˈseˌsīl] - spread over a relatively large area of the vocal fold
Abuse (one time), unilateral, breathy/hoarse
Voice therapy to reduce vocal misuse/abuse, surgery
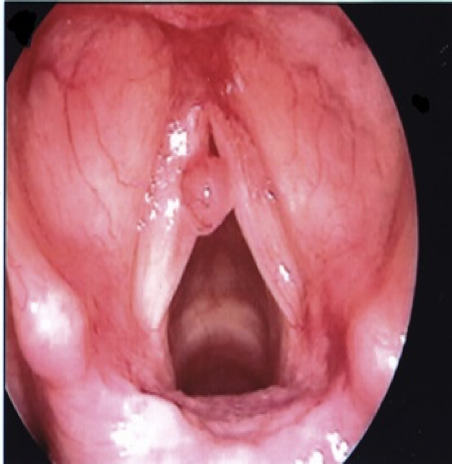
Contact Ulcers
Contact ulcers and the granulomas that develop at sites of ulceration arise at the vocal processes (on the vocal folds between the arytenoids cartilages)
Site is further back than the midpoint where nodules and polyps typically form
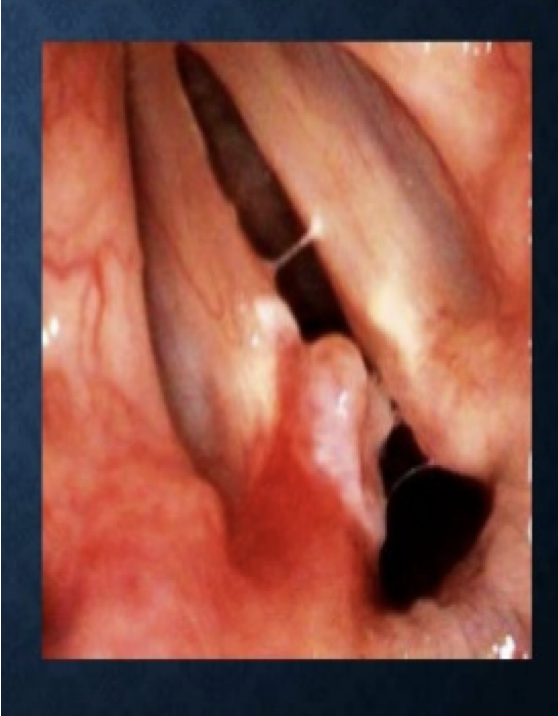
Causes:
- Excessive slamming together of the arytenoid cartilages during the production of low pitches
- Frequent nonproductive coughing and throat clearing
- Gastric reflux
- Intubation trauma
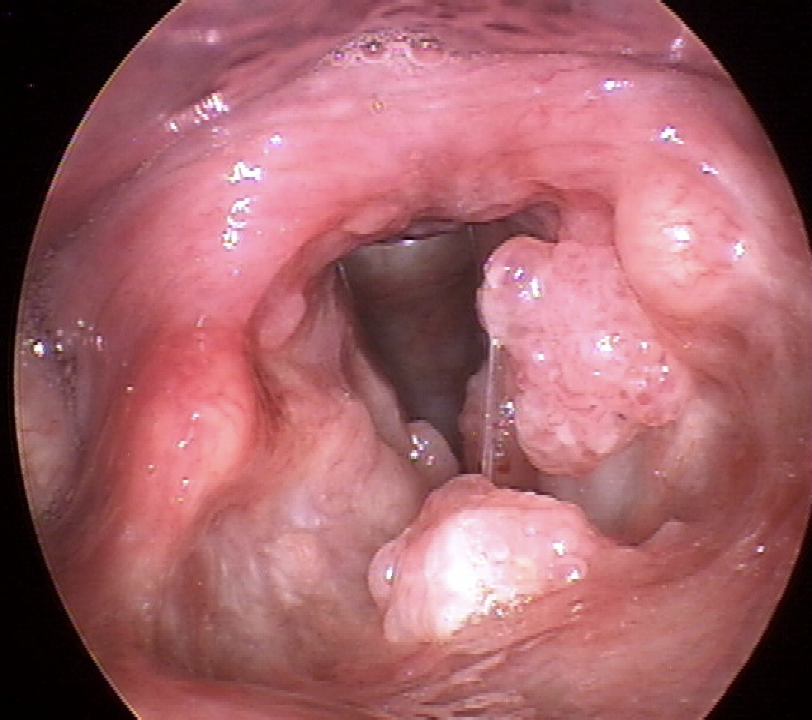
Papilloma
The human papillomavirus can cause warts on the vocal folds
Grow large
Not common
Hoarse voice quality
Surgery, developing good vocal hygiene
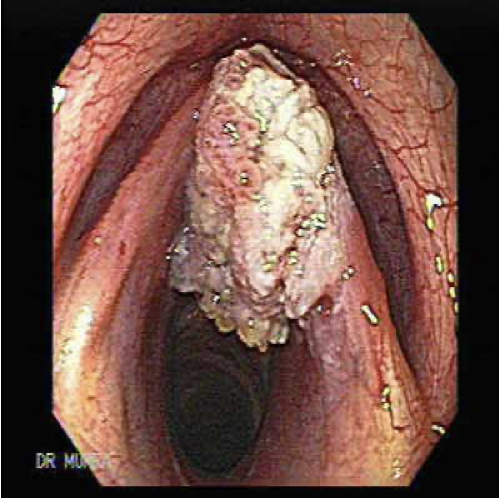
Carcinoma
Carcinoma - Cancer of the larynx
Frequently arises from exposure to inhaled smoke
Preoperative and postoperative care is laryngectomy is needed
Voice Disorders Resulting from Neurological Impairment
- Paresis - partial loss of the capacity to carry out a voluntary movement
- Paralysis - total loss of the capacity to carry out a voluntary movement
Paralysis
- Paralysis Causes - Cranial nerve cut in surgery (usually vegas), Stroke
Treatment for Unilateral Vocal Fold Paralysis
- Unaffected side “overadducts” to approximate the paralyzed fold
- Surgery involves physically moving the affected vocal fold closer to midline so that the unaffected fold can contact it during phonation
Bilateral Paralysis
- Bilateral paralysis is less frequent
- Results from CNS damage
- If neural input to both recurrent laryngeal nerves is eliminated both fold assume a static position, glottis is compromised resulting in difficulty breathing (dyspnea)
- Surgery
- Voice typically remains functional
Spasmodic Dysphonia
Rare disorder
Accepted as a neurological problem involving a disturbance in the basal ganglia that causes disordered muscle tonicity
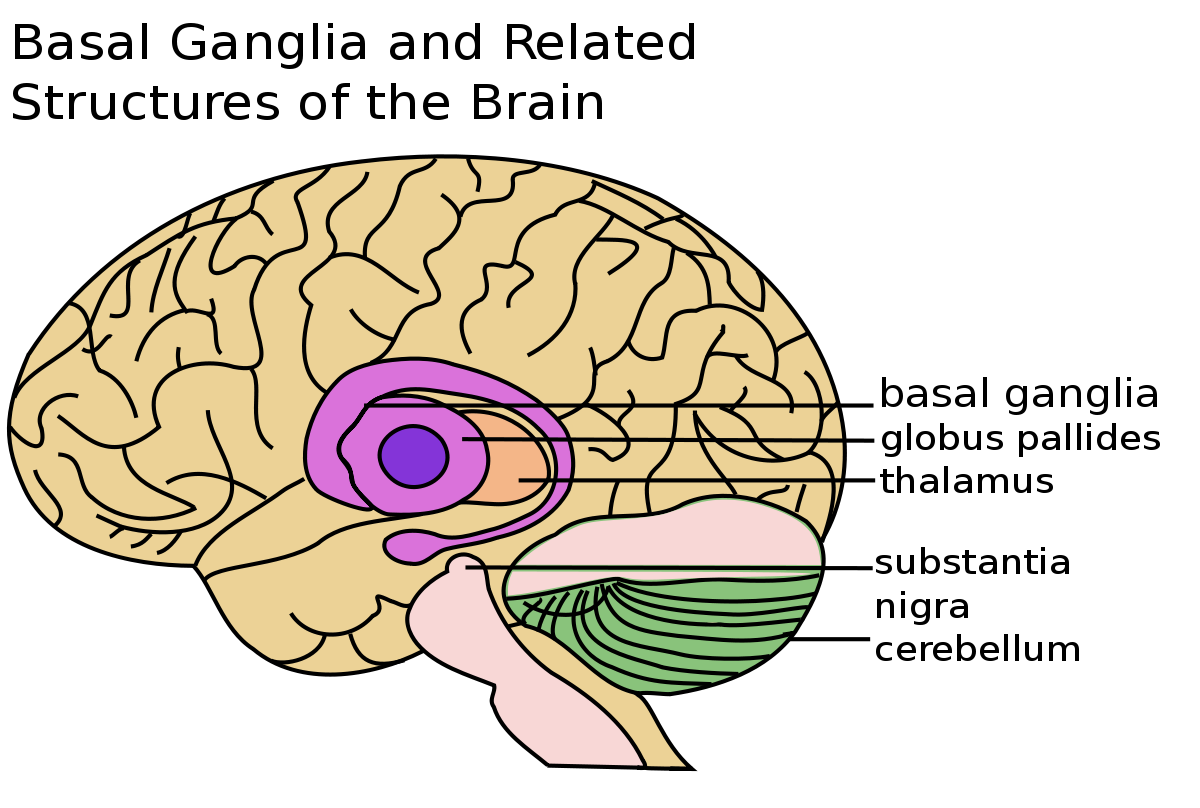
Types:
- Adductor spasmodic dysphonia - strain-strangled voice quality, uncontrolled contractions of the adductor muscles
- Abductor spasmodic dysphonia - causes inappropriate contraction of the laryngeal abduction muscles, periods of aphonia
- Mixed spasmodic dysphonia - sudden abductions as well as sudden adductions
- Dysphonia Treatment - Botox into the vocal folds
Vocal Abnormalities Unrelated to Structural Change
- Conversion Aphonia/Dysphonia - patient reports change/loss of voice but medical examination fails to uncover an organic cause for the problem
- Psychogenic cause of the voice disorder may be suspected
- Sudden onset
- Careful interview
- Restored within an hour
- Referral to a mental clinician
Voice Disorders
- Puberphonia - mutational falsetto involves the continued use of a high-pitched voice by a post pubertal male
- Functional disorder
- Easy correction
- Muscle Tension Dysphonia - caused by inordinate tension in the laryngeal muscles
- Result from the simultaneous contraction of the muscles that close and open the vocal folds
- Hypertensive, “knots”
- Benefits from laryngeal massage
- Hoarse
- Report fatigue and laryngeal discomfort
- Hard driven, upwardly mobile, Type A personalities
Voice Evaluation
Voice Evaluation Team - otolaryngologist, speech therapist
Voice Evaluation Interview - History (how voice disorder started, etc.)
Perceptual Assessment - clinician makes judgements regarding the pitch, volume, and quality of voice during a variety of tasks (sometimes recorded)
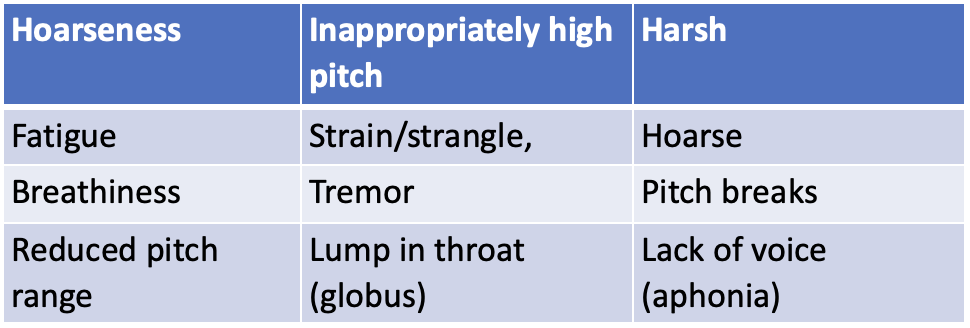
Clinicians use scales for grading vocal parameters
Assessments
- The Consensus Auditory Evaluation of Voice (CAPE-V)
- The Voice Handicap Index (VHI)
Instrumental Evaluation
- Flexible videoendoscopy
- Stroboscopy - slow motion technique that allows the clinician to examine closely the movement characteristics of the vocal folds
- Visi-Pitch - provides objective data on a number of acoustic parameters
Laryngectomy
- Laryngectomy - removal of the larynx (cancer)
- Surgical removal of the larynx requires that the trachea be redirected to an opening on the front of the neck known as the tracheal stoma
- Artificial larynx
- Electrolarynx
Esophageal Speech
- Esophageal Speech - air is actively injected down the esophagus past an area known as the pharyngeal-esophageal (PE) segment
- Air is released and passes by the PE segment and draws the walls of the esophagus into vibration, much like air passing through the true vocal cords
- Esophageal walls are much larger in mass - esophageal speech is much lower in pitch
Tracheoesophageal Speech
- Tracheoesophageal Speech - air is routed from the lungs into the esophagus via a tracheoesophageal speech prosthesis
- Additional surgery to create a small opening between the trachea and esophagus in which the prosthesis is inserted
- Cover the stoma or be fitted with a valve
- Most natural speech with the least therapy
Prevention of Voice Disorders
- Vocal Hygiene is daily regimen of good habits to maintain the health of your vocal folds
- These include eliminating inappropriate vocal habits and situations that place unnecessary wear and tear on the voice and common-sense behaviors which contribute to efficient voice production and overall voice health
- The following is a list of some tips for keeping your voice healthy:
- Avoid irritants:
- cigarettes and secondhand smoke
- manage reflux with over the counter (OTC) medication/see an ENT who specializes in voice disorders for prescription medications which may be less drying
- Take care of your body:
- Maintain good hydration: Drink 6-8 ounce glasses of water/day
- Rest
- Exercise
- Good Nutrition
- Maintain good vocal habits:
- Avoid throat clearing and coughing
- Avoid whispering
- Warm up your voice before making big demands on it
- Avoid repeated stress on the voice
- Use good posture
- Control environmental factors that may negatively impact your voice