AP Human Geography Unit 6A
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Imported from: https://quizlet.com/995411132/ap-human-geography-unit-6a-flash-cards/?funnelUUID=0f54077c-cb73-4036-987b-c05df5f384a5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
bid-rent theory (curve)
Explains how the demand for and price of land decrease as its distance from the central business district increases
Boomburb
A place with more than 100,000 residents that is not a core city in a metropolitan area; a large suburb with its own government
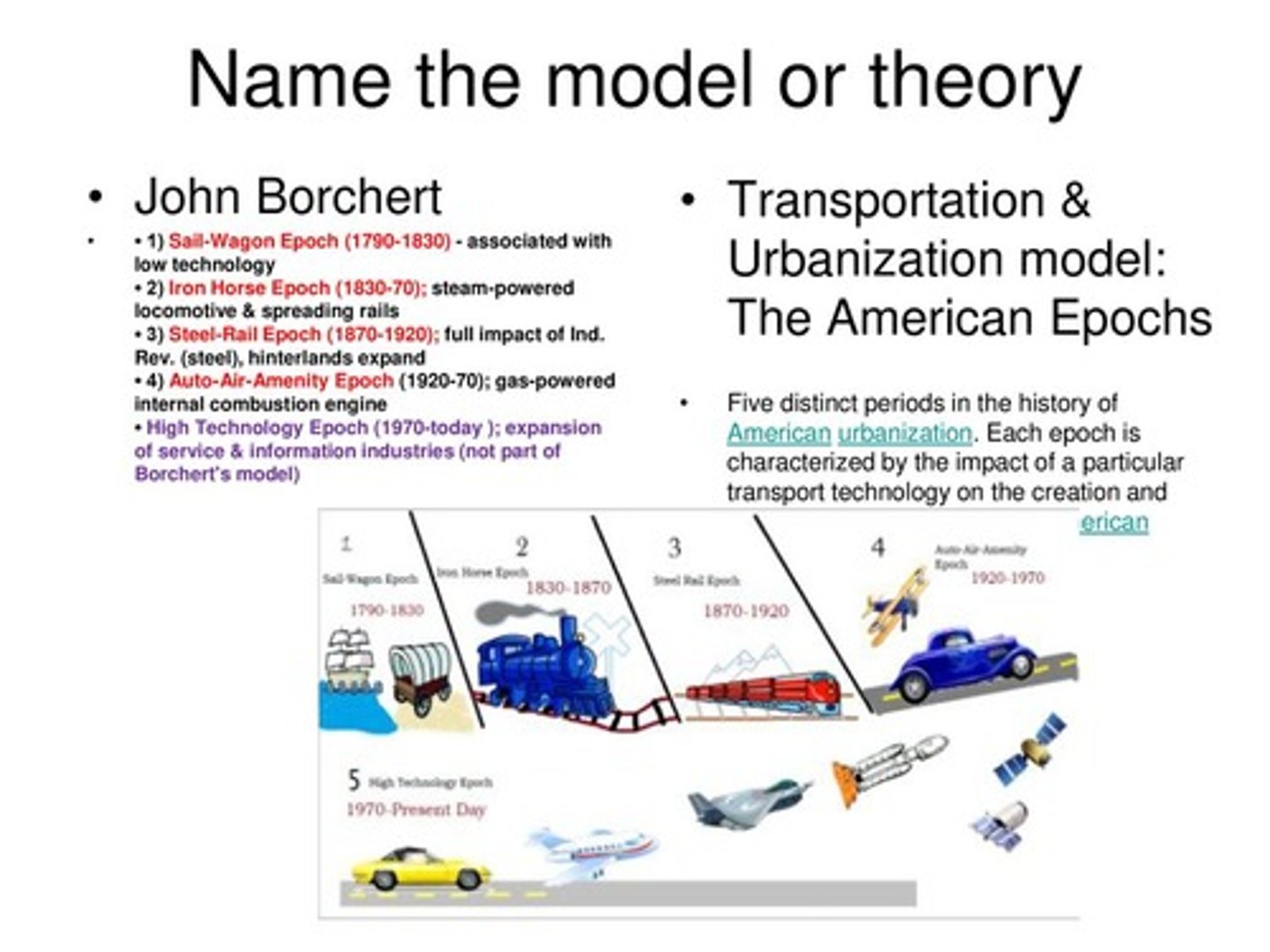
Borcherts transportation model
development of cities in relation to the development of transportation and communication. According to Borchert's model a city's urban layout owes a great deal to what forms of transportation and communication were available when the city was settled.
central business district (CBD)
A dense cluster of offices and shops located at a city’s most accessible point, usually its center
Central place
A settlement that makes certain types of products and services available to consumers
Central place theory
A model, developed by Walter Christaller, that attempts to understand why cities are located where they are
City
A relatively large, densely populated settlement with a much larger population than rural towns and villages; cities serve as important commercial, governmental, and cultural hubs for their surrounding regions
City-state
A sovereign state comprising a city and its immediate hinterland.
concentric zone model
A model of a city's internal organization developed by E. W. Burgess that shows rings of factory production and different residential zones radiating outward from a central business district
disamenity zones
the very poorest parts of cities that in extreme cases are not even connected to city services (amenities) and are controlled by gangs and drugs (Favelas in Rio)
Counter-urbanization
Net migration from urban to rural areas in more developed countries.
Ecumene
The portion of Earth's surface with permanent human settlement
Edge city
A concentration of business, shopping, and entertainment that developed in the suburbs, outside of a city's traditional downtown or central business district
Exurb
A semi rural district located beyond the suburbs that is often inhabited by well-to-do families
favelas (barrios)
illegal housing settlements, usually made up of temporary shelters that surround large cities.
Griffin-Ford model
A model of the internal structure of the Latin American city developed by Ernst Griffin and Larry Ford
High-order services
larger market area services that are purchased less frequently than lower-order goods and services.
Low-order services
smaller market area services that are purchased more frequently than higher-order goods and services.
Market area
The area surrounding a central place from which people are attracted to use the place's goods and services (also known as hinterland).
Megacity
A city with more than 10 million residents
Megalopolis
A continuous urban complex in the northeastern United States.
Metacity
A city with more than 20 million residents
Metropolitan area
An area composed of a heavily populated urban core and its less populated surrounding areas
Metropolitan statistical area (MSA)
In the United States, a region with at least one urbanized area as its core
Micropolitan statistical area
In the United States, a region with one or more urban clusters of at least 10,000 people as its cores (but less than 50,000)
Multiple nuclei model
A model of a city's internal organization, developed by Chauncy Harris and Edward Ullman, showing residential districts organized around several nodes (nuclei) rather than one central business district
Nodal city (region)
like a functional region because it is defined by a social or economic function that occurs between a node or focal point and the surrounding areas. For example the circulation area of the New York Times is a functional region and New York is the node.
periodic markets
When small vendors from all around meet up at a certain location to sell goods sometimes weekly and sometimes annually (Farmers Market)
peripheral model (galactic city model)
A model of North American urban areas consisting of inner cities surrounded by large suburban residential and business areas tied together by a beltway or ring road.
Primate city
A city that is MORE than twice as large than any other city in the country and that dominates the country's economic, political, and cultural life
Range
In central place theory, the distance people will travel to acquire a good
Rank-size rule
A pattern of settlements in a country such that the nth largest settlement is l/n the population of the largest settlement.
Reurbanization
The growth in population in metropolitan central cores, following a period of absolute or relative decline in population.
Sector model (Hoyt's)
A model of the internal structure of cities in which social groups are arranged around a series of sectors, or wedges, radiating out from the central business district.
Settlement
A permanent collection of buildings and inhabitants
Shantytowns
Unplanned slum development on the margins of cities, dominated by crude dwellings and shelters made mostly of scrap wood, iron, and even pieces of cardboard.
Sprawl
The tendency of cities to grow outward in an unchecked manner
squatter settlements
An area of degraded, seemingly temporary, inadequate, and often illegal housing
Suburbanization
he growth of cities outside of an urban area. They grow in the galactic/edge city model because of the interstate highway and the availability of goods outside of the city.
Suburb
A residential or commercial area situated within an urban area but outside the central city.
Threshold
In central place theory, the number of people required to support businesses
Urban
Relating to a city
Urban area
A central city and its surrounding built-up suburbs; density of 1,000+
Urban hierarchy
A ranking of cities, with the largest and most powerful cities at the top of the hierarchy
Urbanization
The movement of people from rural areas to cities
World cities (global cities)
A world center of trade, finance, information, and migration