7 Science: Chapter 3 Review
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
mitosis
division of the nucleus; results in two genetically identical nuclei; consists of four steps
mitotic phase
the part of the cell cycle where the cell divides; consists of mitosis and cytokinesis
cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm; the last step of the mitotic phase
furrow
created by animal cells during cytokinesis; the furrow or indent, deepens until the two identical daughter cells fully split apart.
cell plate
new cell wall forming between new cells during cytokinesis in plant cells
prophase
chromosomes condense, nuclear envelope and nucleolus dissolves, spindle apparatus forms
metaphase
sister chromatids line up in the middle of the cell
anaphase
the sister chromatids are pulled apart and begin moving to opposite sides fo the cell by shortening spindle fibers
telophase
nucleus re-forms, chromosomes relax; spindle apparatus disappears
kinetochore
physical spot on a chromosome that spindle fibers attach to
centromere
central region where two chromtids are held together
stem cell
unspecialized cell that can give rise to one or more types of specialized cells
organ
A collection of tissues that carry out a specialized function of the body
tissue
A group of similar cells that perform the same function.
organ system
group of organs that work together to perform a complex function
spindle apparatus
consists of centrioles and spindle fibers/microtubules; aids in mitosis and cytokinesis
interphase
consists of G1, S, and G2; longest part of the cell cycle
S phase
the second step of interphase; replication of DNA (the S stands for synthesis because new DNA is being made)
prokaryote
a unicellular organisms that does not have organelles; bacteria and archaea
eukaryote
a multicellular or unicellular organism with membrane-bound organelles, including a nucleus; examples include plants, animals, and fungi.
purpose of cell division
multicellular organisms use mitosis to repair damage, replace worn out cells, and grow.
unicellular eukaryotes use mitosis to reproduce
Remember, prokaryotes do not undergo mitosis because they don’t have a nucleus!
meristem
a region in plants where undifferentiated cells are actively dividing, allowing for growth and the formation of new tissues; plants have a root meristem and a stem meristem.
chormatin
the relaxed form of DNA
sister chromatids
the identical copies of a chromosome that are joined together by a common centromere, created during DNA replication during S phase.
chromosome
a structure within cells that contains genetic material, consisting of DNA and proteins, and is visible during cell division.
connective tissue
a type of animal tissue that supports and protects: examples include bones, cartilage, and blood
nervous tissue
a type of animal tissue that brings information to and from the central nervous system; helps an organism to sense external information and respond to it.
muscle tissue
a type of animal tissue responsible for movement, consisting of cells that can contract and relax.
epithelial tissue
a type of animal tissue that forms protective layers on body surfaces and lines cavities and organs
dermal tissue
a type of plant tissue that supports, protects, and prevents water loss.
vascular tissue
a type of plant tissue that transports nutrients around the plant
ground tissue
a type of plant tissue that is the site of photosynthesis
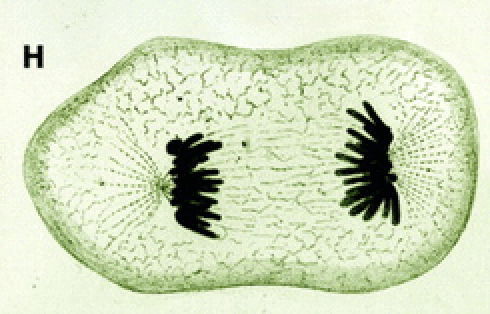
What phase of mitosis is shown in the picture?
anaphase
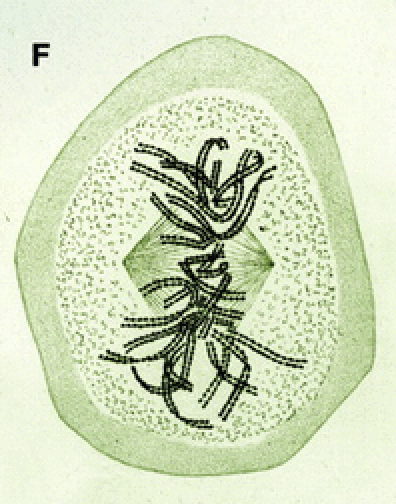
What phase of mitosis is shown in the picture?
metaphase
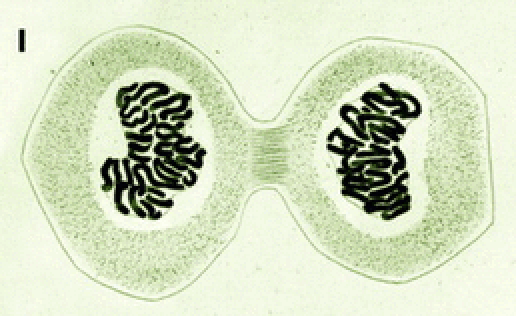
What phase of mitosis is shown in the picture?
telophase (cyotkinesis is also occuring)