Edexcel A Level Business - Theme 2: Managing Business Activities
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
148 Terms
Source of finance
A source, either within or outside of a business, from which a business can get access to money
Internal source of finance
A source of finance that comes from within a business
Personal funds
An internal source of finance where the business owner's personal wealth is used in the business
Retained profit
An internal source of finance where the profits from the previous year are used in the business
Sale of assets
An internal source of finance where the business sells assets that they own (buildings, vehicles, equipment) to raise money
External source of finance
A source of finance that comes from outside of the business
Loan capital
An external source of finance where the business borrows money for an agreed length of time
Overdraft
An external source of finance (loan capital) where a business is able to go into an agreed negative balance on their current account. This is a short term measure
Bank loan
An external source of finance (loan capital) where a business borrows an agreed amount of money from a bank, but must pay back interest
Share capital
An external source of finance where a business sells a share in the business in exchange for money
Venture capitalist
An investor or business specialist who seeks to invest in businesses they feel can make them a profit
Leasing
Where a business rents the use of something (buildings, vehicles, equipment) for a monthly fee for a fixed period of time
Government grants
Where a business receives an amount of money from Government for a specific purpose. These are usually provided when Government benefits from the operation of the business.
Trade credit
Where a business is given a period of time to pay for something, effectively receiving a loan of the items with payment at a later date. This is often 30 days
Debentures
A long term source of finance where a business takes out a long-term loan from another company
Crowdfunding
An example of peer to peer funding where a business can raise money from a larger "crowd" of investors, who each take a small stake through contributing a small amount each
Working capital
The money invested into a business for use in day to day operations. Usually calculated by current assets - current liabilities.
Short term finance
Finance available for the next 12 months
Medium term finance
Finance available for between 1 and 5 years
Long term finance
Finance available for more than 5 years
Unlimited liability
Where the owner of a business is liable for all debts of the business. This is the case for unincorporated businesses
Limited liability
Where the business is only liable for debts up to the value of the assets and capital of the business. This is the case for incorporated businesses
Business plan
A document setting out the format of the business idea, including projected aims, objectives, information on the product/service and finance projections
Business model
The plan implemented by a company to generate revenue and make a profit from operations
Cash flow
The money that comes in to and out of a business
Cash inflow
Money coming into a business
Cash outflow
Money going out of a business
Cash flow forecast
A projection of cash inflows and outflows over a period of time (6 months or a year)
Net cash flow
Cash inflows - Cash Outflows. This shows how much cash you should have at the end of a period of time given how much money is coming in and going out.
Sales forecast
A projection of how many sales a business is expecting to receive over a period of time
Consumer trends
Patterns in consumer behaviour that show the popularity or growth/decline of a product/service
Economic variables
Something that has an impact on a forecast involving the economy. For example, an increase in inflation, in interest rates, in foreign exchange rates.
Competitor actions
Actions carried out by competing businesses that will impact on a business
Extrapolation
Using trends established by historical data to make predictions about future values, assuming that trend will continue going forwards
Correlation
A method of sales forecasting, looking at the strength of a relationship between two variables
Independent variable
A variable that causes another variable to change
Dependent variable
A variable that is influenced by another variable
Positive correlation
When the independent variable increases, so does the dependent variable
Negative correlation
When the independent variable increases, the dependent variable falls
No correlation
When there is no relationship between two variables
Line of best fit
This indicates the strength of a correlation. It is a line drawn through the middle of the data points. The closer the data points are to the line, the stronger the correlation.
Confidence intervals
The percentage probability that an estimated range of possible values includes the actual value being estimated.
Sales volume
The number of sales made in a time period
Sales revenue
Selling price x Quantity sold. The total amount received through selling a good/service
Demand
The quantity of a product consumers are willing and able to buy
Costs
Anything that costs a business money
Total costs
Fixed costs + Variable costs
Fixed costs
Costs that remain the same each money no matter how much output. Examples include rent, some utility bills, salaries
Variable costs
Costs that change depending on the level of output. Examples include raw materials used in production, some utility bills, wages.
Profit
Revenue - Total Costs
Contribution
The amount of each sale that is left after the cost of sales is taken off. This goes towards paying the fixed costs of a business
Contribution per unit
Selling price - Variable cost per unit
Total contribution
Contribution per unit x Quantity sold
OR
Total Revenue - Total Variable Costs
Break even output
Fixed costs / Contribution per unit. This shows the amount of units that must be sold in order to break even (meet all costs with revenue)
Break even chart
The chart that shows the costs and revenues on a graph, showing the point at which revenues meet with total costs.
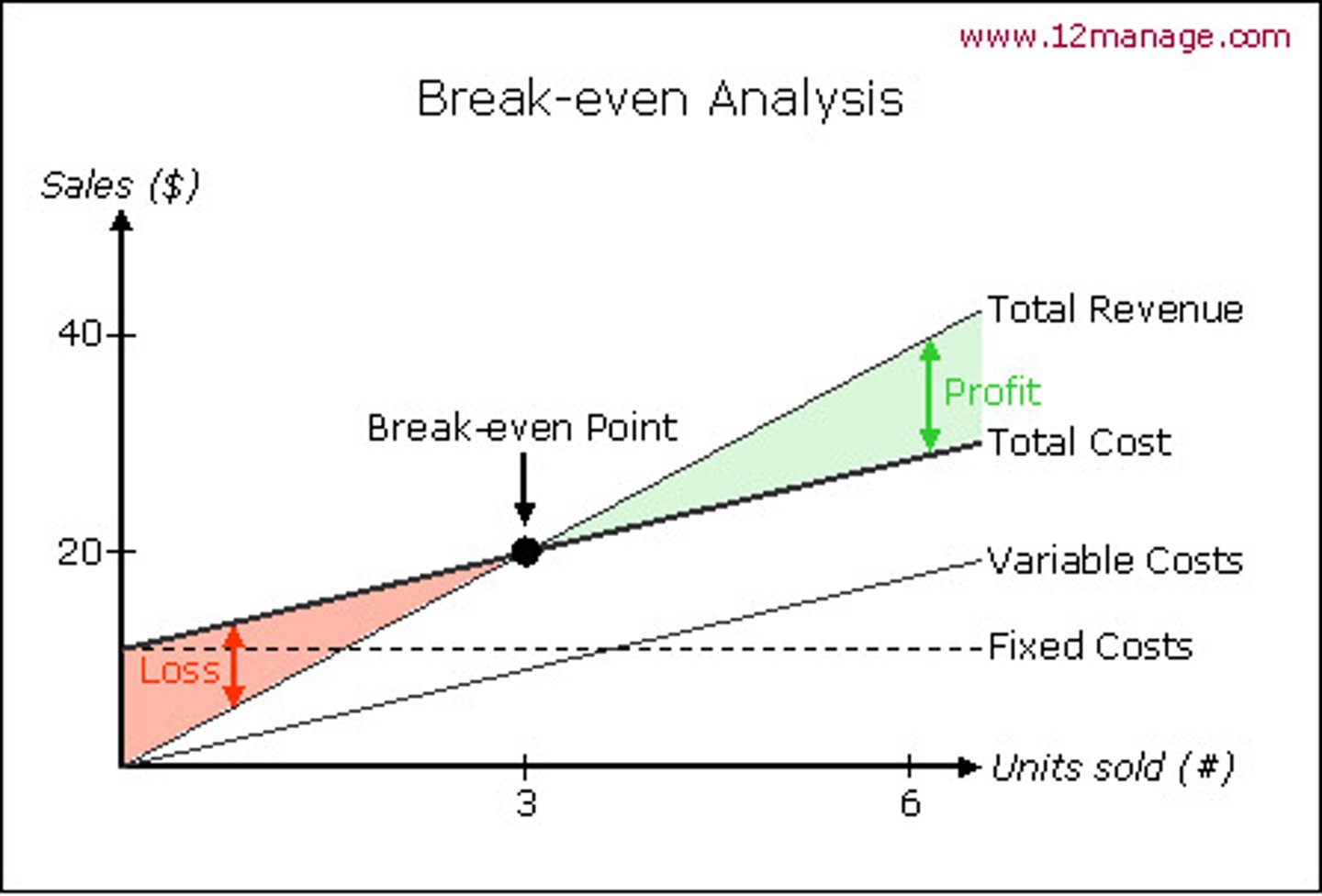
Margin of safety
Actual output - Break even output. This shows how many sales the business was above the break even point.
Budget
A financial plan for the future concerning the revenues and costs of a business
Historical budgeting
Using last year's figures as the basis for the next year's budget
Zero budgeting
Setting budgets at £0 and people will have to put proposals forwards for sales and costs
Revenue / income budget
A budget showing expected revenues and sales
Cost / expenditure budget
A budget showing expected costs based on sales
Profit budget
A budget based on both the sales and cost budgets
Variance
Looking at the difference between a forecast budget and an actual budget
Favourable variance
Actual figure - Budgeted figure
WHEN spending is less than budgeted, or revenue is more than budget
Adverse variance
Actual figure - Budgeted figure
WHEN spending is more than budgeted, or revenue is less than budget
Gross profit
Revenue - Cost of sales
Operating profit
Gross profit - Fixed overheads
OR
Revenue - Cost of sales - Fixed Overheads
Net profit
Operating profit - Financing costs and tax
OR
Revenue - Cost of sales - Fixed overheads - Financing costs and tax
Profitability
The extent to which a business is able to make a profit
Liquidity
The extent to which a business is able to use cash to meet debts as they are due
Statement of comprehensive income
(Income statement) Measures the performance of a business over a given time period, comparing the income of the business against the cost of goods or services and expenses
Statement of financial position
(Balance sheet) A snapshot of a business' assets (what it owns) and liabilities (what it owes)
Current assets
What a business owns and will be able to turn into cash in the next 12 months (i.e. stock, money in the bank)
Assets
What a business owns
Fixed assets
What a business owns that will last for over a year (i.e. a building, machinery)
Liabilities
What a business owes
Long term liabilities
What a business owes over a longer term than the next 12 months (i.e. mortgages, long term loans)
Current liabilities
What a business owes within the next 12 months (i.e. suppliers debt, overdrafts, short term loans)
Credit control
The management of accounts owed on credit by the customers of a business
Debt factoring
Selling the rights to collect amounts owed by customers in order to release cash flow
Business failure
When a business fails and goes out of existence.
Management control
The systems and process enabling a business to be managed effectively, such as decision making, management authority and financial planning
External shock
A change in the external business environment that significantly impacts a business
Production
The amount of output produced in a period of time
Job production
A method of production where items are produced in small numbers or on a one off basis, usually to a customer specification (wedding cakes, building projects)
Batch production
A method of production where similar items are produced together, so each batch goes through one stage of the production process before moving to the next
Flow production
A method of production of associated with high volumes of the same product, where when one task is finished the next much be started immediately.
Cell production
A method of production where work is organised into teams who work together in a cell. Teams are given responsibility of doing a part of production as it moves through the process.
Lean production
A method of production that aims to maximise revenues while minimising costs. This involves ensuring minimal waste through quality control at each step of the process.
Productivity
The relationship between inputs into the production process and the resulting output
Unit cost
Total costs / number of units produced.
The amount it costs to produce each unit.
Non-productive (idle) resources
Any resources not being used by a business, so if an employee is left with spare time or a machine is not operating. A sign of inefficiency.
Efficiency
How effectively a business uses it's resources to achieve outputs with minimal wasted resources / time / effort / money
Economies of scale
Cost advantages that a business can exploit by expanding their scale of production, reducing the average unit costs of production
Internal economies of scale
Economies of scale arising from the growth of the business itself
External economies of scale
Economies of scale occurring from the growth of the industry as a whole
Labour-intensive business
A business with a high proportion of its costs related to the employment of people
Capital-intensive business
A business with relatively low labour costs, but high costs arising the extensive use of machinery
Production capacity
The measure of how much output it can achieve in a given time
Capacity utilisation
The proportion of a business' capacity that is being used within a specific time period. What percentage of the total capacity was produced?