Pharm 3
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/145
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:12 PM on 3/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
146 Terms
1
New cards
N/V receptors
CNS= stimulating the vomiting center in the medulla oblongata
Vomiting center: histamine, serotonin, muscarinic, dopamine (NK1)
Vestibular system= Labyrinth stimulated >> Histamine and muscurinic
\
Chemo receptor trigger zone=dopamine receptors (NK1) and serotonin receptors
\
GI and heart= serotonin receptors
Vomiting center: histamine, serotonin, muscarinic, dopamine (NK1)
Vestibular system= Labyrinth stimulated >> Histamine and muscurinic
\
Chemo receptor trigger zone=dopamine receptors (NK1) and serotonin receptors
\
GI and heart= serotonin receptors
2
New cards
causes of vomiting
ingestion
metabolic (pregnancy)
neurologic
presence of. noxious stimuli
gruesome sight
pungent odor
infection
anxiety
medications (chemo)
motion sickness
post op
metabolic (pregnancy)
neurologic
presence of. noxious stimuli
gruesome sight
pungent odor
infection
anxiety
medications (chemo)
motion sickness
post op
3
New cards
Phenothiazines MOA
block dopamine and provide anticholinergic activity
4
New cards
Phenothiazines types
Promethazine (Phenergan)
Prochlorperazine (Compazine)
inexpensive
Prochlorperazine (Compazine)
inexpensive
5
New cards
Phenothiazines contraindications
\-Pregnancy cautious use
\-pushed slowly IV due to phlebitis
AE: \*sedation. May produce EPS therefore caution with Parkinson’s (Parkinson’s is lack of dopamine)
\-Interaction with other CNS depressants: potentiates depression
\-potential for abuse
\-pushed slowly IV due to phlebitis
AE: \*sedation. May produce EPS therefore caution with Parkinson’s (Parkinson’s is lack of dopamine)
\-Interaction with other CNS depressants: potentiates depression
\-potential for abuse
6
New cards
Antihistamines MOA in N/V
mainly for motion sickness
\
interrupt visceral afferent pathways that stimulate N/V.
\
interrupt visceral afferent pathways that stimulate N/V.
7
New cards
types of antihistamines used for N/V
hydroxyzine (Vistaril)
meclizine (Antivert)
dimenhydrinate (Dramamine)
scopolamine (Transderm Scop) (prescribed)
meclizine (Antivert)
dimenhydrinate (Dramamine)
scopolamine (Transderm Scop) (prescribed)
8
New cards
antihistamines contraindications
\
contraindicated with asthma, glaucoma, GI or urinary obstruction, Lactation, CNS depressants
AE:
\-sedation, drowsiness, confusion
\-Anticholinergic effects
Cant pee/cant see/cant spit/cant shit
\
contraindicated with asthma, glaucoma, GI or urinary obstruction, Lactation, CNS depressants
AE:
\-sedation, drowsiness, confusion
\-Anticholinergic effects
Cant pee/cant see/cant spit/cant shit
\
9
New cards
Benzodiazepines MOA
ex. ativan
Useful in anticipatory N/V, i.e, chemotherapy
by inhibiting vomiting center
Useful in anticipatory N/V, i.e, chemotherapy
by inhibiting vomiting center
10
New cards
Benzodiazepines contraindications
\
\
\
\
\
\
not to be used in pregnancy
\
Contraindicated in renal or hepatic failure
\
AE: CNS depression, amnesic effect, constipation, HA, appetite changes, CNS depression
\
Contraindicated in renal or hepatic failure
\
AE: CNS depression, amnesic effect, constipation, HA, appetite changes, CNS depression
11
New cards
Serotonin Antagonists MOA
Block 5HT3 receptors in Chemo receptor trigger zone and UpperGI tract for chemo induced N/V, radiation, post op
ex. Ondansetron (Zofran), (oral/IV/SL)
granisetron (Kytril)
\
\
ex. Ondansetron (Zofran), (oral/IV/SL)
granisetron (Kytril)
\
\
12
New cards
Serotonin Antagonists contraindications
\
SIGNIFICANT: Prolonged PR interval, QT interval and widened QRS. Cautious use with severe cardiac dysfunctions and arrhythmias.
\-Pregnancy safe
\-Cautious use with lactation
AE: headache, diarrhea, abd pain, increased LFT's (baseline LFT"S), HTN, fatigue, pruritus, fever
\
SIGNIFICANT: Prolonged PR interval, QT interval and widened QRS. Cautious use with severe cardiac dysfunctions and arrhythmias.
\-Pregnancy safe
\-Cautious use with lactation
AE: headache, diarrhea, abd pain, increased LFT's (baseline LFT"S), HTN, fatigue, pruritus, fever
\
13
New cards
Metoclopramide (Reglan) MOA
enhances GI motility and gastric emptying. Inhibits dopamine receptors in Chemo receptor trigger zone
Used for dm gastroparesis, post op gastric stasis, GERD, CINV
Used for dm gastroparesis, post op gastric stasis, GERD, CINV
14
New cards
Metoclopramide (Reglan) contraindication
AE: EPS, diarrhea, drowsiness
MAOIs cause HTN crisis
MAOIs cause HTN crisis
15
New cards
Corticosteroids side effects
AE: steroid psychosis, aggression, insomnia, hyperglycemia
16
New cards
Corticosteroids MOA
\
unknown. inhibition of prostaglandins for Chemo induced N/V
ex Dexamethasone (Decadron)
methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol)
unknown. inhibition of prostaglandins for Chemo induced N/V
ex Dexamethasone (Decadron)
methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol)
17
New cards
Cannabinoids MOA
\
unknown. Theorized effect on opiate receptors in CNS for CINV and appetite stimulation
ex dronabinol (Marinol)
unknown. Theorized effect on opiate receptors in CNS for CINV and appetite stimulation
ex dronabinol (Marinol)
18
New cards
Cannabinoids contraindications
Best given 6-12 hrs before chemo.
AE: sedation, ataxia, dysphoria. Tolerance with repeated dosing, appetite stimulation
Pregnancy avoid
Avoid in Lactation
AE: sedation, ataxia, dysphoria. Tolerance with repeated dosing, appetite stimulation
Pregnancy avoid
Avoid in Lactation
19
New cards
Antacids MOA
coat stomach and neutralize acid
20
New cards
Antacids contraindications
\-magnesium preparations: diarrhea
\-aluminum and calcium preparations: constipation
\-decrease absorption of other meds
\-aluminum and calcium preparations: constipation
\-decrease absorption of other meds
21
New cards
first line for N/V
phenothiazine
\
\
22
New cards
second line for N/V
antihistamine or anticholinergic
\
\
23
New cards
third line for N/V
evaluate for another cause
24
New cards
causes of constipation
diet, lifestyle, medication, and diseases
more frequent in females
more frequent in females
25
New cards
fiber requirements
American diet 5-14 Gms fiber; recommended 20-35 Gms fiber
26
New cards
bulk forming laxative uses
ex. metamusil
* Bulk stimulates movement of the intestine and pulls water into the stool to swell and increase stool bulk.
**Preferred agent for relief of constipation**
\-Can be used as antidiarrheal
* Bulk stimulates movement of the intestine and pulls water into the stool to swell and increase stool bulk.
**Preferred agent for relief of constipation**
\-Can be used as antidiarrheal
27
New cards
bulk forming laxative contraindications
\*\*contraindicated in Esophageal Strictures, Gi ulcerations, Gi stenosis
and Gi obstruction
\*\*Cautious use in DM because of carbohydrate content from fiber. Many now use in sugar-free form
* contains aspartame; Avoid in patients with gluten intolerance
* May cause absorption blocking with quinolones or TCN.
* Not useful in opioid induced constipation
\
\
and Gi obstruction
\*\*Cautious use in DM because of carbohydrate content from fiber. Many now use in sugar-free form
* contains aspartame; Avoid in patients with gluten intolerance
* May cause absorption blocking with quinolones or TCN.
* Not useful in opioid induced constipation
\
\
28
New cards
Hyperosmotic Laxatives MOA
ex. miralax
\-Metabolized to solutes in the intestine to draw fluid into stool by increasing osmotic pressure.
\-Increased osmotic pressure stimulates intestinal motility.
* suppository form increases rectal stimulation
\-Metabolized to solutes in the intestine to draw fluid into stool by increasing osmotic pressure.
\-Increased osmotic pressure stimulates intestinal motility.
* suppository form increases rectal stimulation
29
New cards
Hyperosmotic Laxatives contraindications
\-contraindicated in appendicitis, acute abd, fecal impaction, intestinal obstruction
\-Lactulose containing products>> caution in diabetics
\-Not useful in changed colonic transit time, IBS, severe bloating or fullness.
\-Lactulose containing products>> caution in diabetics
\-Not useful in changed colonic transit time, IBS, severe bloating or fullness.
30
New cards
saline laxatives MOA
ex.mag citrate/ milk of mag
\-used for pre procedure bowel prep
Draw water into intestine via osmosis into a salt >>which increases intraluminal pressure >>which increases motility.
\
\-used for pre procedure bowel prep
Draw water into intestine via osmosis into a salt >>which increases intraluminal pressure >>which increases motility.
\
31
New cards
saline laxatives contraindications
\-Low salt diet
\-Renal disease: can cause hypokalemia, hypermag, hypocalcemia, hypernatremia
\-Caution in elderly
\-Separate administration from Azole antifungals, quinolones, and TCN.
\-Renal disease: can cause hypokalemia, hypermag, hypocalcemia, hypernatremia
\-Caution in elderly
\-Separate administration from Azole antifungals, quinolones, and TCN.
32
New cards
stimulant laxatives MOA
ex. doculax/senna; castor oil
\-Increase peristalsis of intestine and promotes fluid accumulation.
\-Increase peristalsis of intestine and promotes fluid accumulation.
33
New cards
stimulant laxatives contraindications
\-can become dependent with long term treatment
\*\*high potential for abuse
\
\-contraindicated with fecal impaction, GI obstruction, or cause an exacerbation of hemorrhoids
\*\*high potential for abuse
\
\-contraindicated with fecal impaction, GI obstruction, or cause an exacerbation of hemorrhoids
34
New cards
surfactant laxatives MOA/use
(stool softners ) ex. docusate sodium or colace
laxative of choice to prevent straining due to constipation
\
\-Reduces surface tension of liquid contents of bowel.
\-Incorporates more liquid into stool forming a softer mass.
laxative of choice to prevent straining due to constipation
\
\-Reduces surface tension of liquid contents of bowel.
\-Incorporates more liquid into stool forming a softer mass.
35
New cards
surfactant laxatives contraindications
\-no contraindications
\-interacts with mineral oil
Clinical Pearl: can be used in the ear to soften cerumen before irrigation.
\-interacts with mineral oil
Clinical Pearl: can be used in the ear to soften cerumen before irrigation.
36
New cards
Lubricant laxative MOA
ex. mineral oil
used to prevent straining in high-risk patients (post surgery, CVA, hernia, hemorrhoids)
used to prevent straining in high-risk patients (post surgery, CVA, hernia, hemorrhoids)
37
New cards
Lubricant laxative contraindications
\-contraindicated in Elderly, children, and bedbound (increased risk aspiration)
\-rectal seepage in large amounts
\-will impair absorption of fat soluble vitamins and warfarin
\-rectal seepage in large amounts
\-will impair absorption of fat soluble vitamins and warfarin
38
New cards
Chloride Channel Activator MOA
One drug currently: lubiprostone (Amitiza).
\-used for chronic constipation prone IBS
\-MOA unknown: enhances chloride-rich intestinal fluid to pull water into intestine.
\-used for chronic constipation prone IBS
\-MOA unknown: enhances chloride-rich intestinal fluid to pull water into intestine.
39
New cards
Chloride Channel Activator contraindications
contraindicated in pregnant women and children, mechanical obstruction
\
no interactions
\
no interactions
40
New cards
Guanylate Cyclase-C Agonist MOA
used for chronic idiopathic constipation (CIC) or IBS
\
\-Increases intracellular cGMP which stimulates secretion of chloride and bicarb into the intestinal lumen to increase stool transit time
\
\-Increases intracellular cGMP which stimulates secretion of chloride and bicarb into the intestinal lumen to increase stool transit time
41
New cards
Guanylate Cyclase-C Agonist contraindications
\-contraindicated in Children < 6 years
\-Bowel obstruction
\-no other interactions
\-Bowel obstruction
\-no other interactions
42
New cards
Peripherally Acting Mu-opioid Receptor Antagonist MOA
\*\*used for opioid induced constipation
(contains same ingredients as naloxone)
\-Blocks opioid binding to the mu receptor
(contains same ingredients as naloxone)
\-Blocks opioid binding to the mu receptor
43
New cards
Peripherally Acting Mu-opioid Receptor Antagonist contraindicaions
* contraindicated in suspected GI obstruction or potential for GI perforation
\-Some patients may experience opioid withdrawal
* interacts with other meds metabolized by CYP3A4
or other opioid antagonists
\-Some patients may experience opioid withdrawal
* interacts with other meds metabolized by CYP3A4
or other opioid antagonists
44
New cards
Serotonin-4 Receptor Agonist MOA
only one left due complications
\
GI pro kinetic agent
\
\
GI pro kinetic agent
\
45
New cards
Serotonin-4 Receptor Agonist contraindications
\-Contraindicated in mechanical obstruction or hypersensitivity
\-works similar to ssri; Monitor for suicidal ideation, self-injurious ideation, and new onset or worsening depression
\-works similar to ssri; Monitor for suicidal ideation, self-injurious ideation, and new onset or worsening depression
46
New cards
first line for constipation?
TLCs >>>then bulk forming lax as first choice
ex. psyllium (Metamucil® or fibercon
\
dry stool or straining? stool softener or glycerin syrup
ex. psyllium (Metamucil® or fibercon
\
dry stool or straining? stool softener or glycerin syrup
47
New cards
second line for constipation?
hyper osmotic ex. miralax
\
(if contraindicated? saline/ osmotic laxative)
\
(if contraindicated? saline/ osmotic laxative)
48
New cards
third line for constipation?
A stimulant ex. senna
\
\***remember high potential for abuse**
\-mineral oil for those who need to avoid straining
\
\***remember high potential for abuse**
\-mineral oil for those who need to avoid straining
49
New cards
travelers diarrhea treatment
prophylactic agents used: Pepto-Bismol--2 tabs with meals and bedtime.
Empiric agents: floroquinolone at sx onset.
Empiric agents: floroquinolone at sx onset.
50
New cards
Diarrhea lasting 2-4 weeks without sx
they might have giardia
\
\-metronidazole for empiric anti-Giardia therapy
\
\-metronidazole for empiric anti-Giardia therapy
51
New cards
Anti-motility Agents MOA
ex. loperamide (Imodium), diphenoxylate with atropine (Lomotil)
\
\-derivative of an opioid;
Slows GI motility by effecting intestinal musculature and increases transit time for an increased absorption of water.
\
\-atropine prevents euphoric/analgesic
\
\-derivative of an opioid;
Slows GI motility by effecting intestinal musculature and increases transit time for an increased absorption of water.
\
\-atropine prevents euphoric/analgesic
52
New cards
Anti-motility Agents contraindication
\-exacerbates infectious diarrhea
\
\-not recommended for kids under 4
\
\-atropine side effects
\
\-Diphenoxylate may potentiate CNS depression.
(drowsiness/dizziness)
\-loperamide has high first pass effect--caution in liver failure
\
\-not recommended for kids under 4
\
\-atropine side effects
\
\-Diphenoxylate may potentiate CNS depression.
(drowsiness/dizziness)
\-loperamide has high first pass effect--caution in liver failure
53
New cards
Atypical Antidiarrheals MOA
ex. pepto, kaopectate
\-Antisecretory, antimicrobial, and adsorbent properties
\-best for travelers diarrhea
\-Antisecretory, antimicrobial, and adsorbent properties
\-best for travelers diarrhea
54
New cards
Atypical Antidiarrheals contraindication
Contains salicylate: caution ASA sensitivity or therapy
\
\-Do not use in children with viral infection due to Reyes Syndrome
\
AE: black stools, black tongue, tinnitus
\
\-Do not use in children with viral infection due to Reyes Syndrome
\
AE: black stools, black tongue, tinnitus
55
New cards
Adsorbents
ex . Kaolin, pectin (Kaopectate) attapulgite (Donnagel),
\
\
Adsorbs or holds water and solidify stools.
\
\
Adsorbs or holds water and solidify stools.
56
New cards
Absorbents
ex. Polycarbophil (FiberCon, Fiberall)
\
Absorbs water in GI tract
\
may absorb nutrients and other meds
\
Absorbs water in GI tract
\
may absorb nutrients and other meds
57
New cards
Semisynthetic Antibiotic MOA
ex. rifaximin
\-Suppresses diarrhea by altering the growth of the bacteria and is effective against non invasive strains of ECOLI
\-Suppresses diarrhea by altering the growth of the bacteria and is effective against non invasive strains of ECOLI
58
New cards
Semisynthetic Antibiotic contraindications
\-Peripheral edema, nausea, dizziness, fatigue, muscle spasms
\-Post marketing effects: exfoliative dermatitis, rash, angioneurotic edema, urticaria
\-Post marketing effects: exfoliative dermatitis, rash, angioneurotic edema, urticaria
59
New cards
first line diarrhea
TLCs (brat diet, decrease fiber, lactose, and gluten) and diet >> if not then loperamide
60
New cards
second line diarrhea
Adsorbent or bismuth subsalicylate:
\*\*do not use bismuth with flu in those under 18. bismuth is main ingredient in pepto
\*\*do not use bismuth with flu in those under 18. bismuth is main ingredient in pepto
61
New cards
third line for diarrhea
diphenoxylate with atropine (lomotil)
62
New cards
common side effects of anti consitpation meds
\-Gi upset
\-Diarrhea
\-Nausea
\-Cramps
\-Bloating
flatulance
dehydration
\
\-Diarrhea
\-Nausea
\-Cramps
\-Bloating
flatulance
dehydration
\
63
New cards
causes of GERD
\-Transient Lower esophageal spincter relaxation
\-Abdominal strain from increased gastric volume or pressure
\-Hiatel hernia
\-Impaired esophageal defense mechanisms
\-Motility Abnormalities
\-Abdominal strain from increased gastric volume or pressure
\-Hiatel hernia
\-Impaired esophageal defense mechanisms
\-Motility Abnormalities
64
New cards
Treatments for GERD
diet
sleeping with HOB raise
antacids
H2 receptors blockers
PPIs
\
\
sleeping with HOB raise
antacids
H2 receptors blockers
PPIs
\
\
65
New cards
two main causes of PUD
\-infection from H pylori
\-long tern NSAIDS use
\-long tern NSAIDS use
66
New cards
PUD pharmaceutical treatment
Treatment of H. pylori = 2 antibiotics + mucus protection
\
ex . Clarithromycin + Amoxicillin OR Metronidazole + Tetracycline
\
\
Mucosa Protectants
\-H2 Receptor Antagonists
\-Proton Pump Inhibitors
\-Bismuth Subsalicylate
\-Antacids
\-Sucralfate
\-Misoprostol
\
\
ex . Clarithromycin + Amoxicillin OR Metronidazole + Tetracycline
\
\
Mucosa Protectants
\-H2 Receptor Antagonists
\-Proton Pump Inhibitors
\-Bismuth Subsalicylate
\-Antacids
\-Sucralfate
\-Misoprostol
\
67
New cards
H2 receptor antagonists MOA
ex. (-tidine) famotidine (Pepcid)
__Suppress__ gastric acid and pepsin secretion by competitively and reversibly binding H2 receptors
__Suppress__ gastric acid and pepsin secretion by competitively and reversibly binding H2 receptors
68
New cards
H2 receptor antagonists contraindications
AE: blood dyscrasias, bradycardia, confusion
Interactions: warfarin, phenytoin, theophylline
Interactions: warfarin, phenytoin, theophylline
69
New cards
Proton pump inhibitors MOA
ex. (-prazole) omeprazole (Prilosec)--OTC
\-lansoprazole (Prevacid)--OTC
\-pantoprazole (Protonix)--IV
\
\-Bind to the proton pump of parietal cell to block secretion of hydrogen into gastric lumen
\
\-__Inhibits__ acid production; relieves pain; heals ulcers
\*\*more rapid then H2 blockers
\-lansoprazole (Prevacid)--OTC
\-pantoprazole (Protonix)--IV
\
\-Bind to the proton pump of parietal cell to block secretion of hydrogen into gastric lumen
\
\-__Inhibits__ acid production; relieves pain; heals ulcers
\*\*more rapid then H2 blockers
70
New cards
Proton pump inhibitors contraindications
Take 30-60 mins before meal
\
AE: Diarrhea/constipation, headache, Abd pain
\
AE w/ Long-term use: hypergastrinemia, fractures, c. diff colitis, bacterial enteritis, Vitamin B12 deficiency, hypomagnesemia
\
\
\
AE: Diarrhea/constipation, headache, Abd pain
\
AE w/ Long-term use: hypergastrinemia, fractures, c. diff colitis, bacterial enteritis, Vitamin B12 deficiency, hypomagnesemia
\
\
71
New cards
high risk groups for DM
\
hispanic, black, and alaskan native
hispanic, black, and alaskan native
72
New cards
4 major classifications of diabetes
type 1 - insulin dependent
type 2 - non insulin dependent (most common)
gestational - occurs during pregnancy
diabetes secondary- secondary to other conditions like pancreatic disease, long term steroids, hormonal abnormalities
type 2 - non insulin dependent (most common)
gestational - occurs during pregnancy
diabetes secondary- secondary to other conditions like pancreatic disease, long term steroids, hormonal abnormalities
73
New cards
type 1 cause
genetic predisposition or autoimmune response
74
New cards
type 2 cause
pancreas produces less insulin than body needs OR
adipose and muscle cells become less sensitive to insulin
adipose and muscle cells become less sensitive to insulin
75
New cards
type 3 cause
pregnancy cause the woman to become intolerant to glucose
76
New cards
type 2 risk factors
•Family history of diabetes
•Obesity; sedentary lifestyle
•Race/ethnicity
•Age older than 45 years
•Previously identified as having IFG (impaired fasting glucose)
•Hypertension
•HDL
•Obesity; sedentary lifestyle
•Race/ethnicity
•Age older than 45 years
•Previously identified as having IFG (impaired fasting glucose)
•Hypertension
•HDL
77
New cards
pathogenesis or (manor of development )of DM 2
•Insulin resistance
•Impaired insulin secretion
•Elevated glucose production by the liver
•Impaired insulin secretion
•Elevated glucose production by the liver
78
New cards
Main symptoms of DM?
•Polyuria (excessive urination)
•Polydipsia (increased thirst)
•Weight loss
•Polyphagia (increased hunger and caloric intake)
•Blurred vision
•Polydipsia (increased thirst)
•Weight loss
•Polyphagia (increased hunger and caloric intake)
•Blurred vision
79
New cards
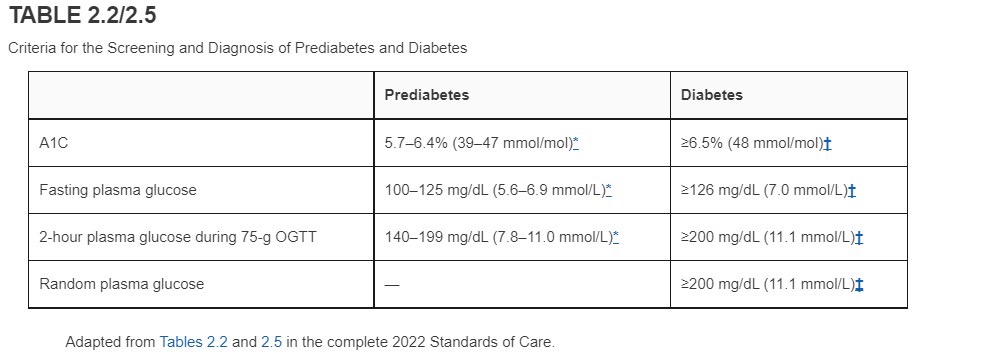
DM criteria
if A1C is greater than or equal to 6.5= DM diagnosis
Fasting glucose greater than 126= DM diagnosis
random glucose greater than 200= DM dianosis
Fasting glucose greater than 126= DM diagnosis
random glucose greater than 200= DM dianosis
80
New cards
Effective treatment programs for DM
•Self-monitoring blood glucose (SMBG)
•Medical nutrition therapy; regular exercise
•__Drug therapy__ individualized for each patient
•Oral glucose-lowering agents for some type 2 patients
•Instruction in the __prevention and treatment__ of acute and chronic complications, including hypoglycemia
•Medical nutrition therapy; regular exercise
•__Drug therapy__ individualized for each patient
•Oral glucose-lowering agents for some type 2 patients
•Instruction in the __prevention and treatment__ of acute and chronic complications, including hypoglycemia
81
New cards
Goals for drug therapy in DM
ADA = A1C less than 7
ACCE= endocrinologist less than 6.5
\
**Both ADA and ACCE**
•Preprandial plasma glucose level 80–130 mg/dL
•Postprandial plasma glucose level
ACCE= endocrinologist less than 6.5
\
**Both ADA and ACCE**
•Preprandial plasma glucose level 80–130 mg/dL
•Postprandial plasma glucose level
82
New cards
Goals for drug therapy in DM (other labs)
\*\*\*Microalbumin (random collection)
83
New cards
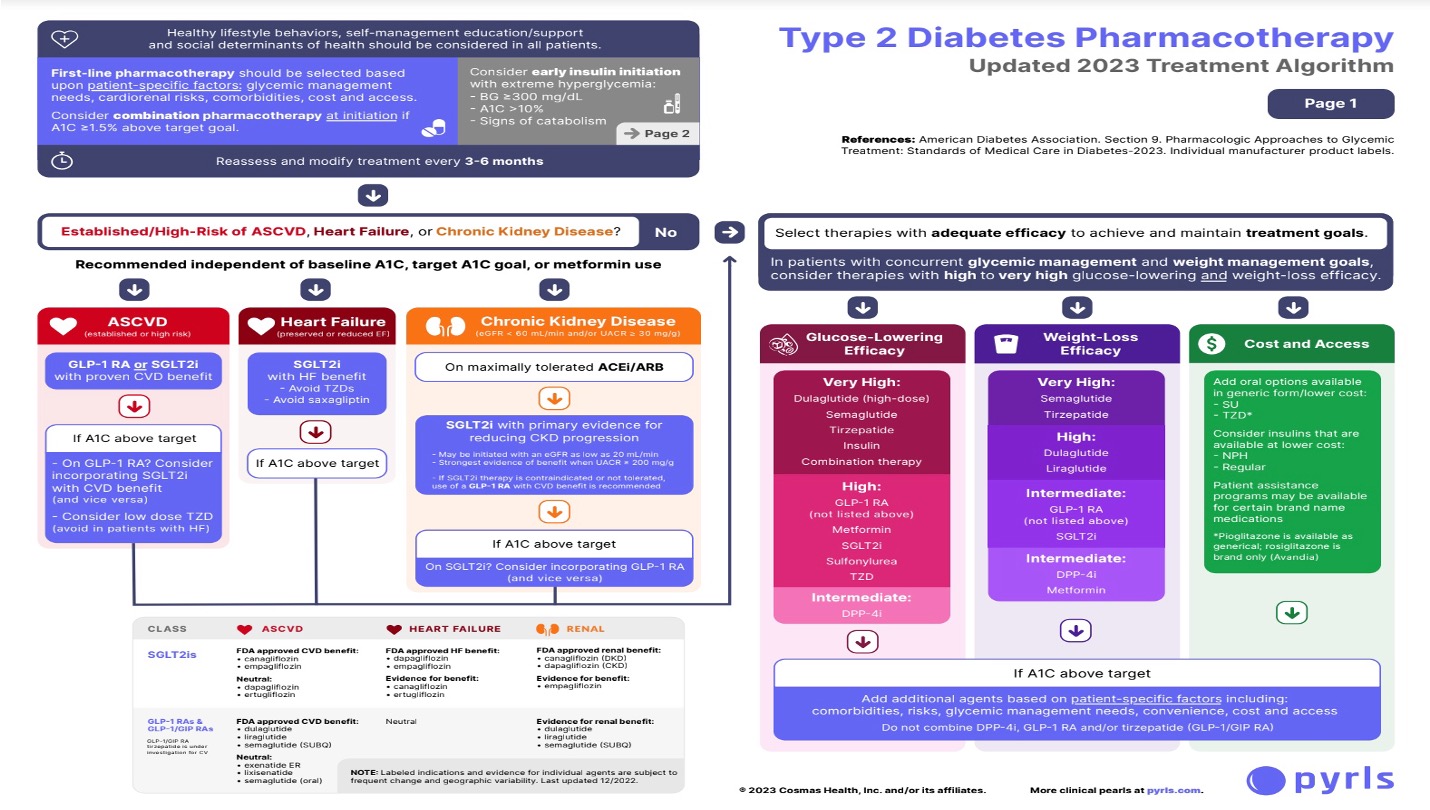
DM chart
**metformin no longer first line**
\
if CVD risk >> GLP1 recepter agonist or SGLT2
if HF risk>>> SGL2 ; avoid Thiazolidinediones
if CKD>>> SGLT2; make sure on ace or arb
\
Therapy chosen due to treatment goals: glucose lowering efficiency, weight loss efficiency, cost and access
\
if CVD risk >> GLP1 recepter agonist or SGLT2
if HF risk>>> SGL2 ; avoid Thiazolidinediones
if CKD>>> SGLT2; make sure on ace or arb
\
Therapy chosen due to treatment goals: glucose lowering efficiency, weight loss efficiency, cost and access
84
New cards
What is the drug of choice for DM1 or DM2 with failed oral therapy?
insulin
85
New cards
what are the two ways to use inulin (or the two types of insulin) ?
basal- steady amount (intermediate and long acting)
bolus - short acting
bolus - short acting
86
New cards
rapid acting insulin
\
\
\
RADID ACTING>>>LISPRO/ aspart (novolog)/ glulisine (apidra)
\
ONSET less then 30 min
\
PEAK 30 min -3 hr
\
DURATION 3-5 hr
\
\
RADID ACTING>>>LISPRO/ aspart (novolog)/ glulisine (apidra)
\
ONSET less then 30 min
\
PEAK 30 min -3 hr
\
DURATION 3-5 hr
87
New cards
short acting insulin
EX HUMULIN R ;NOVALIN R
\
ONSET 30 min
\
PEAK 2-4 hr
\
DURATION 6-8
\
ONSET 30 min
\
PEAK 2-4 hr
\
DURATION 6-8
88
New cards
intermediate acting insulin
NPH (ex. novolin n, humalin n)
\
ONSET 1-4 hr
\
PEAK 4-12 hr
\
DURATION 14-26 hr
\
ONSET 1-4 hr
\
PEAK 4-12 hr
\
DURATION 14-26 hr
89
New cards
long acting insulin
ex. detemir (levemir) glargine (lantus)
\
ONSET 1-2 hr
\
PEAK no peak
\
DURATION 24 hrs
\
ONSET 1-2 hr
\
PEAK no peak
\
DURATION 24 hrs
90
New cards
ultra long acting insulin
EX GLARGINE (toujo); degludec (tresiba)
\
ONSET 30 min-4 hrs
\
PEAK no peak
\
DURATION 36-42 hr
\
ONSET 30 min-4 hrs
\
PEAK no peak
\
DURATION 36-42 hr
91
New cards
combo insulin
**•70/30-NPH/regular ratio**
•50/50- NPH/regular ratio
•75/25-NPL/lispro ratio
•70/30-NPA/aspart ratio (NOT GOING TO ASK TYPES )
\
ONSET 5-15 min
\
PEAK ??
\
DURATION 10-16 hr
•50/50- NPH/regular ratio
•75/25-NPL/lispro ratio
•70/30-NPA/aspart ratio (NOT GOING TO ASK TYPES )
\
ONSET 5-15 min
\
PEAK ??
\
DURATION 10-16 hr
92
New cards
inhalation insulin contraindications
•Acute bronchospasm has been observed in patients with asthma and COPD.
•Contraindicated in patients with chronic lung disease
* not recommended for DKA
* not recommended for smokers or recent smokers
* •Contraindication: Hypoglycemia, COPD, hypersensitivity.
•AE: hypoglycemia, cough, throat pain or irritation, headache.
•Contraindicated in patients with chronic lung disease
* not recommended for DKA
* not recommended for smokers or recent smokers
* •Contraindication: Hypoglycemia, COPD, hypersensitivity.
•AE: hypoglycemia, cough, throat pain or irritation, headache.
93
New cards
inhalation insulin types
ex Afrezza-brand name (inhalation powder)
\
•a form of Rapid acting insulin
•used for Type 1 and Type 2
•Preprandial dosing; use before meals
\
•a form of Rapid acting insulin
•used for Type 1 and Type 2
•Preprandial dosing; use before meals
94
New cards
recommendations for type 1
basal+ rapid acting
\
or combo intermediate + short acting
.4-.5 per units day (weight based)
\
\
or combo intermediate + short acting
.4-.5 per units day (weight based)
\
95
New cards
recommendations for type 2
start on basal insulin
96
New cards
sensitizers- biguanides MOA
ex. metformin (Fortamet and Glumetza)
\
•Inhibits the production of hepatic glucose, reducing intestinal glucose absorption and improving glucose uptake and utilization
•Benefits: do not cause hypoglycemia and does not promote weight gain.
•Can combine with other hypoglycemics.
\
\
•Inhibits the production of hepatic glucose, reducing intestinal glucose absorption and improving glucose uptake and utilization
•Benefits: do not cause hypoglycemia and does not promote weight gain.
•Can combine with other hypoglycemics.
\
97
New cards
sensitizers- biguanides contraindications
•Contraindications: Renal dysfunction, \***Heart failure**, pregnancy
•Stop for 48-72 hrs pre and post radiographic dye studies. Can cause metabolic acidosis.
•AE: GI upset, acidosis. I have seen edema, water retention.
•Stop for 48-72 hrs pre and post radiographic dye studies. Can cause metabolic acidosis.
•AE: GI upset, acidosis. I have seen edema, water retention.
98
New cards
sensitizers- TZDs MOA
ex- piogiltazone or rosiglitazone
\
MOA: increase insulin sensitivity in skeletal muscle and fat
\
\
MOA: increase insulin sensitivity in skeletal muscle and fat
\
99
New cards
sensitizers- TZDs contraindications
\-liver function tests are a MUST
\-stop if liver function tests are 3x then normal
•Hypoglycemia when used with insulin or sulfonylureas
•AE: reduce oral contraceptives, increased plasma volume, weight gain
•Can cause or worsen HF
•Increased risk of bladder cancer
\
\
\-stop if liver function tests are 3x then normal
•Hypoglycemia when used with insulin or sulfonylureas
•AE: reduce oral contraceptives, increased plasma volume, weight gain
•Can cause or worsen HF
•Increased risk of bladder cancer
\
\
100
New cards
secretagogues two types
sulfonylureas and meglintinides