Geo Notes - Sem 2 2024
Water in the world
Water Resources
How the Hydrosphere impacts the other spheres |
Biosphere: Lithosphere: |
|
Different types of water resources:
Groundwater
Wastewater
Surface water
Rainwater
Stormwater
Fog Harvesting:
What it is Works by capturing moisture blown in from the ocean using mesh structures (need wind, consistent fog and light winds), the gravity then collects water. |
Pros
|
Cons
|
Cloud seeding:
What it is Cloud seeding is the process in which planes, canons and even drones are used to scatter silver iodide into the clouds this process clumps particles together to speed up precipitation. Cloud seeding is an artificial weather modification technique that involves introducing cloud condensation nuclei into the atmosphere, which enhances a cloud’s ability to produce rain and snow. 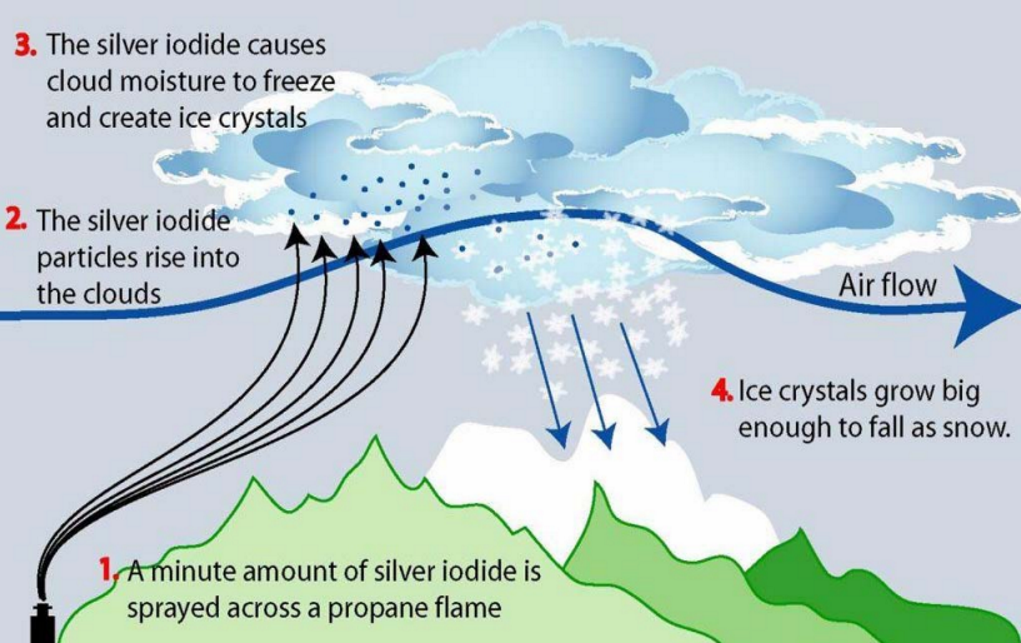 |
Pros
|
Cons
|
Desalination:
What it is Desalination is the process of removing salt from seawater the two types include thermal and reverse osmosis. 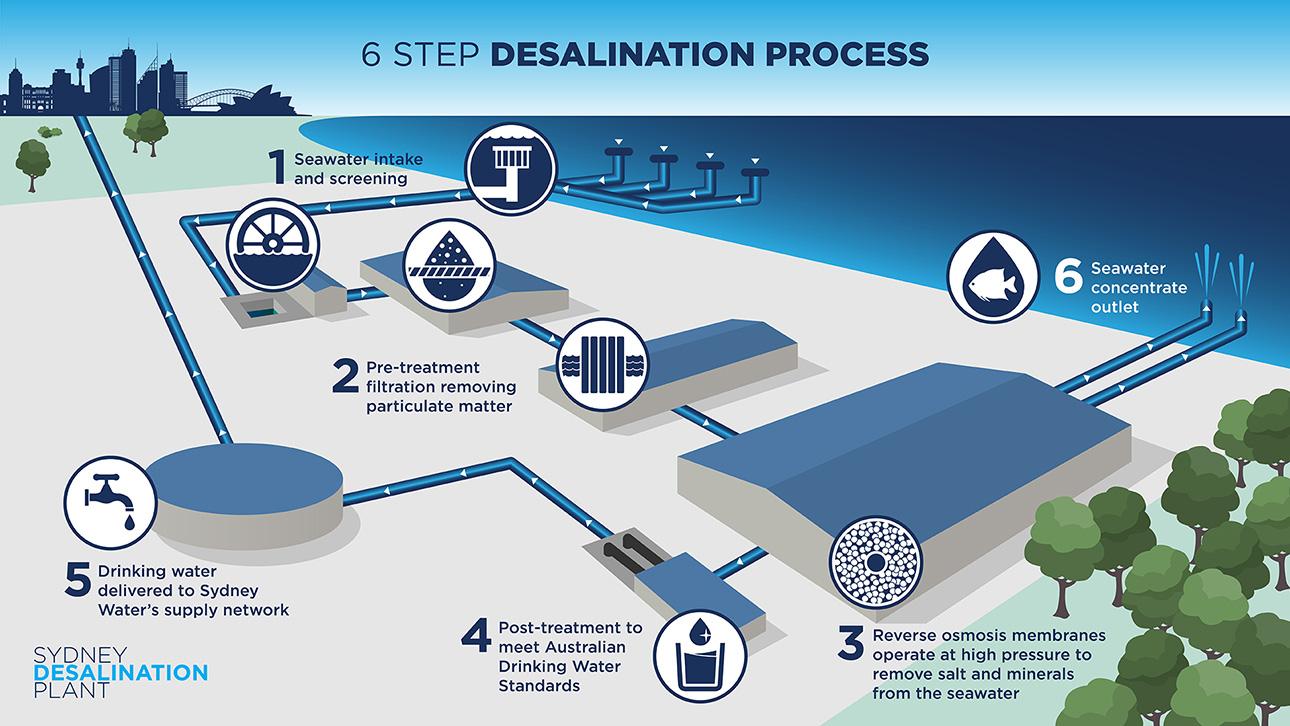 |
Pros
|
Cons
|
Different forms of water and their potential sustainable uses
Solid - Glaciers, ice, and snow, uses include towing icebergs which supply’s fresh water for areas experiencing freshwater scarcity
Liquid - Stormwater, freshwater, brine, saline, and brackish (mix of fresh + salt). Brackish water can be used in agriculture, saline is used for plant desalination, freshwater is used for hydroelectric power generation, and stormwater is used for harvests
Gas - Steam, fog, clouds water in air molecules. Geothermal steam is used for geothermal power generation, fog harvesting, and cloud seeding.
The Water cycle
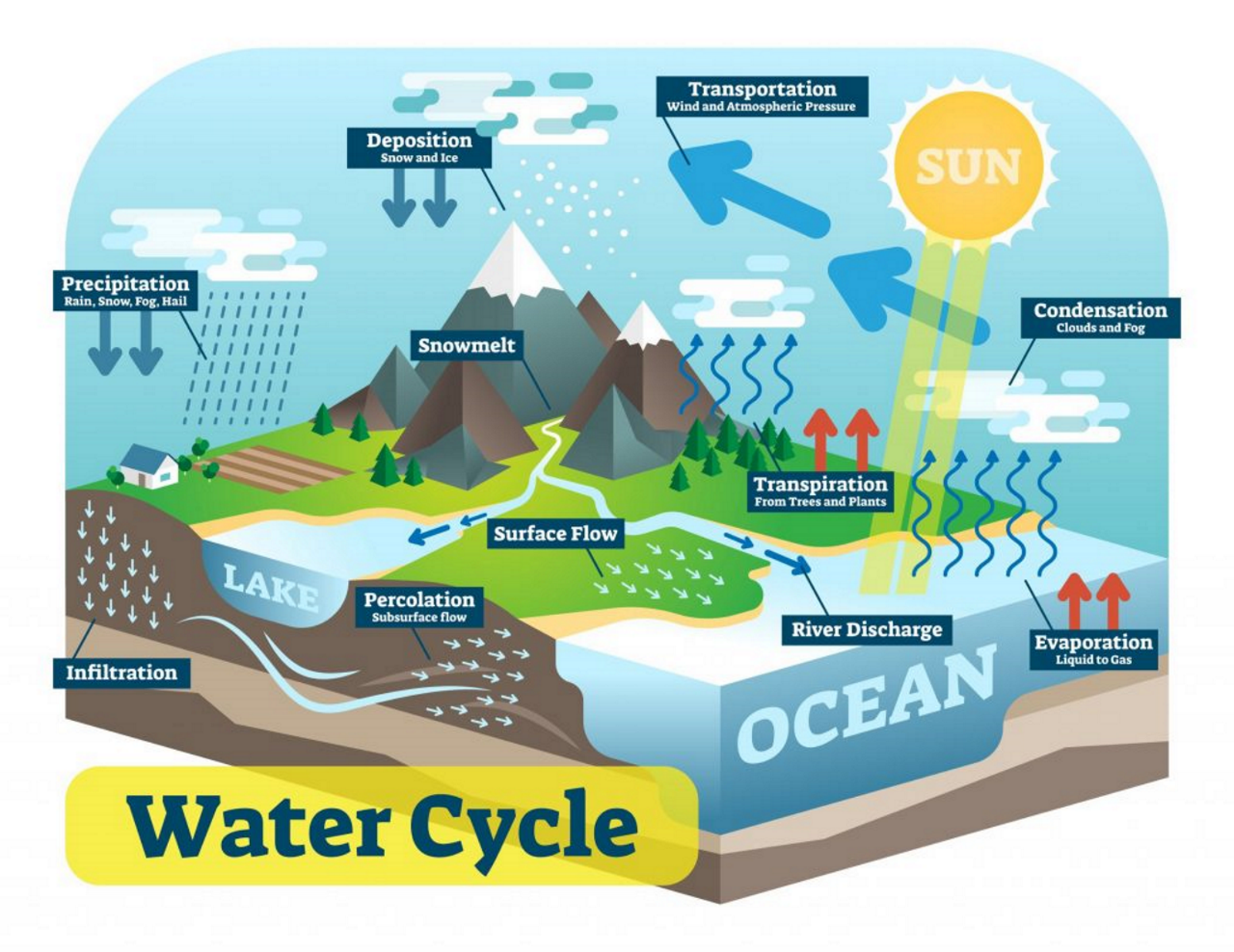
Terms:
Term: Definition: |
Condensation The process of changing a gas into a liquid |
Evaporation The process of changing a liquid into a gas |
Groundwater Water located underneath the Earth’s surface |
Infiltration The movement of water through soil, moving downwards |
Percolation The filtration of water down through soil and porous rocks |
Photosynthesis The process plants use to turn light energy, water and carbon dioxide into an energy source(glucose); oxygen is also produced throughout this process |
Sublimation The process of turning a solid into gas, without passing the liquid state |
Surface runoff Water that moves on the earths surface, e.g. rivers and streams |
Transpiration The process where water moves through a plant and evaporates from the leaves (or other parts of the plant) via openings called stomata |
Vapour A substance in the gaseous state |
Water storages (PERTIC) Water flows (OAISG) |
Precipitation Evaporation Runoff Transpiration Oceans and seas Atmosphere Ice, snow and permafrost Soil water Groundwater |
Catchment: A water catchment is an area where water runoff is collected by the natural landscape, they are usually located at the lowest point in a basin shaped part of the land
Factors affecting global water flows:
Latitude
Altitude
Topography
Location
Climate change
Interconnections
Personal connections and globalisation
Word Meaning |
Interconnections |
Globalisation The process through which and increasingly free flow of ideas, people, goods, services, and capital leads to the integration of economies and societies. |
Examples of personal connections with place: Examples of personal connections with elements of the wider world: |
|
Technology
The benefits of information technology |
Benefits Cons |
|